AP State Syllabus AP Board 7th Class Science Solutions Chapter 3 Animal Fibre Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Science Solutions 3rd Lesson Animal Fibre
7th Class Science 3rd Lesson Animal Fibre Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
In sericulture industry do which stages of silkworm weavers buy? Why do they do so?
Answer:
- The eggs of silk moth are called ‘seeds’.
- These moths are kept in grill mesh boxes in separate rooms.
- These are also called ‘Chilakalu’. Another name for them is ‘Bombyx Mori’.
- White cloth pieces or paper are arranged at the time of laying eggs.
- Moths lay hundreds of eggs on them.
- A female moth lays around 500 eggs in one go and dies.
- Farmers from different places come and purchase these eggs.
Question 2.
Which place in our state is called silk city?
Answer:
Dharmavaram in our state is called the silk city.
![]()
Question 3.
Prepare a chart showing life cycle of silk worm and display that in the classroom.
Answer:

Life Cycle
- Eggs
- Worm
- Big size worm
- Grown worm
- Larva
- Caterpillar
- Cocoon
- Pupa
- Matured pupa
- Imago
Question 4.
Why are cocoons stiffled?
Answer:
- The cocoons have to be stiffled to kill the Larva inside.
- If the Larva inside is not killed, it will cut its way out after growing into a moth and spoil the cocoon.
- If such a thing happens continuous thread of silk from such a cocoon is not possible to get.
Question 5.
What will happen if cocoon is not boiled? (OR)
Generally larvae of silk moth are killed by a process of stiffing to collect silk from a cocoon. What will happen if the cocoon is not boiled?
Answer:
- If the cocoon is not boiled, the larva inside the cocoon grows and cuts its way out after growing into a moth and spoil the cocoon.
- In such a case we won’t be able to obtain quality fibre for fabric.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the differences between fleece of Angora goat and camel?
Answer:
| Angora goat fleece | Camel fleece |
| 1) Angora goat live in Kashmir. | 2) Angora goat have soft hair. |
| 1) Camel live in Rajasthan. | 2) Camels have rough and coarse hair. |
Question 7.
Make a flow chart showing various stages of production of woollen fabric.
Answer:
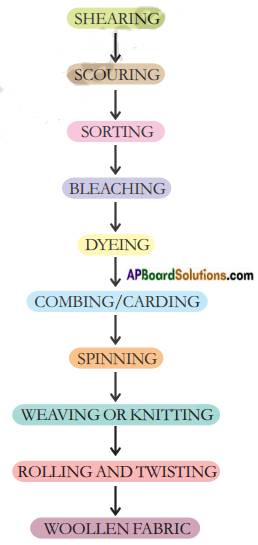
Question 8.
In what way is knitting different from weaving?
Answer:
- Strands of yarn are arranged in vertical and horizontal rows in a loom to weave fabric.
- Two sets of yarn arranged together to make fabric is called weaving.
- Wool can be knit easily because it has a natural bend or crimp on it.
- By making knots with loops and rings of a long thread of yarn, woolen fabrics are knitted.
- In addition to handmade process of knitting, handlooms and powerlooms are also used on which woolen yarn is woven to fabric.
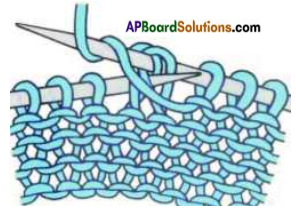
- Woolen threads are stretched from the top of loom to the bottom. These are called warp threads. The threads that go side to side are weft threads.
- A shuttle like a big needle takes the weft threads over and under warp threads. One more important part of the loom is the harness.
- The harness lifts every other warp thread so that the weft threads go over one and under the next. All types of yarn whether cotton or silk or wool etc. are woven in this manner.

![]()
Question 9.
Prepare a scrap book with pictures of different wool yielding animals.
Answer:

The student is advised to prepare this scrap book independently.
Question 10.
Fill up the blank and give your reasons for the statement.
…….. fabric protect us from cold.
Answer:
Woolen fabric protect us from cold. Because wool is a poor conductor of heat. Air trapped in between the woolen fibres and our body prevents the flow of heat from our body to surroundings.
Question 11.
If you are going to visit Dal lake at Kashmir which type of clothes would you like to keep in your luggage? Why?
Answer:
- In Kashmir, it would be very cold.
- Unless one wears clothes to protect himself from this chill weather, It becomes difficult to carry on with the day to day activities.
- Woolen clothes protect from chill weather.
- The gap between the threads of the woolen cloth is filled with air.
- Air and wool are bad conductors of heat.
- Woolen clothes are best to wear in Kashmir.
- So I keep woolen clothes in my luggage when I am going to visit Kashmir.
Question 12.
Do you find any similarities between silk and wool weaving? What are they?
Answer:
- Both silk and wool weaving is done on power looms as well as on handlooms.
- Woolen threads are stretched from the top of the loom to the bottom. These are called warp threads.
- The threads that go side to side are weft threads.
- A shuttle like a big needle takes the weft threads over and under warp threads.
- One more important part of the loom is the harness.
- The harness lifts every other warp thread so that the weft threads go over one and under the next.
- All types of yarn whether cotton or silk or wool etc. are woven in this manner.
![]()
Question 13.
Write 5 differences between wool and silk manufacturing.
Answer:
| Silk | Wool |
| 1) The silk yarn is obtained from the cocoon of the silk moth. | 1) The fleece of the sheep along with a thin layer of skin is removed from its body. This process is called shearing. |
| 2) For obtaining silk, moths are reared and their cocoons are collected to get silk thread. | 2) The sheared skin with hair is thoroughly washed in tanks to remove grease, dust and dirt. This is called scouring. |
| 3) The process of taking out threads from the cocoon for use as silk is called reeling the silk. | 3) The hairy skin is sent to a factory where hair of different textures are separated. |
| 4) Tassar, Mooga, Kosa etc., are different varieties of silk. | 4) The small fluffy fibres called burrs are picked out from the hair. |
| 5) Silk fibres obtained by reeling the spun into silk threads, which are woven into silk cloth by the weavers. | 5) Fibres are straightened, combed and rolled into yarn. The longer fibres are made into wool for sweaters and the shorter fibres are spun and woven into woolen cloth. |
Question 14.
Observe designs on silk sarees, trace them in your notebook and make your own designs.
Answer:
![]()
Question 15.
In East India silk is called pat. You may collect different pieces of silk fabric from cloth stores and write the names of the type of fabric and make a chart.
Answer:

 Answer:
Answer: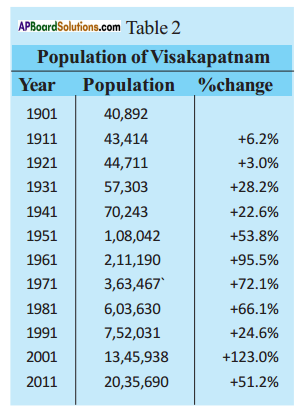
 Observations :
Observations :
 Answer:
Answer:
 Answer:
Answer: Repeat this kind of study for any other country of your choice.
Repeat this kind of study for any other country of your choice.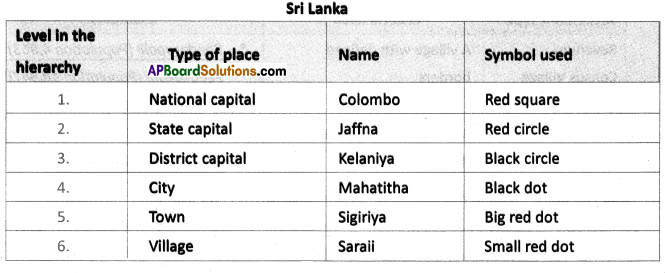
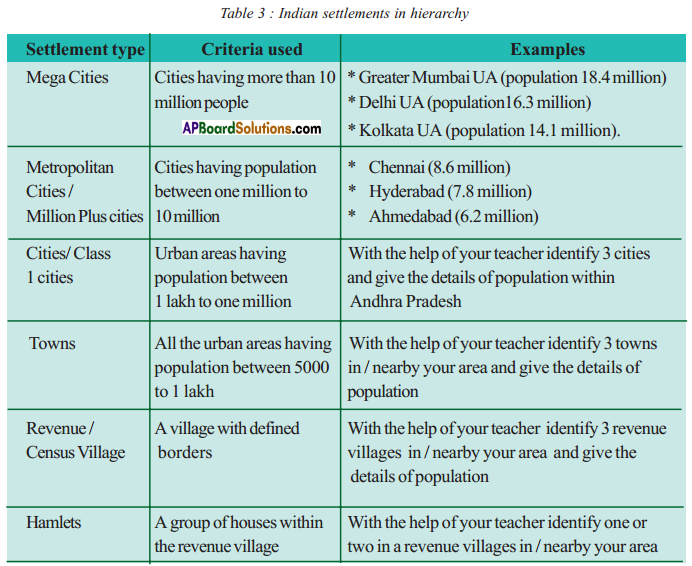

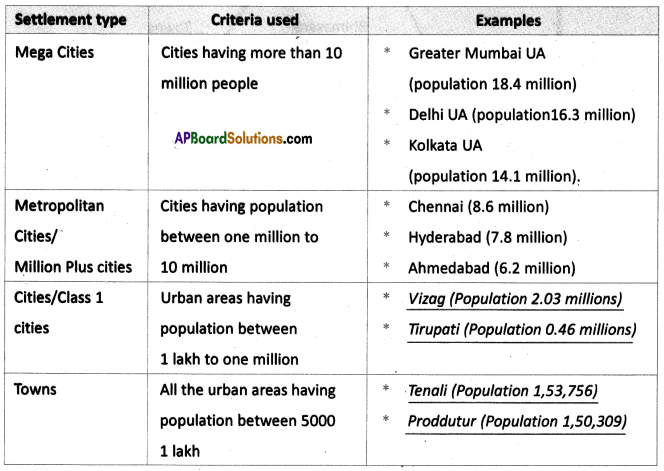
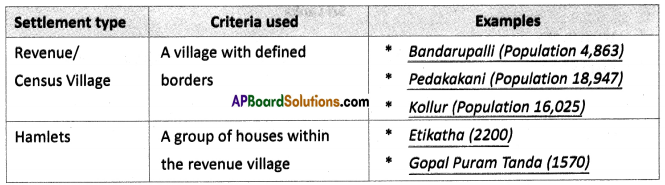
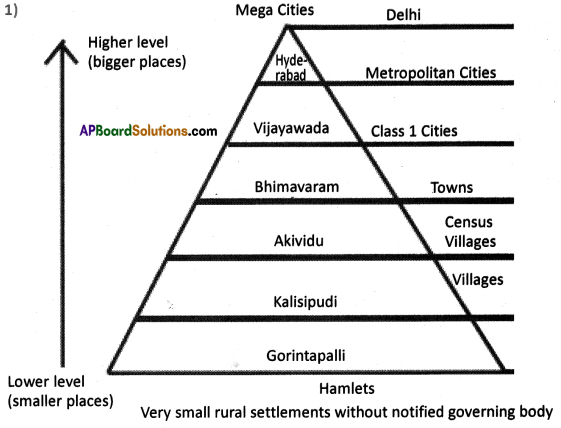
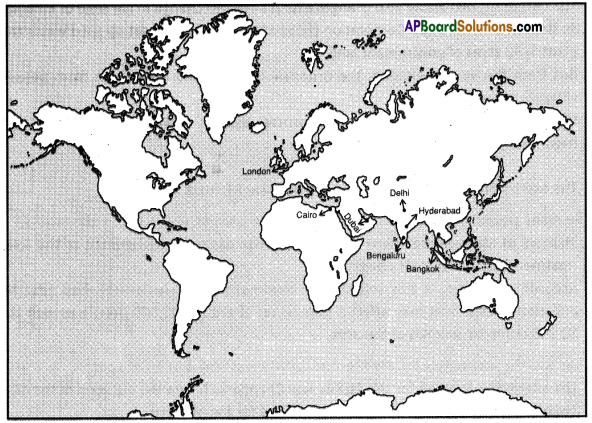

 Answer:
Answer: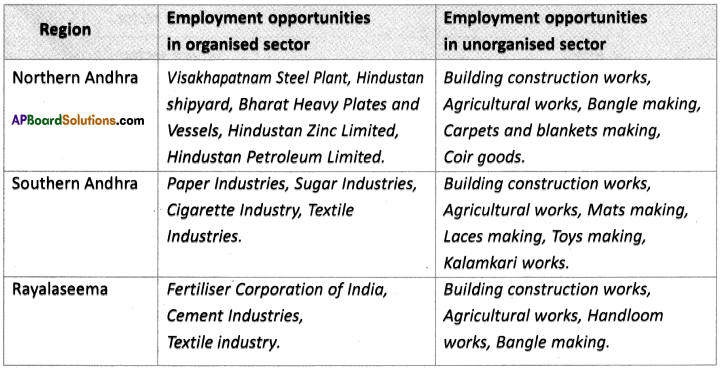
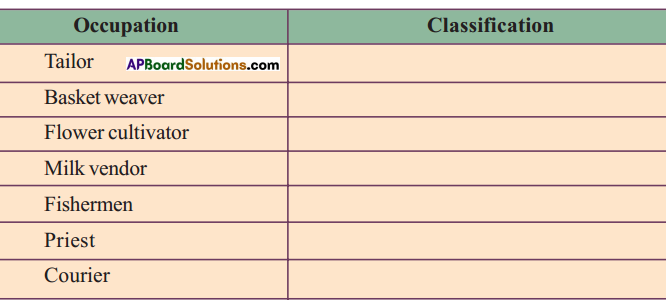
 Answer:
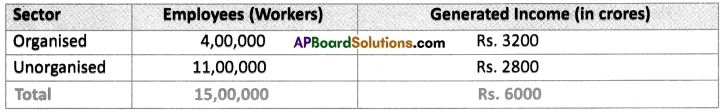
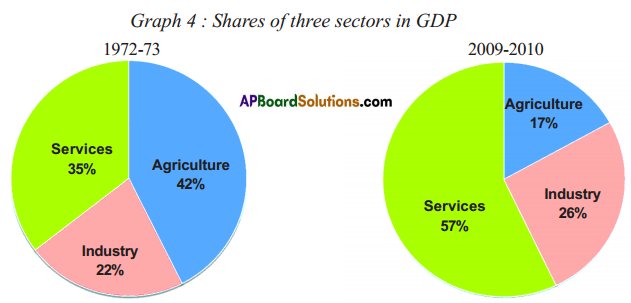
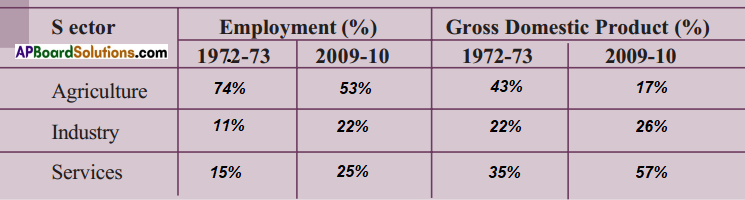
Answer: (i) What are the major changes that you observe from the above table?
(i) What are the major changes that you observe from the above table?
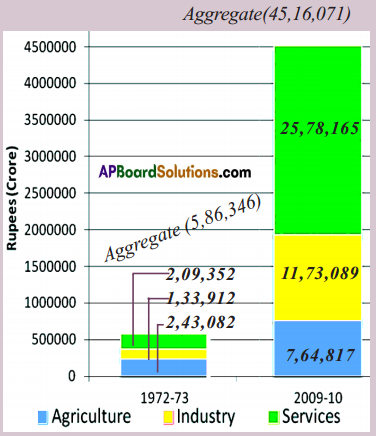 (a) Which was the largest producing sector in 1972 – 73 ?
(a) Which was the largest producing sector in 1972 – 73 ? Discuss : To find out the total value of goods produced should we add them up?
Discuss : To find out the total value of goods produced should we add them up? Answer:
Answer: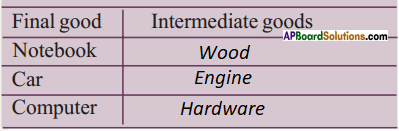
 Discuss : Why do both methods give the same result ?
Discuss : Why do both methods give the same result ?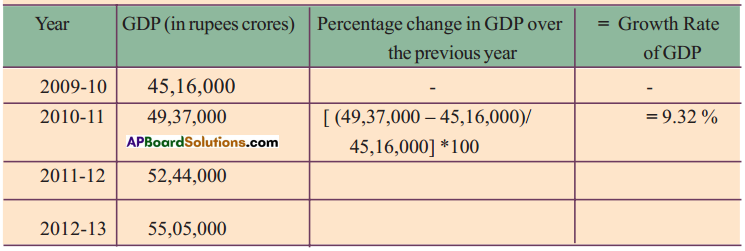 Answer:
Answer: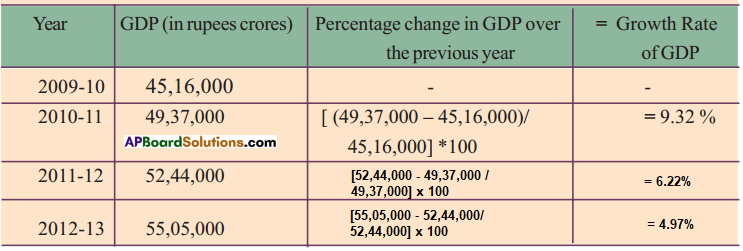
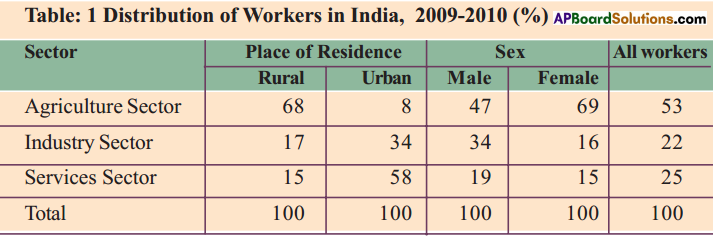 Read the above table and fill in the blanks.
Read the above table and fill in the blanks.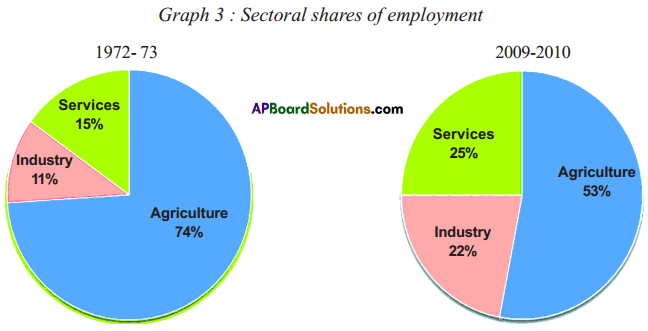





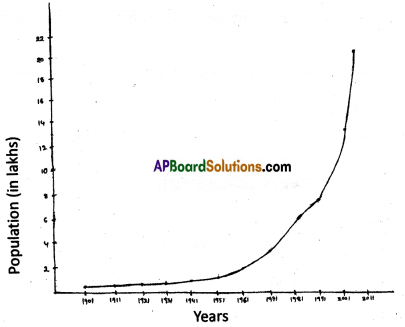
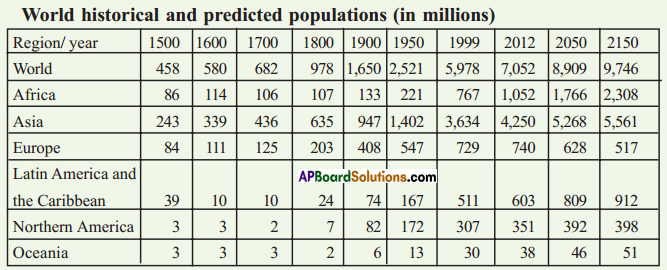 (a) Identify roughly how many centuries it took for the world population to double for the first time.
(a) Identify roughly how many centuries it took for the world population to double for the first time.

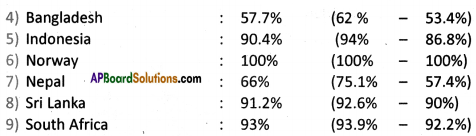
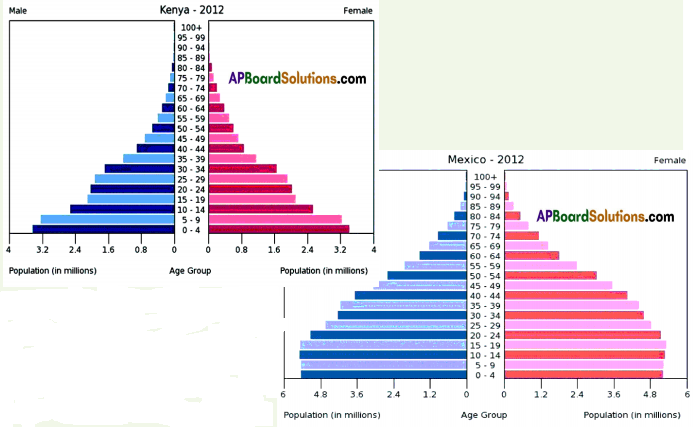
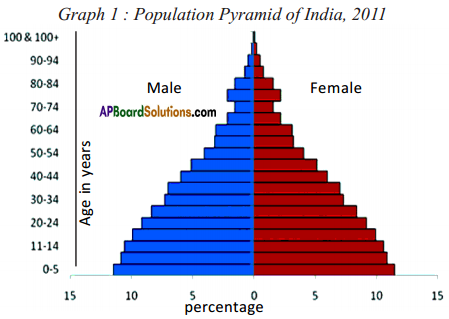 (a) Which country’s population is likely to grow ?
(a) Which country’s population is likely to grow ?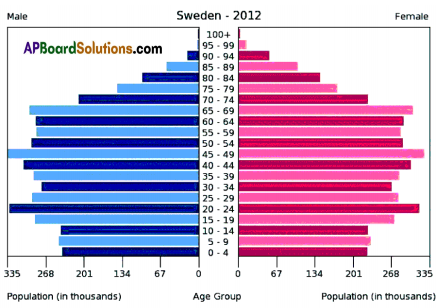
 Answer:
Answer: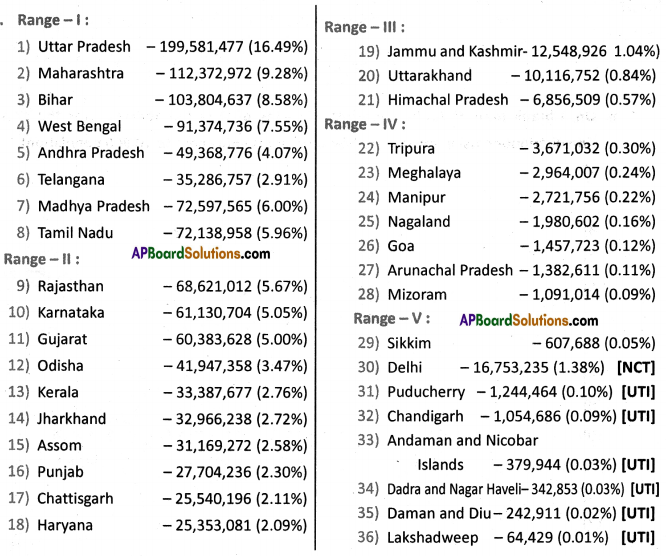
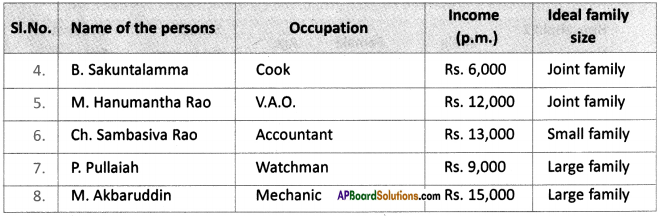
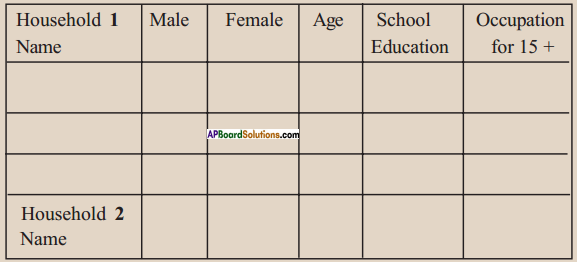


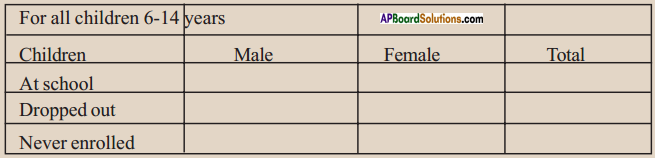
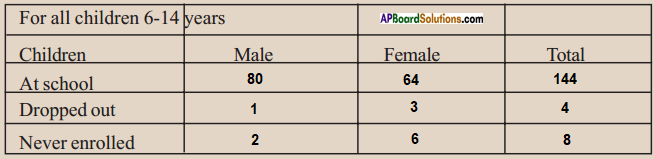
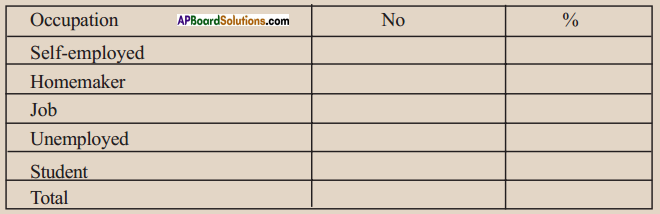
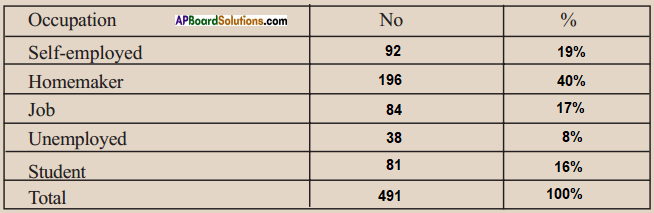
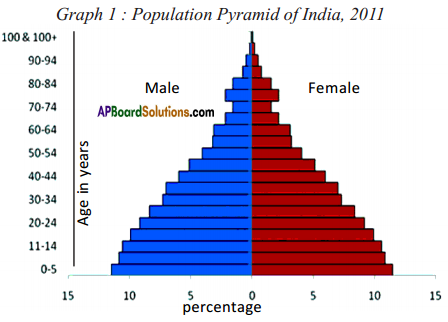 (a) From the age pyramid given above, identify a rough estimate of the percentage of children in the population.
(a) From the age pyramid given above, identify a rough estimate of the percentage of children in the population.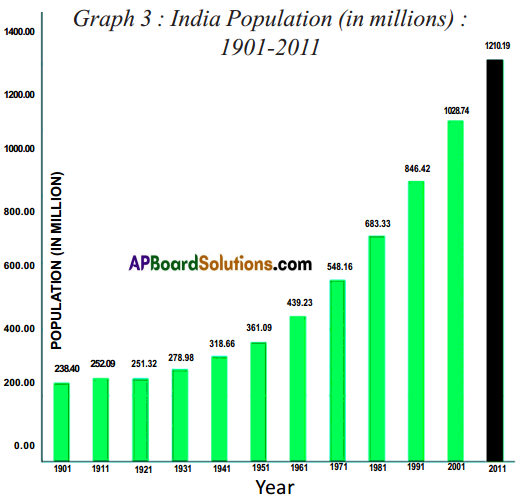
 Answer:
Answer: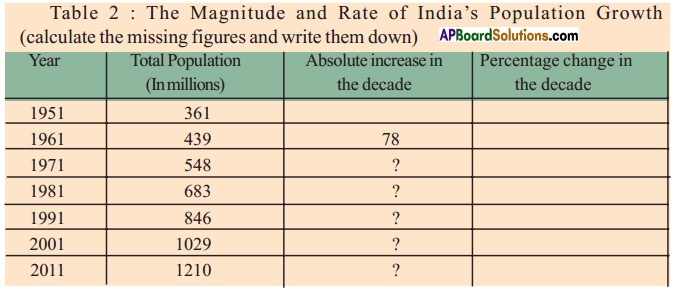
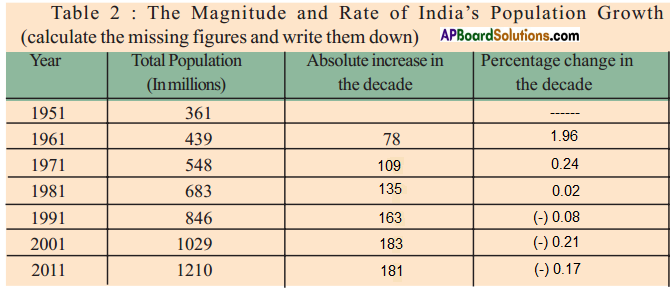
 I observe that family planning was planned in the second generation itself. So the growth rate is decreasing at present.
I observe that family planning was planned in the second generation itself. So the growth rate is decreasing at present.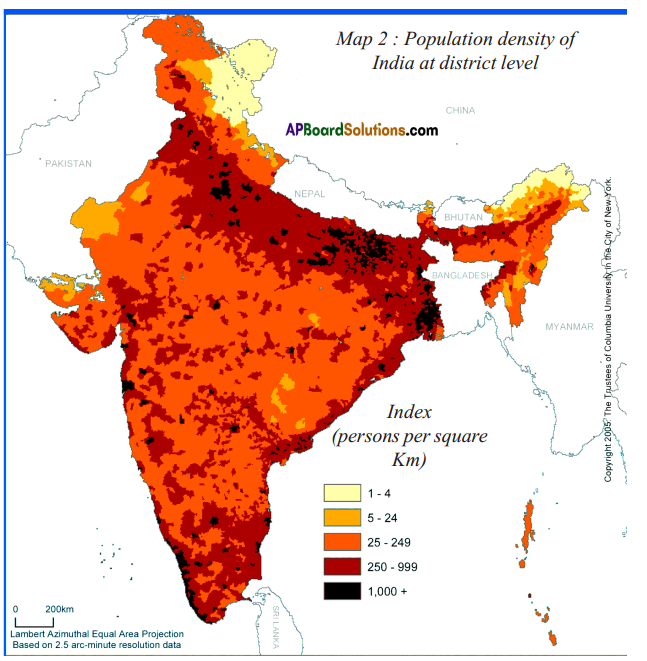 Answer:
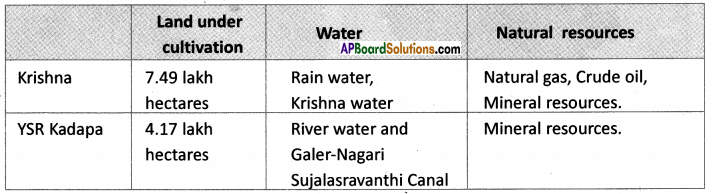
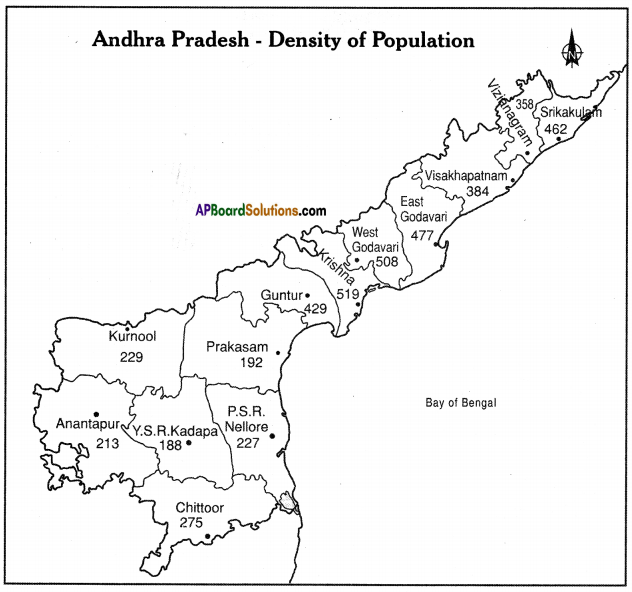
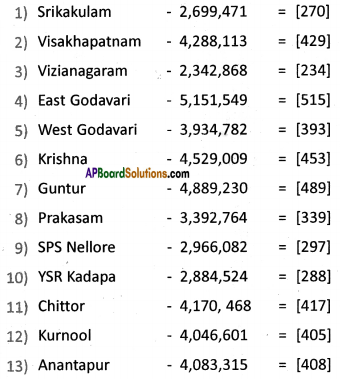
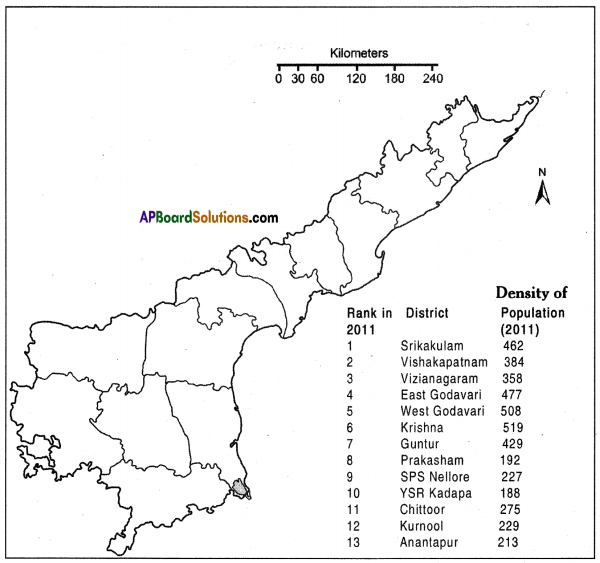
Answer: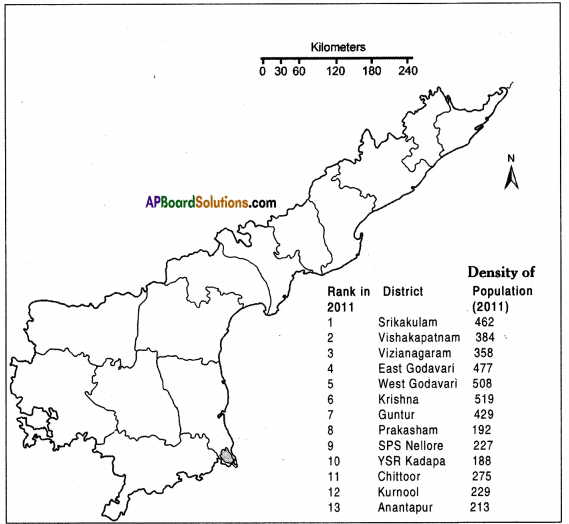 Here are the data for the population density of Andhra Pradesh – 2011. On the above blank district map of AP plot them in ranges.
Here are the data for the population density of Andhra Pradesh – 2011. On the above blank district map of AP plot them in ranges.