Practicing the Intermediate 2nd Year Maths 2B Textbook Solutions Inter 2nd Year Maths 2B Integration Solutions Exercise 6(f) will help students to clear their doubts quickly.
Intermediate 2nd Year Maths 2B Integration Solutions Exercise 6(f)
I. Evaluate the following integrals.
Question 1.
∫ex(1 + x²) dx
Solution:
∫ex(1 + x²) dx = ∫ex + ∫x² . ex dx
= ex + (x².ex – 2 ∫x.exdx)
= ex + x².ex – 2(x.ex – ∫ex dx
= ex + x².ex – 2x. ex + 2ex + C
= ex(x² – 2x + 3) + C
Question 2.
∫x² e-3x dx
Solution:

Question 3.
∫x³ eax dx
Solution:
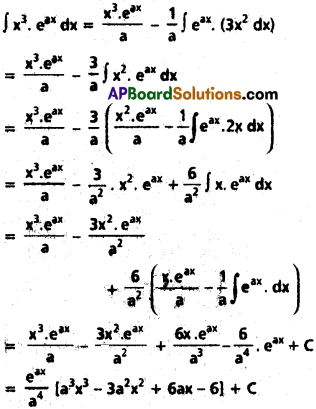
II.
Question 1.
Show that
∫xn.e-x dx = -xn e-x + n∫xn-1.e-x dx
Solution:
∫xn.e-x dx = \(\frac{x^ne^{-x}}{(-1)}\) + ∫e-x. nxn-1 dx
= -xn . e-x + n∫xn-1e-x dx
Question 2.
If In = ∫cosn x dx, than show that
In = \(\frac{1}{n}\) cosn-1 x sin x + \(\frac{n-1}{n}\) In-2.
Solution:
In = ∫cosn x dx = ∫cosn-1 x. cos x dx
= cosn-1x . sin x – ∫sin x.(n – 1)cosn-2x (-sin x)dx
= cosn-1x . sin x + (n – 1) ∫cosn-2x(1 – cos² x)dx
= cosn-1x . sin x + (n – 1)In-2 – (n – 1) In
∴ In(1 + n – 1) = cosn-1x. sin x + (n – 1) In-2
In = \(\frac{\cos ^{n-1} x \sin x}{n}+\frac{n-1}{n}\)In-2
![]()
III.
Question 1.
Obtain reduction formula for In = ∫cotn x dx, n being a positive integer, n ≥ 2 and deduce the value of ∫cot4 x dx.
Solution:
In = ∫cotn dx = ∫cotn-2 x . cot² x dx
= ∫cotn-2 x . (cosec² x – 1) dx
= ∫cotn-2 x . cosec² x dx – In-2
= – \(\frac{cot^{n-1}x}{n-1}\) – In-2
n = 4 ⇒ I4 = –\(\frac{cot^{3}x}{3}\) – I2
n = 2 ⇒ I2 = – cot x – I0 where I0 = ∫dx = x
I2 = – cot x – x
I4 = –\(\frac{cot^{3}x}{3}\) – (-cot x – x) + C
= –\(\frac{cot^{3}x}{3}\) + cot x + x + C
Question 2.
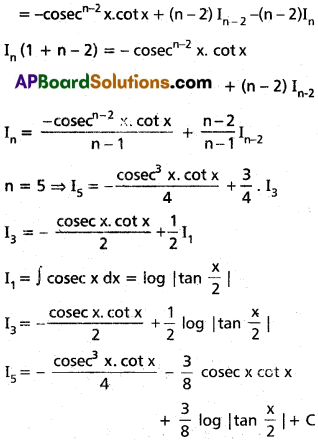
Obtain the reduction formula for In = ∫cosecn x dx, n being a positive integer, n ≥ 2 and deduce the value of ∫cosec5 x dx.
Solution:
In = ∫cosecn x dx
= cosecn-2 x(-cot x) + ∫cot x. (n – 2)cosecn-3 x. (cot x)dx
= -cosecn-2x. cot x + (n – 2)∫cosecn-2x. (cosec² x – 1)dx
Question 3.
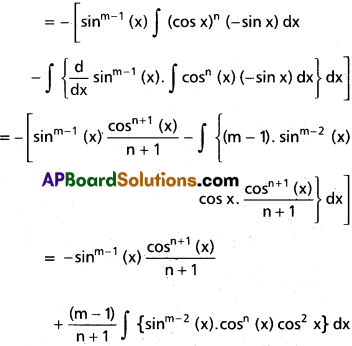
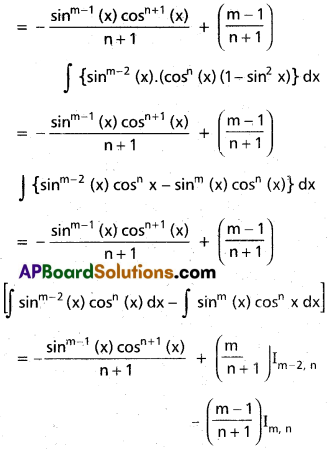
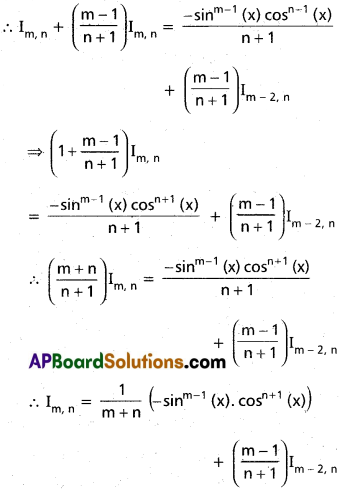
If Im, n = ∫sinm xcosn xdx, then show that
for a positive integer m ≥ 2.
Solution:
Im, n = ∫(sinm x) (cosn x) dx
= ∫sinm-1 (x).(cos x)n. sin x dx
= ∫sinm-1 (x)(cos x)n(-sin x) dx
Question 4.
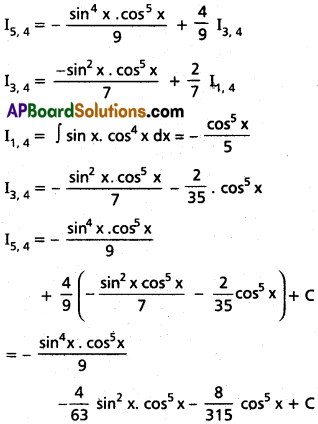
Evaluate ∫sin5 x cos4 x dx
Solution:
Reduction formula
Im, n = \(\frac{-\sin ^{m-1} x \cdot \cos ^{n+1} x}{m+n}+\frac{m-1}{m+n}\).Im-2, n
![]()
Question 5.
If In = ∫(log x)n dx, then show that In = x(log x)n – nIn-1, and hence find
∫(log x)4 dx.
Solution:
In = ∫(log x)n dx
= (log x)n. x – ∫x . n . (log x)n-1 . \(\frac{1}{x}\)dx
= x.(log x)n – n∫(log x)n-1 dx
= x(log x)n – n . In-1
I4 = x(log x)4 – 4 . I3
I3 = x(log x)³ – 3 . I2
I2 = x(log x)² – 2 . I1
I1 = x log x I0 where I0 = ∫dx = x
I1 = x log x – x
I2 = (x (log x)² – 2x log x = 2x
I3 = x(log x)³ – 3(x (log x)² – 2x log x + 2x)
= x . (log x)³ – 3x (log x)² + 6x(log x) – 6x
I4 = x(log x)4 – 4[x . (log x)³ – 3x(log x)² + 6x(log x) -6x] + C
= x[(log x)4 – 4(log x)³ + 12(log x)² – 24(log x) + 24] + C