SCERT AP Board 10th Class Social Solutions 3rd Lesson Production and Employment Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Social Studies Solutions 3rd Lesson Production and Employment
10th Class Social Studies 3rd Lesson Production and Employment Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve your learning
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks using the correct option given in the bracket:
(i) Employment in the service sector ——– increased to the same extent as production. (has/ has not)
(ii) Workers in the ——– sector do not produce goods. (service / agricultural)
(iii) Most of the workers in the ——– sector enjoy job security. (organized / unorganized)
(iv) A ——– proportion of laborers in India are working in the unorganized sector. (large/small)
(v) Cotton is a ——– product and cloth is a ——– product. (natural / manufactured)
Answer:
(i) has not
(ii) service
(iii) organized
(iv) large
(v) natural, manufactured
![]()
Question 2.
Choose the most appropriate answer.
(a) Production of a commodity, mostly through the natural process, is an activity in ——– sector.
(i) primary
(ii) secondary
(iii) tertiary
(iv) information technology
Answer:
(i) primary
(b) GDP is the total value of ——– produced during a particular year.
(i) all goods and services
(ii) all final goods and services
(iii) all intermediate goods and services
(iv) all intermediate and final goods and services
Answer:
(ii) all final goods and services
(c) In terms of GDP the share of service sector in 2009-10 was ——– .
(i) between 20 and 30 per cent
(ii) between 30 and 40 per cent
(iii) between 50 and 60 per cent
(iv) 70 per cent
Answer:
(i) between 50 and 60 percent
![]()
Question 3.
Find the odd one out and say why.
(i) Teacher, doctor, vegetable vendor, lawyer
Answer:
Vegetable vendor.
- The remaining three are the occupations of educated skilled labour.
- Vegetable vendor need not have education.
(ii) Postman, cobbler, soldier, police constable
Answer:
Cobbler.
- The remaining three are government servants.
- Cobbler is self-employed person.
Question 4.
Do you think the classification of economic activities into primary, secondary and services sectors is useful? Explain how.
Answer:
Classification of economic activities into primary, secondary and tertiary is useful.
- If all the economic activities are remained in only one sector, it would be difficult for the calculation of National Income, Per capita Income, etc. parameters.
- Concentration on various economic activities for their growth will not be possible.
- Allocation of funds, administration of sectors all becomes a tough task.
- Classification of activities paves way for smooth functioning of the various calculations concerned.
![]()
Question 5.
For each of the sectors that we came across in this chapter, why should one focus on employ¬ment and GDP? Could there be other issues which should be examined? Discuss.
Answer:
We are studying about the production in our country and the employment in the country. So for each of the sectors we come across one focussed on employment and GDP.
Yes other issues which should be examined are:
- We should know the life expectancy of the people.
- Should prepare a developmental plan and should discuss to which sector will give importance.
- To know the poverty and unemployment range and try to abolish.
- Balanced regional development.
- Modernization of technology.
- Self-reliance of the country.
- How to achieve surplus food production in the country.
Question 6.
How is the service sector different from other sectors? Illustrate with a few examples.
Answer:
- Service sector is different from the other two sectors, agricuture and industry.
- Agriculture and industry sectors produce goods whereas service sector does not produce any good.
- In agriculture and in industrial sector they need the help of service sector in the production of their goods.
- But service sector does not need the help of agriculture or industry in its service.
- Without service sector the needs of people for their physical and mental growth are not fulfilled.
- Service sector is the lifeline of people.
- Growth in service sector indicates modernisation.
![]()
Question 7.
What do you understand by underemployment? Explain with an example each from the urban and rural areas.
Answer:
- The situation of underemployment could be understand as each one is doing some work, but no one is fully employed.
- Here people are apparently working but all of them are made to work less than their potential.
- This underemployment has different areas facets in rural and urban areas.
- In rural areas this could be clearly understood from the example of disguised unemployment.
- Though there is need of 2 persons for the land they have, the entire family of village formers depend on agriculture, which will not sufficiently provide work.
- In urban areas also people work as casual labour in many factories. If there is demand, the factories give them opportunities and if there is no demand, the people are asked to go back without work.
Question 8.
The workers in the unorganised sector need protection on the following issues:
Wages, safety and health. Explain with examples.
Answer:
- Unorganised sector workers need protection on issues of wages, safety and health.
- There is low paid and irregular working days nature of their work.
- They are not given paid leave, holidays with payment and payment for overtime work.
- So they need protection for their wages on par with any organised sector employment.
- There is no security of job for them.
- So they must be provided with safety of the job.
- They do not have leave due to sickness and if they are absent, they lose their wages.
- There must be the protection for their health with paid holidays and medical insurance.
- They are not even provided with safe working environment.
- There must be protection for their safe working environment.
Question 9.
A study in Ahmedabad found that out of 15,00,000 workers in the city, 11,00,000 worked are in the unorganised sector. The total income of the city in this year (1997-1998) was Rs. 6000 crores. Out of this Rs. 3200 crores was generated in the organised sector. Present this data as a table. What are the ways for generating more employment in the city?
Answer:
Contribution of organised and unorganised sectors in Ahmedabad in 1997-98:
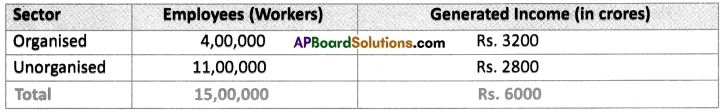
- Government must provide more incentives to people who are engaged in unorganised sector.
- Government should give waiver of certain taxes, exemptions of certain taxes and encourage many others to take up the establishments.
![]()
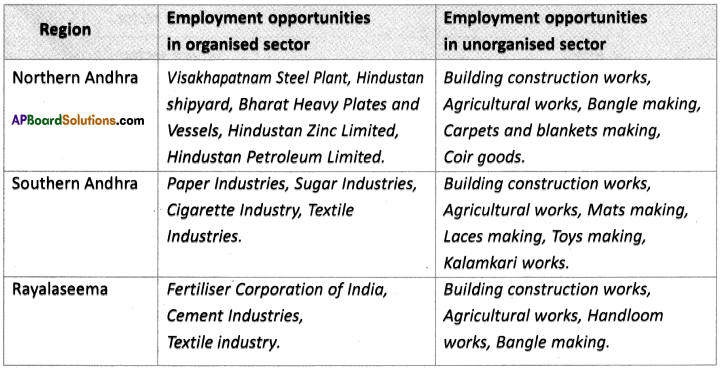
Question 10.
Complete the given table with employment opportunities in organised sector and unorganised sector in various regions of our state.
 Answer:
Answer:
10th Class Social Studies 3rd Lesson Production and Employment InText Questions and Answers
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 28
![]()
Question 1.
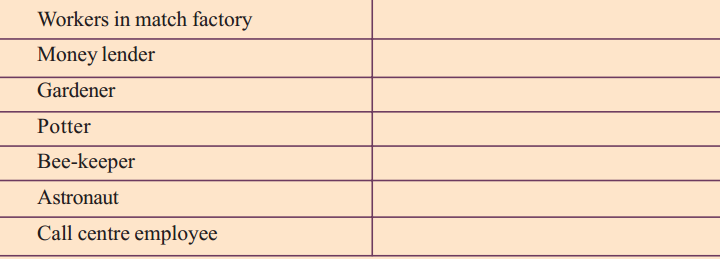
Classify the following list of occupations under agriculture, industry and service sectors. Give reasons for your classification :
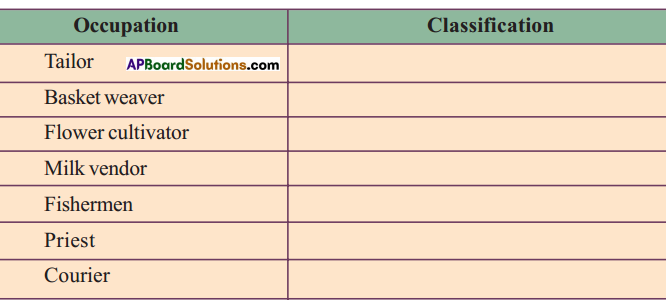
 Answer:
Answer:
| Occupation | Classification |
| Tailor | Basket weaver |
| Flower cultivator | Milk vendor |
| Fishermen | Primary sector |
| Priest | Service sector |
| Courier | Service sector |
| Workers in match factory | Secondary sector |
| Moneylender | Tertiary sector |
| Gardener | Primary sector |
| Potter | Secondary sector |
| Bee-keeper | Tertiary sector |
| Astronaut | Tertiary sector |
| Call centre employee | Tertiary sector |
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 29
![]()
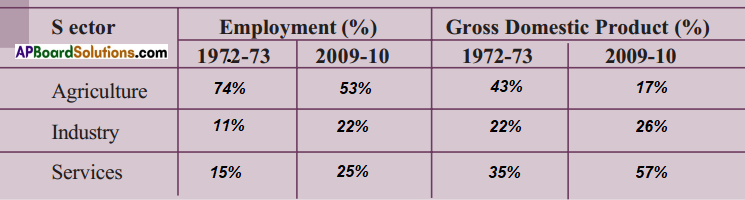
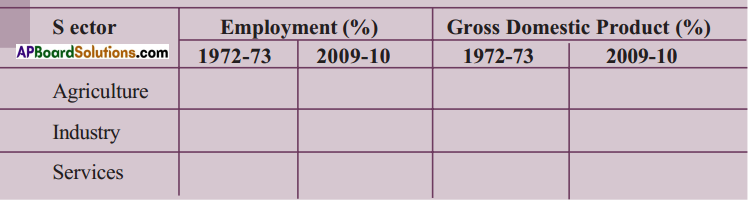
Question 2.
The following table shows the percentage of workers employed in different sectors in India in 1972-73 and in 2009-2010, i.e., after 37 years.
 (i) What are the major changes that you observe from the above table?
(i) What are the major changes that you observe from the above table?
Answer:
- The percentage of workers employed in agricultural sector was decreased by 21%.
- The percentage of workers employed in industrial sector was increased by 11%.
- The percentage of workers employed in service sector was increased by 10%.
- These changes suggest that India is a developing country in its economy,
(ii) From what you have read before, discuss what could be some of the reasons for these changes.
Answer:
- After the planning was started in India, factories came up and started expanding.
- People began to use many more goods.
- Industrial sector became the dominant sector and the importance of agriculture declined.
- In the past 50 years, there has been a further shift from industry to service sector.
- The service sector has become the most important in terms of total production.
Question 3.
Observe the pictures and mention the sector which they belong to :

- ——–
- ——–
- ——–
- ——–
Answer:
- Agricultural sector
- Primary sector (Mining)
- Service sector
- Industrial sector
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 30
![]()
Question 4.
Observe the following graph and answer the given questions.
Graph : GDP by Agriculture, Industry and Service Sectors (Rs. in Crores)
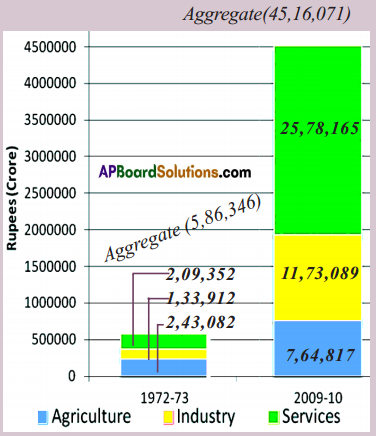 (a) Which was the largest producing sector in 1972 – 73 ?
(a) Which was the largest producing sector in 1972 – 73 ?
Answer:
- Agriculture was the largest producing sector in 1972 – 73.
- Out of the aggregate GDP of 5,86,346 the contribution of agriculture was 2,43,082 and the remaining industry was 1,33,912 and services was 2,09,352.
(b) Which was the largest producing sector in 2009 -10 ?
Answer:
- Services vyas the largest producing sector in 2009 -10 .
- Out of the aggregate GDP of 45,16,071 the contribution of service was 25,78,165 and the remaining industry was 11,73,089 and agriculture was 7,64,817.
(c) Fill in the blank :
The total value of production of goods and services in India increased approximately ——– times between 1972 – 73 and 2009 – 10.
Answer:
8
![]()
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 31
Question 5.
 Discuss : To find out the total value of goods produced should we add them up?
Discuss : To find out the total value of goods produced should we add them up?
Answer:
1) No. We should not add them all.
2) The value of final good (Idli, Dosa) includes the value of all the intermediate goods that are used in making final good.
3) Goods such as paddy, rice and husk are at the intermediary stages.
4) They are not being used by the final consumer.
5) They are used as inputs to make final good. If we add them to final good, we are double counting.
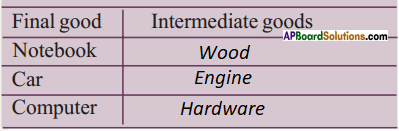
Question 6.
In the above example, paddy or rice is the intermediate good and idli is the final good. The following are a few goods we consume in our daily lives. List some of the intermediate goods against each one.
 Answer:
Answer:
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 32
![]()
Question 7.
 Discuss : Why do both methods give the same result ?
Discuss : Why do both methods give the same result ?
Answer:
Value added at all stages = Rs. 2500 + Rs. 1100 + Rs. 1400 = Rs. 5000. Stage 3 (sale of Idli and Dosa) = Rs. 5000
- Whatever may be the method the value of final goods/services does not change.
- In the first method, we do not add up the intermediate goods as the result in double counting.
- But we calculated the value of the final goods (Idli, Dosa) that were produced.
- In the second method, at every stage we counted the value added.
- Finally we added up all the values added and got the final good value.
- Thus both the methods give the same result.
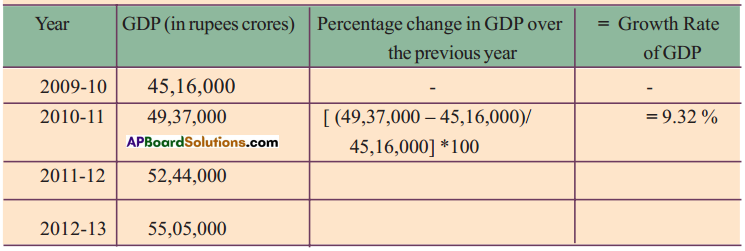
Question 8.
The value of GDP is given the following table. Compute the growth rate of GDP as shown for 2010 – 11?
 Answer:
Answer:
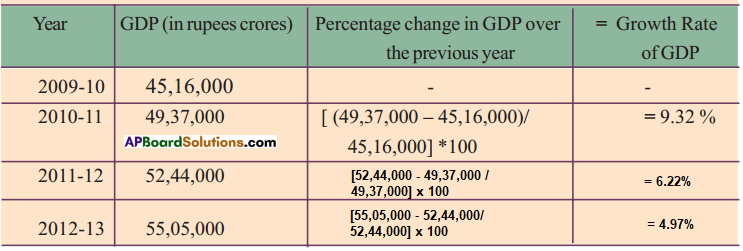 10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 34
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 34
![]()
Question 9.
Can you find out some examples of trade, hotels, transport and communication ?
Answer:
- Different types of shops, showrooms, supermarkets, groceries, hardware merchants, steel merchants, rice traders, fancy and general stores, malls and shopping complex are included in this.
- Different types of tiffin centers, hotels are included in this.
- Various types of vehicles like auto, rickshaw, jeep, van, truck, lorry, bus, passenger train, express train, goods train, double decker train, boat, ship, steamer, helicopter, aeroplane etc. are included in this.
- Newspaper, journals, magazines, e-books, televisions, news channels, sport channels, devotional channels, land lines, cell phones, fax, email, internet and satellite services are included in this.
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 35
Question 10.
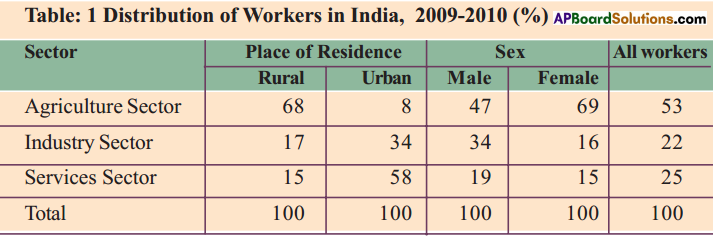 Read the above table and fill in the blanks.
Read the above table and fill in the blanks.
- Majority of workers in agriculture are living in ——– areas.
- Most ——– workers are employed in agriculture sector. Only a small section of ——– is in industrial sector.
- More than 90% of urban workers are getting employment in ——– and ——– sectors.
- Compared to males, female workers are getting employment in ——– and ——– sectors only to a small extent.
Answer:
- rural
- female, 16%
- industrial, service
- industrial, service
![]()
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 36 & 37
Question 11.
Observe the following pie charts.
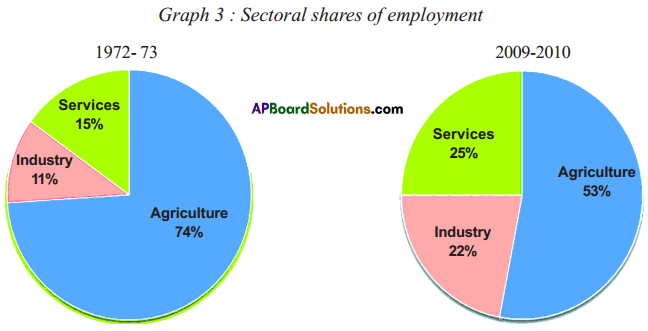
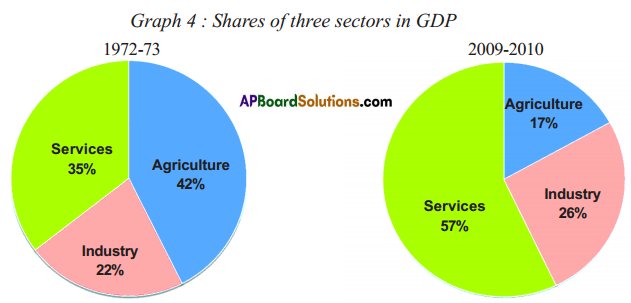
Look at the above pie charts and fill in the following table.
Answer: