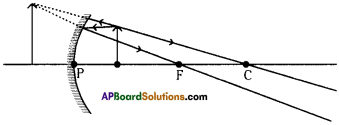
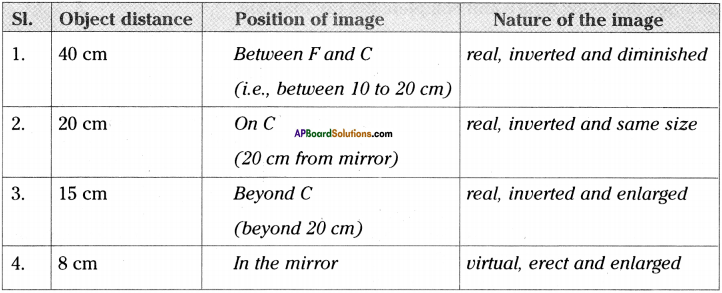
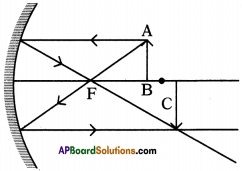
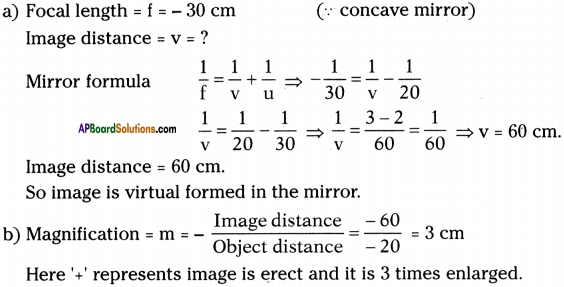
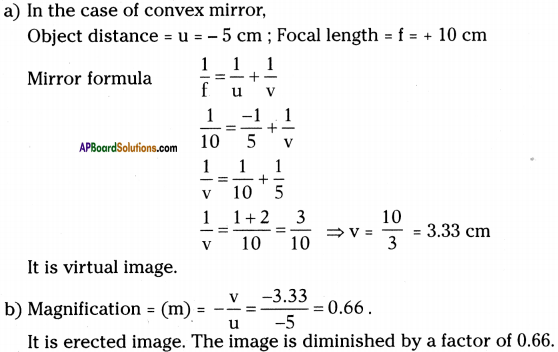
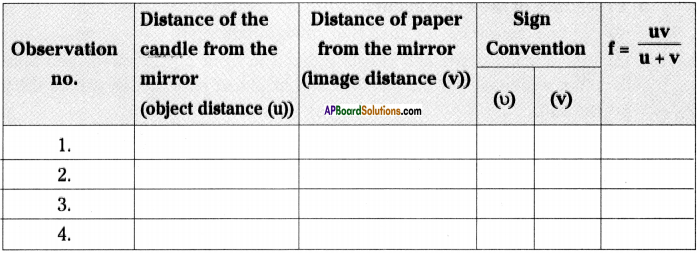
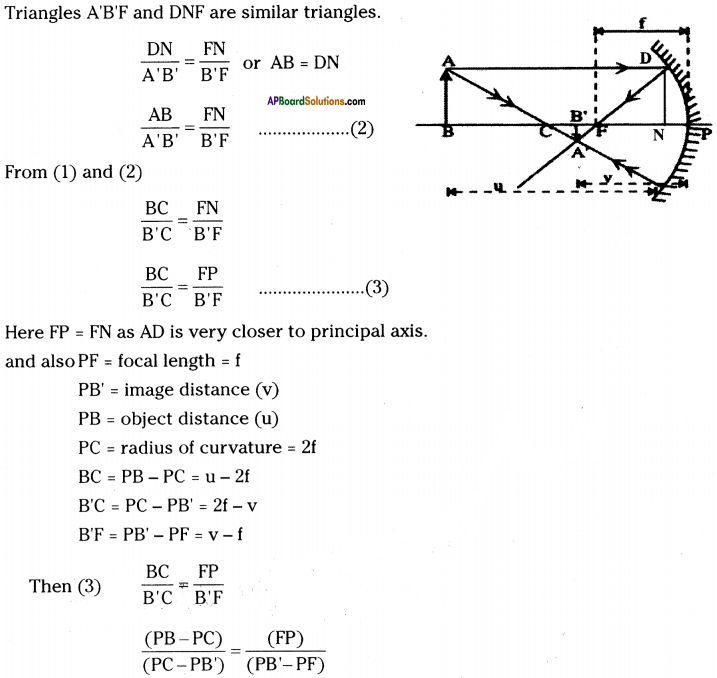
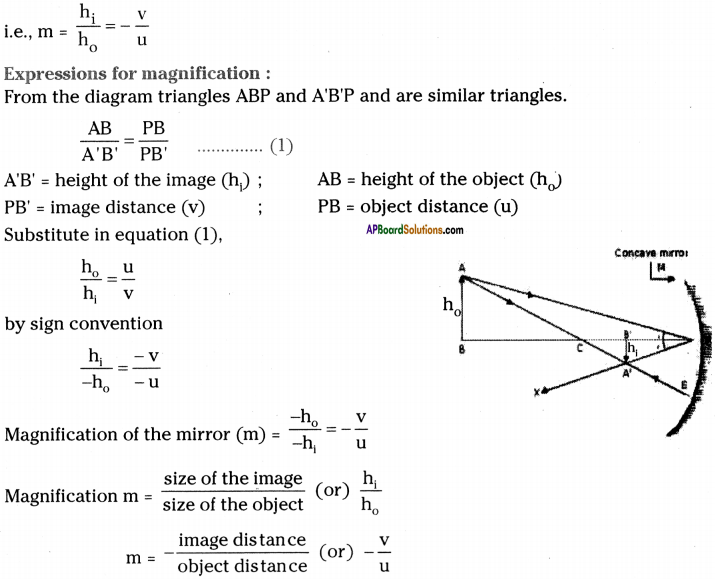
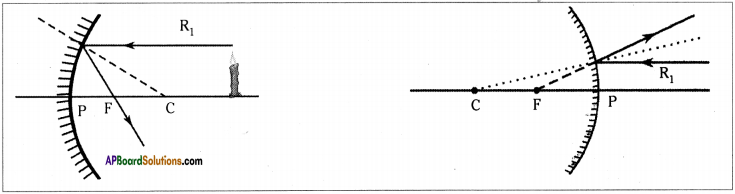
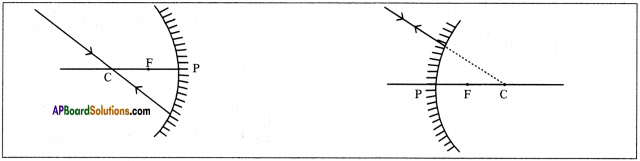
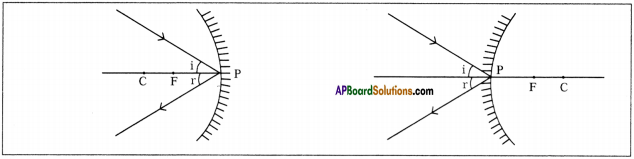
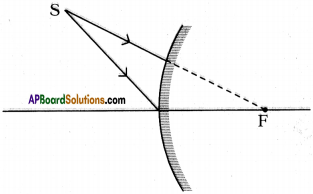
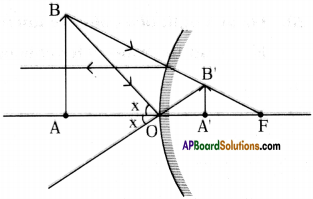
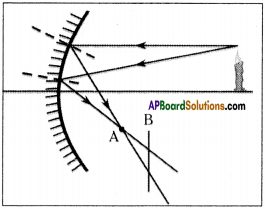
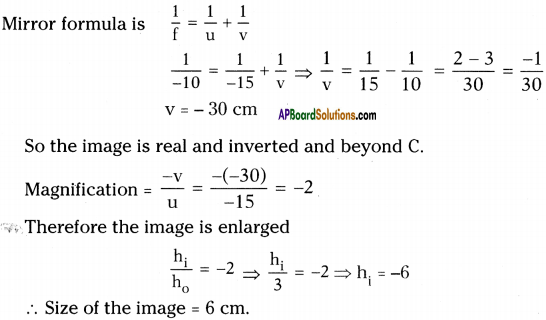
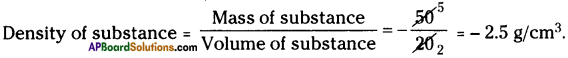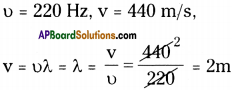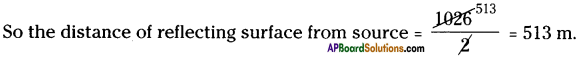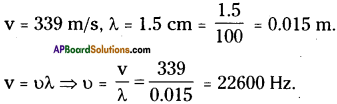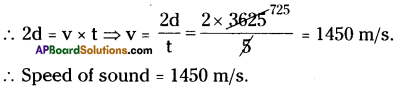SCERT AP Board 9th Class Social Solutions 11th Lesson The Government Budget and Taxation Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Social Studies Solutions 11th The Government Budget and Taxation
9th Class Social Studies 11th Lesson The Government Budget and Taxation Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Why does the government need a budget? Why does the budget talk of taxes?
Answer:
- In most modern societies, the government is responsible for a number of crucial functions.
- These include the more traditional functions like defending the country, maintaining law and order, the provision of public facilities, establishment of factories, and other developmental and welfare activities.
- Revenues are necessary to finance the expenditures of the government.
- In order to steamline the income and expenditure, every government prepares a budget for each financial year.
- Deficit, between expenditure and revenue, will usually be filled by imposing additional taxes.
- Hence the budget always talks of taxes.
Question 2.
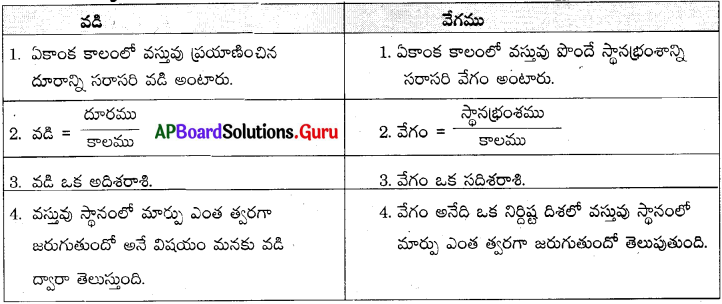
What is the difference between income tax and excise duty?
Answer:
| Income Tax | Excise Duty |
| 1. Income tax is levied on annual personal incomes of individuals. | 1. Excise duty is levied on the production or manufacture of goods. |
| 2. Income tax is a direct tax. | 2. Excise duty is an indirect tax. |
| 3. The tax burden will be on the same person on whom the tax is levied. | 3. Excise duty is charged from the factory itself but the burden is shifted to those who buy the goods. |
| 4. Income tax does not affect the prices of goods. | 4. These taxes raise the overall prices of goods. |
Question 3.
Match the following.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. Excise duty | a) levied on the yearly incomes of the individuals |
| 2. Sales tax | b) levied on the yearly profits of the companies and business establishments |
| 3. Customs duty | c) levied on the production or manufacture of goods |
| 4. Income tax | d) levied when goods are sold |
| 5. Corporate tax | e) levied on goods brought from abroad |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. Excise duty | c) levied on the production or manufacture of goods |
| 2. Sales tax | d) levied when goods are sold |
| 3. Customs duty | e) levied on goods brought from abroad |
| 4. Income tax | a) levied on the yearly incomes of the individuals |
| 5. Corporate tax | b) levied on the yearly profits of the companies and business establishments |
Question 4.
You are expected to pay taxes on steel, matches, clocks, cloth, iron ; a tax increase on which of these would affect the prices of other commodities the most and why?
Answer:
The taxes on iron and steel increase or affect the cost of other goods because they are intermediate goods.
![]()
Question 5.
Ordinary food items, such as grain, pulses, oil are used by all. Then why is it said that imposing tax on them will have a greater effect on the poor?
Answer:
- Ordinary food items, such as grains, pulses, oil, etc., are goods that are essentials,
- The poor spend almost all of their income on these goods.
- Hence imposing tax on them will have a greater effect on the poor.
Question 6.
A group of four friends decided to stay together by contributing money towards the rent of a house. The rent was rupees 2000 per month.
• How could this be shared among them?
• We also know that two of them earned Rs. 3000 rupees per month and the other two Rs. 7000 per month. Is there some other way of sharing the cost so that each one of them feels the same pinch?
• Which way of sharing would you prefer and why?
Answer:
1. One method of sharing the rent is the distribution of the rent equally among all the four members. Then each one has to pay Rs. 500/- (i.e. 2000/4 = 500).
2. Another method of sharing is that everyone has to pay 10% of their earnings as rent. In that case –
a) Two of them whose income is Rs. 3000/-
have to pay 10% of 3000/- = 300/- each.
b) Two of them whose income is Rs. 7000/-
have to pay 10% of 7000/- = 700/- each.
In my opinion 2nd method of sharing is the best as low income people are paying the lower share whereas high income people are paying the higher share of rent.
Question 7.
Tax on income or tax on commodities. Which of the two affects the rich more and which affects the poor more? Explain with reasons.
Answer:
- Tax on income is a direct tax. According to the rules of income tax, those with higher incomes have to pay greater part in tax.
- Those who are less well-off pay not only lower taxes but a smaller proportion of their income as taxes.
- Hence tax on income affects the rich more.
- Tax on commodities is an indirect tax.
- Whether rich or poor, everyone has to pay the same amount of tax when they buy commodities.
- The tax on commodities does not distinguish between the rich and the poor.
- Hence tax on commodities affects the poor more.
![]()
Question 8.
How would VAT reduce the evasion of taxes on goods?
Answer:
- All producers and traders will have to keep genuine record of their sale and purchase.
- Everyone has to keep proper records and ask for bills for purchase.
- It is only on this basis they can show the tax already paid on cost of inputs.
- The tax inspectors will be able to match records of the seller and purchaser for verification.
- These records and verifications in VAT reduce the evasion of taxes on goods.
Question 9.
What is the difference between Excise duty and Customs duty?
Answer:
| Excise Duty | Customs Duty |
| 1. Excise duty is charged from the factory itself. It as levied on the production or manufacture of good. | 1. Customs duty is levied on goods brought from abroad. |
| 2. Taxing certain goods raise overall prices. | 2. Only machines or raw materials which are imported and taxed raise the overall prices of that good. |
Question 10.
Is there any hike in the bus fares recently? If so, try to know the reasons for it.
Answer:
1) It was directly related to the fact that there was a hike in the price of petroleum (product both petrol) and diesel. As price for petrol and diesel has increased nearly 45 times past 2 – 3 months it has come around with a difference of approximately 4 Rs. per liter.
2) So, as to balance this gap and the loss incurred by this the bus fare had been hiked by 40 paisa per kilometer.
Question 11.
Read the paragraph under the heading ‘Direct Taxes’ (Income Tax is charged only for…) and answer the following :
| Income tax is charged on personal income of individuals. There can be a variety of sources of individual incomes like wages, salaries, and pensions. An Individual-can also earn interest income on money that is kept in banks. A person might, also get rent.on properties that he own like house rent. All these are considered as incomes on which taxes have to be paid. Income tax is charged only for those who earn above a certain amount. This is charged as a percentage of the income earned. Those who earn a higher income have to pay a greater proportion of their income as tax. |
Why do high income earners pay more tax?
Answer:
- What kind of tax we follow depends on the values that the society as a whole holds.
- Many societies feel that it is not fair that a few people have lakhs of rupees, while others do not have enough to eat.
- The poor or the low income group cannot meet their daily expenses.
- Then why should tax be imposed on them?
- The poor should not feel the pinch of tax.
- Hence collection of more tax from the higher income group is justifiable.
![]()
Question 12.
What is the effect of black money on our economy?
Answer:
- Black money circulation in the parallel economy is a big menace to the economy.
- It is also a cause of big loss in the tax-revenues for the government. As such it needs to be curbed.
- Its elimination will benefit the economy in more than one way. It will also generate more revenues for the government.
Question 13.
Bring a few wrappers of soaps, toothpastes, tablet strips or any other things of daily use which contain MRP Discuss the rate mentioned and the rate at which they are so!d. Talk about the profit that the retailer gets.

Answer:
Please scan the some of the wrappers of Biscuits, toothpaste, soaps, etc. with MF The MRP that are printed on the wrappers are fixed by the manufactures. The Manufactures incude the cost of production, tax, VAT, commissions, transportation cost and profits etc. From them retailer bought the goods on wholesale and he mix up again transportation cost, tax, vat and his profit. In that retailer get more profits because he bought the good with low cost he sold more cost. Again he mix up the VAT & Tax also profit to him.
9th Class Social Studies 11th Lesson The Government Budget and Taxation InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Can you guess from where does the government get money for pubficfacilitiesand other activities? (Text Book Page No. 132)
Answer:
Government raises the revenue required to meet expenditure. The following are the types of revenue of government.
- 1) Taxation –
a) Direct taxation,
b) Indirect taxation - Charging for services directly provided to the public.
- Profits from state-owned enterprises.
- Borrowings from domestic markets and international sources.
Question 2.
| Cost of manufacturing including profit of the manufacturer | Rs. |
| 10,000 | |
| Excise Tax | 1,200 |
| Cost of Transport, Storage | 1,000 |
| Profit to the Retail Traders | 1,000 1 |
| Sales tax | 1,650 |
| Price for the consumer | 14,850 |
In the example of the TV, what proportion of the cost of the TV did the consumer pay as tax? (Text Book Page No. 136)
Answer:
12% of the cost of the TV is charged as tax. The consumer pays Rs. 1,200 by way of tax.
![]()
Question 3.
Fill in: (Text Book Page No. 138)
The purchases by Tara, Sajida and Preeti show __________ tax rates across goods. (same/different)
Answer:
different (same/different)
Can you guess why this should be so?
In case of Tara VAT = 5% of 5,000 = Rs. 250
In case of Sajida VAT = 12.5% of 9,165 = Rs. 1,146
In case of Preeti VAT = 0 (No VAT on LPG) = Rs. 0
Question 4.
You might think it would be fair for everyone to pay the same amount of tax. Consider the following three prople : (Text Book Page No. 139)
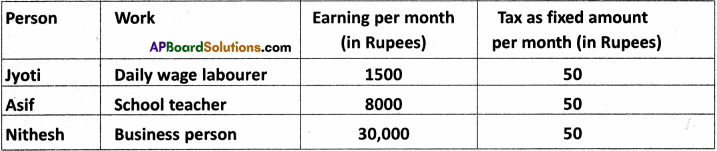
Would it really be fair if each of the three people has to pay the same amount? If Jyoti cannot even afford to feed her children properly, is it fair for her to pay 50 rupees as tax?
Answer:
- According to the rules of income tax, those with higher incomes have to pay greater part in tax.
- Those with less well-off pay have to pay lower taxes.
- In the above example, Jyothi, Asif, and Nithesh are paying same tax of Rs. 50/- though their incomes vary a lot. Hence this type of taxation is not fair.
Question 5.
You might think it would be more fair to ask each person to pay a certain pecentage of what they earn as tax. Supposing everyone paid 10% in taxes, calculate how much each person would pay? (Text Book Page No. 139)
| Person | Earning per month (in Rupees) | Tax as fixed amount per month (in Rupees) |
| Jyoti | 1500 | |
| Asif | 8000 | |
| Nithesh | 30,000 |
Would this be fair? Still Jyoti may not have enough to live. Asif may not have enough for repairing of his house. But Nithesh would have plenty of money for all basic necessities even if he had to pay 20% of his income as taxes.
Answer:
- Tax rate is same for all people i.e. 10%.
- So Jyothi has to pay 10% of 1500 i.e., Rs. 150/-
- Asif has to pay 10% of 8000 i.e., Rs. 800/-
- Nithesh has to pay 10% of 30000 i.e., Rs. 3000/-
This is not fair. This is against the progressive taxation which insists that the rate of tax has to be increased when income increases.
Hence charging 20% of tax on Nithesh is quite fair.
![]()
Question 6.
To make taxes more fair you might then say only the people earning more than a certain amount say Rs. 7000 per month have to pay taxes. You might also say that the richest people should pay greater proportion of their earnings as taxes. For example
| If you earn (in Rupees) | You will pay as tax |
| Less than 7000 | 0% |
| 7001 to. 15000 | 10% |
| 15,001 to 25,000 | 20% |
| More than 25,000 | 30% |
Calculate how much each person will pay. (Text Book Page No. 139)
| Person | Earning per month (in Rupees) | Tax as fixed amount per month (in Rupees) |
| Jyoti | 1000 | |
| Asif | 6000 | |
| Nithesh | 20,000 |
Would this be fair?
Answer:
- As per the above rule, people below Rs. 7000/- income are exempted from taxation.
- Hence Jyothi and Asif need not have to pay taxes.
- Nithesh’s income is Rs. 20,000/-
- As per table he has to pay 20% of tax.
- Tax to be paid by Nithesh = 20,000 x 20/100 = 4000/-
This type of taxation is called progressive taxation. The tax rate increases as income increases.
The above taxation satisfies the principle that the richest people should pay greater portion of their earnings as taxes.
Hence this method is the fair way of taxation.
Question 7.
With the help of this pie chart, answer the following questions.
Expenditure of the Government (Center and States), in 2011-12

In 2011-12 the government spent around Rs.23,00,000 crores.
1. Calculate the expenditure of the government on food subsidy. (Text Book Page No. 133 & 134)
Answer:
Total government expenditure = 23,00,000 crores
Share of food subsidy = 3%
Total food subsidy = 23,00,000 × 3/100 = 69,000 crores.
2. Discuss on what all was this money spent and the purpose for this?
Answer:
- The government has assumed responsibility for supply of essential commodities like wheat, rice, sugar, edible oils and kerosene etc.
- The prices of goods sold through Public Distribution System (PDS) are less than ‘ that of the market price and the difference in price – is borne by the government.
- So the government spends 69,000 crores on-food subsidy.
![]()
Question 8.
Relate some of the expenditure in the pie-chart to the roles played by the government. (Text Book Page No. 134)
Answer:
Roles of government and expenditure spent
| 1. Defence | 7% |
| 2. Railways, transport and communication | 6% |
| 3. Education, etc. | 12% |
| 4. Health and sanitation | 4% |
| 5. Housing and urban development | 3% |
| 6. Rural development (e.g. NREGA) | 4% |
| 7. Power, irrigation and flood control | 6% |
| 8. Fertilizer subsidy | 2% |
| 9. Administration | 8% |
| 10. Pensions | 7% |
| 11. Interest payment | 17% |
| 12. Food security | 3% |
| 13. Others | 21% |
| Total expenditure | 100% |
Question 9.
Collect and list out some details of government expenditure from reading the newspapers of your region. (Text Book Page No. 132)
Answer:
- Government expenditure is also known as public expenditure.
- From the point of view of development, public expenditure is classified as
1. Development expenditure
2. Non-development expenditure. - From the point of view of creation of capital assets, public expenditure is classified as
1. Revenue expenditure
2. Capital expenditure
| Revenue Expenditure | Capital expenditure |
| 1. General Administration | 1. Construction of irrigation projects |
| 2. Defence (Daily expences) | 2. Establishment of basic industries, power projects |
| 3. Maintenance of schools, hospitals, roads, pensions etc. | 3. Construction of National highways etc. |
Question 10.
If the tax on iron is increased, what other things will this affect? Give some examples. (Text Book Page No. 136)
(OR)
Explain the example given in below picture. Write the relationship between indirect taxes and consumers.
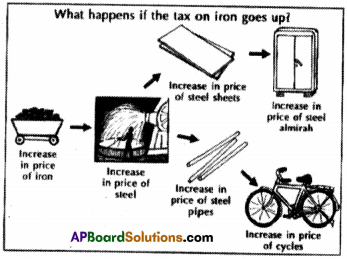
Answer:
- If the price of iron is increased it will directly affect the price of steel.
- Increase in the price of steel leads to increase in the prices of steel sheets and steel pipes.
- Increase in steel sheets will lead to increase in steel almirah and increase in price of steel pipes leads to increase in the prices of cycles and the chain goes on.
Question 11.
We read about some of the major taxes collected by the government. Fill the table from the information given below. Income Tax: 12%; Corporation Tax: 24%; Customs Duty: 10%; Excise Duties: 16%; Service Taxes: 5%; Sales Tax: 23%; Other Indirect Taxes: 10%. (Text Book Page No. 141)
| Taxes | Percentage of Total Tax |
| Direct Taxes | 36% |
| Indirect Taxes | |
| Total taxes | 100% |
Answer:
Taxes Collected by the Government
| Taxes | Percentage of Total Tax |
| Direct Taxes | 36% |
| Income tax | 12% |
| Corporate Tax | 24% |
| Indirect Taxes | 64% |
| Customs duty | 10% |
| Excise duty | 16% |
| Service taxes | 05% |
| Sales taxes | 23% |
| Other taxes | 10% |
| Total taxes | 100% |
1) Which kind of taxes generate more revenues for the government?
Answer:
- Indirect taxes generate more income. They contribute 64% of all the taxes.
- Corporate tax contributes 24% of th? taxes and.sales tax contributes 23% of the taxes.
![]()
Question 12.
Kranti has an income of Rs. 1,75,000 per year and has to pay an income tax of Rs. 3000. Kamlesh’s annual income is Rs.3,00,000 and he has to pay an income tax of Rs.5,500.
a) Who pays more income tax? (Text Book Page No. 141)
b) Who has to pay a larger part of the income as tax?
c) In such a situation, the person with higher income is paying a _________
(smaller/greater/equai) part of the income as tax.
Answer:
a)
- Kranti pays 3% of her income as tax.
- Kamiesh’s pays 2.75% of her income as tax.
- When we take rate of tax into consideration, Kanti is paying high rate.
- When we consider the amount of tax paid Kamlesh pays more tax.
b) Kranti has to pay a larger part of the income as tax i.e. 3% when compared with Kamlesh who pays 2.75% as tax.
c) smaller
Question 12.
In your city/town/village, what are the roles that you have seen the government playing? Discuss. (Text Book Page No. 132)
Answer:
- Maintenance of law and order.
- Provision of education facilities.
- Looking after of health and sanitation.
- Construction of roads,, highways, dams, irrigation projects.
- Establishment of factories etc.
Question 13.
In the year 1947-48, the budget for independent India was only Rs. 197 crores. What could be the reasons for such an increase in the budget since then? (Text Book Page No. 134)
Answer:
- Increase in the cost of different goods.
- Increase of cost of exports.
- Decrease in the value of money.
- Change of roles played by government i.e., provision of subsidized fertilizers, food, development of infrastructure facilities etc.
![]()
Question 13.
Why do you think has the Parliament been given power over the government’s budget? (Text Book Page No. 134)
Answer:
- Our government is a representative form of government.
- All the Parliament members are people’s representatives.
- Hence they are given power, on behalf of the people, to talk on budget and to decide on budget. No tax is levied without Parliament’s approval.
Question 14.
Petrol, diesel, etc., are used to run vehicles, motor pumps, generator sets etc. What will happen if the tax on diesel and petrol goes up? (Text Book Page No. 135)
Answer:
- Increase in the prices of diesel and petrol leads to the increase in the cost of transportation.
- Which in turn rise the prices of important commodities.
Question 14.
What is your opinion about value added taxes? Discuss. (Text Book Page No. 138)
Answer:
- The tax paid by the manufacturer under VAT system is smaller since she does not have to pay tax on inputs.
- Non-payment of tax is expected to be more difficult.
Due to above advantages, the VAT tax is to be levied.
Question 15.
If there are two people manufacturing the same goods and one of them evades paying taxes, what advantages could he/she get over the other? (Text Book Page No. 136)
Answer:
The margin of his/her profit may go up.
![]()
Question 16.
There have been continuous attempts by the government to reduce fertiliser subsidy. This means that the government would no longer control the price of fertiliser. Farmers would have to buy fertilisers at higher market prices. At present, the government has to pay (compensate) the fertiliser producing companies for the losses that they make. Once fertiliser subsidy is removed, it is said this would make space for other important expenditures in the government budget. Some also argue that subsidised fertiliser does not benefit the small farmer but only encourages the large farmers to overuse it.
Imagine you are a farmer using fertilisers in farming, and you genuinely believe that the farmers need subsidized fertiliser. How would you argue your case? Write a
letter to the Finance Minister. (Text Book Page No. 134)
Answer:
|
Kankipadu To Yours sincerely, |