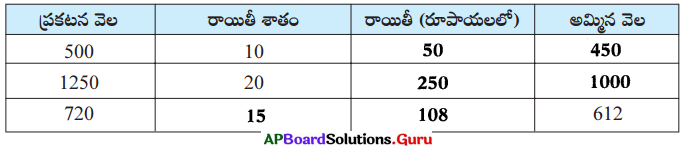
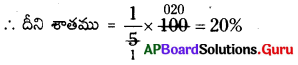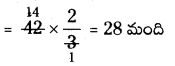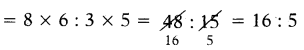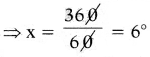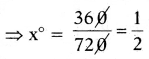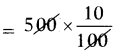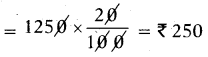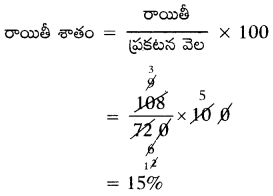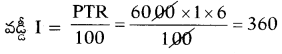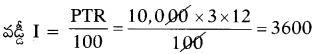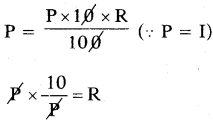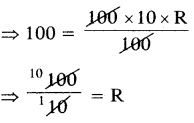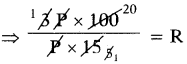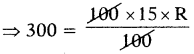These AP 7th Class Science Important Questions 8th Lesson Wonders of Light will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP Board 7th Class Science 8th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Wonders of Light
Question 1.
What is source of light? Give examples.
Answer:
Light comes from different objects called sources, of light. Ex: Sun, candle, tube light.
Question 2.
What are Parallel beam of light rays?
Answer:
Light rays which travel parallel to each other are called Parallel beam of light rays.
Question 3.
What are converging beam of light, rays?
Answer:
Light rays which travel from different directions to meet at a point are called as con¬verging beam of light rays.
Question 4.
What is reflection of light?
Answer:
The process of bouncing back of light rays into the same medium after falling on a smooth or rough surface from the light source is called “reflection of light”.
![]()
Question 5.
How objects are visible?
Answer:
Objects are visible only when light falls on the objects and bounces back to the eye.
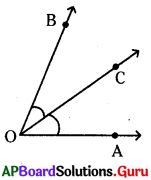
Question 6.
What is angle of incidence?
Answer:
The angle made by incident ray with the normal is called angle of incidence (i).
Question7.
What is angle of reflection?
Answer:
The angle made by the reflected ray with the normal is called the angle of reflection (r).
Question 8.
Write the first law of reflection.
Answer:
The angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection.
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
This is the first law of reflection.
Question 9.
Write the second law of reflection.
Answer:
The incident ray reflected ray and normal to the surface are present in the same plane and incident, reflected rays are on either side of normal. This is the second law of reflection.
Question 10.
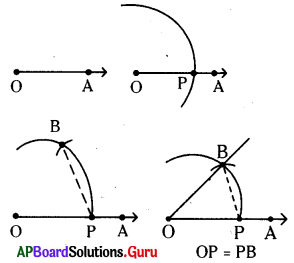
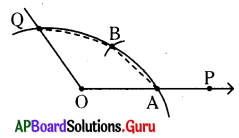
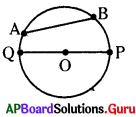
How is the object distance and image distance of a plane mirror?
Answer:
The distance of the object from the mirror is equal to the distance of image from the mirror.
![]()
Question 11.
What is object distance?
Answer:
The distance of the object from the mirror is called object distance.
Question 12.
What is image distance?
Answer:
The distance of the image from the mirror is called image distance.
Question 13.
We are able to see our image in the mirror. Can we get pur image on screen?
Answer:
We cannot get the image formed by a plane mirror on the screen.
Question 14.
What is a real image?
Answer:
The image which can get on a screen is called real image.
Question 15.
What is a virtual image?
A. The image which cannot get it on screen is called virtual image.
Question 16.
How is the nature of the image formed by a plane mirror?
Answer:
The nature of the image formed by a plane mirror is virtual and erect image.
Question 17.
What is Periscope?
Answer:
Periscope is an instrument used in submarines to see the objects or persons above the water level.
![]()
Question 18.
What is the use of a Periscope?
Answer:
We can use this to see the objects outside the room through the window while hiding ourself in the room.
Question 19.
What is a convex mirror?
Answer:
The spherical mirror which has reflecting surface bent outward is called convex mirror.
Question 20.
What is a concave mirror?
Answer:
The spherical mirror which has reflecting surface bent inward is called concave mirror.
Question 21.
What is a lens?
Answer:
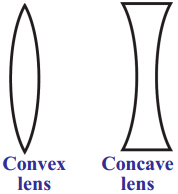
A piece of glass or any other transparent material with curved sides is called a lens.
Question 22.
What is a convex lens?
Answer:
Lens which is thick in center and thin at the edges is called convex lens.
Question 23.
What is a concave lens?
Answer:
Lens which is thin in the Centre and thick at the edges is called concave lens.
Question 24.
What basic principle is involved in a periscope?
Answer:
Periscope is prepared based on the principle of reflection of light from plane mirrors.
Question 25.
What are the uses of a concave mirror?
Answer:
Concave mirrors are used by dentists, ophthalmologists, ENT doctors and also in head lights of vehicles.
Question 26.
What are the uses of a convex mirror?
Answer:
Convex mirrors are used as rearview mirrors in vehicles and safety mirrors at curved roads.
Question 27.
How white light is composed?
Answer:
White light is composed of seven colours.
![]()
Question 28.
Why do dentists use a concave mirror?
Answer:
Dentists also use concave mirrors to get a bigger image of the teeth.
7th Class Science 8th Lesson Wonders of Light Short Questions and Answers
Question 1.
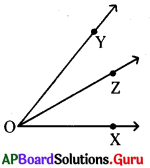
What is a beam of light? How many types of beam of lights are there?
Answer:
The bundle of light rays are called beam of light rays. These are three types.
- Parallel beam of light rays
- Converging beam of light rays
- Diverging beam of light rays.
Question 2.
Write the differences between natural and artificial light sources.
Answer:
| Natural sources of light | Artificial sources of light |
| 1. Objects that emit light on their own are known as natural sources of light. | 1. Objects that release light artificially are called man made sources of light or artificial sources of light. |
| 2. Sources like sun, stars are natural sources of light. | 2. Sources like bulb, torch light, candle artificial sources of light. |
| 3. These emit light on their own. | 3. These don’t emit light on their own. |
Question 3.
What is a ray of light? How does it represent?
Answer:
- The direction or path along which light travels is called a ray of light.
- It is denoted by a straight line with an
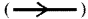 arrow mark.
arrow mark. - The straight line indicates the path of light and arrow mark indicates the direction of light from the source.
Question 4.
Differentiate between regular and irregular reflections.
Answer:
| Regular reflection | Irregular reflection |
| 1. Reflection from a smooth and shiny surface is called regular reflection. | 1. Reflection from an irregular or uneven surface is called irregular reflection or diffused reflection. |
| 2. Clear images are formed in case of regular reflection. | 2. Images are not clear or sometimes cannot form the images at all in case of irregular reflection. |
| 3. Plane mirrors, stable water surfaces, polished metals and stones can give regular reflections. | 3. Rough surfaces, unstable water surfaces, unpolished metals and stones can give irrregular reflections. |
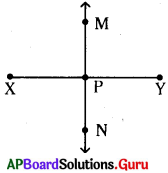
Question 5.
What are the characteristics of image by plane mirror?
Answer:
Characteristics of image by plane mirror:
- Object distance is equal to image distance.
- Size of the object is equal to size of the image.
- The image formed is always virtual and erect.
- Laterally inverted image is formed, (left and right alternates)
![]()
Question 6.
When you are eating food with right hand it appears to be eating with left hand in a mirror. Why?
Answer:
When you are eating food with right hand it appears to be eating with left hand in a mirror. Such a shift of lateral side of images in opposite direction is called lateral inversion. Images formed by plane mirrors undergo lateral inversion.
Question 7.
Write the differences between real and virtual images.
Answer:
| Real images | Virtual images |
| 1. The image which can get on a screen is called real image. | 1. The image which cannot get it on screen is called virtual image. |
| 2. Real image is always inverted. | 2. Virtual image is always erected. |
| 3. Concave mirrors form real images. | 3. Plane mirrors form virtual images. |
| 4. We cannot see directly in the mirror. | 4. We can see directly in the mirror. |
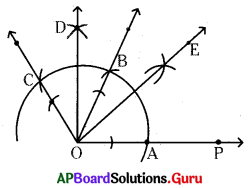
Question 8.
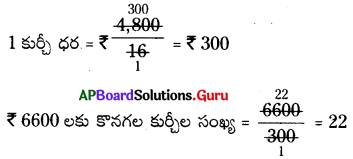
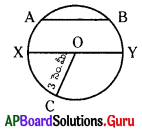
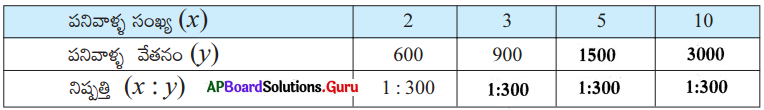
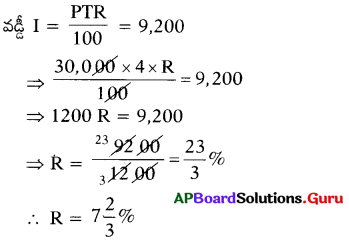
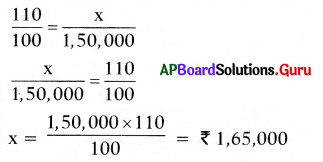
Find the number of images will be formed, if the two mirrors are kept at an angle 50° between them?
Answer:
If the two mirrors are kept at an angle 50s between them, then the number of images between them are,
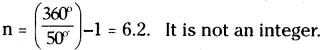
Seven is the next integer after 6.2.
So, the number of images formed will be seven
Question 9.
Write the differences between a convex mirror and a concave mirror.
Answer:
| Convex mirror | Concave mirror |
| 1. The spherical mirror which has Reflecting surface bent outward is called convex mirror. | 1. The spherical mirror which has Reflecting surface bent inward is called concave mirror. |
| 2. The light is diverged by the convex mirror. | 2. The light is converged by the concave mirror. |
| 3. It is used in vehicles as rear view mirrors. | 3. It is used by dentists and ophthal-mologists. |
| 4. A convex mirror always forms virtual, erect, smaller image irrespective of the position of the object. | 4. A concave mirror forms real and virtual images, erect and inverted images smaller, same size and bigger images depending on the position of object in front of it. |
Question 10.
Write the characteristics of image formed by a concave mirror and a convex mirror.
Answer:
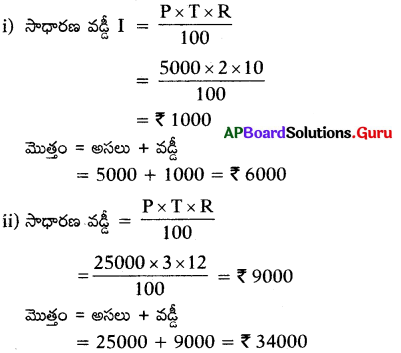
1) Characteristics of image formed by a concave mirror :
A concave mirror forms real and virtual images, erect and inverted images, smaller, same size and bigger images depending on the position of object infront of it.
2) Characteristics of image formed by a convex mirror :
A convex mirror always forms virtual, erect, smaller image irrespective of the position of the object.
![]()
Question 11.
How the ENT doctors are using a concave mirror?
Answer:
- Concave mirrors are used by ENT doctors as Head mirrors.
- They have this mirror strapped on their head.
- Light from the bulb is made to fall on the mirror gets reflect from it.
- This reflected light is focused into the throat or ear of the patient. So that the doctor can examine inner parts clearly.
Question 12.
How the ophthalmologists are using a concave mirror?
Answer:
- Ophthalmologists use a special instrument called Ophthalmoscope.
- It is fitted with a.concave mirror having a small hole near its center.
- The concave mirror helps the doctor to direct a beam of light into the patient’s eye and see his/her retina clearly through the hole in the mirror.
Question 13.
Why the surface of reflection in a torch light or a headlight of vehicle is made with a concave mirror, behind the bulb?
Answer:
- The surface of reflection in a torch light or a headlight of vehicle is made with a concave mirror, behind the bulb.
- Light released from the bulb falls on the concave surface.
- After reflection from concave surface, all the light rays travel parallel to each other.
- So that we can observe focused light at a distance.
Question 14.
Why do convex mirrors use beside the drivers in vehicles?
Answer:
- The convex mirrors which are used beside the drivers in vehicles are called rear view mirrors. .
- These mirrors form images of objects spread over a large area.
- So, these help the driver to see the traffic behind them.
Question 15.
Write the uses of convex mirrors.
Answer:
- Large convex mirrors kept at the corners of curved roads to avoid accidents.
- Convex mirrors form images of vehicles on both sides of curved road.
- These mirrors are also used at the junctions of roads.
- These mirrors used as rear view mirrors in vehicles.
Question 16.
Which colour of light is better to see? Why?
Answer:
- Yellow light is better to see.
- Yellow light has been proven effective in protecting retina than blue light which causes damage to retina.
Question 17.
What is the rule of 20 – 20 – 20?
Answer:
While watching TV or computer a simple rule 20 – 20 – 20 helps us in protecting eyesight. After 20 minutes of watching TV or computer screen, take 20 seconds break and watch the TV or computer around 20 feet away.
Question 18.
Akshaya got many doubts while her brother is burning a paper with a magnifier. What would be those doubts?
Answer:
- How does a magnifier burn the paper?
- Why are the sun rays passing through the magnifier, without reflecting back?
- What is the shape of the magnifier?
- What happens to the sun rays after passing through the magnifier?
Question 19.
Guess, what will happen if a concave mirror or a plane mirror is used as a rear view mirror?
Answer:
- Generally convex mirror is used in rear view mirror.
- Because these mirrors form images of objects spread over a large area.
- The images’formed by the convex mirror have the characteristics like erect, virtual and smaller images.
- So, these help the driver to see the traffic behind them.
- If we U9e a concave mirror instead of a convex mirror it does not form any images of the rear objects.
- If we use a plane mirror instead of a convex mirror we cannot see the images of the rear objects totally.
Question 20.
Ramesh is not able to identify different spherical mirrors. Explain him, the differ-ences between concave and convex mirrors by asking some questions.
Answer:
- How the shining surface of the mirrors are bent?
- What do we call the mirror, if it has reflecting surface bent inwards?
- What do we call the mirror, if it has reflecting surface bent outwards?
- How is your image in the both the mirrors?
- Which mirror forms smaller image?
- Which mirror can form your image on the wall?
![]()
Question 21.
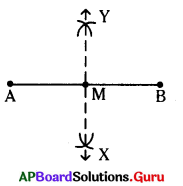
Guess, why does we cannot see our face on a wall clearly?
Answer:
Light rays coming from the face fall on the wall and suffer irregular reflection, because wall has rough surface. Irregular reflection causes formation of no image on the wall or sometimes not cleared images.
Question 22.
How do you show the parallel light by an activity?
Answer:
- Take a plank and cardboard.
- Make small slits on cardboard.
- Keep the cardboard on the plank perpendicular to it. Keep it in sunlight during afternoon.
- The light rays from the sun fall on the cardboard and passed through the slits. We can observe that the light rays are travelling parallel to each other.
Question 23.
How do make your own spherical mirrors?
Answer:
- Take a silver paper used for decoration.
- Paste the silver paper without folds on a postcard size chart paper.
- Allow it to dry by keeping it under some heavy books.
- Bend the sheet slightly forward as its shiny surface comes inwards.
- It works as a concave mirror.
- Now bend the sheet slightly backward as its shiny surface comes out wards.
- It works as a convex mirror.
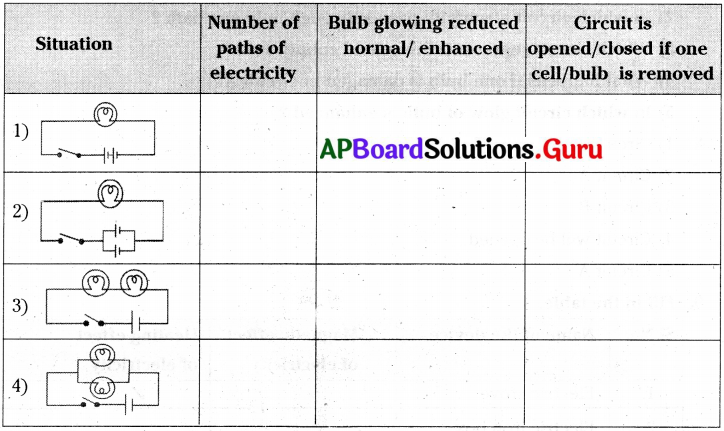
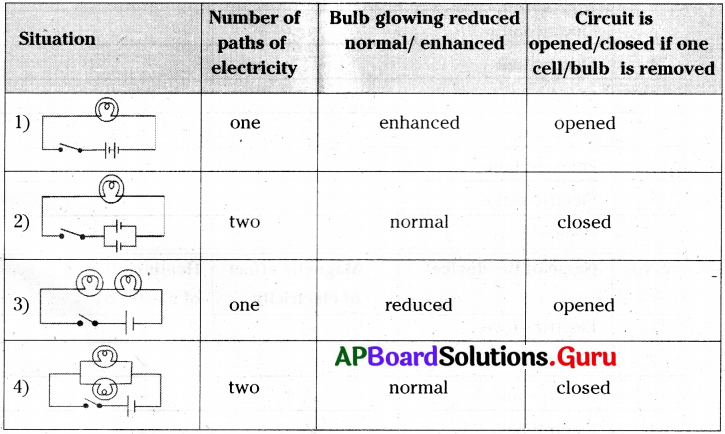
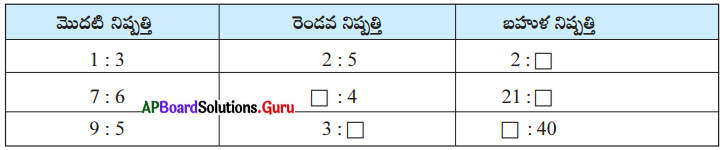
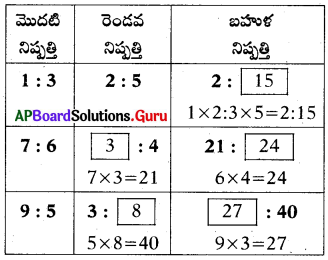
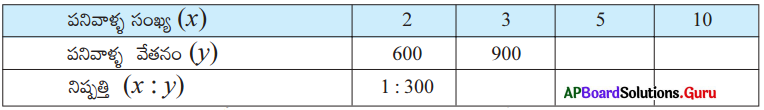
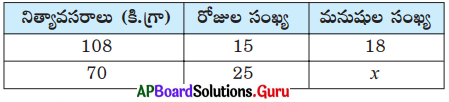
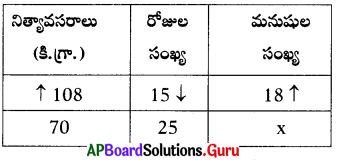
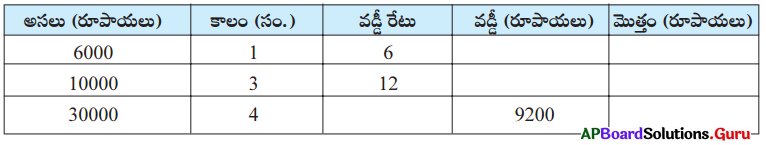
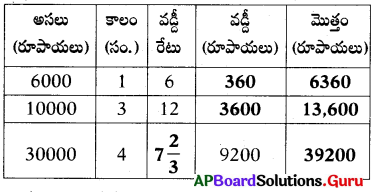
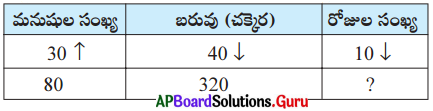
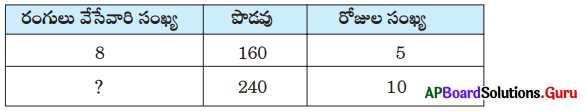
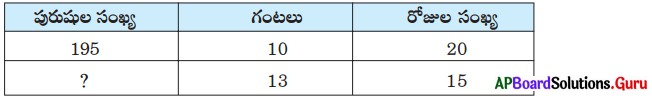
Question 24.
Fill in the table with suitable answer.
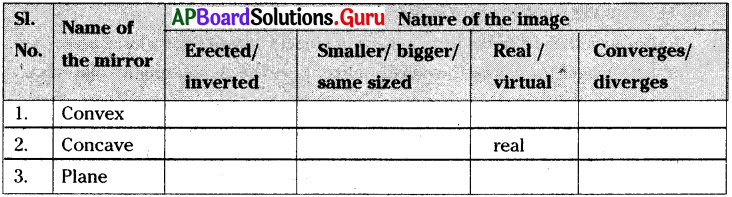
Answer:
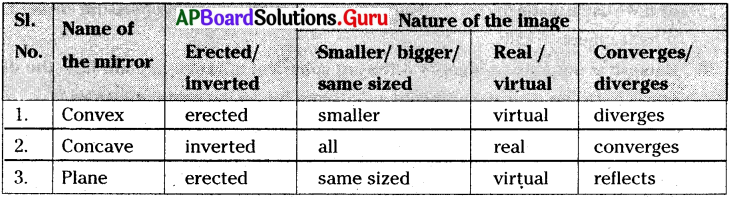
Question 25.
How do you appreciate the role of the spherical mirrors in our daily life?
Answer:
- Concave and convex mirrors are spherical mirrors.
- Concave mirrors are used by dentists, ophthalmologists, ENT doctors and also in head lights of vehicles.
- Convex mirrors are used as rear view mirrors in vehicles and safety mirrors at curved roads.
- Hence, I appreciate the role of the spherical mirrors in our daily life.
Question 26.
What precautions do you take to watch a TV?
Answer:
While watching TV or computer a simple rule 20 – 20 – 20 helps us in protecting eyesight. After 20 minutes of watching TV or computer screen, take 20 seconds break and watch the TV or computer around 20 feet away.
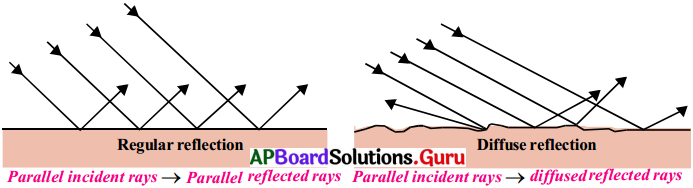
Question 27.
Draw the diagrams of regular reflection and diffused reflection.
Answer:
Question 28.
Draw the diagram of a source of light.
Answer:

Question 29.
Draw the diagram showing the reflection of an incident ray.
(OR)
Draw the diagram showing an incident ray, reflected ray and a normal.
Answer:
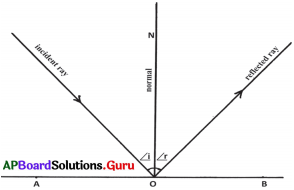
Question 30.
Draw the diagram of a periscope and lable its inner parts.
Answer:
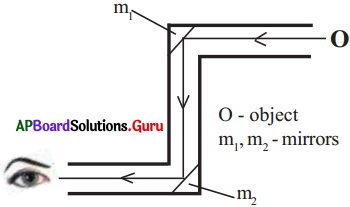
Question 31.
Draw the diagram of a convex mirror and concave mirror.
Answer:

Question 32.
Draw the diagram of a light ray.
Answer:
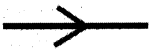
Question 33.
Draw the diagrams of a convex lens and a concave lens.
Answer:
Question 34.
Draw the diagram of arrangement of the apparatus in the activity of verifi¬cation of the laws of reflection.
Answer:

7th Class Science 8th Lesson Wonders of Light Long Questions and Answers
Question 1.
a) What is reflection of light?
b) How many types of reflection are there? What are they?
c) Write the laws of reflection.
Answer:
a) The process of bouncing back of light rays into the same medium after falling on a smooth or rough surface from the light source is called “reflection of light”.
b) Reflections are of two types :
1. Regular reflection
2. Diffused reflection.
Reflection from a smooth and shiny surface is called regular reflection. Reflection from an irregular or uneven surface is called irregular reflection or diffused reflection.
c) Laws of reflection :
There are two laws of reflection.
1. Angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
2. The incident ray reflected ray and normal to the surface are present in the same plane. Incident and reflected rays are on either side of normal.
Question 2.
Draw the reflected ray to the given incident ray.
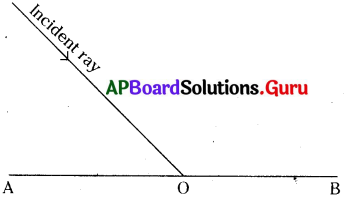
Answer:

Question 3.
Answer the following.
1) What is light?
2) What is source of light?
3) How do you classify the light sources?
4) What are the different types of light beams? Explain.
Answer:
1) Light is a form of energy.
2) Light energy releases from different objects called sources of light.
3) Sources which release light energy on their own are called natural sources.
Ex: sun, stars.
Sources which need the human involvement to release light energy are called manmade sources of light.
Ex: torch light, candle, bulb etc.
4) Actually, light is not a single ray, but a bundle of rays. This bundle of light rays are called beam of light rays. These are three types :
i. Parallel beam of light rays :
Light rays which travel parallel to each other are called Parallel beam of light rays.
ii. Converging beam of light rays :
“Light rays which travel from different directions to meet at a point are called as Converging beam of light rays”.
iii. Diverging beam of light rays :
“Light rays which travel from a source moving in different’ directions are called as Diverging beam of light rays.”
![]()
Question 4.
What precautions do you take while watching TV or modern gadgets? Why?
Answer:
- Light plays an important role in the sensation of vision.
- Now a day’s people, due to the usage of modern gadgets, like mobile phone, com-puters, televisions through which light enters the eyes.
- Watching TV too much or sitting very close to it may make your eyes-tired cause dryness of eyes and gradually lead to headache.
- While using computer or TV ensures that your room is well lighted.
- While watching TV or computer a simple rule 20 – 20 – 20 helps us in protecting eyesight.
- After 20 minutes of watching TV or computer screen, take 20 seconds break and watch the TV or computer around 20 feet away.
- Reduce blue light in cell phones and computers are switched on power saving mode during night.
- Yellow light has been proven effective in protecting retina than blue light which causes damage to retina.
Question 5.
How do you appreciate the role of the reflection of light in our daily life?
Answer:
- The process of bouncing back of light rays into the same medium after falling on a smooth or rough surface from the light source is called “reflection of light”.
- When light falls on an object it reflects back. Reflected ray when reaches to our eyes, causes sensation of vision.
- If there is no phenomenon of reflection, we cannot see the colourful world.
- Periscope is prepared based, on the principle of reflection of light from plane mirrors.
- Kaleidoscope is prepared based on the principle of multiple reflection of light from plane mirrors.
- The dentists, ophthalmologists, ENT doctors etc. give us treatment by using reflection of light through the concave mirrors.
- The drivers of the vehicles observe the rear objects of his vehicles by using reflection of light through the convex mirrors.
- Hence, I appreciate the role of the reflection of light in our daily life.
AP Board 7th Class Science 8th Lesson 1 Mark Bits Questions and Answers Wonders of Light
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer and write its letters in the brackets.
1. This is not a natural sources of light.
A) sun
B) stars
C) moon
D) none
Answer:
C) moon
2. Example to human involvement is needed to release light
A) sun
B) stars
C) candle
D) none
Answer:
C) candle
3. Light rays which travel from a source moving in different directions are called as of light rays.
A) parallel
B) converge
C) diverge
D) B and C
Answer:
C) diverge
4. Which of the following does not give regular reflection?
A) mirror
B) cloth
C) new steel plate
D) polished marble
Answer:
B) cloth
5. In case of irregular reflection images cure
A) not clear
B) cannot form
C) clear
D) A & B
Answer:
D) A & B
![]()
6. These are in the same plane.
i. The incident ray
ii. normal to the surface
iii. The reflected ray
A) i,ii
B) i,iii
C) ii, iii
D) i,ii,iii
Answer:
D) i,ii,iii
7. Angle between normal and the incident ray
A) angle of incidence
B) angle of reflection
C) angle of vision
D) A & B
Answer:
A) angle of incidence
8. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the image of the plane mirror?
A) Object distance is equal to image distance.
B) Size of the object is equal to size of the image.
C) The image formed is always real and erect.
D) Laterally inverted image is formed.
Answer:
C) The image formed is always real and erect.
9. The distance of the object from the mirror is …………….. the distance of image from the mirror.
A) is equal to
B) is greater than to
C) is less than to
D) A & C
Answer:
A) is equal to
10. The size of image is not equal to that of the object in any situation.
A) plane mirror
B) convex mirror
C) concave mirror
D) none
Answer:
B) convex mirror
11. The distance of the image from the mirror is called
A) Image distance
B) Object distance
C) Normal
D) None
Answer:
A) Image distance
12. This type of image can catch on the screen
A) real
B) virtual
C) both
D) none
Answer:
A) real
![]()
13. Image formed by a plane mirror
A) erect & real
B) inverted & virtual
C) erect & virtual
D) inverted & real
Answer:
C) erect & virtual
14. No. of images formed when the angle between two plane mirrors is 60°
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
Answer:
B) 5
15. No. of images formed when the angle between two plane mirrors is 90°
A) 4
B) 2
C) 1
D) 3
Answer:
D) 3
16. No. of images formed when the angle between two plane mirrors is 0°
A) infinity
B) 5
C) 6
D) 0
Answer:
A) infinity
17. No. of images formed is 1, then the angle between two plane mirrors is
A) 0°
B) 90°
C) 180°
D) 360°
Answer:
C) 180°
18. The instrument which is used in submarines to see the objects or persons above the water level.
A) microscope
B) telescope
C) kaleidoscope
D) periscope
Answer:
D) periscope
![]()
19. Angle between two plane mirrors in periscope is
A) 0°
B) 90°
C) 180°
D) 360°
Answer:
A) 0°
20. The steel spoon can act as …
A) plane mirror
B) convex mirror
C) concave mirror
D) B & C
Answer:
D) B & C
21. The mirror forms all types of images
A) plane mirror
B) convex mirror
C) concave mirror
D) B & C
Answer:
C) concave mirror
22. The mirror is used as rear view mirror
A) plane mirror
B) convex mirror
C) concave mirror
D) B & C
Answer:
B) convex mirror
23. Which rule we should follow to protect eyes while watching TV or computer?
A) 20-20-20
B) 40-4-40
C) 10-10-10
D) 12-12-12
Answer:
A) 20-20-20
24. Which light is not dangerous to our eye?
A) yellow
B) red
C) blue
D) violet
Answer:
A) yellow
![]()
25. Which colour of light is composition of all colours?
A) yellow
B) red
C) blue
D) white
Answer:
D) white
II. Fill in the blanks
1. Light is a form of ………………. that helps us to see all the things around us.
2. Light comes from different objects called ………………. .
3. Objects that emit light are known as ………………. .
4. Sources that release light artificially [with human involvement] are called ………………. sources of light or artificial sources of light.
5. ………………. source emit light on their own.
6. The direction or path along which light travels is called ………………. .
7. The straight line indicates the of light and arrow mark indicates the ………………. of light from the source.
8. A bundle of light rays are called ………………. of light rays.
9. Light rays which travel parallel to each other are called ………………. of light rays.
10. Light rays which travel from different directions to meet at a point are called as ………………. of light rays.
11. Light rays which travel from a source moving in different directions are called as ………………. of light rays.
12. The process of bouncing back of light rays into the same medium after falling on a smooth or rotigh surface from the light source is called ………………. .
13. Objects are visible only when ………………. falls on the objects and bounces back to the eye.
14. Light rays from the sun fall on the mirror and bounced back and formed a spot of light on the wall. It is the image of ………………. .
15. The light rays that fall on the objects are called ………………. .
16. The light rays that bounce back from the objects are called ………………. .
17. Reflection from a ………………. surface is called regular reflection.
18. Reflection from an irregular or uneven surface is called ………………. reflection.
19. Clear images are formed in case of ………………. reflection.
20. Angle of ………………. is equal to Angle of reflection.
21. Incident and reflected rays are on either side of ………………. .
22. The angle made by incident ray with the normal is called ………………. .
23. The angle made by the reflected ray with the ………………. is called the angle of reflection.
24. The distance of the object from the mirror is called ………………. .
25. The distance of the image from the is called image distance.
26. When you are eating food with right hand it appears to be eating with left hand. This characteristic is called ………………. .
27. The image which cannot catch on the screen is called ………………. .
28. Plane mirror forms ………………. image.
29. The relation between number of images formed and the angle between two plane mirrors is ………………. .
30 . ………………. is an instrument used in submarines to see the objects or persons above the water level.
31. ………………. mirror reflect the light in different directions.
32. ………………. mirror reflect the light to one point.
33. A ………………. mirror forms real and virtual images, erect and inverted images, smaller, same size and bigger images depending on the position of object infront of it.
34. Ophthalmoscope is fitted with a ………………. mirror having a small hole near its center.
35. Dentists also use ………………. mirrors to get a bigger image of the teeth.
36. ………………. mirrors are used in head lights of the vehicles.
37. A piece of glass or any other transparent material with curved sides is called ………………. .
38. Lens which is thick in center and thin at the edges is called ………………. lens.
39. Lens which is thin in the centre and thick at the edges is called ………………. lens.
40. ………………. light has been proven effective in protecting retina than blue light which causes damage to retina.
41. Splitting of white light into seven colours is called ………………. .
Answer:
- energy
- sources of light
- sources of light
- man made
- natural
- a ray of light
- path, direction
- beam
- parallel beam
- Converging beam
- Diverging beam
- reflection of light
- Light
- sun
- incident rays
- reflected rays
- smooth and shiny
- irregular or diffused
- regular
- incidence
- normal
- angle of incidence
- normal
- object distance
- mirror
- lateral inversion
- virtual image
- virtual
- 360°/θ -1
- periscope
- convex
- concave
- concave
- concave
- concave
- concave
- a lens
- convex
- concave
- Yellow
- dispersion
III. Match the following
1.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Natural source | a. cloth |
| 2) Artificial source | b. steel plate |
| 3) Regular reflection | c. star |
| 4) Irregular reflection | d. candle |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Natural source | c. star |
| 2) Artificial source | d. candle |
| 3) Regular reflection | b. steel plate |
| 4) Irregular reflection | a. cloth |
2.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Convex mirror | a. make up |
| 2) Concave mirror | b. ENT doctor |
| 3) Plane mirror | c. magnifier |
| 4) Convex lens | d. rear view |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Convex mirror | d. rear view |
| 2) Concave mirror | b. ENT doctor |
| 3) Plane mirror | a. make up |
| 4) Convex lens | c. magnifier |
3.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Periscope | a. concave mirror |
| 2) Ophthalmoscope | b. convex mirror |
| 3) Road safety | c. convex lens |
| 4) Telescope | d. plane mirror |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Periscope | d. plane mirror |
| 2) Ophthalmoscope | a. concave mirror |
| 3) Road safety | b. convex mirror |
| 4) Telescope | c. convex lens |
4.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Convex mirror | a. inwards curve |
| 2) Concave mirror | b. outwards curve |
| 3) Plane mirror | c. thick at middle |
| 4) Convex lens | d. plane surface |
| 5) Concave lens | e. thin at middle |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Convex mirror | b. outwards curve |
| 2) Concave mirror | a. inwards curve |
| 3) Plane mirror | d. plane surface |
| 4) Convex lens | c. thick at middle |
| 5) Concave lens | e. thin at middle |
5.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Virtual image | a. pass through one point |
| 2) Real image | b. bundle of rays |
| 3) Ray | c. caught on the screen |
| 4) Beam | d. seen in the mirror |
| 5) Converging | e. path of light |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Virtual image | d. seen in the mirror |
| 2) Real image | c. caught on the screen |
| 3) Ray | e. path of light |
| 4) Beam | b. bundle of rays |
| 5) Converging | a. pass through one point |
6.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Incident angle | a. perpendicular line to surface |
| 2) Reflecting angle | b. angle of incidence angle of reflection |
| 3) Normal | c. angle between normal and reflected ray |
| 4) First law of reflection | d. normal, incident ray, reflected ray are in one plane |
| 5) Second law of reflection | e. angle between normal and incident ray |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Incident angle | e. angle between normal and incident ray |
| 2) Reflecting angle | c. angle between normal and reflected ray |
| 3) Normal | a. perpendicular line to surface |
| 4) First law of reflection | b. angle of incidence angle of reflection |
| 5) Second law of reflection | d. normal, incident ray, reflected ray are in one plane |
7.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Convex mirror | a. converges |
| 2) Concave mirror | b. diverges |
| 3) Plane mirror | c. parallel rays |
| 4) Sun | d. irregular reflection |
| 5) Thermocol sheet | e. regular reflection |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Convex mirror | b. diverges |
| 2) Concave mirror | a. converges |
| 3) Plane mirror | e. regular reflection |
| 4) Sun | c. parallel rays |
| 5) Thermocol sheet | d. irregular reflection |
Do You Know?
→ We cannot see the real image with our naked eye. But we can catch it on screen. Whereas we can see the virtual image in the mirror with our naked eye. But we cannot catch it on screen.
![]()
→ In olden days the concave mirrors can also be used as weapons. Archimedes, a Greek scientist used this mirror as weapon, 2000 years ago. When the Romans attacked Syracus, a coastal City – state in Greece, Archimedes arranged concave mirrors. The mirrors could be moved in any direction. They were positioned such that they reflected the sunlight on the Roman soldiers. The soldiers were dazzled by the sunlight. They did not know what was happening. Roman soldiers got confused and returned back.
→ Convex mirrors are used in Automatic Teller Machine (ATM) for security purpose to get a wider background look. This is to avoid others from over looking at your password.



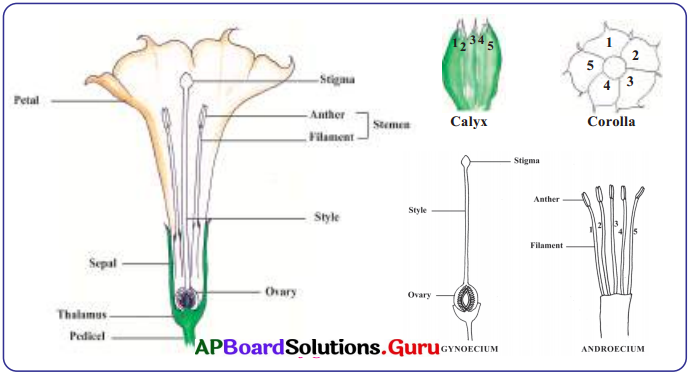

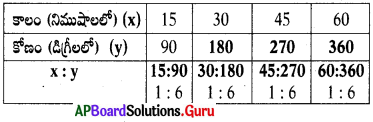
 This diagram indicates
This diagram indicates