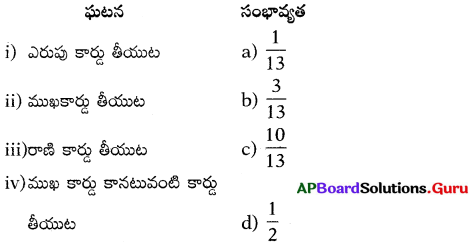
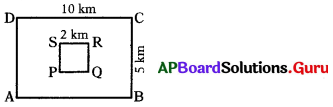
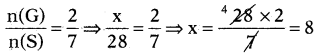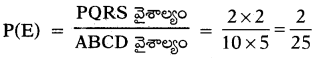These AP 7th Class Science Important Questions 12th Lesson Soil and Water will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP Board 7th Class Science 12th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Soil and Water
Question 1.
What are the most important resources for the living things?
Answer:
- The soil and water are the most important resources for living things.
- There is no life without these resources.
Question 2.
What is soil? Name the branch of science that deals with the scientific study of soil?
Answer:
- The upper most layer of earth’s crust is known as soil.
- The scientific study of soil is called “Pedology”.
Question 3.
Why soil is so important for plants?
Answer:
- Soil is a substratum in which plants get nutrients.
- Soil is a habitat for plants and many animals.
Question 4.
What is the pleasant smell after rain is known as? Mention the reason for the pleasant smell of soil after rain?
Answer:
- The pleasant smell after the rain is known as ‘Petrichor scent’.
- It is because of the rising of a substance called geosmin from the soil into the air when it rains.
- It is produced by the spores of actinomycetes bacteria.
![]()
Question 5.
Why soil is an important resource?
Answer:
- Human beings depend on soil for their basic needs.
- It has become an important part of our life.
Question 6.
What is Pedogenesis?
Answer:
The process of formation of soil from the parent rock by the process of weathering is called pedogenesis.
Question 7.
What is humus?
Answer:
- Dead and decayed organic matter that mixes with soil is called humus.
- Humus levels in the soil indicates the soil fertility.
Question 8.
What are the components of soil?
Answer:
The following are the components of soil.
1) Water , 2) air , 3) organic matter, 4) inorganic matter, 5) living organisms.
Question 9.
What is Edophology? What are edaphic factors?
Answer:
- The science dealing with the influence of soil on organisms, especially on plants is called Edophology.
- The factors that contribute to soil composition are called edaphic factors.
Question 10.
What is soil profile?
Answer:
- The sequence of horizontal and various components, layers of soil at a place is called soil profile.
- Each layer has a distinct colour, texture, depth and chemical composition. These layers are called horizons.
Question 11.
What are the crops grown in black soils?
Answer:
Farmers grow paddy, sugarcane and cotton crops in black soils.
Question 12.
Mention the crops grown in loamy soils?
Answer:
Most of the farmers practice aquaculture and grow flowers, vegetables, millets, tobacco and fruits.
Question 13.
What are the crops grown in Sandy soils?
Answer:
- Farmers grow groundnuts and castor in some places.
- Cotton, red’gram and tomatoes are also grown in sandy soils of Chitoor.
Question 14.
What are the crops grown in black soils with light clay?
Answer:
- Farmers mostly grow cotton and chillies in black soils which have light clay.
- These soils can be seen in Kadapa.
![]()
Question 15.
What are the crops grown in the loamy soils of Kurnool?
Answer:
- Farmers grow paddy, jowar and bengal gram.
- These loamy soils of Kurnool consists of sand also.
Question 16.
Name the crops grown in red sandy soils of Visakhapatnam?
Answer:
Farmers grow crops such as cashew, sugafedne arid paddy.
Question 17.
When do we celebrate the world water day?
Answer:
We celebrate the world water day on 22nd of March.
![]()
Question 18.
What is “Water Action Decade”? What is it’s aim?
Answer:
- Recognizing the growing challenges of water scarcity UNO launched the Water Action Decade – 2018 to 2028 on 22nd March, 2018.
- It’s aim is to mobilize action that will help and transform our views of management of water.
Question 19.
What happens if sewage and water from industries contaminate the water resources?
Answer:
- Sewage contains the soluble and insoluble organic and inorganic impurities and disease causing microorganisms.
- If this contaminated water mix up with drinking water it causes diseases such as diarrhoea, cholera, dysentery, typhoid and hepatitis.
Question 20.
How can we prevent contamination of water resources?
Answer:
Contamination of water resources can be prevented by treating sewage water properly before releasing it into water resources.
Question 21.
What would happen if same crop is cultivated continuously in the same field?
Answer:
- It decreases the soil fertility.
- Yield decreases in the next crop.
Question 22.
Write a short note on modern water purifiers?
Answer:
- Modern water purifiers have a filtet unit and facilities to let the ultra-violet rays to pass through.
- Ultra-violet rays are used instead of chlorine treatment to kill the germs.
Question 23.
Why should we use clay idols instead of idols made of plaster of paris?
Answer:
- During festivals like Vinayaka Chavithi we use idols of Ganesh made of plaster of paris and chemical colours which causes severe damage to our environment.
- Instead of these chemical idols we should use clay idols and celebrate festivals in an ecofriendly way.
Question 24.
For which purposes are we using fresh water?
Answer:
Fresh water has been the constant and essential companion of human beings throughout history. Water is used in great quantities in agriculture and industries.
Question 25.
Which type of soil is suitable for growing cotton?
Answer:
- Black soil is suitable for growing cotton.
- Black soil is sticky in nature. It retains water for a long time.
- This soil is suitable for the growth of cotton, sugarcane and paddy.
![]()
Question 26.
Which type of soil is generally seen in our state?
Answer:
In our state we see the following types of soils.
а) Black soil b) Red soil c) Red sandy soil d) Alluvial soil e) Loamy Soil
7th Class Science 12th Lesson Soil and Water Short Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Soil is useful for us in many ways. What are they?
Answer:
- Soil is needed for agriculture.
- It is needed for construction of buildings.
- It is needed for extraction of minerals from mines.
- oil is very useful for making utensils and pottery.
- For making toys and idols soil is useful.
- Multani soil is used in making cosmetics.
Question 2.
Mention the different horizons in soil profile?
Answer:
- O horizon (Surface litter)
- A horizon (Top soil)
- B horizon (Sub soil)
- C horizon (Regolith)
- R horizon (Bedrock)
Question 3.
What types of soils are there in your village?
Answer:
- Types of soil differ from village to village.
- For guidance a village in Krishna District is identified and details are given here.
- There is black soil in the village. This soil can retain water for a long time.
- Here farmers grow cotton, sugarcane and paddy.
Question 4.
What is weathering?
Answer:
- In nature due to the action of various natural agents such as wind, water, sun and climate the bigger rocks (Parent rock) gradually breakdown and give small particles which forms the soil.
- The process of formation of soil due to natural agents like wind, water and sunlight is called weathering.
Question 5.
What are the common soil problems tested at soil testing centres?
Answer:
The common soil problems tested at soil testing centres include :
- Low organic matter like carbon
- Available minerals in soil – nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
- Availability of micro nutrient levels
- Poor drainage
- Soil temperature
- Soil moisture
- Soil contamination
- acidic or basic nature of soil (pH)
![]()
Question 6.
How can you say soil is a precious resource? Give reasons.
Answer:
- Soil is a precious resource.
- It is the basis for growth of plants.
- It is habitat for micro organism, animals, reptiles etc.
- Soil is used for various purposes.
- Almost all the things in our surroundings directly or indirectly depend on soil.
Question 7.
Why is top soil more useful for us?
Answer:
- The top organic layer of soil, made up mostly of leaf litter and humus (decomposed organic matter).
- This layer is soft and porus. It contains nutrients which help in the growth of plants.
- Top soil is capable of retaining water in it.
- It is a good habitat for many living organism.
Question 8.
What do farmers do to preserve the fertility of the soil?
Answer:
- It is very important to preserve the fertility of soil.
- You know farmers can’t continue the same type of crops in their fields.
- They know continuous cultivation of same agriculture crops reduce the soil fertility.
- enerally, farmers cultivate pulses after completion of paddy.
- This kind of rotation of crops retains soil fertility and productivity.
- Conservation of soil is important factor in agriculture.
Question 9.
How is the formation of soil happened why are farmers and Engineers testing the soil?
Answer:
Soil Formation:
- Soil is formed slowly as rock (the parent material) erodes into tiny pieces near the Earth’s surface.
- Organic matter decays and mixes with inorganic material (rock particles, minerals and water) to form soil.
- These days farmers test the soil in the field using soil technologies in order to grow suitable crops in the fields.
- Engineers also test the soil profile before constructing multi storied buildings, bridges and dams.
Question 10.
How can the soil erosion be prevented?
Answer:
- Our farmers grow big trees around the fields to stop winds.
- They don’t keep the lands vacant.
- Farmers generally use vacant lands to grow grass and other plants.
- These grass plant roots hold the soil particles and prevent soil erosion during heavy rains.
![]()
Question 11.
‘Soil is a good habitat’ Explain the statement.
Answer:
- Soil is a good habitat. We depend on it for agricultural and construction purposes, making utensils, toys etc.
- We know that plants depend on soil for nutrients like mineral salts and water from the soil
- Animal life such as burrows or eggs of insects are found in the soil.
Question 12.
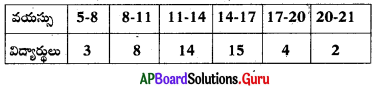
Read the below table and answer the following questions.
| Type of Soil | Character of Soil |
| Clay Soil | easy to roll into a ball |
| Loamy soil | breaks on bending |
| Light clay | easy to make a ring |
| Sandy soil | not easy to roll into a ball |
a) What is the character of loam soil?
b) What is the difference between clay soil and sandy soil?
Answer:
a) When you try to make a cylinder, it can break. This is the light loam soil,
b) Clay Soil : It is very easy to roll into a ball.
Sandy Soil: It is not easy to roll into a ball.
Question 13.
What questions you would ask soil scientist to know the nature of soils?
Answer:
- Why should we know the nature of soil?
- Which type of soil is good for growth of the plants?
- Are the soils same through out the world?
- If the soil is spoiled, what would happen to plants and animals?
7th Class Science 12th Lesson Soil and Water Long Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How can we conserve the water resources?
Answer:
Conservation of water resources :
Conservation of water can be done using the 4R principle. They include Recharge, Reuse, Revive and Reduce.
Recharge:
The ground water can be recharged by collecting the rain water from the top of the buildings by the process of rainwater harvesting. Percolation tanks, Check dams and Contour trenches cdso help to recharge ground water.
Reuse:
The waste water treated in sewage treatment plants can be used for household activities such as washing vehicles, watering plants and for construction purpose.
Revive:
The practice of reviving the groundwater in drought prone areas is very familiar in olden days. At present the problem of water scarcity can be solved by renovating and reviving the step wells (Digudu Bavulu).
Reduce:
The use and wastage of water can be reduced through different measures. For example we can reduce the wastage of water in agriculture using modern methods of irrigation such as Drip irrigation.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the different stages in purification of water?
Answer:
- Water in rivers, reservoirs and lakes may contain many impurities.
- Under safe drinking water supply scheme, the water is purified through physical and chemical treatment which includes.
a) Coagulation : Adding chemicals to bind with impurities in water forming heavy particles.
b) Sedimentation : Making these heavy particles to settle at the bottom.
c) Filtration: Passing the upper water through filters to remove remaining undissolved particles.
d) Disinfection : Adding chlorine or bleaching powder to kill disease causing micro organisms.
Question 3.
What are the different stages involved in sewage water treatment? Explain with the help of a flow chart.
Answer:
- Water consisting domestic and industrial wastes is treated at sewage or waste water treatment plant.
- It involves 3 stages. They are
a) Primary treatment (Physical process)
b) Secondary treatment (Biological process)
c) Tertiary treatment (Chemical process) - These processes can be explained with the help of the following flow chart.
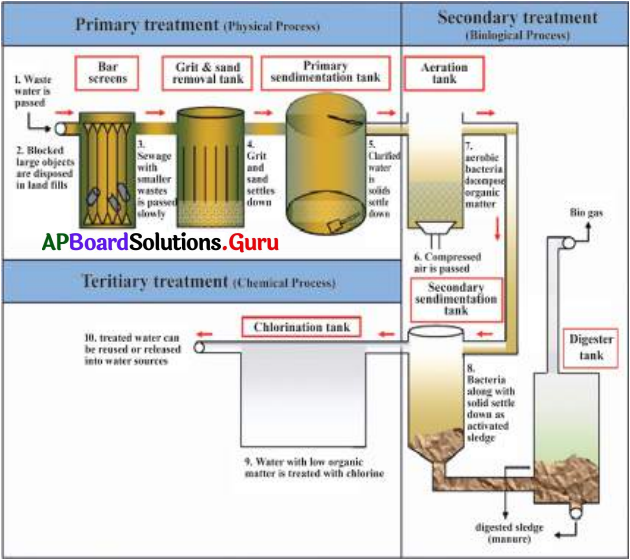
Question 4.
Fresh water is scarce. What is your contribution to make your family members aware of the need to save water?
Answer:
I shall see that my family members follow the following methods of using water.
- Pick up water that is required for drinking. Donot throw away the water left out in the glass.
- Water used for cleaning rice and vegetables will be sent to the garden in the backyard.
- For bath, required water is to be used
- I suggest the members to use mild soaps as the water after bath can be sent to plants in the garden of the house.
- No spill out of water from the tap must be seen by every family member.
- ‘Think’ before you use every drop of water is the suggestion I put before the family members.
Question 5.
Prepare afleast 5 slogans on “Don’t waste water”.
Answer:
5 slogans on Don’t waste water’.
- ‘Water is our currency. Use it with care’
- ‘Water is our life. Save it’.
- ‘Water is precious. Use it but do not throw it’.
- ‘Save water. Never become a partner for its shortage’.
- ‘Water is life. Life is not water’.
Question 6.
How can we conserve water? Write some practices that can be adopted.
Answer:
a) 1) We perform many activities in our daiiy life using water.
2) We can conserve water by adopting certain good practices.
b) Some practices that can be adopted:
- Water is precious. We should not waste it.
- Collect water in a bucket after cleaning rice, dal and vegetables in the kitchen which contains peels of vegetables.
- We can use this water for our cattle.
- We should not throw solid food remains, tea leaves and oily wastes down the drain.
- We must make a channel so that the kitchen and bath room water flows to the coconut and banana plants in our garden.
- We should use only mild soaps and detergents so that this water may not harm our plants.
- Any leakage of water from any tap must be repaired immediately.
![]()
Question 7.
Give reasons for low percolation rate of clayey soil as compared to sandy soil.
Answer:
- Clayey soil mainly contains clay.
- Only small percentage of sand and slit are present in the clayey soil.
- Humus is also present in this soil.
- The components having good percolation capacity are not present in the clayey soil in the desired proportion.
- So clayey soil has low percolation rate as compared to sandy soil.
Question 8.
Describe the soil profile.
Answer:
The sequence of horizontal and various components, layers of soil (horizons) at a place is known as Soil profile. Each layer has a distinct colour, texture, depth and chemical composition.These layers are called Horizons.
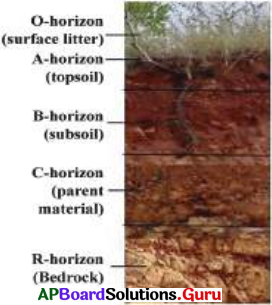
O Horizon (surface litter) –
is the uppermost, thin horizon, made up of leaf litter and decomposing organic matter.
A Horizon (Top Soil) –
is generally dark consisting dead, decomposed organic matter (humus) mixed with mineral particles. It is soft, porous and retains water hence seeds germinate easily. Plants and many other living organisms get shelter in this fertile layer.
B Horizon (Subsoil) has a lesser amount of humus but consists of clay and more amounts of minerals hence it is harder and more compact. d C
Horizon (Regolith) consists of broken rocks with very little organic matter.
R Horizon (Bedrock) is made up of un weathered rock (bedrock) which is hard and difficult to dig with a spade.
AP Board 7th Class Science 12th Lesson 1 Mark Bits Questions and Answers Soil and Water
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer and write its letters in the brackets.
1. This is a good habitat for many small organisms.
A) Soil
B) Air
C) Water
D) Fire
Answer:
A) Soil
2. Which of the following soil is used for making utensils and pottery?
A) Shadu soil
B) Multani soil
C) China clay
D) Sandy soil
Answer:
C) China clay
3. Which of the following soil is use in cosmetics?
A) Shadu soil
B) Multani soil
C) Terracotta soil
D) China clay
Answer:
B) Multani soil
4. Which of the following soil is used for making toys and idols?
A) Shadu soil
B) Multani soil
C) Terracotta soil
D) China clay
Answer:
A) Shadu soil
5. The forming process of soil is known as
A) Pedology
B) Weathering
C) Pedogenesis
D) Sedimentation
Answer:
B) Weathering
6. Dead and decayed organic matter that mixes with soil is called …………
A) Soil profile
B) Horizons
C) Humus
D) Particles
Answer:
C) Humus
![]()
7. The sequence of horizontal and various components, layers of soil at a place is known as
A) Soil profile
B) Horizons
C) Humus
D) Particles
Answer:
A) Soil profile
8. This type of soil ball can be easily made into a cylinder and a ring.
A) Sandy soil
B) Loamy soil
C) Clayey soil
D) All of the above
Answer:
C) Clayey soil
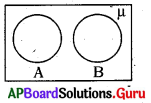
9. ![]() This figure shows
This figure shows
A) Sandy soil
B) Loamy soil
C) Clayey soil
D) All of the above
Answer:
B) Loamy soil
10. Which of the following soil is well aerated and drains quickly?
A) Deltaic alluvial soil
B) Sandy soil
C) Loamy soil
D) Clayey soil
Answer:
B) Sandy soil
11. Deltaic alluvial soil is found in the following districts.
A) Krishna and Nellore
B) East and West Godavari
C) Prakasam and Kurnool
D) Visakhapatnam and Vijayanagaram
Answer:
B) East and West Godavari
12. Black soil is found in the following districts
A) Krishna and Nellore
B) East and West Godavari
C) Prakasam and Kurnool
D) Visakhapatnam and Vijayanagaram
Answer:
A) Krishna and Nellore
13. The percentage of ground and surface water is
A) 1%
B) 2%
C) 3%
D) 97%
Answer:
A) 1%
![]()
14. The percentage of fresh water is
A) 1%
B) 2%
C) 3%
D) 97%
Answer:
C) 3%
15. The percentage of marine water is
A) 1%
B) 2%
C) 3%
D) 97%
Answer:
D) 97%
16. The process of entry of water into the ground is
A) Ground water
B) Percolation
C) Infiltration
D) Water table
Answer:
C) Infiltration
17. The absorption and downward movement of water through the soil layers is
A) Ground water
B) Percolation
C) Infiltration
D) Water table
Answer:
B) Percolation
18. The wells, tube wells and hand pumps get water present in the
A) Infiltrations
B) Water tables
C) Aquifers
D) Soil profiles
Answer:
C) Aquifers
19. Adding chemicals to bind with impurities in water, forming heavy particles is
A) Coagulation
B) Sedimentation
C) Filtration
D) Disinfection
Answer:
A) Coagulation
20. Adding chlorine or bleaching powder to kill disease causing micro organisms is
A) Coagulation
B) Sedimentation
C) Filtration
D) Disinfection
Answer:
D) Disinfection
![]()
21. Digudu Bavulu is an example for this conservation of water resources.
A) Recharge
B) Reuse
C) Revive
D) Reduce
Answer:
C) Revive
22. Percolation tanks, check dams and contour trenches help to this conservation of water resources
A) Recharge
B) Reuse
C) Revive
D) Reduce
Answer:
C) Revive
23. Drip irrigation is an example for this conservation of water resources.
A) Recharge
B) Reuse
C) Revive
D) Reduce
Answer:
D) Reduce
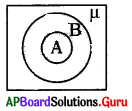
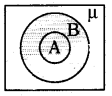
24. Assertion (A) : Soils can be classified on the basis of proportions of particles of various sizes present in them.
Reason (R) : In loamy soil the proportion of large and fine particles is almost same.
A) Both A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation of ‘A’.
B) Both A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation of A’.
C) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false.
D) ’A’ is false but ‘R’ is true.
Answer:
B) Both A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation of A’.
25. Assertion (A) : Soil is formed by weathering of rocks.
Reason (R) : The process of breaking down of rocks by the action of wind, water, sun and climate is called weathering.
A) Both A’ and ’R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation of ‘A’.
B) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation of ‘A’.
C) ‘A’ is true but ’R’ isdalse.
D) ’A’ is false but ‘R’ is true.
Answer:
A) Both A’ and ’R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation of ‘A’.
![]()
26. Statement (i) : Paddy and sugar cane grow very well in sandy soil.
Statement (ii) : Capacity to hold water is much in sandy soil than clayey soil.
Statement (iii) : Clayey soil has poor air circulation.
A) Statement (i) and (iii) are incorrect while (ii) is correct.
B) Statement (i) and (ii) are incorrect while (iii) is correct.
C) All statements are correct.
D) All statements are incorrect.
Answer:
B) Statement (i) and (ii) are incorrect while (iii) is correct.
27. Assertion (A) : Cleaning of water is a process of removing pollutants before it enters a water body.
Reason (R) : The process of cleaning of water and removal of pollutants from it is called “sewage treatment”.
A) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation of ‘A’.
B) Both A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation of A’.
C) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false.
D) A’ is false but ‘R’ is true.
Answer:
B) Both A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation of A’.
28. World water day is on
A) 22nd March
B) 20th March
C) 22nd April
D) 20th April
Answer:
A) 22nd March
29. Micro organisms in water cause the disease.
A) Cold
B) Fever
C) Body Pains
D) Cholera
Answer:
D) Cholera
30. Chemical used to disinfect water.
A) Oxygen
B) Chlorine
C) Fluorine
D) Nitrogen
Answer:
B) Chlorine
31. Essential for metabolic activity.
A) CO<sub>2</sub>
B) Rain
C) Water
D) Minerals
Answer:
C) Water
32. Chlorine passing into water is called
A) Aeration
B) Chlorination
C) Purification
D) Filteration
Answer:
B) Chlorination
![]()
33. Pumping of water into air for purification is called
A) Chlorination
B) Purification
C) Aeration
D) Filteration
Answer:
C) Aeration
34. Which of the following is the top most layer of soil?
A) “O” Horizon
B) “R” Horizon
C) “A” Horizon
D) “B” Horizon
Answer:
A) “O” Horizon
35. Waste water released by different users are collectively called
A) Mud
B) Sewage
C) Sludge
D) None of these
Answer:
B) Sewage
36. Sewage contain
A) suspended impurities
B) dissolved impurities
C) disease causing bacteria
D) all of these
Answer:
D) all of these
37. The process involved in treatment of sewage water
A) physical process
B) chemical process
C) biological process
D) all of these
Answer:
D) all of these
38. Which gas kills harmful disease causing organisms in waste water?
A) Fluorine
B) Chlorine
C) Oxygen
D) Bromine
Answer:
B) Chlorine
39. How much percentage of precipitated water exist in glaciers?
A) 1%
B) 2%
C) 3%
D) 7%
Answer:
B) 2%
40. Sita collects the water that used after cleaning rice, dal and vegetables in the kitchen and uses it to water the garden. This can be called ___
A) Stagnation of water
B) Reuse of water
C) Storing of water
D) Recovering of water
Answer:
B) Reuse of water
41. Soil is a good
A) habitat
B) material
C) source for plant
D) living place for snails
Answer:
A) habitat
![]()
42. Soil contains
A) Waste material
B) Humidity
C) Rocks
D) Minerals
Answer:
D) Minerals
43. This soil layer is made up of humus
A) R Horizon
B) A Horizon
C) B Horizon
D) C Horizon
Answer:
B) A Horizon
44. Soil is formed from
A) Rocks
B) Sand
C) Clay
D) Pebbles
Answer:
A) Rocks
45. Percolation rate of water is highest in
A) Rocky soil
B) Black soil
C) Sandy soil
D) Clayey soil
Answer:
C) Sandy soil
46. Percolation rate of water is lowest in
A) Black soil
B) Sandy soil
C) Clayey soil
D) All the above
Answer:
C) Clayey soil
47. Water holding capacity of soil depends on
A) Soil type
B) Rain
C) Place
D) None
Answer:
A) Soil type
48. Below the ‘O’ Horizon and above the ‘B’ Horizon this is found
A) B Horizon
B) A Horizon
C) C Horizon
D) R Horizon
Answer:
B) A Horizon
49. Percolation rate is highest in
A) Sandy soil
B) Clayey
C) Loamy
D) All
Answer:
A) Sandy soil
50. Removal of top soil by wind, water is called
A) soil profile
B) soil fertility
C) percolation
D) soil erosion
Answer:
D) soil erosion
![]()
51. Wheat, gram, and paddy are grown In
A) Sandy soil
B) Black soil
C) Clayey and loamy
D) All
Answer:
C) Clayey and loamy
52. This is called regolith
A) R Horizon
B) C Horizon
C) A Horizon
D) O Horizon
Answer:
B) C Horizon
53. This is called sub soil
A) B Horizon
B) C Horizon
C) R Horizon
D) O Horizon
Answer:
A) B Horizon
54. Study of soil is called
A) Morphology
B) Pedology
C) Biology
D) Ecology
Answer:
B) Pedology
55. Cotton is grown in
A) sandy
B) clayey
C) sandy loam
D) heavy loam
Answer:
C) sandy loam
56. The factors responsible for soil erosion
A) wind
B) water
C) deforestation
D) all of these
Answer:
D) all of these
57. It is also called top soil
A) A-horizon
B) B-horizon
C) C-horizon
D) R-horizon
Answer:
A) A-horizon
58. Animals plants and microbes activities are more in this horizon
A) A-horizon
B) R-horizon
C) C-horizon
D) 0-horizon
Answer:
A) A-horizon
59. The right sequence of horizons of the soil from top to bottom is
A) A, B, C, O, R
B) O, A, B, C, R
C) C, A, B, O, R
D) R, C, B, A, O
Answer:
B) O, A, B, C, R
![]()
60. Read the statements:
P : Water percolation rate is more to sandy soil.
Q : Water percolation rate is more to loamy soil.
A) Only P is correct
B) Only Q is correct
C) P & Q are correct
D) P & Q are wrong
Answer:
A) Only P is correct
II. Fill in the mlanks
1. The scientific study of soil is called …………….. .
2. The upper most layer of earth’s crust is …………….. .
3. The pleasant smell after the rain is known as …………….. .
4. The substance responsible for petrichor scent is …………….. .
5. Geosmin is produced by …………….. .
6. The breakdown of parent rock into small particles by the action of wind, water, heat and climate is known as …………….. .
7. The process of formation of soil from weathering is known as …………….. .
8. Natural weathering takes a time period of …………….. .
9. Dead and decayed organic matter that mixes with soil is called …………….. .
10. The factors that contribute to soil composition are called …………….. .
11. The science dealing with the influence of soil on organisms, especially on plants is called …………….. .
12. In soil profile, bed rock is present in …………….. horizon.
13. In soil profile, surface litter is present in …………….. horizon
14. …………….. horizon consists of broken rocks with very little organic matter.
15. …………….. soil is less aerated and water held longer.
16. …………….. soil has good aeration, water held but drains slowly.
17. …………….. soil is well aerated and drains quickly.
18. The ratio of the mass of water held in the soil is called …………….. .
19. Paddy is grown in …………….. soil.
20. Cotton is grown in …………….. soil.
21. Cashew is grown in …………….. soil.
22. …………….. is very useful to the farmers to know about the current health of the farm’s soil and how to improve it.
23. Preventing the degradation of soil is known as …………….. .
24. The loss of fertile top soil due to heavy winds and floods is known as …………….. .
25. Water action decade is …………….. .
26. The process of entry of water into the ground is called …………….. .
27. The upper level at which water stands in the ground is called …………….. .
28. The percentage of water present in seas and oceans is …………….. .
29. The percentage of fresh water present on earth is …………….. .
30. The wells, tube wells and hand pumps get water from …………….. .
31. Indiscriminate digging of bore wells leads to …………….. .
32. During purification of water, …………….. chemicals are used for disinfection.
33. Percolation tanks, check dams and contour trenches are helpful in …………….. .
34. Digudu Bavulu are very helpful in …………….. .
35. Best method to prevent soil erosion is …………….. .
Answer:
- Pedology
- soil
- petrichor scent
- geosmin
- the spores of Actinomycetes
- weathering
- Pedogenesis
- 500 -1000 years
- Humus
- edaphic factors
- Edaphology
- R
- O
- C
- Clayey
- Loamy
- Sandy
- moisture content
- clayey
- black
- sandy
- Soil testing
- soil conservation
- Soil erosion
- 2018-2028
- infiltration
- Water table
- 97%
- 3% only
- Aquifer
- depletion of ground water table
- chlorine and bleaching powder
- recharge ground water
- reviving of ground water
- planting trees
III. Match the following.
1.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. Weathering | a) Pedology |
| 2. Sandy soil | b) Water held longer |
| 3. Clayey soil | c) Good aeration water drains slowly |
| 4. Loamy soil | d) Water drains quickly |
| 5. Soil Science | e) Formation of soil |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. Weathering | e) Formation of soil |
| 2. Sandy soil | d) Water drains quickly |
| 3. Clayey soil | b) Water held longer |
| 4. Loamy soil | c) Good aeration water drains slowly |
| 5. Soil Science | a) Pedology |
2.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. O Horizon | a) Bed rock |
| 2. A Horizon | b) Regolith zone |
| 3. B Horizon | c) Sub soil |
| 4. C Horizon | d) Top soil |
| 5. R Horizon | e) Surface litter |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. O Horizon | e) Surface litter |
| 2. A Horizon | d) Top soil |
| 3. B Horizon | c) Sub soil |
| 4. C Horizon | b) Regolith zone |
| 5. R Horizon | a) Bed rock |
3.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. Geosmin | a) Dead and decayed organic matter |
| 2. Check dam | b) 500 -1000 years |
| 3. Weathering | c) Formation of soil |
| 4. Pedo genesis | d) Water Conservation |
| 5. Humus | e) Actinomycetes |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. Geosmin | e) Actinomycetes |
| 2. Check dam | d) Water Conservation |
| 3. Weathering | b) 500 -1000 years |
| 4. Pedo genesis | c) Formation of soil |
| 5. Humus | a) Dead and decayed organic matter |
4.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. Percolation | a) Forming heavy particles |
| 2. Soil erosion | b) Drop in rainfall |
| 3. Deforestation | c) Chlorine, bleaching |
| 4. Disinfection | d) Loss of top soil |
| 5. Coagulation | e) Downward movement of water |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. Percolation | e) Downward movement of water |
| 2. Soil erosion | d) Loss of top soil |
| 3. Deforestation | b) Drop in rainfall |
| 4. Disinfection | c) Chlorine, bleaching |
| 5. Coagulation | a) Forming heavy particles |
5.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. Recharge | a) Soil health |
| 2. Reuse | b) Digudu Bavulu |
| 3. Revive | c) Drip irrigation |
| 4. Reduce | d) Treated sewage |
| 5. Soil testing | e) Checkdams and percolation tanks |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1. Recharge | e) Checkdams and percolation tanks |
| 2. Reuse | d) Treated sewage |
| 3. Revive | b) Digudu Bavulu |
| 4. Reduce | c) Drip irrigation |
| 5. Soil testing | a) Soil health |
Do You Know?
→ The pleasant smell ‘after the rain’ is known as petrichor scent. It is due to raising of substance called Geosmin from the soil into the air, when it rains. It is produced by the spores’of by Actinomycetes bacteria.
→ The science dealing with the influence of soil on organisms, especially on plants is called Edaphology. The factors that contribute to soil composition are called edaphic factors.
→ Engineers test the soil profile before constructing multi-storeyed buildings, bridges and dams. They conduct environmental site assessment and make predictions on long term effect of soil on the constructions and give necessary suggestions.
![]()
→ Water action decade 2018-2028 :
The UN General Assembly announced that the world will face 40 percent shortfall in fresh water resources by 2030 coupled with a rising world population the world is rushing towards a global water crisis. Recognizing the growing challenge of water scarcity UNO launched the Water Action Decade ( 2018-2028) on 22 March 2018, to mobilize action that will help and transform our vision of management of water.
→ Do you know how modern water purifiers work? Modern Water purifiers that are used to purify water at home have a filter unit and facilities to let Ultra Violet rays to. pass through. Ultra Violet rays are used instead of chlorine treatment to kill the germs.