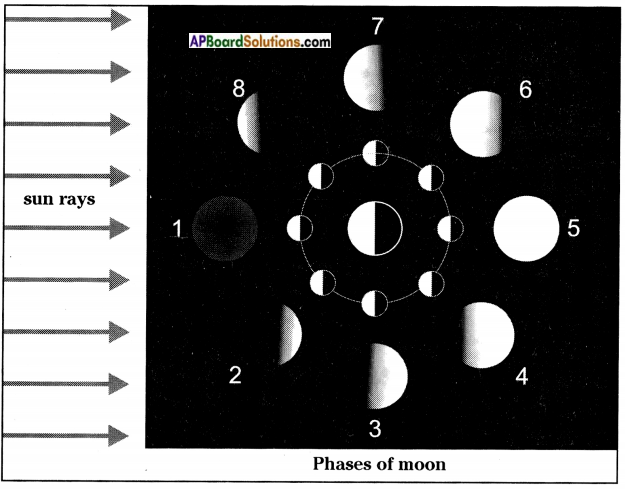
AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Physical Science Important Questions Chapter 5 Metals and Non-Metals
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Physical Science Important Questions 5th Lesson Metals and Non-Metals
8th Class Physical Science 5th Lesson Metals and Non-Metals 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is meant by lustrous material?
Answer:
The material which show brightness on surface and reflect the light are called lustrous material.
Question 2.
What is malleability? Which materials have malleability?
Answer:
The property of material by which they can beaten into thin sheets is called malleability. Generally metals exhibit malleability property, e.g.: Iron, copper, etc.
![]()
Question 3.
What is ductility? Which materials show ductility?
Answer:
The property of drawing materials to make fine wires is called ductility. Generally metals show ductility, e.g.: Gold, copper, etc.
Question 4.
Have you observed materials used to make school bell or bells in temple ?
Answer:
Generally they are made up of metals.
Question 5.
Why do wooden bells not used in temple?
Answer:
Wood does not give a ringing sound when it is hit with a hammer. That means it does not show sonorous property. So wooden bells are not used in temple.
Question 6.
What is meant by sonorous?
Answer:
The ability to material to produce a particular sound when it is dropped on the hard surface is called sonorous.
Question 7.
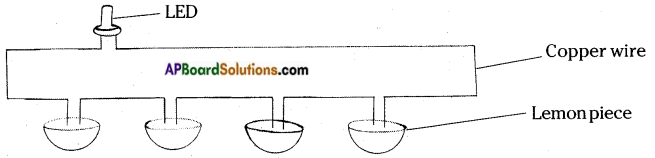
Is ductility is the only property to use them as connecting wires in electric circuits?
Answer:
No, it is one of the cause. The other thing is metals are very good conductors of electricity. So they easily allows the passage of current. So they are used as connecting wires.
![]()
Question 8.
What does cooking appliances conduct?
Answer:
Cooking appliances conduct heat from heating device like gas stove or electric stove.
Question 9.
What is the nature of metallic and non-metallic oxides?
Answer:
Generally metallic oxides are basic in nature and non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature.
Question 10.
What happen when keep an iron rod in open place for one or two days?
Answer:
Rusting takes place on iron. The reason is iron react with air that contains oxygen and moisture forms a reddish brown coating (rust) due to formation of iron oxide.
Question 11.
Why do some metals do not get rust?
Answer:
Metal with very low reactivity do not react with air. So they do not get rust. They also called as noble metals, e.g.: Gold, platinum.
Question 12.
What happens when magnesium ribbon is exposed to air?
Answer:
It becomes dull when it is exposed to air due to formation of magnesium carbonate. That’s why magnesium ribbon should be cleaned with sand paper before any chemical reaction.
Question 13.
Why does silver objects and jewellery become black after sometime?
Answer:
Silver articles are black after sometime because they react with oxygen in air and form silver oxide.
Question 14.
Why statues and vessels made up of copper become dull green after certain time?
Answer:
The statues and vessels made up of copper became dull because they react with air and form copper hydroxide and copper carbonate which appears as dull green coating.
![]()
Question 15.
What happens when non-metals are added to water?
Answer:
They do not react with water.
Question 16.
How do you test hydrogen gas?
Answer:
If we place a burning match stick near a test tube containing hydrogen gas it puts out the match stick with pop sound and the gas burns with blue flame.
Question 17.
What happens when acids are added to non-metals?
Answer:
Non-metals do not react with acids.
Question 18.
What is a displacement reaction?
Answer: A more reactive metal displace a less reactive metal from its compound in aqueous solution is called displacement reaction.
Question 19.
Which metal has highest ductility?
Answer:
Gold. One gram of gold can be drawn into a wire of length one kilometre.
Question 20.
Why sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene?
Answer:
Sodium and potassium are highly reactive. They react vigorously with oxygen and water. A lot of heat is generated in the reaction. Therefore these metals are stored in kerosene.
Question 21.
Is all metals are hard?
Answer:
No. Sodium and potassium are soft. So they can be cut with a knife.
Question 22.
Which non-metal has lustrous surface?
Answer:
Iodine has lustrous surface.
Question 23.
Which non-metal is extremely hard?
Answer:
Diamond (allotrope of carbon) is extremely hard.
![]()
Question 24.
Why immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances?
Answer:
Metals are good conductors of heat. So immersion rods for heating liquids are made
up of metals.
Question 25.
Why does copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution?
Answer:
Copper is less reactive than zinc. So it cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
Question 26.
Why does aluminium foils are used to wrap food items?
Answer:
It does not readily react with food items. So aluminium foils are used for wraping food items.
Question 27.
The doctor reported iron deficiency in my body. Where is iron in my body?
Answer:
Iron is present in haemoglobin. Which gives red colour to blood.
Question 28.
I heard that magnesium is found in plants. In what form is it found in them?
Answer:
Magnesium is present in chlorophill. It is in Mg(II) state.
![]()
Question 29.
Gold jewellery does not become dull. Why?
Answer:
Gold and platinum does not react with components of air. So, gold and platinum does not rust. So gold jewellery does not become dull.
8th Class Physical Science 5th Lesson Metals and Non-Metals 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are physical properties of non-metals?
Answer:
Physical properties of non-metals:
- They are non lustrous.
- They are non sonorous.
- They are soft.
- They does not show malleability and ductility.
- They are bad conductors of heat and electricity.
Question 2.
Is our body is a metal or a non-metal?
Answer:
Most of the human body is made of water (H2O). It is not surprising that majority of a human body’s mass is oxygen. Carbon, the basic unit of organic molecules is the second. 99% of human body is made up of just six elements. Oxygen (65%), carbon (18%), hydrogen (10%), nitrogen (3%), calcium (1.5%), phosphorous (1%). Which shows our body has almost 97% of non-metals. So we may consider our body as non-metal.
Question 3.
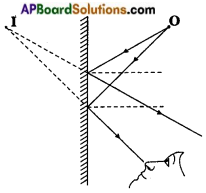
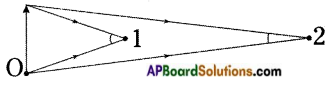
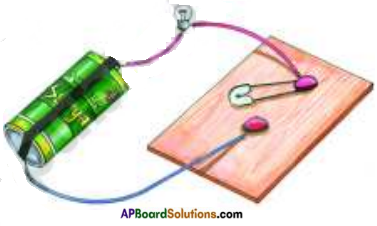
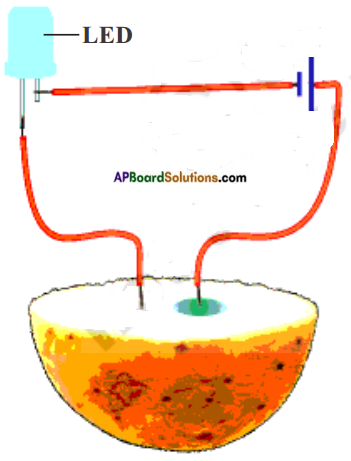
Draw a diagram which shows metals are good conductors of electricity.
Answer:
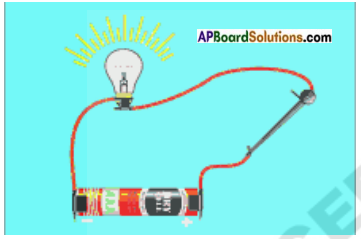
![]()
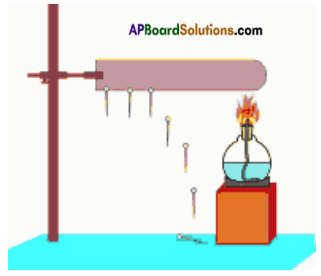
Question 4.
Draw a diagram which show metals are good conductors of heat.
Answer:
Question 5.
Explain about ductility.
Answer:
- Some materials cannot be drawn into wires.
- Property of drawing a material to make fine wires is called ductility.
- Most metals are ductile.
Question 6.
How do you appreciate the efforts of man to use the Metals in making tools?
Answer:
- Early human beings made their tools from stone and wood.
- Later they used the bones of animals.
- Then they discovered metals like copper and iron.
- Tools made of copper and iron are much stronger than tools made of stone and wood.
- Metals had the advantage of not just being harder but they can be heated in a fire and moulder or cast into different shapes. So it became possible to make a wider range of tools with such metals.
- Hence the efforts of man to use the metals in making tools appreciated.
![]()
Question 7.
You came to know that the Diamond is a hardest material and it is a non-metal and similarly Mercury is a soft material and it is a metal.Write down the questions raised in your mind.
Answer:
- Are all metals hard?
- Are there any non-metals hard like diamond?
- Are there any metals soft like mercury?
- What makes mercury so soft and diamond so hard?
- Can we distinguish those metals and non-metals depending on their opposite properties like these examples?
Question 8.
Taking the example of magnesium and sulphur explain how metals and non-metals produce with different characteristics.
Answer:
- Magnesium in the presence of oxygen burns to produce basic magnesium oxide. When it its added to water, it produces magnesium hydroxide, which turns the red litmus solution into blue.
- Sulphur combines with oxygen, it forms acidic oxide. It get changed into sulphurous acid when react with water. This turns the blue litmus solutions into red.
Question 9.
What happens when
a) Dilute sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate?
b) Iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution?
Answer:
a) Copper sulphate is formed and hydrogen gas is released.
copper + dilute sulphuric acid → copper sulphate + hydrogen gas
b) Brown coating is deposited on the Iron nails. This is because of displacement of copper from copper sulphate solution by Iron.
Iron + Copper sulphate(solution) → Iron sulphate(solution) + Copper
8th Class Physical Science 5th Lesson Metals and Non-Metals 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What happens when magnesium, sulphur burnt in the presence of oxygen ? Write the word equation.
Answer:
When magnesium is burnt in the presence of oxygen it burns brilliantly and forms white ashes of magnesium oxide.

When sulphur is burnt in the presence of oxygen, it forms a yellowish gas called sulphur dioxide.

![]()
Question 2.
What are uses of various non-metals?
Answer:
Uses of non-metals:
- Oxygen is essential for all living beings.
- Nitrogen as fertilizer enhance the growth of plants.
- Chlorine is used to purify the water.
- Sulphur is used in making fire works, crackers, gun powder, match sticks and anticeptic ointments.
- Activated carbon is used as decolourising agent and also in water purification systems.
- Tincture iodine is used in medical purpose.
Question 3.
What are the uses of metals?
Answer:
Uses of metals:
- Gold, silver, copper are used in making jewellery.
- Silver foil is used in decoration of sweets.
- Aluminium foil is used in inner packing of food materials and toffees.
- Aluminium and copper mixture is used in currency coins, medals and statues.
- Zinc and iron mixture is used in making of iron sheet.
- Most of agricultural instruments are made by iron.
- Electrical appliances, automobiles, satellites, aeroplanes, cooking utensils, machinery decorative materials are made by metals.
Question 4.
Prepare a table of various metals and non-metals used in our daily life and their usage.
Answer:
| Metals/non-metals | Their usage |
| 1) Gold | Jewellery |
| 2) Silver | Jewellery |
| 3) Copper | Jewellery, utensils, electrical appliances |
| 4) Aluminium | Utensils, packing of food, aeroplanes, satellites |
| 5) Iron | Utensils, electric appliances, agricultural tools |
| 6) Iodine | Medical purpose |
| 7) Chlorine | Purification of water |
| 8) Nitrogen | Fertilizers |
| 9) Sulphur | Gun powder, matchsticks, fire works, crackers, antiseptic ointments |
| 10) Oxygen | Essential for all living things to live |
![]()
Question 5.
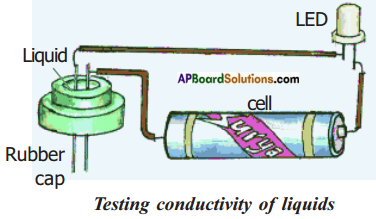
The nature of oxides helps to identify the metals and non-metals conduct an experi-ment to prove this and record the observations.
Answer:
I) Aim: The nature of oxides helps to identify the metals.
Material required : Magnesium sample, spirit lamp, red litmus paper.
Procedure:
- Take a small strip of magnesium and burn it and note the appearance after the reaction.
Reaction: When we burn the sample of magnesium, it reacts with oxygen in air and form magnesium oxide.

- Take magnesium oxide solution and place red litmus in it. Red litmus turns to blue indicates the solution is basic in nature.
Result: Metallic oxides solutions are basic in nature. So if the oxide solution is basic then the oxide is formed by a metal.
II) Aim: The nature of oxides help to identify the non-metals.
Material required: Sulphur sample, spirit lamp, blue litmus paper, deflagrating spoon. Procedure:
- Take a small amount of sulphur powder in a deflagrating spoon and heat it.
- As soon as sulphur starts burning, introduce the spoon into glass jar or tumbler.
- Add small quantity of water into the tumbler and quickly replace the lid. Shake the tumbler well.
Reaction: Sulphur burns and reacts with oxygen in air to give sulphur dioxide.

- Place blue litmus paper in the prepared solution it turns to red indicates the solution is acidic nature.
Result: Non-metallic oxides solution are acidic in nature. So if oxide solution turns blue litmus into red then the oxide is formed by a non-metal.
![]()
Question 6.
Collect the information about metals which we Use in our daily life, and their uses. Write a report on it.
Answer:
- The special properties of metals help us in many ways.
- Metals are lustrous (shining). So, we make ornaments of gold and silver.
- Metals are sonorous. So, we make school bells, temple bells, gongs, etc.
- The malleability of metals help us to make sheets of iron, etc.
- Ductility is the special character of metals which help us in making wires.
- Metals conduct heat and electricity. Hence we make utensils for cooking and electrical wires etc.
- Metals react with oxygen and produce oxides of basic nature.
- Metals react with acids (dilute) and liberate hydrogen gas. So, in the preparation of hydrogen gas, metals come in use.
- Non-metal like sulphur is used in making fire works, crackers, gun powder, matchsticks and antiseptic ointments.
Question 7.
Give reasons for the following.
a) Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items.
b) Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances.
c) Copper cannot displace Iron from its salt solution.
d) Sodium and potassium are stored in Kerosene.
Answer:
a) Aluminium has high malleability. So it is very easy to make aluminium foil compared other metals.
b) Because metals are good conductors of electricity.
c) Iron has more reactivity than copper. So copper cannot displace Iron from its salt solution.
d) Sodium and potassium have high reactivity with water and an even they burn in the presence of air and water. So these metals are stored in Kerosene.
Question 8.
Give reasons for the following.
i) Silver is used in making mirrors.
ii) Aluminium is used to make electrical wires.
iii) Sour food substances should not be stored in aluminium utensils.
iv) Iron is used in constructing bridges and houses.
Answer:
i) Silver has high reflecting power.
ii) Aluminimum is good conductor of electricity.
iii) Sour substances contain acids which react with aluminimum utensils to form toxic substances.
iv) Iron is hard, strong and rigid material.
![]()
Question 9.
Give some differences with examples between metals and non-metals with reference to their properties. Give one exception in each case.
Answer:
a) Lustrous: Metals have shining surfaces. So they are called Lustrous. Whereas non-metals have dull surface so they are non Lustrous.
One of the form of carbon is diamond has most shining look.
Iodine a non-metal also has lustrous surface.
b) Malleability: Metals can be beaten into sheets and non-metals cannot be beaten into sheets. But mercury is a metal which breaks into pieces when hammered.
c) Ductility: Metals are drawn into wires. Non-metals cannot be drawn into wires. Mercury does not show ductility.
d) Conductivity: Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity and non-metals are bad conductors of electricity and heat. Graphite is a non-metal which is good conductor of heat and electricity.
e) Hardness: Metals are usually hard and non-metals are soft. But sodium and potassium are quite soft, they can be cut by using a knife. Diamond is a non-metal which is the hardest substance.
8th Class Physical Science 5th Lesson Metals and Non-Metals Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Predict the reason behind gold and platinum jewellery does not become dull.
Answer:
Gold and platinum does not react with components of air. So, gold and platinum does not rust. So gold jewellery does not become dull.
![]()
Question 2.
Write any two differences between electric conductors and insulators.
Answer:
| Electric conductors | Electric insulators |
| 1) Those substances through which electricity can flow are called conductors. | 1) Those substances through which electricity cannot flow are called insulators. |
| 2) Generally metals are conductors. Eg: Silver, copper |
2) Generally non-metals are insulators. Eg: Rubber, plastic, glass |
Question 3.
Write any four uses of metals in different situations.
Answer:
Uses of metals:
- Gold, silver, copper are used in making jewellery.
- Silver foil is used in decoration of sweets.
- Aluminium foil is used in inner packing of food materials and toffees.
- Aluminium and copper mixture is used in currency coins, medals and statues.
- Zinc and iron mixture is used in making of iron sheet.
- Most of agricultural instruments are made by iron.
- Electrical appliances, automobiles, satellites, aeroplanes, cooking utensils, machinery decorative materials are made by metals.
Question 4.
Explain the reaction of metals with acids.
Answer:
Aim: To find the reactivity of metals with acids.
Apparatus: Test tube, dilute hydrochloric acid, magnesium ribbon, spirit lamp. Procedure:
- Take a magnesium ribbon and rub with a sand paper.
- Put this ribbon into a test tube containing dilute hydrochloric acid.
- A gas is evolved from the test tube.
- Now bring a burning match stick near the mouth of the test tube.
- The gas puts off the match stick and produces a pop sound and gas burns with blue flame.
- Which indicates hydrogen gas is released.
- We will get same results with zinc, iron, copper also.
- Conclusion: Metal reacts with acid and produce hydrogen gas.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain a procedure to do the experiment that magnesium ribbon allows the flow of current.
Answer:
Procedure:

- Arrange ah electric circuit with a battery and bulb.
- Close the circuit using a magnesium ribbon.
- Observe whether the bulb is glow or not.
Observation: Bulb glows.
Conclusion: Magnesium ribbon allows the flow of current.
Question 6.
Suggest an activity to show that the magnesium ribbon reacts with Oxygen to form Magnesium Oxide, which is basic in nature.
Answer:
Aim: To know reaction of oxygen with metals.
Material required: Magnesium strip, spirit lamp or Bunsen burner and litmus papers, distilled water.
Procedure:
- Take a small strip of magnesium.
- Burn it with spirit lamp.
- It burns brilliantly and produce white ashes of magnesium oxide due to reaction between magnesium and oxygen.
- Collect the ash of magnesium in a watch glass and add some distilled water.
- Test the solution with red litmus paper and blue litmus paper.
Observation: Red litmus paper turns into blue in colour.
Conclusion: Metallic oxide solutions are basic in nature.
![]()
Question 7.
Zinc, Copper, Sulphur, Carbon, Categories into these into metals and non-metals and write their uses.
| S.No. | Name | Metal/Non-metal | Use |
| 1.
2. 3. 4. |
Answer:
| S.No. | Name | Metal/Non-metal | Use |
| 1. | Zinc | metal | sheets, batteries |
| 2. | Copper | metal | electrical wires, jewellary, Utensils |
| 3. | Sulphur | non-metal | Gun powder, fireworks, ointments |
| 4. | Carbon | non-metal | Water purifiers, fuel |
Question 8.
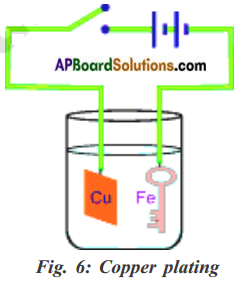
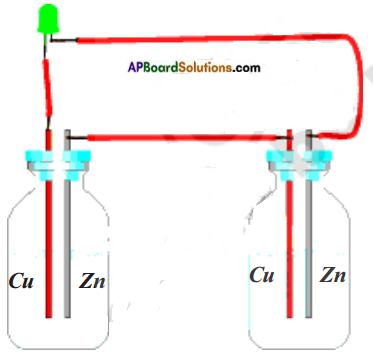
You are given copper sulphate, Iron sulphate, an iron nail and copper wire. How do you test the reactivity of metals iron and copper Explain through an activity.
Answer:
Activity:
- Take two beakers ‘a’ and ‘b’.
- Take 50 ml of water in each.
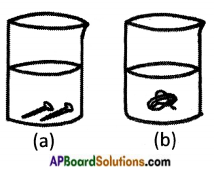
- Dissolve some amount of copper sulphate in beaker ‘a’ and iron sulphate in beaker ‘b’.
- Drop iron nails in beaker ‘a’ and copper wire in beaker ‘b’.
- Leave the beakers for some hours.
Observations:
i) In beaker ‘a’ copper layer forms on the iron nails and blue colour of copper sulphate turns pale blue or white.
ii) No change in beaker ‘b’.
Conclusion:
i) Copper is displaced by iron in beaker ‘a’.
Copper Sulphate + Iron → Iron sulphate + Copper
ii) Iron is not displaced by copper in beaker ‘b’.
Hence iron reactivity is more than copper.
![]()
Question 9.
Draw a diagram of an activity of heat conduction by metals. Why iron, copper and aluminium are used to prepare in the manufacturing of cooking vessels?
Answer:

Iron, Copper and aluminium cooking vessels are preferred due to their high heat conductivity.