AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class English Textbook Solutions Chapter 4C Maestro with a Mission Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class English Solutions Chapter 4C Maestro with a Mission
8th Class English Chapter 4C Maestro with a Mission Textbook Questions and Answers
Comprehension
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Vempati Chinna Satyam left his house on a purpose. Do you think he was successful at the end?
Answer:
Yes, Vempati China Satyam was successful at the end. He wanted to elevate the status of Kuchipudi he had learnt from his great gurus. He decided to dedicate his life for the enrichment of that art form. So, he left his house for Madras. He carved a niche in Telugu film industry as a Kuchipudi dance director. He established Kuchipudi Art Academy in 1963 in Madras. He composed and choreographed as many as 180 solo items and 15 dance dramas. All his disciples were distinguished ones such as Shanta Rao, Yamini Krishna Murthy, Vfyjayanthimala Bali, Hema Malini, Manju Bhargavi, Shoba Naidu, Bala Kondala Rao and Daggubati Purandheshwari. He was conferred many awards. All the Telugu speakers identify themselves with ‘Kuchipudi’. The rest of the world looks at Kuchipudi and Dr. Vempati’s stupendous work with reverent eyes. Thus, Dr. Vempati was successful when he elevated the status of Kuchipudi.
![]()
Question 2.
When the stationmaster asked Satyam “Where are you going, dear?,” he kept silent.
Now choose one of the options that is not the reason for the silence.
a. He was determined to achieve something. [ ]
b. He was determined and confident about his destiny. [ ]
c. He was not determined or confident about his destiny. [ ]
Answer:
c. He was not determined or confident about his destiny. [ ✓ ]
Question 3.
If the eighteen year old lad hadn’t left his village, Kuchipudi would not have gained this popularity. Do you agree/disagree? Why?
Answer:
Yes, I agree with this statement. Kuchipudi originated in the village of Kuchipudi and was performed at temples at the time of annual festivals and in streets on the demand of the people. Only the males perform this art in those days. Though great gurus like Vedantam Lakshminarayana, Chinta Krishna Murthy enriched and transformed it completely, it was not much popular. It was not recognized on a par with other classical dances. The eighteen year old lad wanted to elevate the status of Kuchipudi, left his village and finally succeeded. So, if he hadn’t left his village, Kuchipudi wouldn’t have gained this popularity.
![]()
Question 4.
Is it appropriate to call him Dr. Vempati? Do you agree? Why (not)?
Answer:
Yes, it is appropriate to call him Dr. Vempati. Kuchipudi gained the popularity because of him only. He had been passionate about Kuchipudi since his childhood. Though he was not a good performer of Kuchipudi in the early stages, he didn’t lose hopes. He learnt the difficult aspects of Kuchipudi style from Tadepalli Peraiah Sastry and Vedantam Lakshminarayana Sastry. They inspired him very much. Later he did so much to the development and emergence of Kuchipudi to a full-fledged dance form. So it was appropriate to call him Dr. Vempati.
Writing
Based on the details of the famous singer, S.P. Bala Subrahmanyam given below, write a biographical sketch of him.
Full name: Sirpathi Panditaradhyula Balasubrahmanyam
Date of Birth: 4th June 1946
Place of Birth: Konetammapeta, Nellore District
State: Andhra Pradesh
Educational qualifications: Engineering
Entry into film field: 1966
First Film : Sri Sri Sri Maryada Ramanna
Entry into Bollywood: in 1980
Total number of songs sung: About 40.000
Other credits: Noted dubbing artist.
Actor: Acted in a number of Telugu films
TV programmes: Leading many TV programmes.
Awards:
- National Film Award for best male playback singer — 6 times
- Nandi Awards from Government of Andhra Pradesh — 25 times
- State Award from Tamil Nadu
- State Award from Karnataka
- Padma Shri Award
- Padma Bhushan
Answer:
Mr. S.R Bala Subrahmanyam is a famous singer. His full name is Sripathi Panditaradhyala Bala Subrahmanyam. He was born on 4th June, 1946 at Konetammapeta, Nellore district, Andhra Pradesh. He was a graduate in engineering. His entry into film field was made in 1966. He sang for the film Sri Sri Sri Maryada Ramanna for the first time in his life. He entered Bollywood in 1980. He has sung about 40,000 songs in all the languages till now. He is also a noted dubbing artist. He acted in a number of Telugu films. He has already led a number of TV programmes and is leading many of them now. He was rightly conferred the ‘Padma Bhushan’ and ‘Padma Shri’ Awards by our government. He was given ‘Nation Film Award’ for best male play back singer for six times. He received ‘Nandi Awards’ from government of Andhra Pradesh for 25 times. Tamil Nadu and Karnataka honoured him with ‘State Awards’.
![]()
Listening
I. Listen to the news bulletin read by your teacher and answer the following questions.
The News
This is All India Radio, giving you the news. The headlines. The Government of AP all set to declare a new art & cultural policy. A new cultural programme to be launched to show the Government’s commitment to cultural development of the state. Exhibitions and other activities to mark the new programme.
The news in detail…
The Government of AP is all set to declare a new art and cultural policy. The policy is expected to stress the development of arts and crafts of the state. The Chief Minister is expected to announce the policy today at Ravindra Bharati, Hyderabad.
As per the Government sources, a drive under this programme will benefit the artists of Kuchipudi, Burrakatha, Oggukatha and Harikatha. Puppet shows would be made compulsory in all the Government organized programmes, they said.
According to the Handicrafts Minister, 51 new cultural centres would be started to boost the sales of Nirmal, Etikoppaka and Kondapalli toys. He also stated that handloom weaving would be given due importance. Dharmavaram, Pochampalli, Venkatagiri, Mangalagiri, Ponduru weavers would get interest free loans.
The headlines once again. The Government of AP all set to declare a new cultural policy. That’s the end of this news bulletin.
Have a good day!
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What are the highlights of the news bulletin?
Answer:
The highlights of the news bulletin are:
- The Government of Andhra Pradesh all set to declare a new art and cultural policy.
- Exhibitions and other activities will be conducted to mark the new programme.
- The artists of Kuchipudi, Burrakatha, Oggu katha and Hari katha will be benefited.
- New cultural centres would be started to boost the sales of Nirmal, Etikoppa and Kondapalli toys.
- Dharmavaram, Pochampalli, Venkatagiri, Mangalagiri, Ponduru weavers would get interest free loans.
Question 2.
Where is the art and culture polity programme going to be announced? Who is going to be benefited from this policy?
Answer:
The art and culture policy programme is going to be announced at Ravindra Bharathi, Hyderabad. The artists of Kuchipudi, Burrakatha, Oggu katha and Hari katha are going to be benefited from this policy.
![]()
Question 3.
How will the weavers be benefited from this polity?
Answer:
Dharmavaram, Pochampalli, Venkatagiri, Mangalagiri, Ponduru weavers would get interest free loans.
Study Skills
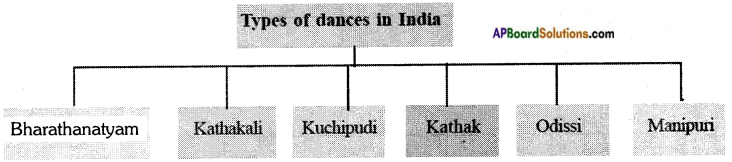
I. India is a land of culture and tradition. One aspect of culture is dance. India has six major types of dances: Bharathanatyam, Kathakali, Kuchipudi, Kathak, Odissi and Manipuri.
The information can be transformed into a tree diagram.
Here is some information about musical instruments in India:
In India, we have some musical instruments. The shehanai is an Indian wind instrument. This is played during auspicious functions. The harmonium is a wind instrument, having its roots in Europe. The sitar is one of the prime musical instruments of Indian music. It is a stringed instrument. The tampura is another stringed instrument. Among the stringed instruments, the veena is the most ancient stringed instrument. The tabla is a percussion instrument. The flute/bansuri is a wind instrument. The violin is a stringed instrument played with a bow.
Now, convert the above information Into a tree diagram.
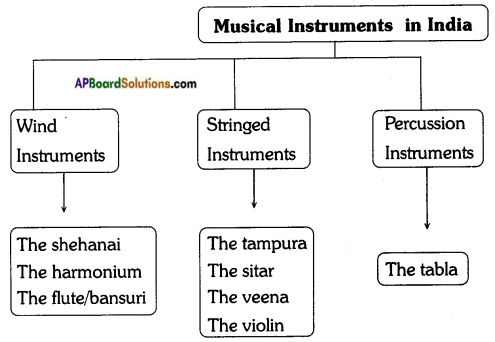
![]()
Project work
Identify a performing artist like a singer, a dancer or any other artist in your village or town. He/She might not be a famous person. Go to him/her. Collect the details about him/her.
You can take the help of the following questions for interviewing.
- Who are your parents?
- What is your place of birth?
- Who taught you this art?
- Are there any specific reasons for taking up this art?
- Does the community around you support you?
- Does this art make you financially independent?
- Would you give any message to the student community?
Fill the following table based on the information you have collected.
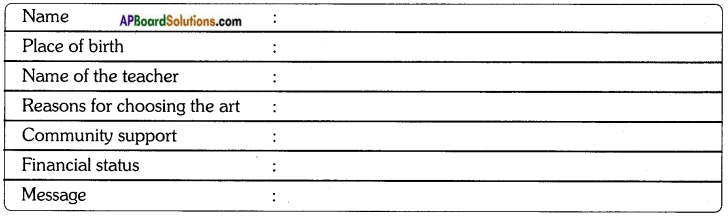
Prepare a brief profile and exhibit it in your classroom.
Answer:
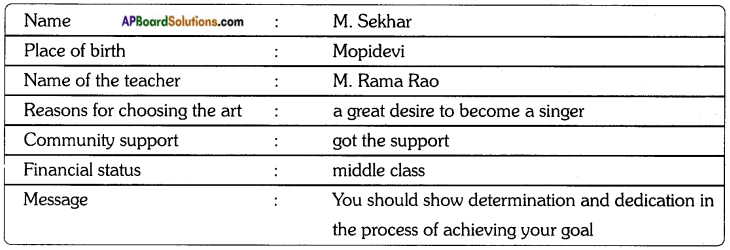
Yesterday, I met M. Sekhar, one of the popular singers in our village. His parents are Chaya Devi and Prakash. He was born at Nuziveedu, his grandparents’ place. He has a passion for singing since his childhood. He wanted to become a play back singer in film industry. After completion of his SSC, he left his village for Hyderabad. He learnt the music from M. Rama Rao, a great guru. The community around him gave him much support in the process of becoming a singer. He got chances to sing in two or three Telugu films. He is a regular singer in all kinds of festive occasions. Now, he is leading a middle-class life. His message to all of us is that we should show determination and dedication in the process of achieving our goal.
![]()
Writing an e-mail
Electronic mail, commonly referred to as email or e-mail, is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients.
In order to send or receive e-mail messages, you need to create an account to access the service. You must need an internet connection for this purpose.
The messages you receive is stored in the mailbox created for your account. You can re-read the message anytime, delete it if you want to or even forward it to others.
- The address of the recipient is to be typed in the ‘to’ text field.
- The subject, if any, of the message is typed in the ‘subject’ field.
- The ‘message’ is to be typed in the message field.
- If you want to attach any files you can attach to the ‘attachment’ field.
- Click on the ‘send’ in order to send the message.
Messages sent by e-mail normally reach a recipient’s account within seconds. Through mails you can send pictures, documents in addition to messages.
You can send anything to anywhere in the world.
Maestro with a Mission Summary in English
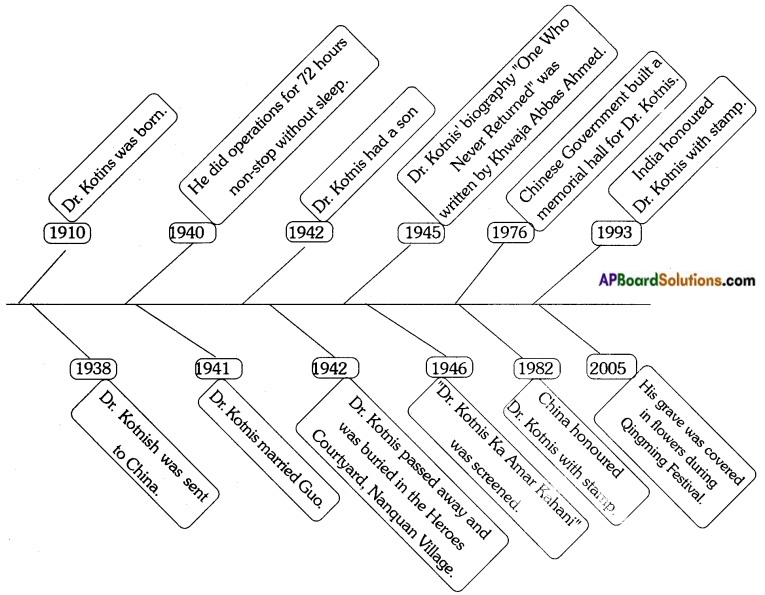
Dr. Vempati Chinna Satyam was born to Venkata Chalamaiah and Varalakshmi on 15th, October 1929. He was survived by his wife Swarajya Lakshmi, two sons and three daughters. He faced many hardships in his childhood. He had a strong desire to learn Kuchipudi. Though his teacher ridiculed him, he didn’t lose his interest in Kuchipudi. His passionate dream was to elevate the status of an art form he had learnt from his great gurus. He decided to dedicate his life for the enrichment of that art form. So, he left his house for Madras when he was eighteen. He walked all the way to Madras. On his long way, he fed himself on plantains and water.
The Kuchipudi dance form originated in the village of Kuchipudi. The art was performed at temples at the time of annual festivals and in streets for a long time. Though it was transformed by great gurus like Vedantam Lakshminarayana, Chinta Krishna Murthy, it was not much popular. It was not recognised on a par with other classical dances. Dr. Vempati learnt the difficult aspects of Kuchipudi style from Tadepalli Peraiah Sastry and Vedantam Lakshminarayana Sastry. He wanted to popularize Kuchipudi all over the world. He gained reputation as a dance director in Telugu film industry by composing the dance sequences in the films “Narthanasala”, “Devadasu” and “Pandava Vanavasam”. He established Kuchipudi Art Academy in 1963 in Madras. Dr. Vempati composed and choreographed as many as 180 solo items and 15 dance dramas. The distinguished performers Shanta Rao, Yamini Krishna Murthy, Vyjayanthimala Bali, Hema Malini, Manju Bhargavi, Shobha Naidu, Bala Kondala Rao and Daggubati Purandheshwari were all Dr. Vempati’s disciples.
![]()
Dr. Vempati was conferred ‘Padma Bhushan’ by the government of India. Andhra University awarded him an honorary doctorate in 1980 and Sri Venkateswara University honoured him with D. Litt. in 1983. The mayor of Miami, USA presented him ‘Golden Key’ in 1981. He was presented ‘Raja-Lakshmi’ award. The TTD made him the ‘Asthana Natyacharya’ in 1976. He led an illustrious life of 83 years and passed away on 29th July 2012. The rest of the world looks at Kuchipudi and Dr. Vempati’s stupendous work with respectful eyes. He is rightly called “Maestro with a Mission” as he remains the source of inspiration for the people who work for Kuchipudi. He remains at the centre stage of Kuchipudi’s surge as a classical dance form in Modem India.
Maestro with a Mission Glossary
passion (n): strong feeling
choreography (n): art of arranging steps for a dance
ardent (adj): serious
oblivion (n): state of being unnoticed
carve a niche (idm): build reputation
reverent (adj): filled with honour
nuance (n): subtle difference
connoisseur (n): judge of an art
coveted (adj): liked by everyone to have
stupendous (adj): amazingly large
![]()
elevate (v): to give something a higher position
transform (v): to change the form of something
humiliated (v): made somebody feel ashamed or stupid and lose the respect of other people
ridiculed (v): made somebody look silly by laughing at them in an unkind way
rudimentary (adj): dealing with only the most basic matters or ideas
lofty (adj): deserving praise because of its high quality
nostalgic (adj): feeling of sadness mixed with pleasure and affection
laurels (n): honour and praise given to somebody because of something that they have achieved
lay-person (n): a person who doesn’t have expert knowledge of a particular subject
distinguished (adj): very successful and admired by other people
conferred (v): gave somebody an award
![]()
reverent (adj): showing great respect and admiration
illustrious (adj): very famous and much admired, especially because of what one has achieved