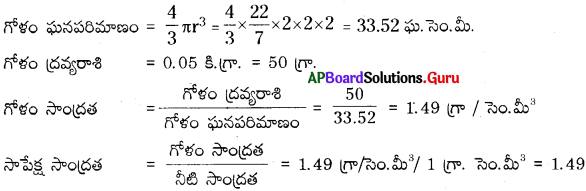
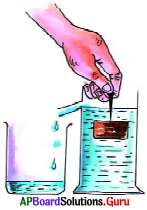
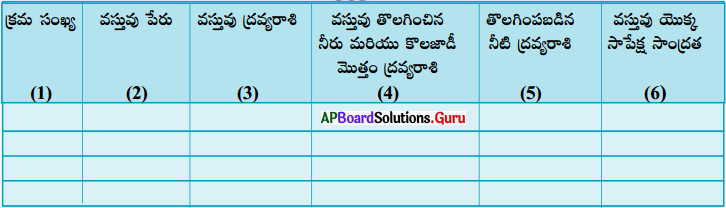
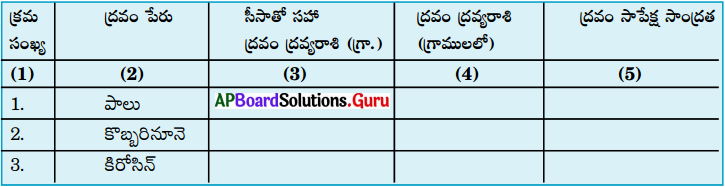
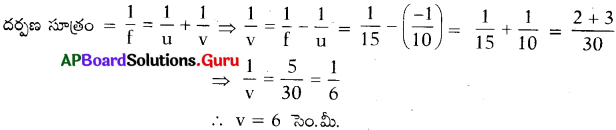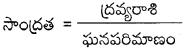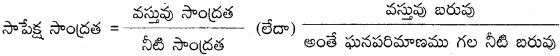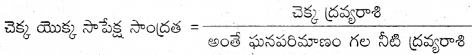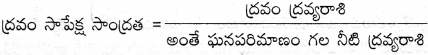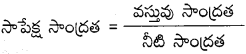AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Physical Science Important Questions Chapter 7 Reflection of Light at Curved Surfaces
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Physical Science Important Questions 7th Lesson Reflection of Light at Curved Surfaces
9th Class Physical Science 7th Lesson Reflection of Light at Curved Surfaces 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which mirror is used as rear-view mirror in the vehicles?
Answer:
Convex mirror is used as rear view mirror in the vehicles.
Question 2.
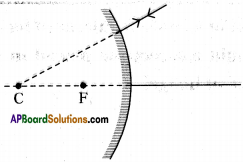
What is the relation between focal length (f) and radius of curvature (R)?
Answer:
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is twice to its focal length.
⇒ R = 2f (or) f = [latex]\frac{R}{2}[/latex].
![]()
Question 3.
Can a virtual image be photographed by a camera?
Answer:
Yes, virtual image can be photographed by a camera.
Question 4.
Complete the diagram and draw the image.
Answer:
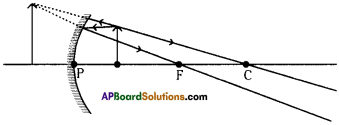
Question 5.
Predict and write the reason, why the value of the distance of the object (u) is always negative in the mirror equation.
Answer:
i) Direction of the incident rays is taken as positive (+ve).
ii) Object distance is measured from the pole to the object in the opposite direction of incident rays.
Question 6.
Which property of concave mirror is used in making the solar cooker?
Answer:
Rays coming parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror is focused at focal point. Based on this property solar cooker is made.
Question 7.
Draw the ray diagram to show the formation of image for the object of height 1 cm. placed at 5 cm. distance, in front of a convex mirror having the radius of curvature R = 5 cm.
Answer:

Question 8.
What is reflection?
Answer:
The light rays falling on a surface are returned into the original medium. This phenomenon is called reflection.
Question 9.
What is the relation between focal length and radius of curvature?
Answer:
Radius of curvature = 2 x focal length
∴ R = 2f (or) f = [latex]\frac{R}{2}[/latex]
![]()
Question 10.
What is the mirror formula for spherical mirrors?
Answer:
The mirror formula is [latex]\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}[/latex]
f = focal length of mirror ; u = object distance ; v = image distance
Question 11.
What is a real image? What is a virtual image?
Answer:
Real image :
The image formed due to convergence of light rays. The real image can be caught on the screen.
Virtual image :
The image that we get by extending the rays backwards is called a virtual image. A virtual image cannot be caught on the screen.
Question 12.
What is focal length?
Answer:
The distance between focus and vertex.
Question 13.
What is radius of curvature?
Answer:
The distance between vertex and centre of curvature.
Question 14.
What is magnification?
Answer:
The ratio of size of image to size of object is called magnification.
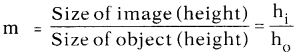
(OR)
The ratio of image distance to object distance is called magnification.
![]()
Question 15.
Why are concave and convex mirrors called spherical mirrors?
Anwer:
The reflecting surface of convex and concave mirror is considered to form a part of the surface of a sphere. So they are called spherical mirrors.
Question 16.
What is a reflecting surface?
Answer:
The surface used for reflection is called reflecting surface.
![]()
Question 17.
What is principal axis?
Answer:
The horizontal line which passes through the centre of curvature is called principal axis.
Question 18.
What is meant by converging of light rays?
Answer:
If light rays after reflection meet at a point, then we say the light rays are converging.
Question 19.
When do you say light rays are diverging?
Answer:
If light rays appear as if they are coming from a point after reflection, then we say light rays are diverging.
Question 20.
When does a ray reflect in the same path from a concave mirror?
Answer:
When it passes through centre of curvature.
Question 21.
When a light ray travelling from parallel to principal axis falls on concave mirror, then what is the path of reflected ray?
Answer:
The reflected ray passes through focal point.
Question 22.
Where do you place the vessel in solar cooker?
Answer:
We place the vessel in solar cooker at the focal point.
Question 23.
Name a mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Answer:
Concave mirror can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Question 24.
Can a convex mirror burn a paper? If not, why?
Answer:
The rays coming parallel to principal axis after reflection diverge from the mirror. So we cannot burn a paper by using a convex mirror.
![]()
Question 25.
Which mirror has wider field of view?
Answer:
A convex mirror has wider field of view, that’s why they are used as rear view mirrors in vehicles.
Question 26.
Why does our image appear thin or bulged?
Answer:
Due to converging or diverging of light rays from the mirror.
Question 27.
Why is angle of incidence equal to angle of reflection when a light ray reflects from a surface?
Answer:
Because light selects the path that takes least time to cover a distance.
Question 28.
Are angle of reflection and angle of incidence also equal for curved surface?
Answer:
Yes, it is equal for curved surfaces like spherical mirrors.
Question 29.
What is a spherical mirror? Give different types of spherical mirrors.
Answer:
If the reflecting surface of mirror is considered to form a part of the surface of sphere, then it is called spherical mirror. Spherical mirrors are of two types :
- Concave mirror
- Convex mirror
Question 30.
Write about various distances related to mirrors.
Answer:
The various distances related to mirrors are
1) Focal length (f) :
The distance between vertex and focus is called focal length.
2) Radius of curvature (R) :
The distance between vertex and centre of curvature is called radius of curvature.
![]()
Question 31.
We wish to obtain an erect image of an object using a concave mirror of focal length of 15 cm. What should be range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object?
Answer:
The range of distance of object is between 0 and 15 cm.
The image is virtual and erect.
The image is larger than the object.
Question 32.
Name some apparatus which can work on the principle of reflection of light.
Answer:
Plane mirror, spherical mirrors, periscope, kaleidoscope.
Question 33.
If you want to get parallel beam by using concave mirror, then where do you keep the source?
Answer:
The object should be kept at focus because the light rays coming from focus after reflection from mirror travel parallel to principal axis.
Question 34.
If you want to form the image of an object at infinity, then where do you keep the object?
Answer:
The object should be kept at focus; then the image would be formed at infinity.
![]()
Question 35.
How do you get a virtual image with a concave mirror?
Answer:
When we place the object between vertex and focus then we will get a virtual image.
Question 36.
Why do dentists use concave mirror?
Answer:
If the object is between mirror and its focus we get enlarged virtual and straight image by using concave mirror. So dentists use this principle to see inner parts of mouth.
Question 37.
A concave mirror produces three times magnified real image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
Answer:
> 10 cm.
Question 38.
What is your opinion on elevating buildings with mirrors?
Answer:
The mirrors used in elevating buildings are reinforced, tough and laminated glasses. These mirrors provide safety and make the buildings attractive.
Question 39.
Identify the mirror having focal length +15 cm.
Answer:
Convex mirror (since the focal length of convex mirror is taken as positive).
Question 40.
If the focal length of mirror is 10 cm, what is that mirror?
Answer:
The mirror is concave (since the focal length of concave mirror is taken as negative).
![]()
Question 41.
Can we focus a sunlight at a point using a mirror instead of magnifying glass?
Answer:
Yes, by using concave mirror we can focus sunlight at a point.
Question 42.
To reduce glaze of surroundings the windows of some department stores, rather than being vertical, slant inward at the bottom. How does this reduce glaze?
Answer:
This slant reflects the sunlight further down towards the ground, then it would happen as if they are vertical.
Question 43.
Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in the vehicles?
Answer:
It gives erect and small image and covers large distance.
Question 44.
An object is placed at a distance 8 cm from a concave mirror of radius of curvature 16 cm. What are the characteristics of image?
Answer:
The image is real, inverted, and same size.
Question 45.
What happens when light falls on an opaque object?
Answer:
Some part of light is reflected back and remaining part is absorbed.
Question 46.
What happens when light is reflected from transparent object?
Answer:
Some part of light is reflected and remaining part is partly transmitted or partly absorbed.
![]()
Question 47.
Which objects at your home act as spherical mirrors?
Answer:
Objects at home that act as spherical mirrors are :
- Spoons
- Spectacles
- Sink
- Cooking vessel
Question 48.
Complete the following ray diagram.
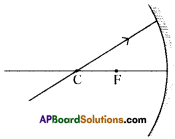
Answer:
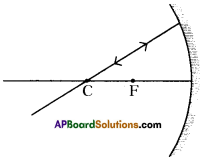
The light ray passing through centre of curvature falls normal to the concave mirror. So it retraces the same path.
Question 49.
If focal length is 20 cm, then what is radius of curvature of mirror?
Answer:
f = 20 cm
R = 2f = 2 × 20 = 40 cm.
Question 50.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is the focal length?
Answer:
Radius of curvature (R) = 20 cm
R 20
Focal length (f) = [latex]\frac{\mathrm{R}}{2}=\frac{20}{2}[/latex] = 10 cm.
Question 51.
The focal length of convex mirror is 16 cm. What is its radius of curvature?
Answer:
f = 16 cm
R = 2f = 2 × 16 = 32 cm
![]()
Question 52.
Write any two uses of concave mirror in our daily life.
Answer:
Uses of concave mirror :
- Concave mirrors are used by dentists to see enlarged image of tooth.
- Concave mirrors are used in car head lights.
Question 53.
Write any two uses of convex mirror in our daily life.
Answer:
Uses of convex mirror :
- Convex mirrors are used as rear view mirrors in vehicles because convex mirrors increase field of view.
- Convex mirrors are used in street light reflectors as they spread light over greater
Question 54.
Suggest a new use with a spherical mirror.
Answer:
Spherical mirrors are newly adapted in ATMs.
Question 55.
Focal length of a concave mirror is x. Find the sum of focal length and radius of curvature.
Answer:
Focal length = x; Radius of curvature = 2 x focal length = 2x.
The sum of focal length and radius of curvature = x + 2x = 3x.
![]()
Question 56.
If the angle between the mirror and incident ray is 40°, then find the angle of reflection.
Answer:
Given that angle between incident ray and mirror = 40°.
Suppose angle of incidence = x.
∴ 40 + x = 90
x = 90 – 40 = 50°.
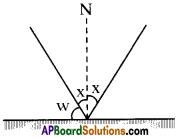
But we know angle of incidence = angle of reflection
∴ Angle of reflection = 50°.
9th Class Physical Science 7th Lesson Reflection of Light at Curved Surfaces 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Your friend has a doubt that whether a concave mirror or a convex mirror is used as a rear view mirror in the vehicles. What questions will you ask to clarify his doubts?
Answer:
- Is the image in a rear-view mirror smaller or larger when compared to real object?
- Which mirror forms smaller image than the object in the given mirrors?
Question 2.
The focal length of a huge concave mirror is 120 cm. A man is standing in front of it at a distance of 40 cm. What are the characteristics of his image in that mirror?
Answer:
i) Image form in the mirror
ii) Virtual image
iii)Erected image
iv) Enlarged image
Question 3.
How can you find out the focal length of concave mirror experimentally when there is no sunlight?
Answer:
Place the object / candle in front of the mirror and adjust the screen to get image on it. Measure the object distance, image distance. Substitute the values (as per sign connection) in mirror formula [latex]\left(\frac{1}{f}\right)=\left(\frac{1}{u}\right)+\left(\frac{1}{v}\right)[/latex]. We get the focal length of mirror.
(OR)
Place the object / candle and the screen at same point in front of the mirror. Adjust this set of material to get sharp image on the screen.
Measure the distance from mirror to object/screen. This distance is the radius of curvature and make it half, it gives focal length of the mirror.
![]()
Question 4.
The magnification of the image by the concave mirror is – 1. Mention the four char-acteristics of image from the above information.
Answer:
- Image will be formed at the centre of curvature (C).
- Image size is equal to that of the object size. ‘
- Inverted image.
- Real image.
Question 5.
Write about different points related to mirrors.
Answer:
The different points related to mirrors are
1) Vertex (P) :
The point where the central axis touches the mirror is called vertex.
2) Focus or focal point (F):
The light rays coming from distinct object appear to meet at point in case of concave mirror and tend to meet at point when drawn backward in case of convex mirror. That point is known as focus or focal point.
3) Centre of curvature (C) :
It is centre of the sphere to which the mirror belongs.
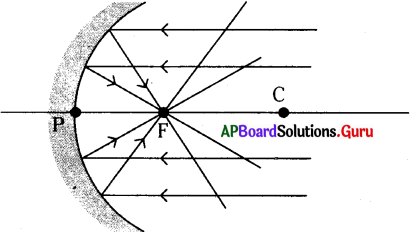
Question 6.
What happens if light rays parallel to principal axis fall on the concave mirror, and draw ray diagram?
Answer:
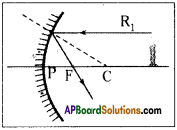
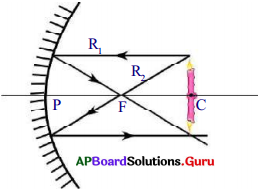
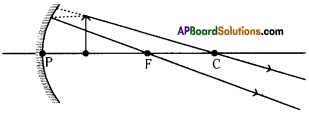
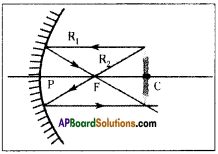
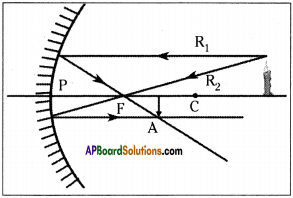
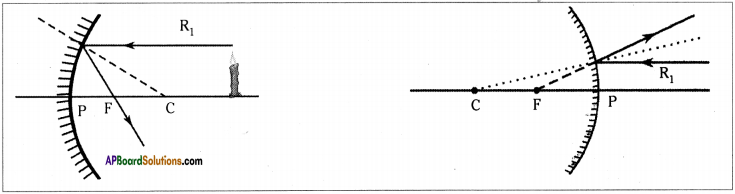
The light rays that are parallel to the principal axis get reflected such that they pass through the focal point of the mirror. R1 is such ray in figure.
Question 7.
What happens to a ray which passes through focal point and falls on the concave mirror, and also draw the ray diagram?
Answer:
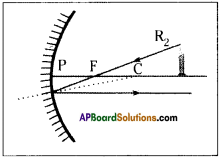
The light ray which goes through the focal point of the mirror travels parallel to principal axis. R2 is such ray in figure.
Question 8.
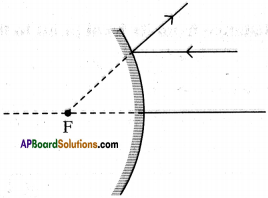
How does an image form due to convex mirror? Draw the ray diagram.
Answer:
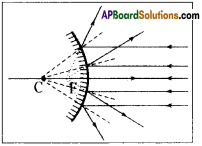
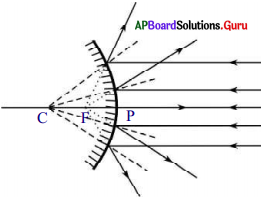
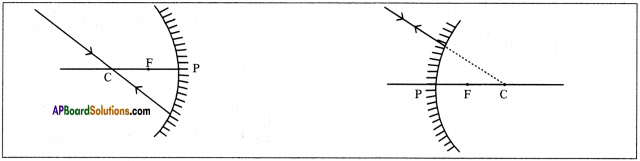
- The parallel rays coming from distance object tend to diverge after reflection.
- If we extend the reflected rays backwards they meet at ‘F’, i.e. focal point of the convex mirror.
Question 9.
Which light ray after reflection will travel along the same path in opposite direction? What can be such a ray for a spherical mirror? Draw the ray diagram.
Answer:
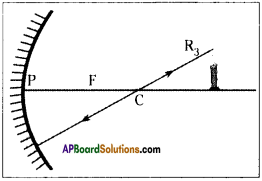
- Any ray that is normal to the surface, on reflection, will travel along the same path but in opposite direction.
- The line drawn from the centre of curvature of mirror is perpendicular to the tangent at the point, the line meets the curve.
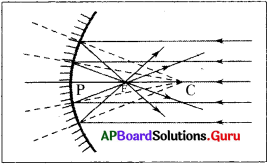
- So if we draw a ray starting from the tip of the object going through the centre of curvature to meet the mirror, it will get reflected along the same line. This ray is shown as R3 in the figure.
Question 10.
What happens if an object is placed at centre of curvature of a mirror? Draw the ray diagram.
Answer:
From the ray diagram we conclude that the image of the object will be formed at the same distance as the object and it will be inverted and of the same size. The image is real because it forms on a screen.
Question 11.
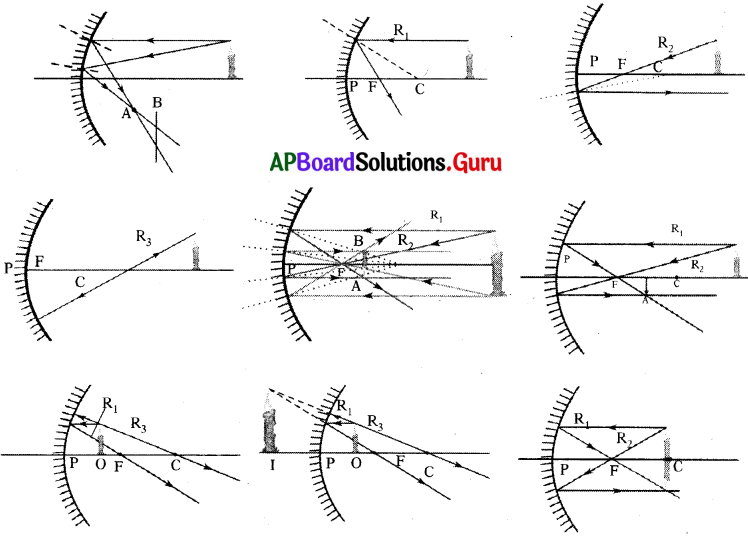
Draw the ray diagrams with convex mirror and write rules of ray diagram of convex mirror.
Answer:
Rule -1 :
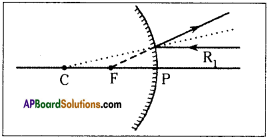
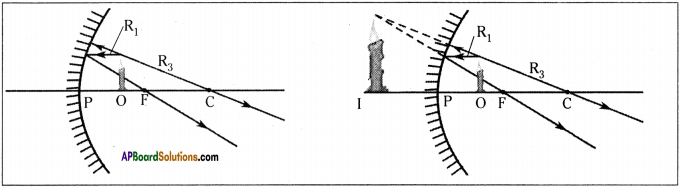
A ray running parallel to main axis, on meeting the convex mirror will get reflected so as to appear as if it is coming from the focal point.
Rule – 2 :
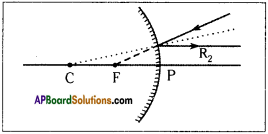
This is converse of rule 1. A ray going in the direction of focal point after reflection will become parallel to main axis.
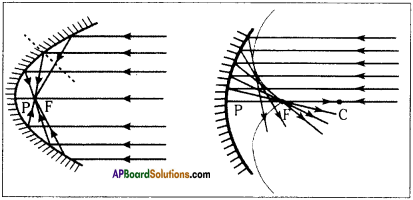
Rule – 3 :
A ray going in the direction of the centre of curvature will get reflected back in opposite direction, and looks like that is coming from the centre of curvature.
Question 12.
Why do we use parabolic mirror instead of concave mirror?
Answer:
- We use parabolic mirror instead of concave mirror because with the concave mirror all the rays coming parallel in it may not be focused at focal point (F).
- Those rays which are very nearer to principal axis will only be focused at focal point.
- It is very effective to make the mirror parabolic in order to make all the rays to converge at focus.
Question 13.
The magnification of mirror is given as – 3. What is the inference do you get from this information?
Answer:
Magnification – ve indicates it is an inverted image. So it is a real image.
Magnification 3 indicates the image size is three times the object size. So the image is enlarged. Since it is forming real image the mirror is concave.
Question 14.
Why are we able to see various objects around us?
Answer:
We are able to see various objects around us due to the diffused light reflected from these objects reaches to our eye which gives sense of vision to those objects.
![]()
Question 15.
Which type of mirror is used as a reflector in street lamp?
Answer:
The reflectors of the street lamp are made in convex in shape so that reflected rays diverge over the larger area on ground. Therefore convex mirror acts as a reflector in street lamp.
Question 16.
Which type of mirror is used in doctor’s head lamp?
Answer:
Doctors use head lamp to examine nose, throat, teeth, etc. of patients. In this lamp a parallel beam of light is allowed to fall on the concave mirror. The reflected light concentrates on focus on the mirror on a smaller area to be examined. So the concave mirror is used in doctor head lamp.
Question 17.
Would you able to burn a paper using concave mirror?
Answer:
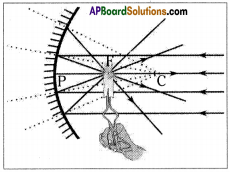
- Concave mirror focuses the parallel sun rays at focal point of the mirror.
- So with a small concave mirror we can heat up and burn a paper.
Question 18.
How do you find the focal length of concave mirror?
Answer:
- Hold a concave mirror such that sunlight falls on it.
- Take a small paper and slowly move it in front of the mirror until we will get smallest and brightest spot of the Sun.
- Find the distance between mirror and image of the Sun that will give the focal length of mirror.
Question 19.
See the table and identify the mirrors in each case.
| Mirror | Magnification |
| X | – 1 |
| Y | + 1 |
| Z | + 0.5 |
Answer:
Magnification negative indicates that it is inverted image and also real. Magnification -1 means same size. So the mirror which gives real image of same size is concave mirror. So ‘X’ is concave.
The magnification +1 means the image is virtual, erect and same size. So the mirror Y is plane.
The magnification + 0.5 means the image is virtual, erect and diminished. So the mirror Z is convex.
Question 20.
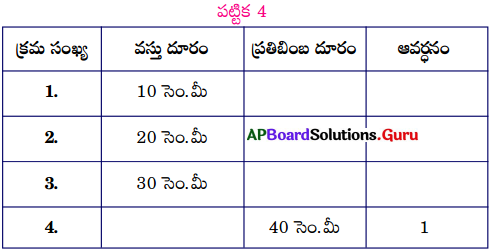
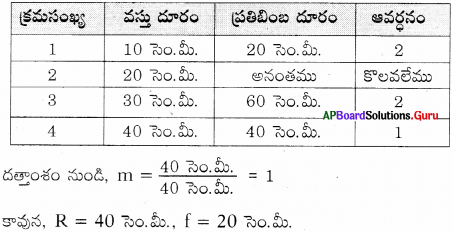
An object is placed at various positions in front of concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. Complete the table by using given information without actually doing the problem.
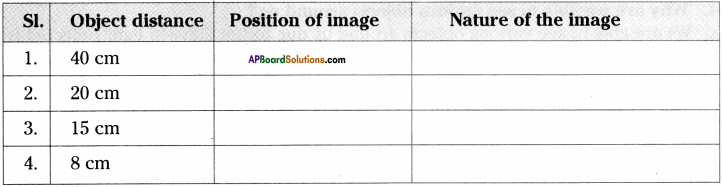
Answer:
Question 21.
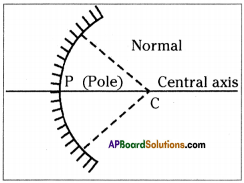
Draw a normal at any point of a concave mirror.
Answer:
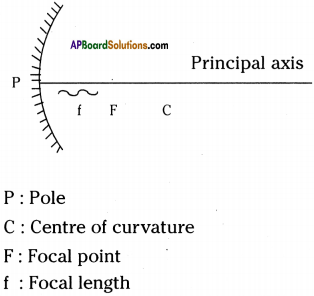
Question 22.
Identify the following in a ray diagram showing the reflection of light in a concave mirror.
a) Pole of the mirror
b) Principal axis
c) Centre of curvature
d) Focal point
e) Focal length
Answer:
Question 23.
Complete the ray diagram.
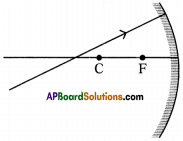
Answer:
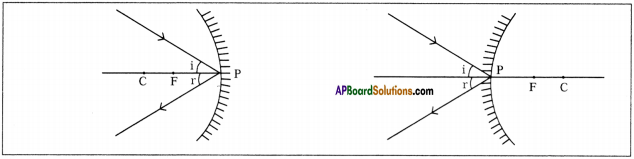
First we have to draw normal at point of contact to the concave mirror and then we have to use laws of reflection to draw the reflecting ray.
Question 24.
Figure shows two parallel light rays falling on a convex mirror. Complete the ray diagram.
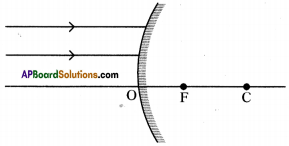
Answer:
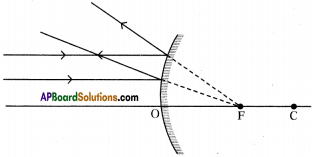
Question 25.
See the belog figure and complete the ray diagram.
Answer:
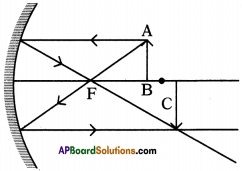
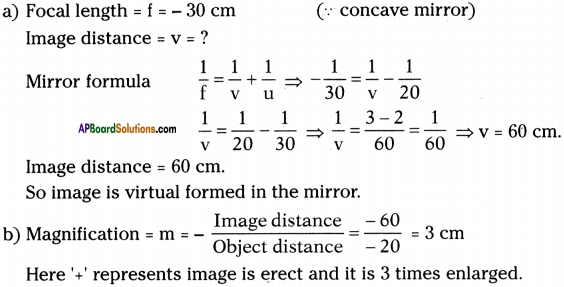
Question 26.
Assume that an object is kept at a distance of 20 cm in front of a concave mirror. If its focal length is 30 cm, then
a) what is the image distance?
b) what the magnification of mirror in this case?
Answer:
Object distance = u = 20 cm
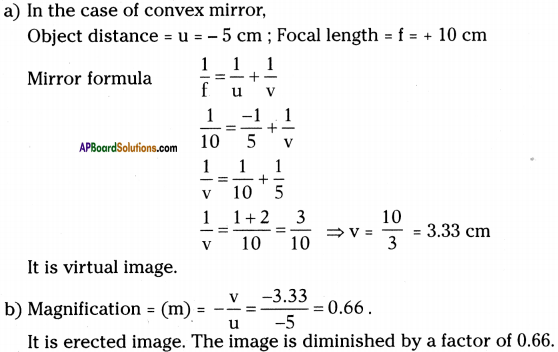
Question 27.
There is an object in front of convex mirror at a distance of 5 cm. If its focal length is 10 cm, then
a) what is the image distance?
b) what is its magnification?
Answer:
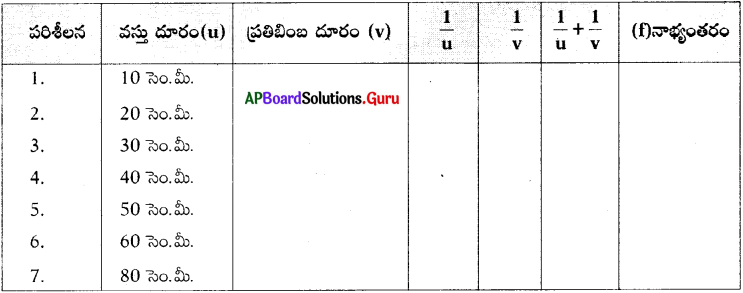
9th Class Physical Science 7th Lesson Reflection of Light at Curved Surfaces 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Sudheer wants to find focal length of a concave mirror experimentally.
a) What apparatus does he need?
b) Is the screen required or not? Explain.
c) Draw the table required to tabulate the values found in his experiment.
d) What is the formula used by him to find focal length?
Answer:
a) Apparatus required to Sudheer are
- Concave mirror,
- White paper or screen,
- Scale,
- V – stand,
- Candle.
b) Yes, screen is required.
To catch and measure the image distance screen is required.
c) Table for observation and calculation of ‘f’.
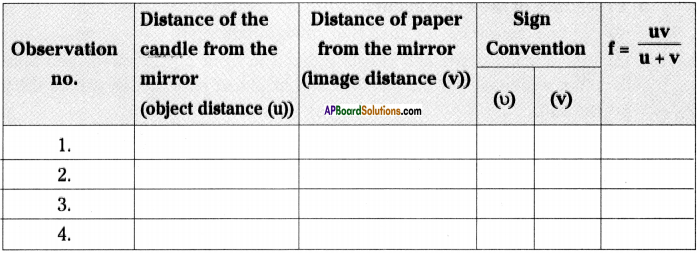
d) Focal length [latex]\Rightarrow \frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{v}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{u}} \text { (or) } \mathrm{f}=\frac{\mathrm{uv}}{\mathrm{u}+\mathrm{v}}[/latex]
This is the formula used by him to find a focal length.
Question 2.
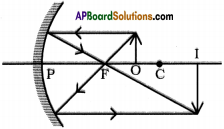
Show the formation of image with a ray diagram when an object is placed on the principal axis of a Concave mirror between focus and centre of curvature of the mirror.
Answer:
Question 3.
An object of 6 cm height is placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror, will the image be formed? What are the characteristics of the image?
Answer:
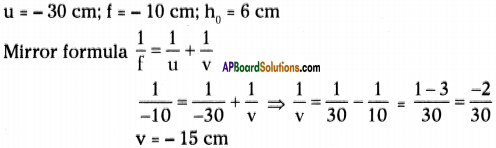
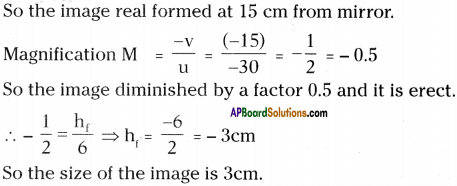
Question 4.
List the materials required for conducting an experiment to find the focal length of a concave mirror. Explain the experimental process also.
Answer:
a) Material required for conducting an experiment to find the focal length of a concave mirror are
- concave mirror
a piece of paper - meter scale.
b) Procedure of the experiment:
- Hold a concave mirror such that sunlight falls on it.
- Take a small paper and slowly move it in front of the mirror and find out the point where we get the smallest and brightest spot, which will be the image of the sun.
- Measure the distance of this spot from the pole of the mirror.
- This distance is the focal length (f) of the mirror.

Another Experiment:
a) Material required :
A candle, paper / screen, concave mirror, V-stand, measuring tape or meter scale.
b) Procedure :
1) Place the concave mirror on V-stand, a candle and meter scale as shown in the figure.
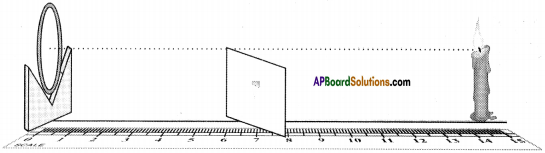
2) Keep the candle at different length from the mirror (10 cm to 80 cm) along the axis and by moving the paper find the position where the sharp image is got on the paper.
3) Measure the image distance (o) and note in the given table.
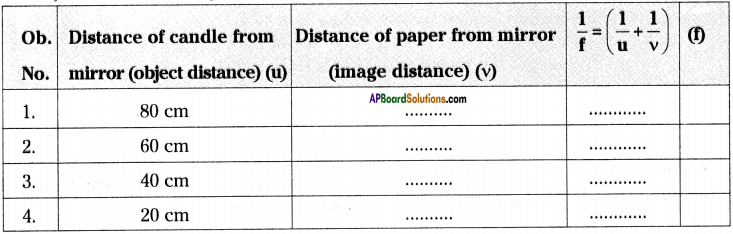
4) Find the average of focal lengths (f) obtained in the experiment.
5) The average T is the focal length of the given mirror.
Question 5.
An object of height 5 cm is placed at 30 cm distance on the principal axis in front of a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. Find the image distance and size of the image.
Answer:
Object distance (u) = – 30 cm, Focal length (f) = – 20 cm, Height of object (ho) = 5 cm, Image distance (v) = ?, Height of image (hi) = ?

∴ The image is real, inverted with a height of 10 cm.
Question 6.
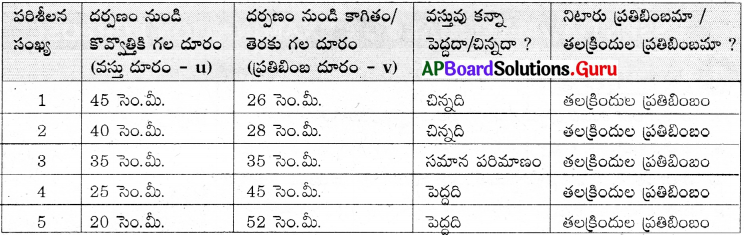
A student conducted an experiment to observe characteristics of images formed by spherical mirrors and recorded his observations as follows. Observe the table and answer the questions.
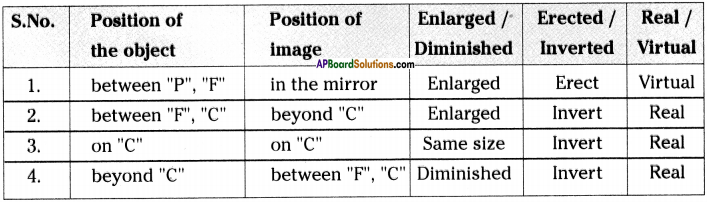
i) Above said information belongs to which spherical mirror?
ii) In which situation, magnification is less than 1.
iii) An object of height 8 cm placed at centre of curvature on principal axis, then where do you get the image and what is its height?
iv) “All real images are inverted”. Justify the statement by using above table.
Answer:
i) It is a Concave mirror.
ii) When object is kept beyond ‘C’ then magnification is less than 1.
iii) Image formed at ‘C’. The height of the image is 8 cm.
iv) According to the table if the image is erected image, it is a real image. In all the other cases every real image is virtual image.
![]()
Question 7.
In the following cases calculate the magnification values for a concave mirror. Give reason.
a) When the object is at the focal point of the mirror.
b) When the object is between focal point and the pole.
Answer:
In the case of concave mirror
a) When the object is at the focal point of the mirror, then its magnification value is -1.
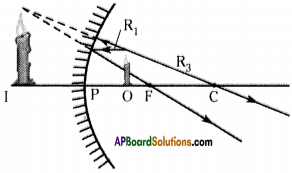
Reason :
In this case size of the image is large, compared with the object. It is called virtual image. Image is formed behind the mirror so magnification has negative sign.
Nature of the object: It is real, inverted, enlarged and forms at infinity.
b) When the object is between focal point (F) and the pole (P) of the mirror, then its magnification value is +1.
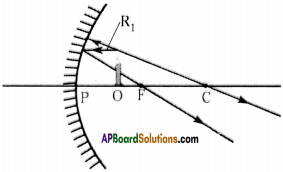
Reason :
In this case image is formed on the same side of the object and it is also virtual image so, the sign of the magnification is positive.
Nature of the object:
It is virtual, erect, enlarged and on the same side of the object.
Question 8.
Write the derivation of mirror formula.
(OR)
Derive [latex]\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{u}+\frac{1}{v}[/latex].
(OR)
A student wants to find the image distance for a given object distance of a mirror. Then derive a formula for the mirror.
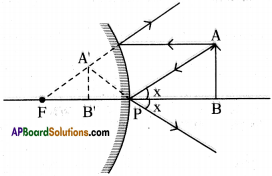
Answer:
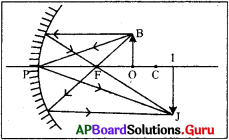
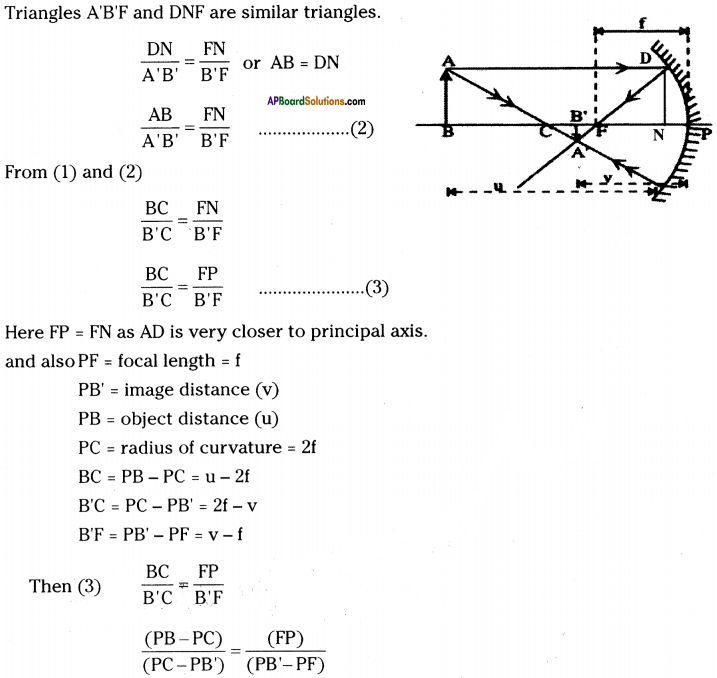
Derivation of mirror formula :
In the figure P = pole, C = centre of curvature and F= focus of the concave miror. Object AB is placed beyond C. Image AB’ is formed in between F and C.
From the diagram triangles A’B’C and ABC are similar triangles.
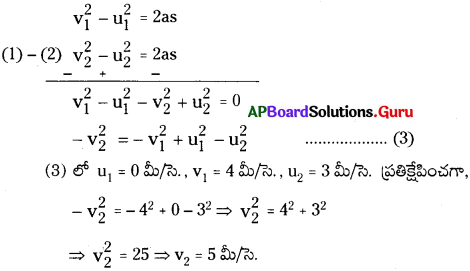
[latex]\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{A}^{\prime} \mathrm{B}^{\prime}}=\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{B}^{\prime} \mathrm{C}}[/latex] ………………… (1)

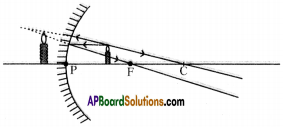
Question 9.
Where is the base of the candle going to be in the image when the object is placed on the axis of the mirror beyond ‘C’?
Answer:
- Any ray starting from a point on the axis and travelling along the axis will reflect on the axis itself.
- So the base of the image is going to be the axis.
- If the object is placed vertically on the axis, the image is going to be vertical.
- Draw perpendicular from point A to axis.
- The intersection point is the point where the base of the image of the candle is going to be formed
Question 10.
What happens if an object placed at a distance less than the focal length of the concave mirror? Draw the ray diagram.
(OR)
When do you get a virtual image by using a concave mirror and draw the ray diagram?
Answer:
- The candle object (0) is placed at a distance less than the focal length of the mirror.
- The first ray (R1) will start from tip of the object and run parallel to axis to get reflected so as to pass through focal length.
- The second ray (R2) is the ray starting from the tip of the object and going through the focal point but it is not possible as such a ray will not meet the mirror.
- The third ray (R3), starting from the tip of the object goes to the centre of curvature but that also seem not to be possible.
- Now consider a ray (R4) that starts from the tip and goes in such a direction that it would go through the centre of curvature if extended backwards.
- This ray is normal to surface and so will be reflected along the same line in opposite direction and will go through centre of curvature.
- The two reflected rays diverge and will not meet.
- When we extend these rays backward they appear to be coming from one point.
- As seen from the figure (2) the image will be erect and enlarged and virtual.
![]()
Question 11.
A person in a dark room looking through a window can clearly see a person outside in the daylight, whereas the person outside cannot see the person inside. Why?
Answer:
- There is usually some reflection that occurs at an interface between the two materials but most often of light passing through.
- Imagine you are inside in the dark. A person outside in bright sunlight is sending out (reflection) lots of light, most of which would come through the window to you, so you see them clearly.
- Since it is so bright outside, there is also a good amount of light which reflects back towards them.
- This can distract them from little bit of light from you that is going towards them, so they have much harder time seeing you.
Question 12.
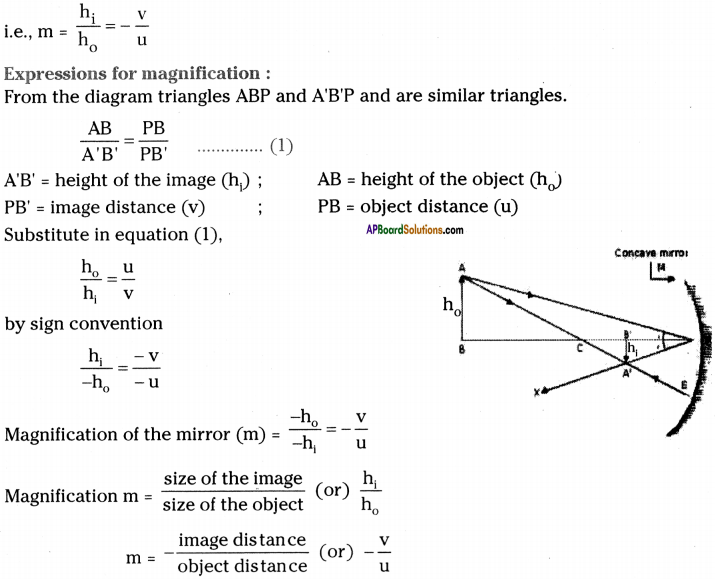
What is magnification? Derive an expression for magnification.
Answer:
Magnification :
The ratio of height of image to height of object is called magnification.
Question 13.
What are the rules to be followed while drawing ray diagrams?
Answer:
Various rules to be followed for drawing ray diagrams.
1) A ray parallel to the principal axis, after reflection will pass through the principal focus in case of a concave mirror or appear to diverge from the principal focus in case of convex mirror.
2) A ray passing through the principal focus of a concave mirror or a ray which is directed towards the principal focus of convex mirror, after reflection will emerge parallel to the principal axis.

3) A ray passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror or directed in the direction of centre of curvature of a convex mirror, after reflection, is reflected back along the same path.
4) A ray incident obliquely to the principal axis, towards a point P on the concave mirror or a convex mirror, is reflected obliquely. The incident ray and reflected rays follow laws of reflection.
Question 14.
How do you make a parallel beam with an experiment?
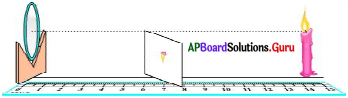
Answer:
Aim :
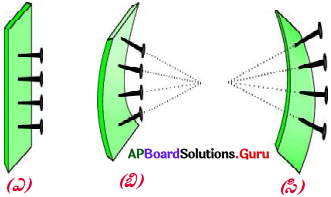
Making a beam of parallel lines.
Material used :
Two pins, thermocol block, candle.
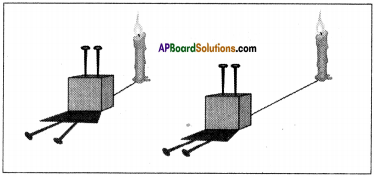
Procedure:
- Stick two pins on a thermocol block.
- The pins are exactly parallel to each other.
- As we can see in the figure, when a source of light is kept very near, we see the shadows diverging (from the base of the pins).
- As we move the source away from the pins, the divergent angle starts reducing.
- If we move the source far away, we will get parallel shadows. Thus we get a beam of parallel lines.
Question 15.
Write a table which shows the image formed by a concave mirror for different positions and also give size and nature of image.
Answer:
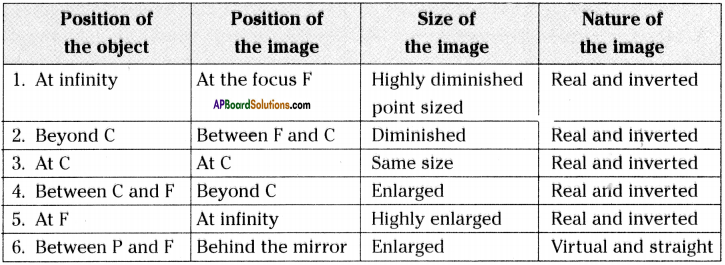
Question 16.
Ray diagrams of concave mirror.
Answer:
Object is placed ‘Infinitely’ :
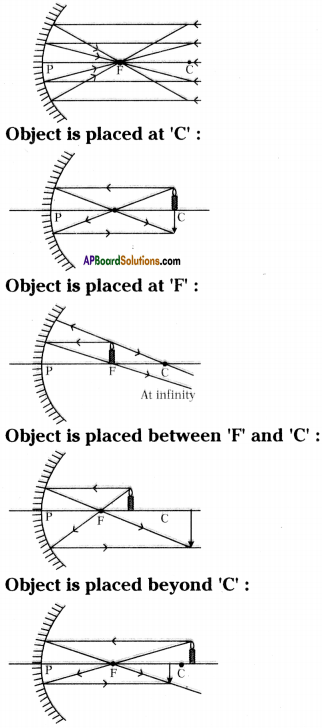
Object is placed between ‘P’ and ‘F :
Question 17.
Complete the following ray diagrams and give reasons.
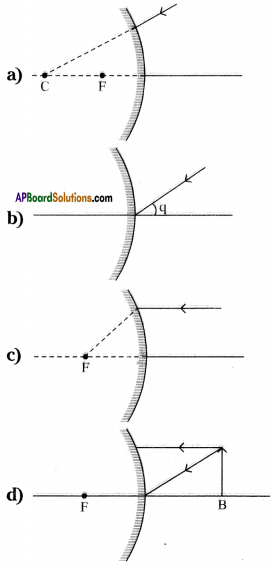
Answer:
a)
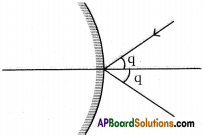
Reason :
The light appears to be passing through centre of curvature after reflection from convex mirror retraces the same path.
b)
Reason :
The light ray making certain angle of incidence ‘q’ with principal axis follows laws of reflection and reflects with same angle q.
c)
Reason :
The light ray which travels parallel to principal axis after reflection from convex mirror diverges from mirror and if we extended the ray backwards it passes through principal focus.
d)
Reason :
The light ray which travels parallel to principal axis after reflection from convex mirror diverges from mirror when the light ray drawn backwards passes through focus and second light ray follows laws of reflection (i.e., ∠i = ∠r).
These extended backward light rays meet and form a virtual, diminished and erect image between pole and focus inside the mirror.
Question 18.
Complete the following diagram to obtain image of object AB.
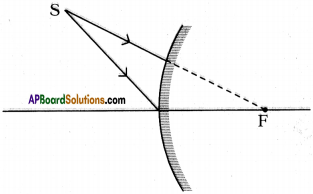
Answer:
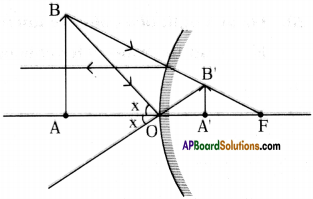
- The light ray which appears to coming from focus after reflection from convex mirror travels parallel to principal axis.
- The light ray which is incident with certain angle ’x’ at pole ‘P’ reflects with same angle from convex mirror.
- These two extended light rays meet at B. So AB’ is the image of the object AB.
Question 19.
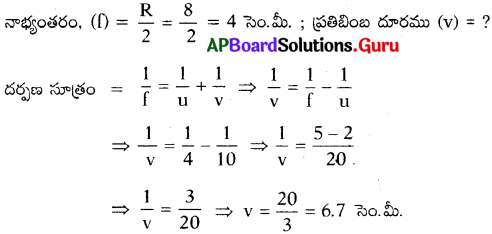
An object 4 cm in size is placed at 25 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Find the nature and size of image.
Answer:
Given that f = – 15 cm ; u = – 25 cm ; h0 = 4 cm ; v = ?

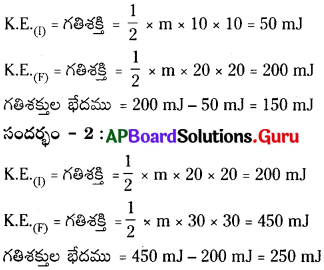
So the image is enlarged and inverted.
Question 20.
Focal length of a concave mirror is f. The distance from its focal point to the object is P. Find the ratio of heights of image.
Answer:
Concave mirror is a part of spherical mirror.

Question 21.
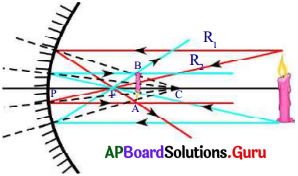
When do we get a blurred image from a distant object by using concave mirror?
Answer:
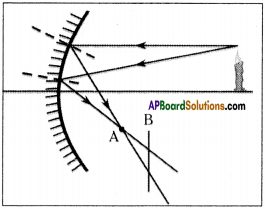
- The diagram shows a few rays starting from the tip of the flame.
- The reflected rays intersect A. So the reflected image of tip of flame will be at intersection point A.
- If we hold the paper at any point before or beyond point A (for example at point B), we see that the rays will meet the paper at different points,
- So the image of the tip of the flame will be formed at different points due to these rays.
- If we draw more rays emanating from the same tip we will see that point A they will meet but at point ‘B’ they won’t.
- So the image of the tip of the flame will be sharp if we hold the paper at A and become blurred (due to mixing of multiple images) when we move the paper slightly in any direction (forward or backward).
![]()
Question 22.
An object of size 7 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed? Find size and nature of the image.
Answer:
Given, h0 = 7 cm ; u = – 27 cm ; f = – 18 cm ; v = ?

Question 23.
An object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror, the radius curvature is 20 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image. (V = -30 cm, m = -2, h2 = -6 cm)
Answer:
h0 = 3 cm; u = -15 cm; r = -20 cm; f = [latex]\frac{r}{2}[/latex] = – 10 cm
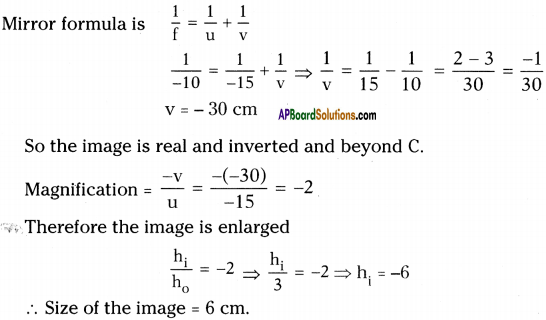
Question 24.
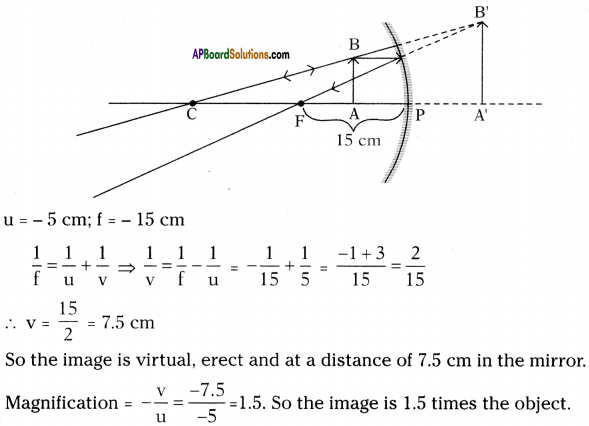
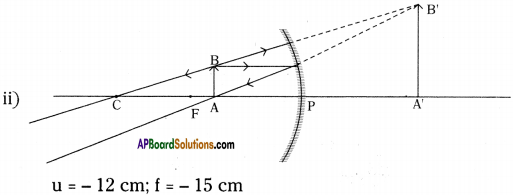
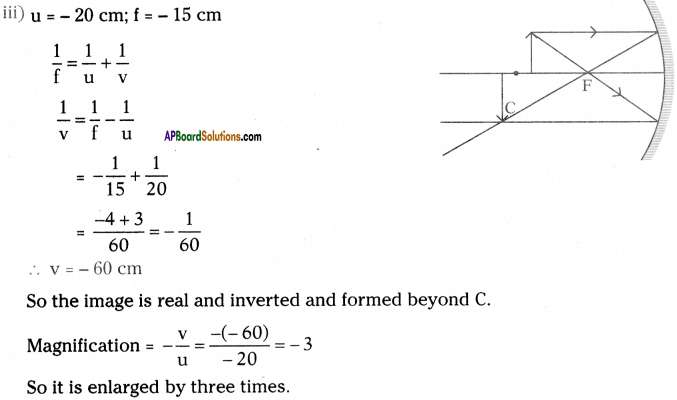
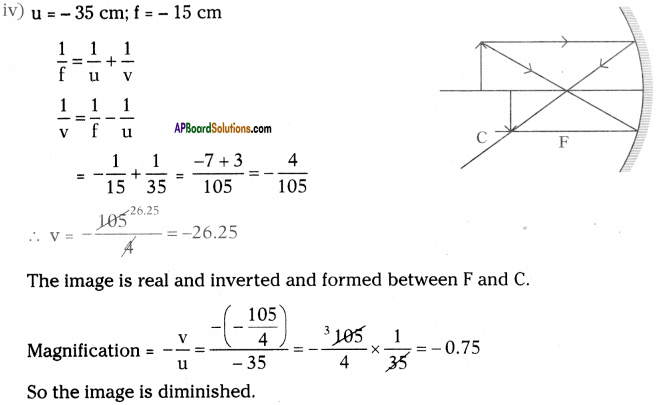
Focal length of a concave mirror is 15 cm. An object of length 5 cm is placed in front of this mirror. Draw neat diagrams to find the length and position of image when object is at (I) 5 cm, 0i) 12 cm, (iif) 20 cm, (jv) 35 cm away from the mirror.
Answer:
i) An object is kept at a distance of 5 cm from the mirror.