AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class English Textbook Solutions Chapter 1C I Will Do It Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class English Solutions Chapter 1C I Will Do It
10th Class English Chapter 1C I Will Do It Textbook Questions and Answers
Comprehension
I. Answer the following questions briefly.
Question 1.
What is the ultimate aim of a bright student? And why?
Answer:
The ultimate aim of a bright student is to continue his/her studies at a world-class educational institute. He/She wants to join it as there are high standards. One will do great things when one studies at a top-class institute. So, a bright student wants to join a top-ranked institute.
(Or)
The ultimate aim of a bright student is to study at IIT. It is because, these institutions maintain high standards. One can do big things if one studies at IIT. Hence, a bright student’s ultimate aim is to study at IIT.
![]()
Question 2.
‘His heart sank in sorrow.’ Whose heart sank in sorrow? Why?
Answer:
Narayana Murthy’s heart sank in sorrow. Because of the poor financial position, Murthy’s father refused to send him to IIT. Though he had passed with a high rank, there was no chance for him to study at IIT which was his dream. So, he was very sorrowful.
Question 3.
How did Murthy react when his father expressed his helplessness to send him to IIT?
Answer:
When his father expressed his helplessness to send him to IIT, Murthy was disappointed. It seemed his dreams had burnt to ashes. His heart sank in sorrow. He didn’t share his feelings with anybody. His heart was bleeding but he didn’t get angry with anybody.
Question 4.
The author calls Murthy an introvert. Which action of Murthy substantiates this claim of the author about Murthy?
Answer:
‘Introvert’ means someone who is quiet and shy, and does not enjoy being with other people. When Murthy’s father refused to send him to IIT, he became sorrowful. Though he was sorrowful, he never shared his unhappiness or helplessness with anybody. He did not reply. He remained silent. So, we can say that Murthy was an introvert by nature.
![]()
Question 5.
What, according to Narayana Murthy, can change the life of a person?
Answer:
According to Narayana Murthy, a person himself can change his life by hard work. It is not the institution or any other thing that can change the life of a person.
Question 6.
How does the motto ‘Powered by intellect and driven by values’ describe Murthy’s life?
Answer:
Murthy really believes in the motto, ‘Powered by intellect and driven by values’. He worked very hard. He didn’t bother about his personal life or comforts. He was a genius right from the beginning. He shared his wealth with others. He never used the help of any caste, community or political connections to go up in life. He proved that it was possible to earn wealth legally and ethically. He built a team of people who were equally good. The above words reveal that he was powered by intellect and driven by values.
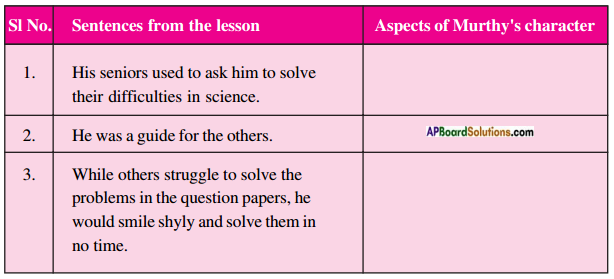
II. Given below are some sentences from the lesson. What do they tell us about Narayana Murthy’s qualities? Use the adjectives given in the box to describe Murthy’s character. You may also use some more adjectives you like.

Answer:
| Sentences from the lesson | Aspects of Murthy’s character |
| 1. His seniors used to ask him to solve their difficulties in science. | bright |
| 2. He was a guide for the others. | intelligent |
| 3. While others struggle to solve the problems in the question papers, he would smile shyly and solve them in no time. | brilliant |
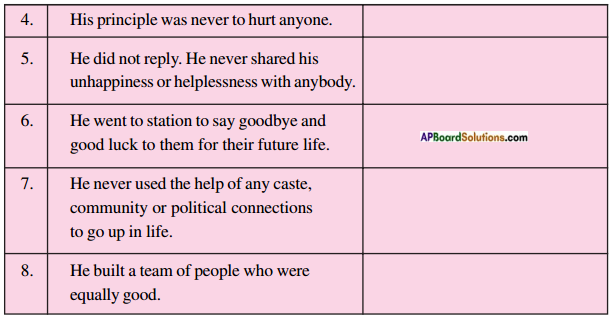
| 4. His principle was never to hurt anyone. | gentle |
| 5. He did not reply. He never shared his unhappiness or helplessness with anybody. | introverted |
| 6. He went to station to say goodbye and good luck to them for their future life. | encouraging |
| 7. He never used the help of any caste, community or political connections to go up in life. | uncompromising |
| 8. He built a team of people who were equally good. | hard-working |
![]()
Vocabulary
Let’s look at some more one-word substitutes.
| Word | Meaning |
| fatalist | a person who believes in fate |
| centenarian | a person who is above hundred years |
| omnipresent | one who is present everywhere |
| mercenary | a person who can do anything for money |
| misogynist | one who hates women |
| monogamy | a practice of having one wife or husband |
| autobiography | a life history written by oneself |
| biography | a life history written by somebody else |
| honorary | a position for which no salary is paid |
| ambiguous | a sentence whose meaning is unclear |
| inimitable | that which cannot be imitated |
| theist | one who believes in God |
| spendthrift | one who spends too much |
| teetotaler | one who abstains from taking alcohol |
Tick (✓) the most appropriate one-word substitutes for the following.
1. A person or thing that cannot be corrected
a) unintelligible
b) Indelible
c) illegible
d) incorrigible
Answer: d
2. A persoiì of good understanding. knowledge and reasoning power
a) expert
b) intellectual
c) snob
d) literate
Answer: b
3. A person who knows many languages
a) linguist
b) grammarian
c) polyglot
d) bilingual
Answer: c
4. One who possesses many talents
a) versatile
b) prodigy
c) exceptional
d) gifted
Answer: a
5. Words inscribed on a tomb
a) epitome
b) epistle
c) epilogue
d) epitaph
Answer: d
![]()
Project Work
You have read about Nick Vujicic, who has accomplished every seemingly impossible thing in life despite having the most difficult form of disability. You have read about Narayana Murthy, who is one of the most remarkable examples to win over the unbeatable difficulties. You may also have heard or read about some remarkable Indian women such as Sudha Murthy, Sudha Chandran, Kiran Bedi and many other women who have crossed all the hurdles to become successful.
Now, work in pairs and collect information about the women who you think have excelled in their lives though they may not have come into limelight.
You may read articles in newspapers, magazines, books (autobiographies, biogra¬phies etc.), browse internet and watch TV reports on women.
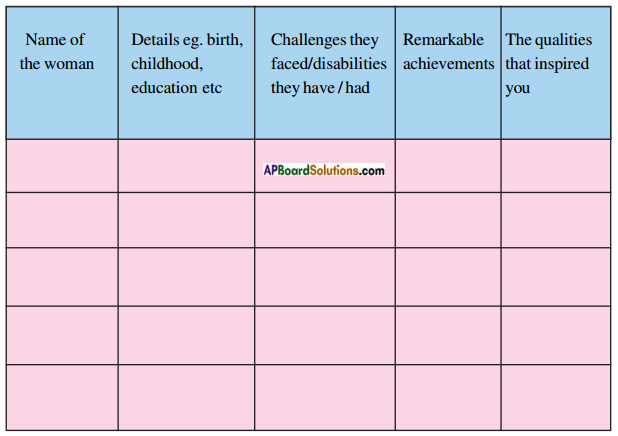
Answer:
| Name of the woman | Details eg. birth, childhood, education, etc. | Challenges they faced/disabilities they have / had | Remarkable achievements | The qualities that inspired you |
| Mary Griffith | A 13 year old girl. She is studying at Mundelein Middle School | She has cerebral palsy | Set records at the National Junior Disability Championship. | Hard work and will power |
| Karin Korb | A 38-year-old woman. She spent her childhood with her grandparents. She had studied well till she broke her back. Later she joined a law school. | She broke her back at age 17 while competing in gymnastics. | Wheelchair tennis competitor | Courage and determination |
| Emily Anne Schaefer | A 44 year old woman. A French town resident. She spent her childhood in a foster s care. | When she was a child, she suffered from traumatic brain injuries. She is developmentally disabled. | The facilitator for the project’s network in Hunterdon County. Despite the trauma, she earned a college degree in fine arts. She is a printmaker and painter, and has self- published two books on art and poetry, | Grit and perseverance |
| Rama Lakshmi | She is the resident of T. Nagar, Tamil Nadu. She was born on 20th May, 1995. Spent her childhood very joyously till she lost her sight in a ghastly incident. Now she is a student of engineering. | She became blind when she was 12 years old in an accident. | She is a playwright and poet. She has written more than twenty poems and eight plays, | Courage and determination |
| Srivalli | She is the resident of Kothapet, Kurnool. She was born in a poor family on 15th August, 1992. She took her degree in arts with distinction marks. |
She lost both her legs in an accident. | She is a wonderful singer. She composes songs. | Will power, determination perseverance |
![]()
I. Based on the information you gather about the persons, prepare a short biographical account of the person you like the most, emphasizing the exemplary work done by him/her and present it to the group/ whole class.
Answer:
Ms. Srivalli was born on 15th August, 1992. She came from a poor family. Her father was a musician and her mother was a teacher. She was a bright student. Unfortunately, she met with an accident when she was eleven and the doctors amputated both her legs. After two years of relentless struggle, she could go back to her school. She could walk with the help of artificial limbs and slowly run. Now, she can do anything like a normal woman. She learnt music from guru Rama Sastry and now she is a good singer and composer of songs. In spite of her disability, she has worked hard with great determination, discipline and dedication and achieved her target.
After she had met with the accident, her heart sank in sorrow. Sometimes she wanted to die. She hated God for doing this to her. She was terrified of her losing both the limbs. Her doctor Mr. Rao always encouraged her by telling her that she could walk and run normally. She tried and tried until she could walk. She didn’t give up at any stage. Srivalli always says, “The challenges in our lives are there to strengthen our convictions. They are not there to run us over.” With the help of her parents, friends . and guru, Srivalli has managed to reach such a position in her life. She has proved that anything can be done, if one tries hard. From her life, we can understand that one need not lose hope. Her life shows us that one s disability can’t prevent one from reaching one’s target. I feel that her life is a source of inspiration to every woman. She is able to do all these only because of her strong will power. Hence, I believe in will power with which one can achieve wonders in one’s life. I would like to wish all the best for her in the future.
II. You may also present this write up on the occasion of “Women’s Day” in your school.
Answer:
Our beloved headmaster, dear teachers and my fellow students!
I wish you a very good morning and welcome you all to the programme. At the outset, I would like to greet all the women a very happy ‘Women’s Day.’
As we all know that 8th March is celebrated as International Women’s Day to commemorate women’s achievements and the contributions made by them to the society This day is also known as the United Nations Day for women’s rights and international peace.
I have a great pleasure to say a few words about a great girl Mary Griffith on this occasion. Mary Griffith, a thirteen year old girl, has set national records in track and swimming. She has been studying at the Mundelein Middle School and has cerebral palsy. In spite of her disability she set her records in 2004 and 2005 at the National Junior Disability Championships. She always say that sports have given her a lot more confidence and taught her to balance her life. Though she has been suffering from cerebral palsy, she hasn’t lost her hope. With great faith and determination she has done so well and set her own records. Her efforts are inspirational to all the women.
We all wish her a great future and with this I will end my speech. I thank one and all for giving me this chance to share my views with you.
![]()
I Will Do It Summary in English
Nagavara Ramarao Narayana Murthy is the founder of Infosys, a leading IT company in the world. He is an icon of simplicity, uncompromising quality and fairness, apart from being a philanthropist. He believes in the motto, ‘Powered by intellect and driven by values.’
As a school going lad, Narayana Murthy was the brightest boy in his class. He could solve the most difficult problems which were very hard for his seniors. He came from a poor but educated family. His father was a high-school teacher. As all other students, Narayana Murthy wanted to get admission in the IIT. He appeared for the entrance test and did well. He always dreamt of studying at IIT. He was thrilled to know that he had passed the test with a high rank.
When Narayana Murthy told his father that he wanted to join IIT, his father reminded him of their poverty. Murthy’s father advised him to stay in Mysore and study as much as he wanted. His father was very sad to say this. Murthy was disappointed and his heart sank in sorrow. He was an introvert so he never shared his sorrowfulness or helplessness with anybody. When his classmates were leaving for Madras, Murthy went to the station to say goodbye to them. Though they were all excited and talking loudly, Murthy remained silent. He wished them and they waved at him as the train slowly left the platform. Even after the train had left, he stood there motionless. He believed that he only could change his life by hard work. He unknowingly followed “Your best friend is yourself and your worst enemy is yourself, the philosophy of the Bhagavath Gita. With great determination, Narayana Murthy reached great heights in his life. He proved that it was possible to earn wealth legally and ethically.
I Will Do It about the Author
Sudha Murthy, wife of N.R. Narayana Murthy, is an Indian social worker and author. Murthy began her professional career as a computer scientist and engineer. She is the chairperson of the Infosys Foundation. She has founded several orphanages, participated in rural development efforts, supported the movement to provide all Karnataka government schools with computer and library facilities, and established the ‘The Murthy Classical Library of India’ at Harvard University.
Murthy also teaches Computer Science. She composed a fiction, Dollar Sose. The present story is an extract from one of her most successful stories ‘How I Taught my Grandmother to Read & Other Stories.’
![]()
I Will Do It Glossary
sharp (adj): quick to notice something/able to grasp quickly
bright (adj): clever / intelligent / sharp / brilliant
unnoticed (adj): ignored / overlooked
spark (n): a small amount of particular quality or feeling
grasp (v): understand something completely
avid (adj): doing something as much as possible
literature (n): written works like novels, plays, poems, technical works, newspapers and magazines
admission (n): the right to join an institution
aspirant (n): someone who hopes to get a position of importance or honour
sleepy (adj): quiet and peaceful
guide (n): a person who can advise others
mandap (n): a raised platform
uitlmate (adj): main and most important / vital / final
D-Day (n): a date on which something important is expected to happen.(From the name given to June 6, 1944. the day on which the US., British, and other armies landed on the beaches of northern France in the Second World War.)
Implied (v): gave the meaning / meant
Anna (n): a word used to address a respectable elder 1 older male
afford (v): pay for / have funds for
expenses (n): expenditure / money that one spends on something
bitter (adj): making somebody feel unhappy
burnt to ashes: lost hopes
fondest (adj): most liking
introvert(n): a quite person who is interested in his / her own thoughts and feelings.
chirping (v): making short high sounds
monsoon (n): rainy season
set in (phr.v.): begin / start
drizzle (v): light rain / sprinkle
motionless (adj): without movement
jealously (adv): being unhappy over something
philosophy (n): attitude / way of life
ethically (adv): morally
pioneer (n): a person who is the first to do something
wave (n): raise or increase
icon (n): a famous person or thing that people admire and see as a symbol of a particular idea, way of life, etc.
uncompromising (adj): unwilling to change opinions or behaviour
philanthropist (n): one who devotes his service or wealth for the love of mankind
powered by intellect and driven by values: According to Narayana Murthy Intellect (mind power) should be the power of every man. He should be driven (influenced) by values.