SCERT AP 10th Class Physics Study Material Pdf 5th Lesson మానవుని కన్ను-రంగుల ప్రపంచం Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 10th Class Physical Science 5th Lesson Questions and Answers మానవుని కన్ను-రంగుల ప్రపంచం
10th Class Physical Science 5th Lesson మానవుని కన్ను-రంగుల ప్రపంచం Textbook Questions and Answers
అభ్యసనాన్ని మెరుగుపరుచుకోండి
ప్రశ్న 1.
హ్రస్వదృష్టి లోపాన్ని మీరెలా సవరిస్తారు?
(లేదా)
కన్ను యొక్క హ్రస్వ దృష్టిని మీరు ఏ విధంగా సవరిస్తారు?
జవాబు:
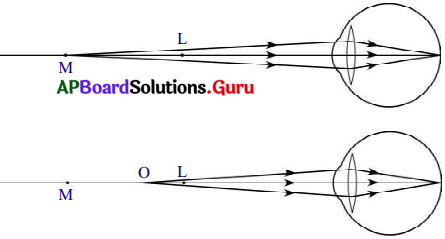
1) ఒక వ్యక్తి గరిష్ఠ దూర బిందువుకు ఆవల ఉన్న వస్తువును చూడలేకపోవు దోషాన్ని “హ్రస్వదృష్టి” అంటారు.
2) ఏ దూరం వద్ద నున్న బిందువుకు లోపల గల వస్తువుకు మాత్రమే కంటి కటకం రెటీనా పై ప్రతిబింబాన్ని ఏర్పరచుకోగలదో ఆ బిందువును గరిష్ఠ దూర బిందువంటారు.
3) గరిష్ఠ దూరబిందువుకు, స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనీస దూరాన్ని తెలిపే బిందువుకు మధ్య వస్తువు ఉన్నప్పుడు కంటి కటకం రెటీనా పై ప్రతిబింబమును ఏర్పరచగలదు.
|4) గరిష్ఠ దూరబిందువు ఆవల ఉన్న వస్తువు యొక్క ప్రతిబింబాన్ని కంటి కటకం రెటీనా కంటే ముందు ఏర్పరుస్తుంది.
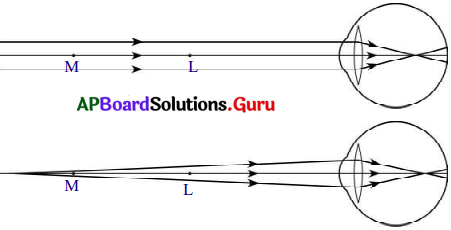
5) కావున ఒక కటకంను ఉపయోగించి గరిష్ఠ దూర బిందువుకు ఆవల ఉన్న వస్తువు యొక్క ప్రతిబింబాన్ని గరిష్ఠ దూర బిందువు మరియు స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనీస దూరాన్ని తెలిపే బిందువుల మధ్యకు తేగలిగితే ఆ ప్రతిబింబం కంటి కటకానికి వస్తువులా పని చేస్తుంది.
6) హ్రస్వదృష్టిని నివారించేందుకు అనంతదూరంలో ఉండే వస్తువు యొక్క ప్రతిబింబాన్ని గరిష్ఠ దూర బిందువు వద్ద ఏర్పరచగలిగే కటకాన్ని ఎంచుకోవాలి.
7) దీని కొరకు ద్విపుటాకార కటకమును వాడాలి.
8) ఈ ద్విపుటాకార కటకం ఏర్పరిచే ప్రతిబింబం కంటి కటకానికి వస్తువు వలె పనిచేసి, చివరకు వస్తు ప్రతిబింబంను రెటీనా పై ఏర్పరచును.
ప్రశ్న 2.
దీర్ఘదృష్టి లోపాన్ని సవరించే విధానాన్ని వివరించండి.
(లేదా)
కన్ను యొక్క దీర్ఘదృష్టిని మీరు ఏ విధంగా సవరిస్తారు?
జవాబు:
1) దీర్ఘదృష్టి గల వ్యక్తి దూరంలో వున్న వస్తువులను స్పష్టంగా చూడగలడు. కానీ దగ్గరి వస్తువులను చూడలేడు.
2) దీనికి గల కారణము కంటి కటక కనిష్ఠ నాభ్యంతరం 2.27 సెం.మీ. కన్నా ఎక్కువగా ఉండడమే.
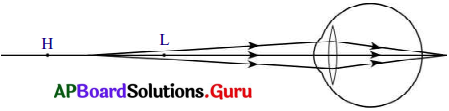
3) పై పటంలో చూపినట్లుగా ఈ సందర్భంలో దగ్గరలోని వస్తువు నుండి వచ్చే కాంతి కిరణాలు కంటి కటకం ద్వారా వక్రీభవనం చెంది ప్రతిబింబం రెటీనాకు ఆవల ఏర్పడుతుంది.
4) వస్తువు కనిష్ఠ దూర బిందువుకు ఆవల ఉంటే, కంటి కటకం రెటీనా పై ప్రతిబింబాన్ని ఏర్పరచగలదు.
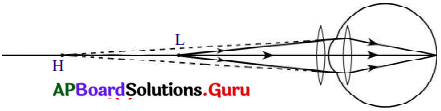
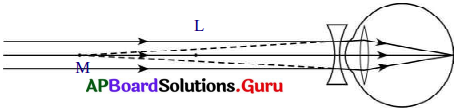
5) కనుక దీర్ఘదృష్టిని నివారించడానికి ద్వికుంభాకార కటకాన్ని ఉపయోగించాలి.
6) ఈ కటకం వలన ఏర్పడే ప్రతిబింబం కంటి కటకానికి వస్తువుగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
7) అందువలన చివరకు కంటి కటకం వలన ఏర్పడే ప్రతిబింబం పటంలో చూపినట్లుగా రెటీనా పై ఏర్పడును.
ప్రశ్న 3.
పట్టక పదార్థ వక్రీభవన గుణకాన్ని ప్రయోగపూర్వకంగా ఎలా కనుగొంటారు?
(లేదా)
పట్టకపు వక్రీభవన గుణకమును కనుగొను కృత్యంను వ్రాయుము. (ప్రయోగశాల కృత్యం)
జవాబు:
ఉద్దేశ్యం : పట్టక వక్రీభవన గుణకాన్ని కనుగొనడము.
కావలసిన వస్తువులు :
పట్టకం, తెల్లని డ్రాయింగ్ చార్ట్ (20 X 20 సెం.మీ.), పెన్సిల్, గుండుసూదులు, స్కేలు మరియు కోణమానిని.
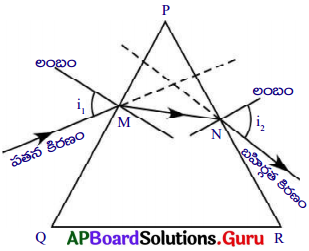
నిర్వహణ పద్దతి :
- ఒక గాజు పట్టకాన్ని తీసుకొని, దాని త్రిభుజాకార పతనకిరణం, AM ఆధారం డ్రాయింగ్ చార్ట్ పై ఉండే విధముగా అమర్చుము.
- పట్టక ఆధారం చుట్టూ పెన్సిల్ తో గీత గీసి పట్టకాన్ని తీసివేయాలి.
- త్రిభుజ భుజం PQ పై ఒక బిందువు ‘M’ ను గుర్తించుము.
- M వద్ద PQ కు లంబాన్ని గీయాలి.
- M వద్ద PQ తో 30° కోణాన్ని గుర్తించి, ఒక రేఖను గీయుము. ఇదియే పతన కిరణం అగును.
- ఈ కోణమును “పతన కోణము” అంటారు.
- పట్టకాన్ని తిరిగి దాని స్థానంలో ఉంచి పతన కిరణం AB పై రెండు గుండు సూదులను నిలువుగా గుచ్చుము.
- పట్టకం రెండోవైపు నుండి గుండుసూదుల ప్రతిబింబాలతో ఒకే వరుసలో ఉండునట్లు C, D బిందువుల వద్ద మరో రెండు గుండు సూదులను గుచ్చుము.
- ఇప్పుడు C, D లను కలుపుము. ఇది బహిర్గత కిరణమును సూచించును.
- పతన కిరణం, బహిర్గత కిరణాలను వెనుకకు పొడిగించిన అవి రెండూ ‘O’ వద్ద ఖండించుకుంటున్నాయి.
- ‘O’ బిందువు వద్ద ఈ రెండు కిరణాల మధ్య కోణమును కొలిచిన, అది విచలన కోణం (d) అగును.
- ఈ విధంగా వివిధ పతన కోణాలకు, విచలన కోణాల విలువలను తెలుసుకొని, వాటిని నమోదు చేయుము.
- ఈ ప్రయోగం ద్వారా పతన కోణం పెరుగుతున్న కొలదీ కొంతమేర విచలన కోణం విలువ తగ్గి తర్వాత పతన కోణంతో పాటుగా పెరగడం గమనించవచ్చును.
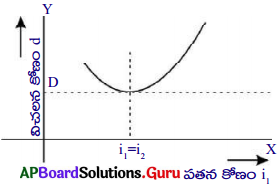
- పతన కోణంను X-అక్షం వెంబడి, విచలన కోణంను Y-అక్షం వెంబడి తీసుకొని గ్రాఫును గీసిన సున్నిత వక్రం ఏర్పడుతుంది.
- ఈ వక్రం ద్వారా కనిష్ట విచలన కోణం ‘D’ ను కనుగొనవచ్చును.
- ‘పట్టక కోణం ‘A’ కనిష్ఠ విచలన కోణం ‘D’ అయితే పట్టక వక్రీభవన గుణకము \(n=\frac{\sin \left[\frac{(A+D)}{2}\right]}{\sin \frac{A}{2}}\) అగును.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 4.
ఇంద్రధనుస్సు ఏర్పడే విధానాన్ని వివరించండి. (కృత్యం – 5)
జవాబు:
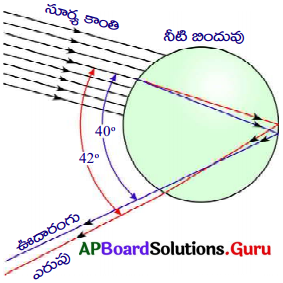
- ప్రకృతిలోని తెల్లని సూర్యకాంతి, అనేక లక్షల నీటి బిందువుల చేత విక్షేపణం చెందడం వల్ల ఇంద్రధనుస్సు ఏర్పడును.
- పటంలో చూపినట్లుగా నీటి బిందువు పై ప్రాంతం నుండి సూర్యుని కాంతికిరణం లోపలికి ప్రవేశించును.
- అక్కడ జరిగే మొదటి వక్రీభవనంలో తెల్లని కాంతి వివిధ రంగులుగా విక్షేపణం చెందును.
- అన్ని రంగులు నీటి బిందువు రెండో వైపుకు చేరాక, సంపూర్ణాంతర పరావర్తనం వల్ల నీటి బిందువులోనే వెనుకకు పరావర్తనం చెందుతాయి.
- ఫలితముగా నీటి బిందువు మొదటి ఉపరితలాన్ని చేరాక, ప్రతీ రంగు మరలా గాలిలోకి వక్రీభవనం చెందును.
- నీటి బిందువులోకి ప్రవేశించే కిరణాలు, బయటకు వెళ్ళే కిరణాల మధ్య కోణం (0° నుండి 42° మధ్య ఎంతైనా ఉండవచ్చు.
- ఆ కోణం 42° లకు దాదాపు సమానంగా ఉన్నప్పుడు ప్రకాశవంతమైన ఇంద్రధనుస్సును మనం చూడగలము.
- ప్రతి నీటి బిందువు కాంతిని ఏడు రంగులలోకి విడగొట్టినా, ఒక పరిశీలకుడు తాను ఉన్న స్థానాన్ని బట్టి, ఒక నీటి బిందువు నుండి వచ్చే రంగులలో ఏదో ఒకదానిని మాత్రమే చూడగలడు.
- సూర్యకాంతి పుంజానికి, నీటి బిందువుచే వెనుకకు పంపబడిన కాంతికి మధ్యకోణం 42° ఉన్నప్పుడే మనకు ఎరుపు రంగు కనబడుతుంది.
- 40° ల నుండి 42°ల మధ్య కోణంలో VIBGYOR లోని మిగిలిన రంగులు కనిపిస్తాయి.
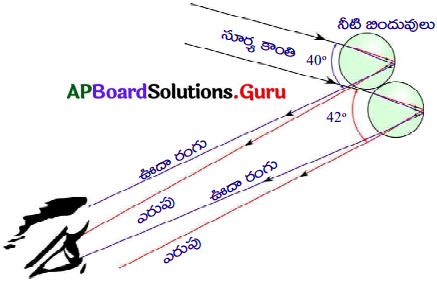
- ఈ విధముగా ప్రకృతిలో ఇంద్రధనుస్సు ఏర్పడును.
ప్రశ్న 5.
ఆకాశం నీలి రంగులో కనబడటానికి గల కారణాన్ని క్లుప్తంగా వివరించండి.
(లేదా)
మనకు ఆకాశము నీలముగా కనబడుటకు గల కారణమును వివరింపుము.
జవాబు:
- ఆకాశం నీలిరంగుగా ఉండుటకు కారణము కాంతి యొక్క పరిక్షేపణము.
- కాంతి పరిక్షేపణమనగా ఒక కణం శోషించుకున్న కాంతిని తిరిగి అన్ని దిశలలో వివిధ తీవ్రతలతో విడుదల చేయడాన్ని “కాంతి పరిక్షేపణం” అంటాము.
- వాతావరణంలో వివిధ పరిమాణాలు గల కణాలుంటాయి.
- వాతావరణంలోని నైట్రోజన్, ఆక్సిజన్ అణువు పరిమాణం నీలిరంగు కాంతి తరంగదైర్ఘ్యంతో పోల్చదగిన విధముగా ఉంటుంది.
- ఈ అణువులు నీలిరంగు కాంతికి పరిక్షేపణ కేంద్రాలుగా పనిచేస్తాయి.
- వాతావరణంలో నైట్రోజన్, ఆక్సిజన్ అణువులు ఎక్కువగా వుండటం వల్ల, అవి నీలిరంగు కాంతికి పరిక్షేపణ కేంద్రాలుగా పనిచేయడం వల్ల ఆకాశం నీలిరంగులో కనిపిస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 6.
అంశం (A) : కాంతి పరిక్షేపణం వలన ఆకాశం నీలిరంగులో కనబడుతుంది.
కారణం (R) : తెల్లని కాంతిలోని వివిధ కాంతులలో నీలిరంగు కాంతి తరంగదైర్ఘ్యం తక్కువ.
a) A, R రెండూ సరియైనవి. మరియు A కు R సరైన వివరణ.
b) A, R రెండూ సరియైనవి. కానీ A కు R సరైన వివరణ కాదు.
c) A సరియైనది. కానీ R సరియైనది కాదు.
d) A మరియు R సరైనవి కావు.
e) A సరియైనది కాదు కానీ R సరైనది.
జవాబు:
a) A, R లు రెండూ సరియైనవి. మరియు A కు R సరైన వివరణ.
కారణము :
ఆకాశం నీలిరంగుకు కాంతి పరిక్షేపణమే కారణము. తక్కువ తరంగదైర్ఘ్యం గల కాంతికి, అధిక తరంగదైర్ఘ్యం గల కాంతితో పోల్చితే పరిక్షేపణ సామర్థ్యం ఎక్కువ.
ప్రశ్న 7.
తరగతి గదిలో ఇంద్రధనుస్సును ఏర్పరిచేందుకు ఒక ప్రయోగాన్ని తెల్పండి. ప్రయోగ విధానాన్ని వివరించండి. (కృత్యం-4)
జవాబు:
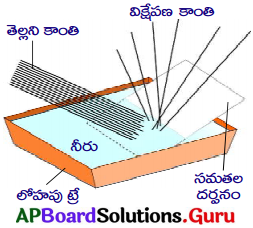
- ఒక లోహపు పళ్ళాన్ని తీసుకొని; నీటితో నింపుము.
- నీటి ఉపరితలంతో కొంతకోణం చేసే విధంగా ఒక సమతల దర్పణమును పటంలో చూపిన విధంగా ఉంచుము.
- పటంలో చూపినట్లుగా నీటి గుండా అద్దం పై తెల్లని కాంతిని ప్రసరింపజేయుము.
- ఈ అమరికకు కొంత ఎత్తులో తెల్లటి కార్డుబోర్డుపై వివిధ రంగులతో ఇంద్రధనుస్సు ఏర్పడుటను గమనించవచ్చును.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 8.
కొన్ని బైనాక్యులర్లందు పట్టకాలను వినియోగిస్తారు. బైనాక్యులర్లలో పట్టకాలు ఎందుకు వినియోగిస్తారో తెలియజేసే – సమాచారాన్ని సేకరించండి.
(లేదా)
పట్టకములకు సంబంధించిన సమాచారాన్ని సేకరించుము. వాటిని బైనాక్యులలో ఎందుకు వాడుతారో వివరింపుము.
జవాబు:
- పరిశీలకునికి దూరపు వస్తువులను పరీక్షించుటకు సమాంతరంగా కదిలే విధంగా రెండు కటకాలను అమర్చుతారు.
- అధిక -పరావర్తనం కోసం బైనాక్యులర్లలో పట్టకాలను ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
- పట్టకాలను ఉపయోగించి బైనాక్యులర్ యొక్క పరిమాణంను తగ్గిస్తారు.
- పట్టకములను ఉపయోగించి వస్తు పరిమాణం మరియు దృక్ తీవ్రతలను పెంచవచ్చును.
- సాధారణంగా బైనాక్యులర్లలో లంబకోణ పట్టకం లేదా ద్విపట్టకాలను ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
- బైనాక్యులలో పట్టకాలను ఉపయోగించి తక్కువ ఖర్చుతోనే వాటి పరావర్తన సామర్థ్యాన్ని 95% వరకు పెంచవచ్చును.
ప్రశ్న 9.
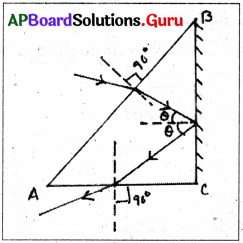
పటంలో పట్టక తలం AB పై పడిన పతన కిరణాన్ని, పట్టక తలం AC నుండి వచ్చే బహిర్గత కిరణాన్ని చూపడం జరిగింది. పటంలో లోపించిన వాటిని గీయండి.
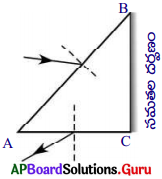
జవాబు:
AB, AC లు వక్రీభవన తలాలు మరియు BC పరావర్తన తలము.
ప్రశ్న 10.
ఆకాశం నీలిరంగులో కనబడడానికి కారణమైన వాతావరణంలోని అణువుల పాత్రను మీరెలా అభినందిస్తారు?
(లేదా)
ఆకాశం నీలి రంగులో కనబడుటకు కారణం ఏమిటి ? ఈ విషయంలో వాతావరణంలోని అణువుల పాత్రను మీరెలా అభినందిస్తారు?
జవాబు:
- ఆకాశం నీలిరంగులో ఉండుటకు ముఖ్యకారణము కాంతి పరిక్షేపణమే.
- వాతావరణంలోని N2, O2 అణువుల పరిమాణం నీలిరంగు కాంతి తరంగదైర్ఘ్యంతో పోల్చదగిన విధముగా ఉంటుంది.
- ఈ అణువులు నీలిరంగు కాంతికి పరిక్షేపణ కేంద్రాలుగా పనిచేస్తాయి.
- వాతావరణంలో నైట్రోజన్, ఆక్సిజన్ అణువుల శాతము ఎక్కువగా ఉండటం వలన, అవి నీలిరంగు కాంతికి పరిక్షేపణ కేంద్రాలుగా పనిచేయడం వలన ఆకాశం నీలిరంగులో కనిపిస్తుంది.
- ఈ విధమైన ఆకాశపు నీలిరంగుకి కారణమైన వాతావరణంలోని N2 మరియు O2ల పాత్రను నేను అభినందించుచున్నాను.
ప్రశ్న 11.
కంటిలోని సిలియరి కండరాల పనితీరును మీరెలా అభినందిస్తారు?
(లేదా)
సిలియరి కండరాల పనితీరు మన కంటికి ఏ విధమైన అవసరమో అభినందించుము.
జవాబు:
కంటిలోని సిలియరి కండరాల పనితీరు కంటిపై ప్రతిబింబంను ఏర్పరుచుటలో ఎంతో అభినందనీయమైనది. ఎందుకనగా
- కంటిలోని కటకానికి ఆనుకొని ఉన్న ఈ కండరాలు కటక వక్రతా వ్యాసార్ధాన్ని మార్చడం ద్వారా కటకం తన నాభ్యంతరమును మార్చుకోవడానికి దోహదపడతాయి.
- దగ్గరలో వున్న వస్తువును కన్ను చూస్తున్నప్పుడు, సిలియరి కండరాలు ఒత్తిడికి గురికావడం వల్ల కంటి కటక నాభ్యంతరం తగ్గుతుంది.
- దూరంలో ఉన్న వస్తువును కన్ను చూస్తున్నప్పుడు, సిలియరి కండరాలు విశ్రాంత స్థితిలో ఉండటం వల్ల కంటి కటక నాభ్యంతరం గరిష్ఠమవుతుంది.
- ఈ విధమైన సర్దుబాటును సిలియరి కండరాలు చేస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 12.
కొన్ని సందర్భాలలో ఆకాశం తెలుపురంగులో కనబడుతుంది. ఎందుకు?
(లేదా)
అప్పుడప్పుడు ఆకాశం తెలుపు రంగులో కనబడుటకు వెనుకన గల కారణాలేమిటో వ్రాయుము.
జవాబు:
- వాతావరణంలో వివిధ పరిమాణాలు గల కణాలుంటాయి.
- ఆ కణాలు వాటి పరిమాణాలకనుగుణంగా వివిధ తరంగదైర్ఘ్యాలు గల కాంతిని పరిక్షేపణం చేస్తాయి.
- వేసవి రోజుల్లో ఉష్ణోగ్రత ఎక్కువగా ఉండడం వల్ల వాతావరణంలోకి నీటి ఆవిరి చేరుతుంది.
- దీని ద్వారా వాతావరణంలో నీటి అణువులు ఇతర పౌనఃపున్యాలు గల కాంతులను పరిక్షేపణం చేస్తాయి.
- N2, O2 ల పరిక్షేపణం వల్ల వచ్చే నీలిరంగు కాంతి, నీటి అణువుల పరిక్షేపణం వల్ల వచ్చే ఇతర రంగుల కాంతులన్నీ కలిసి మన కంటిని చేరినప్పుడు తెలుపురంగు కాంతి కనబడుతుంది.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 13.
తెల్లకాగితానికి నూనె పూస్తే, అది పాక్షిక పారదర్శకంగా పనిచేస్తుంది. ఎందుకు?
(లేదా)
కాగితం (లేదా) న్యూస్ పేపర్ కు నూనెను పూసిన అది పాక్షిక పారదర్శకంగా పని చేయుటకు గల కారణాలను వ్రాయుము.
జవాబు:
- తెల్లని కాగితం కాంతినిరోధములా ప్రవర్తించును.
- తెల్లని కాగితానికి నూనె పూస్తే అది పాక్షిక పారదర్శక పదార్థంగా పనిచేయును.
- కాగితము మరియు నూనెల వక్రీభవన గుణకాలు సమానమైతే, దానిమీద పడిన కాంతి సమాన వక్రీభవన గుణకాల వలన కాగితం నుండి నూనెలోనికి ప్రవేశించునపుడు ఎటువంటి పరిక్షేపణం చెందకుండా ప్రయాణించును.
- ఈ కారణం చేత నూనె పూసిన కాగితము పాక్షిక పారదర్శకముగా పనిచేయును.
ప్రశ్న 14.
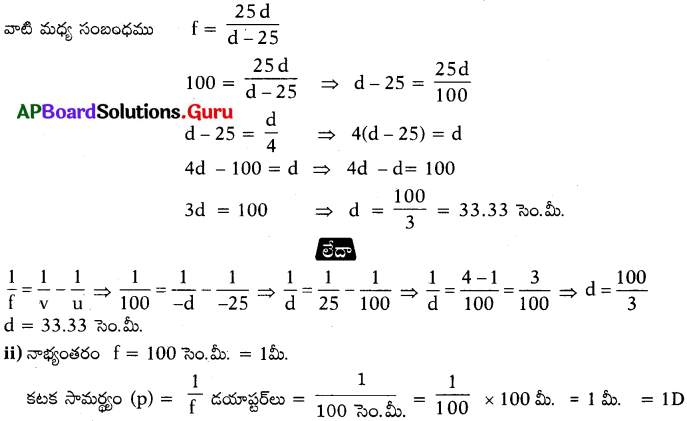
“దీర్ఘదృష్టి” గల ఒక వ్యక్తికి 100 సెం.మీ. నాభ్యంతరం గల కటకాన్ని వాడమని డాక్టర్ సలహా ఇచ్చారు. కనిష్ఠ దూరబిందువు యొక్క దూరాన్ని, కటక సామర్థ్యాన్ని కనుగొనండి. (జవాబు : 33.33 సెం.మీ., 1D)
జవాబు:
వస్తు దూరము u =- 25 సెం.మీ. –
ప్రతిబింబదూరం V = కనిష్ఠ దూరము = -d
నాభ్యంతరము f = 100 సెం.మీ.
కనిష్ఠ దూరము ‘d’ మరియు నాభ్యంతరం ‘f అయిన
ప్రశ్న 15.
ఒక వ్యక్తి దూరంలో ఉన్న వస్తువును చూస్తున్నాడు. అతని కంటిముందు కేంద్రీకరణ కటకాన్ని ఉంచితే, అతనికి వస్తువు పెద్దదిగా కనబడుతుందా? కారణాన్ని తెల్పండి.
(లేదా)
రావు, అతనికి దూరంగా గల వస్తువును చూస్తున్నప్పుడు అతని స్నేహితుడు శ్రీను ఒక కుంభాకార కటకంను అతని కంటి ముందు ఉంచిన అది అతనికి వస్తువును పెద్దదిగా కనబడేటట్లు చేస్తుందా? దీనికి గల కారణాలను వ్రాయుము.
జవాబు:
- ఒక వ్యక్తి దూరంలో వున్న వస్తువును చూస్తున్నప్పుడు, అతని కంటి ముందు కేంద్రీకరణ కటకాన్ని ఉంచిన, వస్తు ప్రతిబింబం మసకబారుతుంది.
- కేంద్రీకరణ (లేక) కుంభాకార కటకపు ప్రతిబింబ విషయం వస్తు స్థానంపై ఆధారపడును.
- దూరంగా ఉన్నటువంటి వస్తువులను చూస్తున్నపుడు కుంభాకార కటకం వలన అవి మసకగా కనిపిస్తాయి.
- ఒకవేళ వస్తువును కుంభాకార కటకపు విషయంలో కటకనాభి, కటక కేంద్రముల మధ్య ఉంచినపుడు నిటారైన, వృద్ధీకరణ చెందిన ప్రతిబింబం ఏర్పడును.
ప్రశ్న 16.
కృత్రిమ ఇంద్రధనుస్సును పొందే విధానాన్ని రెండు కృత్యాల ద్వారా వివరించండి. (AS1)
(లేదా)
మీ ఉపాధ్యాయుడు నిన్ను ఒక ఇంద్రధనుస్సును ఏర్పరచమన్న నీవు ఏ విధంగా ఏర్పరచెదవో ఒక కృత్యంను వ్రాయుము. (కృత్యం : 1)
జవాబు:
- తెల్లని గోడకు దగ్గరగా ఒక టేబుల్ ను ఉంచుము.
- ఒక కార్డ్ బోర్డు షీట్ కు మధ్యలో సన్నని రంధ్రం చేసి, దానిని టేబుల్ పై నిలువుగా అమర్చుము.
- కార్డ్ బోర్డుకు, గోడకు మధ్యలో ఒక పట్టకాన్ని ఉంచుము.
- తెలుపురంగు కాంతినిచ్చే కాంతి జనకాన్ని కార్డ్ బోర్డ్ కు దగ్గరగా ఉంచి, దాని రంధ్రం గుండా కాంతిని ప్రసరింపజేయుము.
- ఈ కాంతి సన్నని పుంజంగా ఉంటుంది. దీనిని పట్టకం యొక్క ఏదో ఒక దీర్ఘచతురస్రాకార తలంపై పడే విధముగా పట్టుకొని పట్టకాన్ని త్రిప్పుతూ ఉంటే, గోడపై ఇంద్రధనుస్సు ఏర్పడుతుంది.
కృత్యం : 2
జవాబు:
7వ ప్రశ్న జవాబు చూడుము.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 17.
పట్టక వక్రీభవన గుణక సూత్రాన్ని ఉత్పాదించండి. (AS1)
(లేదా)
పట్టకపు వక్రీభవన గుణకంను కనుగొను సూత్రంను వ్రాసి, రాబట్టుము.
జవాబు:
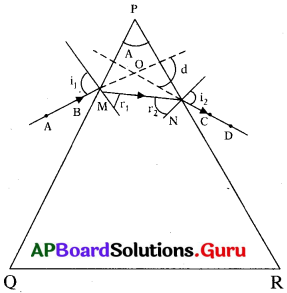
1) పటంలో PQR అను పట్టకం యొక్క పట్టక కోణము ‘A’, పట్టక పదార్థపు వక్రీభవన గుణకము ‘n’, PQ, PRలు వక్రీభవన తలాలు.
2) AB పతన కిరణము, CD బహిర్గామి కిరణము పతన కోణము i1 బహిర్గామి కోణం i2 అనుకొనుము.
3) త్రిభుజము OMN నుండి,
d= i1 – r1 + i2 – r2
∴ d = (i1 + i2) – (r1 + r2) ………. (1)
4) త్రిభుజము PMN నుండి,
A + (90° = r1) + (90° – r2) = 180°
r1 + r2 = A ……………… (2)
5) (1), (2) సమీకరణాల నుండి
=d = (i1 + i2) – A
= A+ d = i1 + i2 ……………………… (3)
6) పతన కోణం, బహిర్గత కోణం, విచలన కోణము మరియు పట్టక కోణాల మధ్య సంబంధమును సమీకరణం- (3) తెలియజేస్తుంది.
7) స్నెల్ నియమం n1 sin i = n2 sin r కనుక, M బిందువు వద్ద, గాలి వక్రీభవన గుణకము n1 = 1, పట్టక వక్రీభవన గుణకము n2 = n, పతన కోణము i = i1, వక్రీభవన కోణం r = r1 లను స్నెల్ నియమంలో ప్రతిక్షేపించగా
sin i1 = n sin r1 ………. (4)
8) అదే విధముగా N బిందువు వద్ద, పట్టక వక్రీభవన గుణకము n1 = n, గాలి వక్రీభవన గుణకము n2 = 1, పతన కోణం i = r2, వక్రీభవన కోణం r= i2, స్నెల్ నియమంలో ప్రతిక్షేపించగా
n sin r2 = sin i2 ………. (5)
9) కనిష్ఠ విచలన కోణం (D) వద్ద పతన కోణం, బహిర్గామి కోణాల విలువలు సమానం. అనగా i1 = i2
10) సమీకరణం (3) నుండి కనిష్ఠ విచలన కోణంకు A + D = i + i
⇒ A + D = 2i1
∴ \(\mathrm{i}_{1}=\frac{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{D}}{2}\)
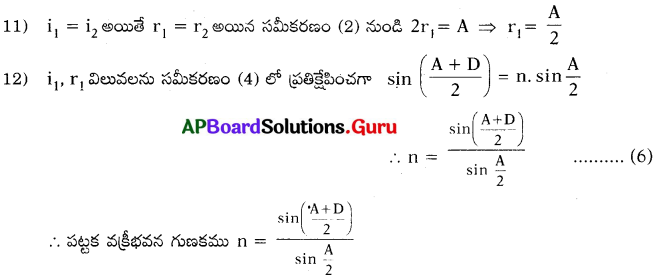
ప్రశ్న 18.
λ1 తరంగదైర్ఘ్యం గల కాంతి n1 వక్రీభవన గుణకం గల యానకం నుండి n2 వక్రీభవన గుణకం గల యానకంలోకి ప్రవేశించింది. రెండవ యానకంలో ఆ కాంతి తరంగదైర్ఘ్యం ఎంత? (AS1)
జవాబు:
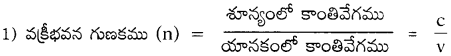
2) రెండు యానకాలలో తరంగదైర్ఘ్యాలు వరుసగా λ1 మరియు λ2 అనుకొనుము.
3) రెండు యానకాల వక్రీభవన గుణకాలు వరుసగా n1 మరియు n2 అనుకొనుము.
4) ఒక యానకపు వేగము (v), తరంగదైర్ఘ్యం (λ) మరియు పౌనఃపున్యాల (υ) మధ్య సంబంధము v = υλ.
5) కాంతి ఒక యానకం నుండి వేరొక యానకంలోకి ప్రవేశించినపుడు, దాని పౌనఃపున్యంలో మార్పు ఉండదు.
6) కావున v1 = υλ1 మరియు v2 = υλ2 అగును.

ప్రశ్న 19.
అంశం (A) : పట్టక వక్రీభవన గుణకం, ఆ పట్టక తయారీకి వాడిన గాజురకంపై మరియు కాంతి రంగుపై మాత్రమే ఆధారపడుతుంది. (AS2)
కారణం (R) : పట్టక వక్రీభవన గుణకం, పట్టక వక్రీభవన కోణంపై మరియు కనిష్ఠ విచలన కోణంపై ఆధారపడుతుంది.
a) A, R రెండూ సరియైనవి. మరియు A కు R సరైన వివరణ.
b) A, R రెండూ సరియైనవి. కానీ Aకు R సరైన వివరణ కాదు.
c) A సరియైనది. కానీ R సరియైనది కాదు.
d) A మరియు R సరైనవి కావు.
e) A సరియైనది కాదు కానీ R సరైనది.
జవాబు:
b) ‘A, R’ లు రెండూ సరియైనవే, కాని A కు R సరైన వివరణ కాదు.
కారణము :
పట్టక వక్రీభవన సూత్రము ప్రకారం వక్రీభవన గుణకము, పట్టకం తయారీకి వాడిన గాజురకంపై మరియు కాంతి రంగుపై ఆధారపడుతుంది.
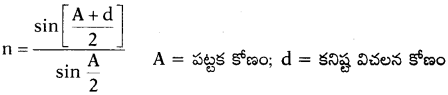
![]()
ప్రశ్న 20.
మన చుట్టూ ఉన్న రంగుల ప్రపంచాన్ని మనం చూడడానికి ఉపయోగపడేది కన్ను. కంటి కటకానికి గల సర్దుబాటు లక్షణం వల్ల ఇది సాధ్యమవుతుంది. ఈ విషయంపై మీ స్పందనను తెలియజేసే విధంగా ఆరు వాక్యాల పద్యాన్ని రాయండి. (AS6)
జవాబు:
ఇంద్రియాలన్నింటిలో కన్నే మిన్నరా
అది లేకపోతే బ్రతుకే సున్నరా
సృష్టిని చూడగల్గడమే మహాభాగ్యంరా
దృష్టిని కల్గి ఉండడమే గొప్ప అదృష్టంరా
మన్నువంటి ఆధారం లేదురా
కన్నువంటి ప్రకాశం లేదురా
‘A’ విటమిన్ లోపిస్తే అంధత్వమేరా
అంధులైతే జీవితమే వృధారా
అందుకే కంటిని జాగ్రత్తగా కాపాడుకోవాలిరా.
ప్రశ్న 21.
గాజు పారదర్శక పదార్థం. ఒక తలం గరుకుగా చేయబడిన గాజు పాక్షిక పారదర్శకంగానూ, తెలుపురంగులోనూ కనబడుతుంది. ఎందుకు?
(లేదా)
సమరీతి, నునుపైన గాజు పారదర్శక పదార్థంగానూ, గరుకు చేయబడిన గాజు పాక్షిక పారదర్శకంగానూ, తెలుపు రంగులో కనబడుటకు గల కారణాలను వ్రాయుము.
జవాబు:
- గాజు ఒక పారదర్శక పదార్థం. ఇది తన గుండా కాంతిని ప్రసారం చేయును.
- గాజును ఒక తలం గరుకుగా చేయడం వల్ల ఆ ఉపరితలంలో అనేక ఎత్తు పల్లాలు అనగా అసమతలం ఏర్పడుతుంది.
- ఇటువంటి అసమతలం క్రమరహిత పరావర్తనమును ఏర్పరుస్తుంది.
- దీనివల్ల కొంతి ప్రసారం జరుగదు.
- దీని ప్రభావం వలన గాజు పాక్షిక పారదర్శకముగా పని చేస్తుంది.
- అందుకనే గరుకుతలం తెలుపురంగులో కనబడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 22.
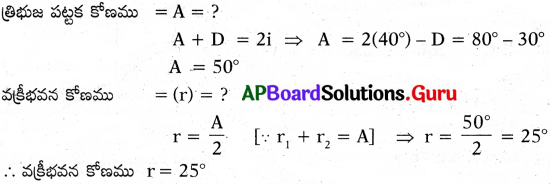
పట్టకం యొక్క ఒక తలంపై 40° కోణంతో పతనమైన కాంతి కిరణం, 30° కనిష్ఠ విచలనాన్ని పొందింది. అయిన పట్టక కోణాన్ని, ఇచ్చిన తలం వద్ద వక్రీభవన కోణాన్ని కనుగొనండి. (జవాబు : 50°, 25°) (AS7)
జవాబు:
పట్టకపు తలంపై పతనమయ్యే కాంతి పతన కోణము = i = 40°
కనిష్ఠ విచలన కోణము = D = 30°
ఖాళీలను పూరించండి
1. స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనిష్ఠ దూరం విలువ …………. (25 సెం.మీ.)
2. రెటీనా, కంటి కటకాల మధ్య దూరం ………….. (2.5 సెం.మీ.)
3. కంటి కటకం యొక్క గరిష్ఠ నాభ్యంతరం విలువ …………… (2.5 సెం.మీ.)
4. మానవుని కంటి యొక్క నాభ్యంతరం మారటానికి దోహదపడే కండరాలు ………………. (సిలియరి)
5. కటకం యొక్క సామర్థ్యం 1D అయిన, ఆ కటక నాభ్యంతరం …………….. (100 సెం.మీ.)
6. హ్రస్వ దృష్టిని నివారించేందుకు ………………….. కటకాన్ని వాడుతారు. (పుటాకార)
7. దీర్ఘదృష్టిని నివారించేందుకు ……………… కటకాన్ని వాడుతారు. (కుంభాకార)
8. పట్టకం కనిష్ఠ విచలన స్థానంలో ఉన్నప్పుడు పతన కోణం ………………….. కు సమానం. (బహిర్గామికోణం)
9. తెల్లని కాంతి వివిధ రంగులుగా (VIBGYOR) విడిపోవడాన్ని ………………… అంటాం. (కాంతి విక్షేపణం)
10. వక్రీభవనం జరిగినప్పుడు కాంతి ………………….. లో మార్పు రాదు. (పౌనఃపున్యం)
సరైన సమాధానాన్ని ఎన్నుకోండి
1. మానవుని కన్ను గ్రహించే వస్తు పరిమాణం ప్రాథమికంగా …. పై ఆధారపడుతుంది.
A) వస్తువు నిజ పరిమాణం
B) కన్ను నుండి వస్తువుకు గల దూరం
C) నల్లగుడ్డు రంధ్రం
D) రెటీనాపై ఏర్పడ్డ ప్రతిబింబ పరిమాణం
జవాబు:
B) కన్ను నుండి వస్తువుకు గల దూరం
2. వివిధ దూరాలలో గల వస్తువులను చూస్తున్నప్పుడు కింది వాటిలో ఏది స్థిరంగా ఉంటుంది?
A) కంటి కటక నాభ్యంతరం
B) కంటి కటకం నుండి వస్తువుకి గల దూరం
C) కంటి కటక వక్రతా వ్యాసార్ధం
D) కంటి కటకం నుండి ప్రతిబింబ దూరం
జవాబు:
D) కంటి కటకం నుండి ప్రతిబింబ దూరం
3. కింది వాటిలో వక్రీభవన సమయంలో మారని విలువ
A) తరంగదైర్ఘ్యం
B) పౌనఃపున్యం
C) కాంతివేగం
D) పైవన్నీ
జవాబు:
B) పౌనఃపున్యం
4. పటంలో చూపిన విధంగా టేబుల్ పై ఉంచిన ఒక సమద్విబాహు పట్టకంపై కాంతి పతనమైంది. కనిష్ఠ విచలనానికి సంబంధించి కింది వాటిలో ఏది సరియైనది?
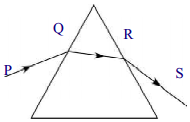
A) ఆధారానికి సమాంతరరేఖ PQ
B) ఆధారానికి సమాంతరరేఖ QR
C) ఆధారానికి సమాంతరరేఖ RS
D) ఆధారానికి సమాంతర రేఖ PQ లేదా RS
జవాబు:
B) ఆధారానికి సమాంతరరేఖ QR
![]()
5. హ్రస్వదృష్టితో బాధపడే వ్యక్తి యొక్క గరిష్ఠ దూరం 5 మీ. దీనిని నివారించి సాధారణ దృష్టి వచ్చేట్లు చేయాలంటే …. ను వినియోగించాలి.
A) 5 మీ. నాభ్యంతరం గల పుటాకార కటకం
B) 10 మీ. నాభ్యంతరం గల పుటాకార కటకం
C) 5 మీ. నాభ్యంతరం గల కుంభాకార కటకం
D) 2.5 మీ. నాభ్యంతరం గల కుంభాకార కటకం
జవాబు:
A) 5 మీ. నాభ్యంతరం గల పుటాకార కటకం
6. సూర్యకాంతిని శోషించుకున్న అణువు వివిధ కాంతి తీవ్రతలతో అన్ని దిశలలోనూ కాంతిని విడుదల చేయడాన్ని …….. అంటాం.
A) కాంతి పరిక్షేపణం
B) కాంతి విక్షేపణం
C) కాంతి పరావర్తనం
D) కాంతి వక్రీభవనం
జవాబు:
A) కాంతి పరిక్షేపణం
10th Class Physical Science 5th Lesson మానవుని కన్ను-రంగుల ప్రపంచం Textbook InText Questions and Answers
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 90
ప్రశ్న 1.
విమానంలో ప్రయాణించే వ్యక్తికి ఇంద్రధనుస్సు ఏ ఆకారంలో కనిపిస్తుందో ఊహించగలరా? మీ స్నేహితులతో చర్చించండి. సమాచారాన్ని సేకరించండి.
జవాబు:
విమానంలో ప్రయాణించే వ్యక్తికి ఇంద్రధనుస్సు పూర్తిగా వృత్తాకారంలో కన్పించును.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 90
ప్రశ్న 2.
మన కంటిముందున్న అన్ని వస్తువులనూ మనం స్పష్టంగా చూడగలమా?
జవాబు:
మన కంటి ముందు 25 సెం.మీ. దూరానికి అవతల ఉన్న అన్ని వస్తువులను మనం స్పష్టంగా చూడగలం.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 91
ప్రశ్న 3.
స్పష్ట దృష్టి యొక్క సరాసరి దూరం విలువ ఎంత?
జవాబు:
స్పష్ట దృష్టి యొక్క కనీస దూరం 25 సెం.మీ.
ప్రశ్న 4.
మీ కంటికి 25 సెం.మీ. దూరంలో ఉంచిన వస్తువు ఆకారం ఎలా ఉన్నా, దానిని పై నుండి కింది వరకు మీరు చూడగలరా?
జవాబు:
చూడలేము. ఎందుకనగా స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనీస దూరం విలువ వయస్సుపై ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది. అదే విధంగా కంటి వద్ద 60° కోణంతో కనబడే వస్తుభాగం మాత్రమే మనం చూడగలం.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 92
ప్రశ్న 5.
స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనీస దూరం, దృష్టికోణం విలువలు వ్యక్తినిబట్టి, వయసునుబట్టి ఎందుకు మారతాయి?
జవాబు:
ఈ విలువలన్నీ కంటి నిర్మాణం మరియు సిలియరి కండరాల పనితీరుపై ఆధారపడి ఉంటాయి కాబట్టి.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 93
ప్రశ్న 6.
వివిధ వస్తుదూరాలకు ఒకే ప్రతిబింబదూరం ఉండడం ఎలా సాధ్యం?
జవాబు:
కటకనాభ్యంతరం విలువను మారుస్తూ ఉంటే వివిధ వస్తు దూరాలకు ఒకే ప్రతిబింబ దూరం ఉండటం సాధ్యపడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 7.
కటకాల గుండా వక్రీభవనం గురించి మీకున్న అవగాహనతో పై ప్రశ్నకు సమాధానం చెప్పగలరా?
జవాబు:
చెప్పగలము. వస్తుదూరం మారినప్పుడు ప్రతిబింబ దూరం స్థిరంగా ఉండాలంటే కటక నాభ్యాంతరం మారాలి.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 94
ప్రశ్న 8.
కన్ను తన నాభ్యంతరాన్ని ఎలా మార్చుకుంటుంది? కనుగుడ్డులో ఈ మార్పు ఎలా జరుగుతుంది?
జవాబు:
కనుగుడ్డులోని కటకానికి ఆనుకుని ఉన్న సిలియరి కండరాలు కటక వక్రతా వ్యాసార్థాన్ని మారుస్తాయి. ఈ మార్పు ద్వారా కన్ను తన నాభ్యంతరాన్ని మార్చుకుంటుంది.
ప్రశ్న 9.
కంటి కటకం నిజ ప్రతిబింబాన్ని ఏర్పరుస్తుందా? మిథ్యా ప్రతిబింబాన్ని ఏర్పరుస్తుందా?
జవాబు:
కంటి కటకం వస్తువు నిజ ప్రతిబింబాన్ని రెటీనా పై తలక్రిందులుగా ఏర్పరుస్తుంది.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 10.
కంటి కటక నాభ్యంతరం మార్పుకు ఏదైనా హద్దు ఉందా?
జవాబు:
అవును. కటక నాభ్యంతరానికి గరిష్ఠ, కనిష్ఠ విలువలుంటాయి.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 95
ప్రశ్న 11.
కంటి కటకం తన నాభ్యంతరాన్ని మార్చుకోలేకపోతే ఏం జరుగుతుంది?
జవాబు:
కంటి కటకం తన నాభ్యంతరాన్ని మార్చుకోలేకపోతే వస్తువును సులభంగా, స్పష్టంగా చూడలేము.
ప్రశ్న 12.
కంటి కటక నాభ్యంతరం 2.27 – 2.5 సెం.మీ.లకు మధ్యస్థంగా లేకపోతే ఏమవుతుంది?
జవాబు:
కంటి కటక నాభ్యంతరం 2.27 – 2.5 సెం.మీ. లకు మధ్యస్థంగా లేకపోతే కంటి దోషాలు ఏర్పడతాయి.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 97
ప్రశ్న 13.
‘కంటి కటక కనిష్ఠ నాభ్యంతరం 2.27 సెం.మీ. కంటే ఎక్కువైతే ఏం జరుగుతుంది?
జవాబు:
- కంటి కటక కనిష్ఠ నాభ్యంతరం 2.27 సెం.మీ. కంటే ఎక్కువైతే దీర్ఘదృష్టి ఏర్పడుతుంది.
- అంటే ఆ వ్యక్తి దూరంలో ఉన్న వస్తువులను స్పష్టంగా చూడగలదు కాని దగ్గరి వస్తువులను చూడలేదు.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 98
ప్రశ్న 14.
దీర్ఘదృష్టిని సవరించడానికి ఏం చేయాలి?
జవాబు:
దీర్ఘదృష్టి సవరణ :
- వస్తువు కనిష్ఠదూర బిందువుకు ఆవల ఉంటే, కంటికటకం రెటీనా పై ప్రతిబింబాన్ని ఏర్పరచగలదు.
- కనుక కనిష్ఠదూర బిందువు (H) కు స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనీస దూరాన్ని తెలిపే బిందువు (L) కు మధ్యనున్న వస్తువు యొక్క ప్రతిబింబాన్ని కనిష్ఠదూర బిందువుకు ఆవల ఏర్పరచగలిగే కటకాన్ని అంటే ద్వికుంభాకార కటకాన్ని ఉపయోగించాలి.
- ద్వికుంభాకార కటకాన్ని వాడటం వల్ల ఇది సాధ్యపడుతుంది.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 99
ప్రశ్న 15.
కంటి డాక్టర్ రాసే ప్రిస్క్రిప్షన్ లోని వివరాలను మీరెప్పుడైనా పరిశీలించారా?
జవాబు:
కంటి డాక్టర్ రాసే ప్రిస్క్రిప్షన్లోని వివరాలను పరిశీలించాను. అవి +, – గుర్తులతో సూచింపబడి ఉంటాయి.
ప్రశ్న 16.
సైట్ పెరగడం లేదా తగ్గడం అంటే ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
కంటి చూపులోని పెరుగుదల లేదా తగ్గుదల.
ప్రశ్న 17.
కటక సామర్థ్యం అంటే ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
కటక సామర్థ్యం :
ఒక కటకం కాంతికిరణాలను కేంద్రీకరించే స్థాయి లేదా వికేంద్రీకరించే స్థాయిని కటక సామర్థ్యం అంటాం. (లేదా) కటక నాభ్యంతరం యొక్క విలోమ విలువను కటక సామర్థ్యం అంటాం.
ఒక కటక నాభ్యంతరం గ అనుకుంటే,
కటక సామర్థ్యం P = 1/f (మీటర్లలో) ; P = 100/f (సెం.మీ.లలో)
కటక సామర్థ్యానికి ప్రమాణం డయాప్టర్ (Dioptre). దీనిని D తో సూచిస్తాం.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 100
ప్రశ్న 18.
పట్టకం అంటే ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
ఒకదానికొకటి కొంత కోణం చేసే కనీసం రెండు సమతలాలతో పరిసరయానకం నుండి వేరుచేయబడి ఉన్న పారదర్శక యానకాన్ని “పట్టకం” అంటారు.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 105
ప్రశ్న 19.
తెల్లని కాంతి రంగులుగా విడిపోవడాన్ని కిరణ సిద్ధాంతంతో వివరించగలమా?
జవాబు:
తెల్లని కాంతి రంగులుగా విడిపోవడాన్ని కిరణ సిద్ధాంతంతో వివరించలేము.
ప్రశ్న 20.
వివిధ రంగులు గల కొంతుల వేగాలు వేర్వేరుగా ఉంటాయా?
జవాబు:
శూన్యంలో వివిధ రంగులు గల కాంతుల వేగాలు స్థిరంగా ఉంటాయి. యానకంలో వివిధ రంగులు గల కాంతుల వేగాలు వేర్వేరుగా ఉంటాయి.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 21.
పట్టకం గుండా తెలుపురంగు కాంతిని పంపితే అది వివిధ రంగులుగా ఎందుకు విడిపోతుందో ఇప్పుడు మీరు ఊహించగలరా?
జవాబు:
శూన్యంలో అన్ని రంగుల కాంతి వేగాలు ఒకటే అయినప్పటికీ, ఒక యానకంలో ప్రయాణించేటప్పుడు కాంతివేగం దాని తరంగదైర్యంపై ఆధారపడును. అందువల్ల కాంతి వివిధ రంగులుగా విడిపోతుంది.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 106
ప్రశ్న 22.
పట్టకం గుండా తెలుపురంగు కాంతిని పంపితే అది వివిధ రంగులుగా ఎందుకు విడిపోతుందో ఇప్పుడు మీరు ఊహించగలరా?
జవాబు:
యానకంలో ప్రయాణించేటప్పుడు కాంతి వేగం దాని తరంగదైర్ఘ్యంపై ఆధారపడుతుంది. అందువల్ల కాంతి వివిధ రంగులుగా విడిపోతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 23.
కృత్యం – 3లో చూసినట్లు ప్రకృతిలో మీరు రంగులు చూడగలిగే సందర్భానికి ఒక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వగలరా?
జవాబు:
ప్రకృతిలో రంగులు చూడగలిగే సందర్భం ఇంద్రధనుస్సు.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 108
ప్రశ్న 24.
ఆకాశం నీలిరంగులో ఎందుకు కనిపిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
వాతావరణంలోని N2, O2 అణువులు సూర్యుని కాంతిలోని నీలం రంగు కాంతిని పరిక్షేపణం చెందించడం వల్ల ఆకాశం నీలి రంగులో కనిపిస్తుంది.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 109
ప్రశ్న 25.
పరిక్షేపణం అంటే ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
ఒక కణం శోషించుకున్న కాంతిని తిరిగి అన్ని దిశలలో వివిధ తీవ్రతలతో విడుదల చేయడాన్ని “కాంతి పరిక్షేపణం” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 26.
స్వేచ్ఛా పరమాణువు లేదా అణువుపై నిర్దిష్ట పౌనఃపున్యం గల కాంతి పతనం చెందితే ఏం జరుగును?
జవాబు:
పరమాణువులు లేదా అణువులపై కాంతి పతనం చెందినపుడు అవి కాంతి శక్తిని శోషించుకుని, అందులో కొంత భాగాన్ని వివిధ దిశల్లో ఉద్గారం చేస్తాయి. ఇదే కాంతి పరిక్షేపణంలోని ప్రాథమిక నియమము.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 94
ప్రశ్న 27.
వస్తువు ఆకారం, పరిమాణం మరియు రంగులలో ఏ మార్పు లేకుండా వస్తువును మనం గుర్తించే విధంగా రెటీనాపై ప్రతిబింబం ఎలా ఏర్పడుతుంది?
జవాబు:
- రెటీనా అనేది ఒక సున్నితమైన పొర.
- దీనిలో దండాలు (rods) మరియు శంఖువులు (cones) అనబడే దాదాపు 125 మిలియన్ల గ్రాహకాలు (receptors) ఉంటాయి.
- ఇవి కాంతి సంకేతాలను (signals) గ్రహిస్తాయి. శంఖువులు రంగును గుర్తిస్తాయి. దండాలు కాంతి తీవ్రతను గుర్తిస్తాయి.
- ఈ సంకేతాలు దాదాపు 1 మిలియన్ దృక్ నాడుల (optic – nerve fibres) ద్వారా మెదడుకు చేరవేయబడతాయి.
- వాటిలోని సమాచారాన్ని మెదడు విశ్లేషించడం ద్వారా వస్తువు ఆకారం, పరిమాణం మరియు రంగులను మనం గుర్తిస్తాం.
ప్రశ్న 28.
కంటి కటకం యొక్క కనిష్ఠ, గరిష్ఠ నాభ్యంతరాలు ఎంత? వాటిని మనం ఎలా కనుగొంటాము?
జవాబు:
గరిష్ఠ నాభ్యంతరం
- పటంలో చూపినట్లు అనంతదూరంలో ఉన్న వస్తువు నుండి వచ్చే
సమాంతర కాంతి కిరణాలు కంటి కటకంపై పడి వక్రీభవనం చెందాక
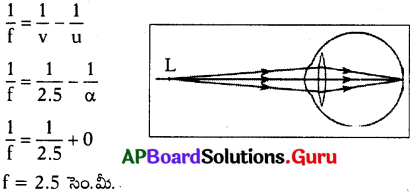
రెటీనా పై ఒక బిందురూప ప్రతిబింబాన్ని ఏర్పరుస్తాయి. - ఈ సందర్భంలో కంటి కటక నాభ్యంతరం గరిష్టంగా ఉంటుంది.
- దీని విలువ fగరిష్ఠ = 2.5 సెం.మీ. ఉండును.
కనుగొనే విధానం :
వస్తుదూరం = µ = α
ప్రతిబింబ దూరం = v = 2.5 సెం.మీ (కంటికటకం నుండి రెటీనాకు దూరం)
నాభ్యంతరం = f = ?
కనిష్ఠ నాభ్యంతరము :
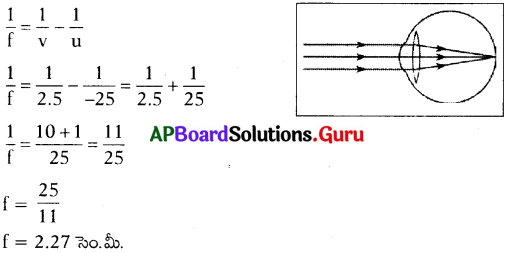
- పటంలో చూపినట్లు కంటి ముందు 25 సెం.మీ. దూరంలో వస్తువు ఉందనుకొనుము.
- ఈ సందర్భంలో కంటి కటక నాభ్యంతరం కనిష్ఠంగా ఉంటుంది.
- దీని విలువ fకనిష్ఠ = 2.27 సెం.మీలుగా ఉండును.
కనుగొనే విధానం :
వస్తు దూరం = u = 25 సెం.మీ.
ప్రతిబింబ దూరం = v = 25 సెం.మీ. (కంటి కటకం నుండి రెటీనాకు గల దూరం)
నాభ్యంతరం = f = ?
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 96
ప్రశ్న 29.
హ్రస్వదృష్టిని సవరించడానికి ఏం చేయాలి?
జవాబు:
హ్రస్వదృష్టికి సవరణ :
- గరిష్ఠదూర బిందువుకు, స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనీస దూరాన్ని తెలిపే బిందువుకు మధ్య వస్తువు ఉన్నప్పుడు కంటికటకం రెటీనా పై ప్రతిబింబాన్ని ఏర్పరచగలదు.
- కాబట్టి ఒక కటకాన్ని ఉపయోగించి గరిష్ఠ దూర బిందువుకు ఆవల ఉన్న వస్తువు యొక్క ప్రతిబింబాన్ని గరిష్ఠ దూరబిందువు (M) మరియు స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనీస దూరాన్ని తెలిపే బిందువు (L) ల మధ్యకు తేగలిగితే, ఆ ప్రతిబింబం కంటి కటకానికి వస్తువులా పనిచేస్తుంది.
- పుటాకార కటకాన్ని వాడడం వల్ల ఇది సాధ్యపడుతుంది.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 97
ప్రశ్న 30.
హ్రస్వదృష్టిని నివారించడానికి వాడవలసిన పుటాకార కటక నాభ్యంతరం ఎంత ఉండాలనేది ఎలా నిర్ణయిస్తాం?
జవాబు:
- హ్రస్వదృష్టిని నివారించడానికి, అనంతదూరంలో ఉండే వస్తువు యొక్క ప్రతిబింబాన్ని గరిష్ఠ దూరబిందువు వద్ద ఏర్పరచగలిగే కటకాన్ని అంటే ద్విపుటాకార కటకాన్ని ఎంచుకోవాలి.
- ఈ కటకం ఏర్పరచే ప్రతిబింబం కంటి కటకానికి వస్తువులా పనిచేసి చివరగా ప్రతిబింబం రెటీనాపై ఏర్పడుతుంది.
- ఈ సందర్భంలో వస్తుదూరం (u) అనంతం. ప్రతిబింబదూరం (v) గరిష్ఠ దూర బిందువుకు గల దూరానికి సమానం. కావున
u = – ∞, v = -D (గరిష్ఠ దూరబిందువుకు, కంటికి గల దూరం) - ద్విపుటాకార కటక నాభ్యంతరం గ అనుకుంటే..
1/f = 1/v – 1/4 సూత్రాన్ని ఉపయోగించినపుడు 1/f = 1/-D ⇒ f = -D - ఇక్కడ f కు ‘ఋణ విలువ’ రావడమనేది పుటాకార కటకాన్ని తెలియజేస్తుంది.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 108
ప్రశ్న 31.
వాననీటి బిందువులతో విక్షేపణం చెందిన కాంతి అర్ధవలయాకారంలో ఎందుకు కన్పిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
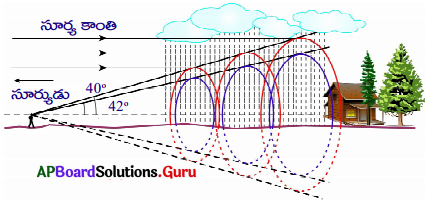
- ఇంద్రధనుస్సు అనునది మనకు కనబడే విధంగా పలుచని ద్విమితీయ చాపం కాదు.
- ఇంద్రధనుస్సు అనేది మీ కంటి వద్ద తన కొనభాగాన్ని కల్గి వున్న త్రిమితీయ శంఖువు.
- పటంలో చూపినట్లు శంఖువు అక్షం వెంబడి మనం భాగం భూమి పైని వాతావరణంలోని కణాల నుండి, శంఖువు కింది సగ భాగం నేలపైని వస్తువుల నుండి వచ్చే కాంతులను మన కంటికి చేరవేస్తున్నాయి.
- కావున గాలిలోని నీటి బిందువుల నుండి వచ్చే కాంతి (శంఖువు పై సగం) మనకు ఇంద్రధనుస్సును అర్ధ చంద్రాకారంలో ఏర్పరుస్తుంది.
- మనం భూమి నుండి నిర్ణీత ఎత్తుకు వెళ్తే ఇంద్ర ధనుస్సును పూర్తి వలయంగా చూడవచ్చు.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 110
ప్రశ్న 32.
వేసవి రోజుల్లో (ఉష్ణోగ్రత ఎక్కువగా ఉన్న రోజుల్లో) ఒక నిర్దిష్ట దిశలో చూస్తున్నపుడు కొన్ని సందర్భాలలో ఆకాశం తెలుపురంగులో కనిపిస్తుంది. ఎందుకు?
జవాబు:
- వాతావరణంలో వివిధ పరిమాణాలు గల కణాలుంటాయి. వాటి పరిమాణాల కనుగుణంగా అవి వివిధ తరంగదైర్యాలు గల కాంతిని పరిక్షేపణం చేస్తాయి.
- ఉదాహరణకు N2, O2 అణువుల కన్నా నీటి అణువు పరిమాణం ఎక్కువ. కాబట్టి అది నీలిరంగుకాంతి కంటే తక్కువ పౌనఃపున్యాలు (ఎక్కువ తరంగదైర్యాల) గల కాంతులకు పరిక్షేపణ కేంద్రంగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
- వేసవి రోజుల్లో ఉష్ణోగ్రత ఎక్కువగా ఉండడం వల్ల వాతావరణంలోకి నీటి ఆవిరి చేరుతుంది.
- తద్వారా వాతావరణంలో నీటి అణువులు అధిక స్థాయిలో ఉంటాయి.
- ఈ నీటి అణువులు ఇతర పౌనఃపున్యాలు (నీలిరంగు కానివి) గల కాంతులను పరిక్షేపణం చేస్తాయి.
- N2, O2, ల పరిక్షేపణం వల్ల వచ్చే నీలిరంగుకాంతి, నీటి అణువుల పరిక్షేపణం వల్ల వచ్చే ఇతర రంగుల కాంతులు అన్నీ కలిసి మన కంటిని చేరినప్పుడు తెలుపు రంగు కాంతి కనబడుతుంది.
![]()
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 111
ప్రశ్న 33.
సూర్యోదయం, సూర్యాస్తమయ సమయాలలో సూర్యుడు ఎర్రగా కనబడడానికి గల కారణం మీకు తెలుసా?
జవాబు:
- సూర్యోదయం, సూర్యాస్తమయ సమయంలో సూర్యుని నుండి వెలువడే కాంతి మీ కంటిని చేరడానికి భూ వాతావరణంలో అధిక దూరం ప్రయాణించాల్సి ఉంటుంది.
- ఎరుపు రంగు కాంతి తప్ప మిగిలిన అన్ని రంగుల కాంతులు అధికంగా పరిక్షేపణం చెంది కాంతి మీ కంటిని చేరే లోపే ఆ రంగులన్నీ కనుమరుగవుతాయి.
- ఎరుపు రంగు కాంతి తక్కువగా పరిక్షేపణం చెందడం వల్ల అది మీ కంటిని చేరును.
- ఫలితంగా సూర్యుడు, సూర్యోదయం మరియు సూర్యాస్తమయ సమయాలలో ఎరుపుగా కన్పిస్తాడు.
ప్రశ్న 34.
మధ్యాహ్న వేళల్లో సూర్యుడు ఎర్రగా ఎందుకు కనబడడో ఊహించగలరా?
జవాబు:
- ఉదయం, సాయంత్రం వేళల కంటే మధ్యాహ్నం సమయంలో వాతావరణంలో సూర్యకాంతి ప్రయాణించే దూరం తక్కువ.
- కాబట్టి కాంతి ఎక్కువగా పరిక్షేపణం చెందక పోవడం వల్ల అన్ని రంగులూ మీ కంటిని చేరతాయి.
- కాబట్టి మధ్యాహ్న వేళల్లో సూర్యుడు తెల్లగా కనబడతాడు.
10th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 98
ప్రశ్న 35.
దీర్ఘదృష్టిని నివారించడానికి వాడవలసిన కుంభాకార కటక నాభ్యంతరం ఎంత ఉండాలనేది ఎలా నిర్ణయిస్తాం?
జవాబు:
1) కటక నాభ్యంతరాన్ని కనుగొనడానికి, స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనీస దూరాన్ని తెలిపే బిందువు (L) వద్ద ఒక వస్తువు ఉన్నదని ఊహించవలెను.
2) పటంలో చూపినవిధంగా L వద్ద ఉన్న వస్తువు ప్రతిబింబాన్ని కనిష్ఠదూర బిందువు (H) వద్ద ఏర్పరచగలిగే ద్వికుంభాకార కటకాన్ని ఉపయోగిస్తే దృష్టిదోషం సవరించబడుతుంది.
3) ఆ ప్రతిబింబం కంటికటకానికి వస్తువుగా పనిచేస్తుంది.
4) కనుక చివరగా కంటి కటకం వలన ఏర్పడే ప్రతిబింబం రెటీనా పై ఏర్పడుతుంది.
5) ఈ సందర్భంలో, వస్తుదూరం

(u) = -25 సెం.మీ.
ప్రతిబింబం దూరం (v) = – d
(కంటికి, కనిష్ఠ దూరబిందువుకు గల దూరం)
మనం వాడే ద్వికుంభాకార కటక నాభ్యంతరం f అనుకుంటే.
1/f = 1/v – 1/4 సూత్రాన్ని ఉపయోగించినపుడు :
1/f = 1/-d – 1/(-25) ⇒ 1/f = -1/d + 1/25
1/f = (d – 25)/25d ⇒ f = 25d(d – 25)
d > 25 కాబట్టి గ విలువ ధనాత్మకం అవుతుంది. అనగా కుంభాకార కటకం వాడాలని తెలుస్తుంది.
పరికరాల జాబితా
పొడవైన కర్ర లేదా పివిసి పైపు ముక్కలు (20, 30, 35, 40, 50 సెం.మీ.,) అడ్డు కడ్డీ, రిటారు స్టాండు, కంటి నిర్మాణం ప్రదర్శించే నమూనా, డ్రాయింగ్ షీట్, పెన్సిల్, గుండుసూదులు, స్కేలు, కోణమానిని, పట్టకం, చిన్న రంధ్రం కలిగిన కార్డుబోర్డు, తెల్లని కాంతి జనకం (టార్చిలైటు), లోహపు పళ్లెం, అద్దం, నీరు, గాజుబీకరు, సోడియం’
థయో సల్ఫేట్, సల్ఫూరికామ్ల ద్రావణాలు
10th Class Physical Science 5th Lesson మానవుని కన్ను-రంగుల ప్రపంచం Textbook Activities
కృత్యములు
కృత్యం – 1
ప్రశ్న 1.
స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనీస దూరమును కనుగొనుటకు ఒక కృత్యాన్ని వ్రాయుము.
జవాబు:
- ఒక పుస్తకాన్ని తెరచి మీ కంటి ముందు కొంతదూరంలో పట్టుకొని చదవడానికి ప్రయత్నించండి.
- నెమ్మదిగా ఆ పుస్తకాన్ని మీ కంటివైపుగా, కంటికి అతి దగ్గరగా చేరే వరకు కదిలించండి.
- పుస్తకంలోని అక్షరాలు మసకబారినట్లుగా అనిపిస్తాయి లేదా మీ కన్ను ఒత్తిడికి గురైనట్లు అనిపిస్తుంది.
- పుస్తకంలోని అక్షరాలను మీ ‘కన్ను ఏ ఒత్తిడి లేకుండా చూడగలిగే స్థానం వరకు నెమ్మదిగా పుస్తకాన్ని వెనుకకు . జరపండి.
- ఈ సందర్భంలో పుస్తకానికి, మీ కంటికి గల దూరాన్ని కొలిస్తే అది దాదాపు 25 సెం.మీ. ఉంటుంది.
- ఈ దూరం వ్యక్తికి, వ్యక్తికీ వయస్సును బట్టి మారుతుంది.
- మన కంటికి ఏ ఒత్తిడి లేకుండా, స్పష్టంగా ఒక వస్తువును మనము చూడాలంటే ఉండవలసిన కనీస దూరాన్ని “స్పష్ట దృష్టి కనీస దూరం” అంటారు.
కృత్యం – 2
ప్రశ్న 2.
“దృష్టికోణం” ను కనుగొనేందుకు ఒక కృత్యాన్ని తెల్పుము.
జవాబు:
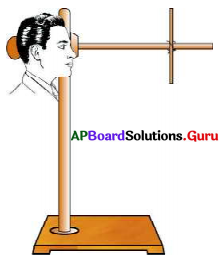
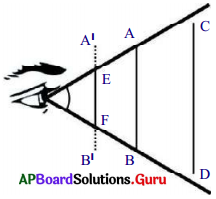
- బట్టలషాప్ లో బట్టల చుట్టలకు వచ్చే కర్రలను లేదా PVC పైపులను సేకరించుము.
- ఈ వస్తువులను 20 సెం.మీ., 30 సెం.మీ., 35 సెం.మీ., 40 సెం.మీ., 50 సెం.మీ. పొడవు గల ముక్కలుగా ఆ కత్తిరించుము.
- ఒక రిటార్ట్ స్టాండును బల్లపై ఉంచి, రిటార్ట్ స్టాండు నిలువు కడ్డీ ప్రక్కన మీ తల ఉండే విధముగా బల్ల దగ్గర నిలబడండి.
- మీ కంటి నుండి 25 సెం.మీ. దూరంలో రిటార్టు స్టాండ్ అడ్డుకడ్డీకి క్లాంప్ ను బిగించి, 30 సెం.మీ. పొడవు గల కర్రను కట్టమని మీ స్నేహితునికి చెప్పుము.
- ఇప్పుడు అడ్డుకడ్డీ వెంబడి మీ దృష్టి సారిస్తూ, కర్రముక్కను పై అంచు నుండి క్రింది అంచు వరకు మొత్తంగా చూడడానికి ప్రయత్నించుము.
- కర్రముక్క 25 సెం.మీ. దూరంలో ఉన్నప్పుడు దాని రెండు చివరలను మీరు స్పష్టంగా చూడలేకపోతే, అడ్డుకడ్డీ వెంబడి కర్రముక్కను వెనుకకు జరుపుము.
- ఏ కనీస దూరం వద్ద మీరు దానిని పూర్తిగా చూడగలరో అక్కడ దానిని అడ్డుకడ్డీకి ఇంప్ సహాయంతో బిగించండి.
- వస్తువు యొక్క చివరి బిందువుల నుండి వచ్చే కిరణాలు కంటి వద్ద కొంత కోణం చేస్తాయి.
- ఈ కోణం 60° కంటే తక్కువగా ఉంటే ఆ వస్తువును పూర్తిగా మనము చూడగలము.
- ఈ కోణం 60° కంటే ఎక్కువగా ఉంటే ఆ వస్తువులో కొంతభాగం మాత్రమే మనము చూడగలము.
- ఏ గరిష్ఠ కోణము వద్ద మనము పూర్తిగా చూడగలమో, ఆ కోణాన్ని “దృష్టికోణం” అంటారు.
- ఈ విధముగా దృష్టికోణమును కనుగొంటారు.
![]()
కృత్యం – 6
ప్రశ్న 3.
కాంతి పరిక్షేపణాన్ని ప్రయోగ పూర్వకముగా వ్రాయుము.
జవాబు:
- ఒక బీకరులో సోడియం థయోసల్ఫేట్ (హైపో) మరియు సల్ఫ్యూరిక్ ఆమ్లాల ద్రావణాన్ని తీసుకొనుము.
- ఈ గాజు బీకరును ఆరుబయట సూర్యుని వెలుగులో ఉంచుము.
- బీకరులో సల్ఫర్ స్పటికాలు ఏర్పడటాన్ని గమనించుము.
- రసాయన చర్య జరుగుతున్న కొలదీ సల్ఫర్ అవక్షేపం (precipitation) ఏర్పడటం గమనించవచ్చును.
- ప్రారంభంలో సల్ఫర్ స్పటికాలు చాలా చిన్నవిగానూ చర్య జరిగే కొలదీ వాటి పరిమాణం పెరుగును.
- మొదట సల్ఫర్ స్పటికాలు నీలిరంగులో ఉం, వాటి పరిమాణం పెరుగుతున్నకొలదీ తెలుపు రంగులోకి మారును. దీనికి కారణం కాంతి పరిక్షేపణము.
- ప్రారంభంలో సల్ఫర్ స్పటికాల పరిమాణం చాలా తక్కువగా ఉండి, అది నీలిరంగు కాంతి తరంగదైర్ఘ్యంతో పోల్చడానికి వీలైనదిగా ఉంటుంది. కావున అపుడు అవి నీలిరంగులో కనబడతాయి.
- సల్పర్ స్పటికాల పరిమాణం పెరుగుతున్న కొలదీ వాటి పరిమాణం ఇతర రంగు కాంతుల తరంగదైర్యాలతో పోల్చడానికి వీలయ్యేదిగా ఉంటుంది.
- అప్పుడు ఆ స్పటికాలు ఇతర రంగుల కాంతులకు పరిక్షేపణ కేంద్రాలుగా పనిచేస్తాయి.
- ఈ అన్ని రంగులూ కలిసి తెలుపు రంగులా కనబడుతుంది.