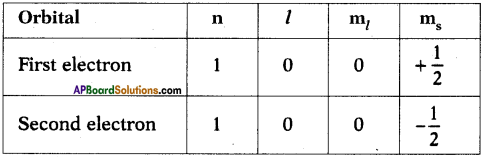
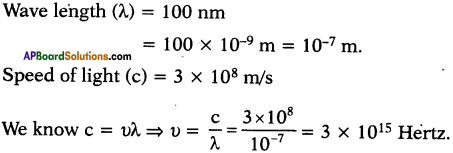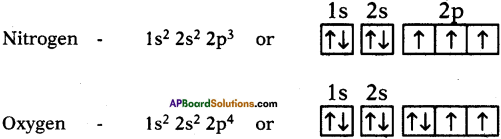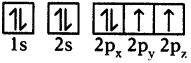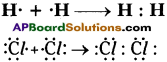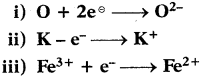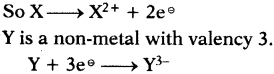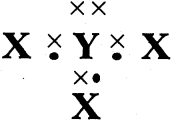AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Physical Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Carbon and its Compounds.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Chemistry Important Questions 14th Carbon and its Compounds
10th Class Chemistry 14th Lesson Carbon and its Compounds 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define Isomerism. (AP March 2016)
Answer:
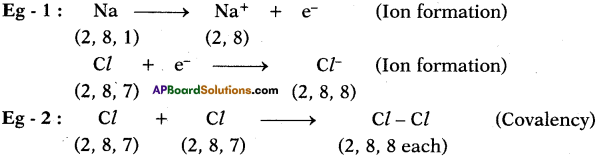
The phenomenon of possessing same molecular formula but different properties by the compounds is known as “Isomerism”.
Question 2.
Give the names of the functional groups. (AP March 2018)
a) – COOR
b) – OH
Answer:
a) Ester
b) Alcohol
![]()
Question 3.
How do you explain the role of Oxygen in combustion process? (TS March 2015)
Answer:
Oxygen helps the combustion (or) No combustion will take place without oxygen.
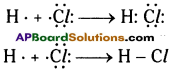
Ex : C + O2 → CO2
Question 4.
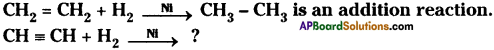
![]()
Predict and write the products. (TS March 2016)
Answer:
![]()
Question 5.
Write two uses of nano tubes. (TS June 2017)
Answer:
- Nano tubes are used as molecule wires.
- In intigrated circuits nano tubes are used to connect the components together.
- Nano tubes are used to incert Bio-molecules into the single cell.
Question 6.
Write two uses of Ethanol in day to day life. (TS March 2018)
Answer:
Ethanol is used in
i) Preparation of Alchoholic drinks
ii) Preparing tincture iodine
iii) Preparing cough syrup and tonics
Question 7.
Write the atomic structure of the following carbon compound. 3, 7-dibromo-4, -6 dichloro – oct-5-ene-l, 2-diol. (TS March 2019)
Answer:
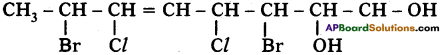
Question 8.
Thanish added acetic acid along with concentrated sulphuric acid to ethanol what would be his observation during the experiment? (AP SCERT: 2019-20)
Answer:
- He may observe that the resulting mixture is a sweet odoured substance.
- The substance is ethyl acetate, an ester.
Question 9.
Why do the various micelles present in water do not come together to form a precipitate? Guess the reason. (TS June 2019)
Answer:
The various micelles present in water do not come together to form a precipitate as each micelle repels the other because of the ion-ion repulsion.
Question 10.
Mention any two uses of graphite in day to day life. (TS June 2019)
Answer:
Uses of graphite in day to day life :
- Pencil lead.
- Lubricant.
Question 11.
What is “Allotropy”?
Answer:
The property of an element to exist in two or more different forms due to the difference in their atomic arrangement is called “Allotropy” and the different forms are called allotropes.
![]()
Question 12.
‘Diamond is a bad conductor of heat.’ Why?
Answer:
Diamond is a bad conductor of heat due to lack of free electrons.
Question 13.
What is ‘cleavage’?
Answer:
Cleavage is a property of splitting of crystals of some minerals in certain directions to produce a flat, even surface.
Question 14.
“Diamond is the hardest natural substance but is brittle.” Why?
Answer:
Diamond is the hardest natural substance but is brittle and can be broken due to the property of cleavage.
Question 15.
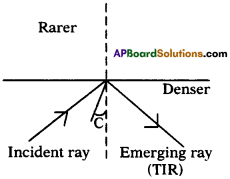
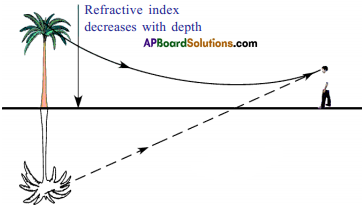
Explain about high refractive index of diamond.
Answer:
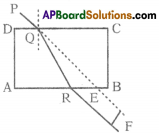
Diamond has a high refractive index, due to which most of the light that enters the diamond gets reflected back internally. This internally reflected light is responsible for the brilliance of a diamond.
Question 16.
What is catenation?
Answer:
Catenation is the phenomenon in which atoms of same element join together to form long chains.
Question 17.
What is an alkyl group?
Answer:
If one hydrogen is removed from an alkane, it is called alkyl group.
Ex : CH4 → methane
CH3 → methyl group
Question 18.
What is polymerization?
Answer:
The reaction in which a large number of identical and simple molecules join together to form a large molecule is called ‘polymerization’.
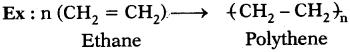
Question 19.
What do you understand by a ‘Functional group’?
Answer:
A group of atoms in carbon compounds showing characteristic properties is called a functional group.
Question 20.
Name some functional groups.
ANswer:
Alcohol – OH, Aldehyde – CHO, Ketone – > C = O, Carboxylic acid (- GOOH), ester (-COOR), and amine – NH2 are some important functional groups.
![]()
Question 21.
What is pyrolysis?
Answer:
Decomposition of a compound on heating in the absence of air is called pyrolysis.
Question 22.
What is hydrocarbon?
Answer:
Compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen are called ‘hydrocarbons’.
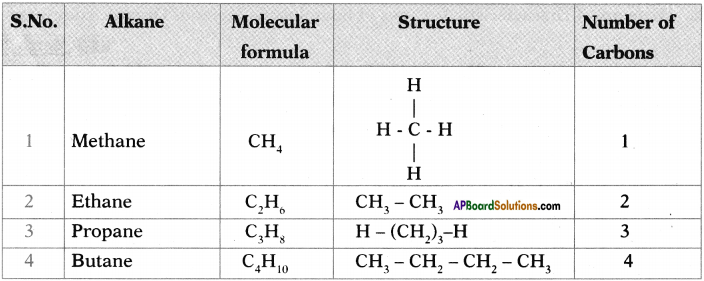
Ex : Alkanes (Saturated hydrocarbons),
Alkenes and Alkynes (Unsaturated hydrocarbons).
Question 23.
What is ‘Saturated hydrocarbon’? (Or) What is an alkane?
Answer:
The valency of carbon is 4, of all the valencies of carbon, are satisfied, the resultant hydrocarbons are referred to as ‘saturated hydrocarbons’ or alkanes. Their general formula is CnH2n+2.
Question 24.
What are ‘Unsaturated hydrocarbons’?
Answer:
The hydrocarbons containing one or more double bonds or triple bonds between two carbon atoms are called ‘unsaturated hydrocarbons’.
Ex : C2H6 and C3H6, etc.
Question 25.
What are alkenes?
Answer:
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons having at least one (C = C) double bond in their structures, Alkenes are also called olefins. Their general formula is CnH2n.
Ex : Ethylene (C2H4) and propene (C3H6), etc.
Question 26.
What are alkynes?
Answer:
Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons having at least one (\(C \equiv C\)) triple bond in their structures. Their general formula is CnH2n-2.
Ex: Acetylene (\(\mathrm{HC} \equiv \mathrm{HC}\))
Question 27.
Mention the natural sources of carbon compounds.
Answer:
Plants, wood, natural gas, coal, petroleum, etc. are the natural sources of carbon compounds.
![]()
Question 28.
Explain about methanol (or) methyl alcohol.
Answer:
Methanol is the simplest alcohol, It is the first member of the homologous series of alcohol. It is also known as wood alcohol, as it was initially obtained by the destructive distillation of wood.
Question 29.
What is organic chemistry?
Answer:
The chemistry of carbon compounds (excluding the carbonates, bicarbonates, carbides, cyanides, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide) is called organic chemistry. The large number of organic compounds necessitated their study in separate branch of chemistry, known as organic chemistry,
Question 30.
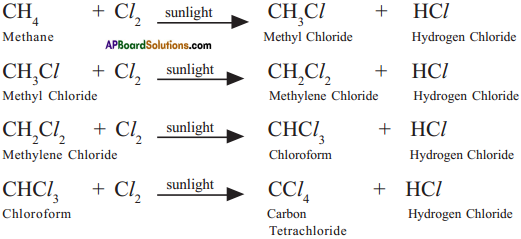
What is halogenation?
Answer:
Alkanes react with halogens in the presence of sunlight. For example, when a mixture of methane and chlorine is exposed to sunlight, a hydrogen atom of methane is replaced by a chlorine atom,

Question 31.
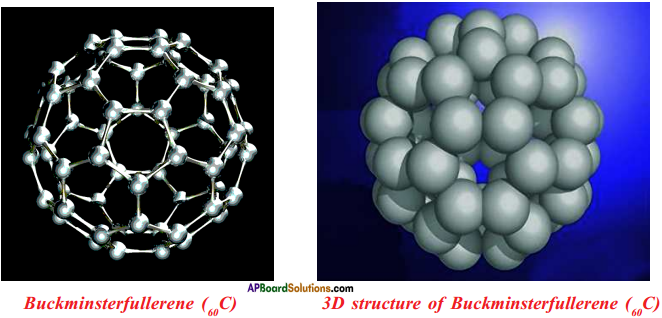
How many rings are there in buckminsterfullerene?
Answer:
In buckminsterfullerene, there are 32 rings, of them 12 are pentagonal rings and 20 are hexagonal rings.
Question 32.
Give example for homologous series.
Answer:
CH4 and C2H6 → These differ by a – CH2 unit.
and C2H6 and C3H8 → These differ by a – CH2 unit.
Question 33.
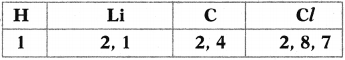
What is hybridisation?
Answer:
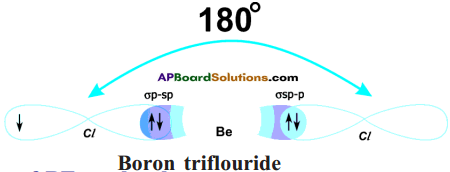
The intermixing of orbitals to form equivalent new orbitals is called hybridisation.
![]()
Question 34.
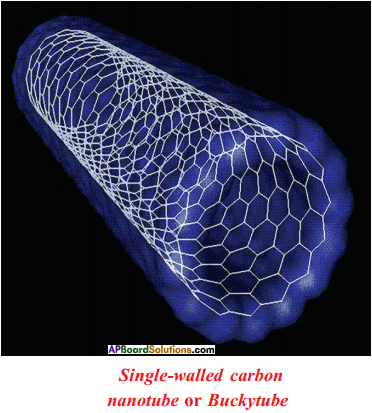
What are nanotubes?
Answer:
Nanotubes are allotropic form of carbon.
Question 35.
What are homologous series?
Answer:
The ierles of carbon compound in which successive compounds differ by -CH2 unit is called homologous series.
Question 36.
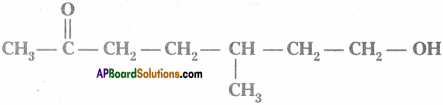
Write the molecular formula of the fourth member of the homologous series of alcohols.
Answer:
CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – OH
Question 37.
What is a catalyst?
Answer:
The substance which does not take part in chemical reaction but changes the rate of reaction.
Question 38.
Why are oils liquids at room temperature?
Answer:
Oils are unsaturated compounds so they are in liquid state.
Question 39.
Why are fats solids at room temperature?
Answer:
They are saturated compounds so they are in solid state.
Question 40.
Do you know the police detect whether suspected drivers have consumed alcohol or not? Explain.
Answer:
Orange Cr2O72- changes bluish green Cr3+ during the process of the oxidation of alcohol. The length of die tube that turned into green is the measure of die quantity of alcohol that had been drunk.
Question 41.
What is pka?
Answer:
The negative value of logarithm of dissociation constant of an acid.
Question 42.
What is Saponification?
Answer:
Alkaline hydrolysis of triesters of higher fatty acids producing soaps is called saponification.
![]()
Question 43.
What is a soap?
Answer:
Sodium or potassium salt of fatty acid.
Question 44.
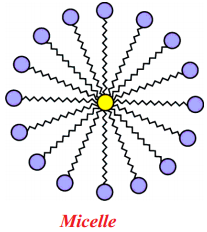
What is micelle?
Answer:
A spherical aggregate of soap molecules in water is called micelle.
Question 45.
What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus papers?
Answer:
Red litmus turns into blue.
Question 46.
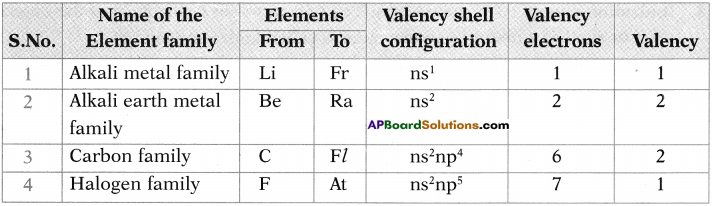
Write the valency of carbon in CH3 – CH3, CH2 = CH2 and \(\mathrm{HC} \equiv \mathrm{CH}\)?
Answer:
The valency of carbon in CH3 – CH3 is 4.
The valency of carbon in CH2 = CH2 is 3.
The valency of carbon in \(\mathrm{HC} \equiv \mathrm{C}\) – H is 2.
Question 47.
Out of butter and groundnut oil which is unsaturated in nature?
Answer:
Groundnut oil is unsaturated in nature.
Question 48.
What are hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts in soap?
Answer:

Question 49.
Name the carboxylic acid used as preservative.
Answer:
Acetic acid is used as preservative.
Question 50.
Why does graphite act as a good conductor of electricity?
Answer:
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity because of delocalized x electron system.
Question 51.
Among objects made of glass and diamond, which one shines more? Why?
Answer:
Diamond shines more because of low conical angle of 24,4° and also high refractive
Question 52.
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds.
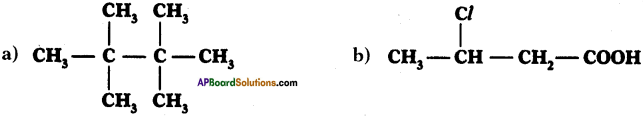
Answer:
a) 2, 2, 3, 3 – tetra methyl butane
b) 3-chloro butan-l-oic acid.
Question 53.
What is the difference between combustion and oxidation reaction?
Answer:
Combustion is an oxidation reaction where a compound is burnt in the presence of oxygen, whereas oxidation is addition of oxygen which does not require any burning.
Question 54.
Write the order of priority of functional groups for naming carbon compounds.
Answer:
![]()
Question 55.
What is glycerol?
Answer:
The trihydroxy alcohol is called glycerol.
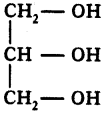
Question 56.
What do you mean by CMC?
Answer:
CMC means Critical Micelle Concentration.
Question 57.
Name the simplest chloride of saturated hydrocarbon.
Answer:
Chloro methane or methyl chloride.
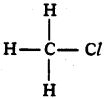
Question 58.
Write the IUPAC name of next homolog of CH3CH2CHO.
Answer:
The next homolog of CH3CH2CHO is CH3CH2CH2CHO (its IUPAC name is butanol). Since homologs differ by – CH2.
Question 59.
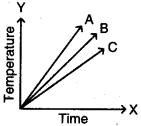
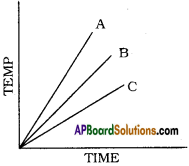
How do physical properties like boiling point and melting point vary as the number of carbon atoms increases in a homologous series?
Answer:
There is regular gradation in physical properties of homologous series. So the physical properties like boiling point and melting point vary.
![]()
Question 60.
What is meant by Hybridisation?
Answer:
Mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a degenerated new type of orbitals.
Question 61.
Write any two uses of Graphite.
Answer:
i) Conductor
ii) Lubricant
Question 62.
Write any two examples to Amorphous form of carbon.
Answer:
i) Coke
ii) coal
iii) charcoal.
Question 63.
Write any two examples to crystalline forms of carbon.
Answer:
i) Diamond
ii) graphite
Question 64.
What are the applications of Buckminster fullerene?
Answer:
i) Antioxidants
ii) Anti aging and damage agent in cosmetic sector.
Question 65.
What is meant by catenation?
Answer:
Binding of an element to itself through covalent bonds to form chain or ring molecules.
Question 66.
Write any one use of nanotubes.
Answer:
i) Used as molecular wires.
ii) Used in integrated circuits.
Question 67.
On which reason, graphite is used as lubricant and as the lead in pencils?
Answer:
Graphite has free electrons.
Question 68.
How many isotopes are there for C4H10, what are they?
Answer:
i) n – Butane
ii) Iso – Butane
Question 69.
CH3 – CH = CH – CH3, how many sigma bonds are present in the above compound?
Answer:
11
Question 70.
Write the IUPAC name of Ethyle alcohol.
Answer:
Ethanol.
![]()
Question 71.
Classify the following into alkanes, alkenes and alkynes.
C12 H22, C10 H22, C11 H22
Answer:
i) C10 H22 – Alkanes
ii) C11 H22 -Alkenes
iii) C12 H22-Alkynes
Question 72.
Hi ……… I am carboxylic acid. I am used in the making vinegar, who am I?
Answer:
Acetic acid.
Question 73.
What does IUPAC represent?
Answer:
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
Question 74.
Write any one example for esterification reaction.
Answer:
CH3COOH + C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
Question 75.
A compound with molecules formula C2H6O is used in cough syrup. Identify the compound.
Answer:
Ethyl Alcohol.
Question 76.
Which substance is added for the denaturation of ethyl alcohol?
Answer:
Pyridine.
Question 77.
What is the abbreviation of CMC?
Answer:
Critical Micelle Concentration.
Question 78.
Write the names of polar end and non-polar end in a soap.
Answer:
Polar end – COO– Na+, Non-polar end – R.
![]()
Question 79.
Write the IUPAC name of the alcohol which one carbon atom.
Answer:
Methanol.
Question 80.
Write the chemical equation which indicates the preparation of ethanol industrially?
Answer:
![]()
Question 81.
What is the formula of chloroform? Write its one use.
Answer:
CHCl3, Anesthetic.
Question 82.
Which type of hydrocarbons are participate in addition reaction?
Answer:
Unsaturate Hydrocarbons.
Question 83.
What are the oxidising agents used in oxidisation of C2H5?
Answer:
K2Cr2O7, KMn04.
Question 84.
What is meant by catalyst?
Answer:
To change die rate of reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change.
Question 85.
What are the main constituents of LPG?
Answer:
Butane, Methane.
Question 86.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons?
Answer:
Saturated house single bonds, unsaturated have multiple bonds.
Question 87.
Describe a test for carboxylic acid.
Answer:
React with metals liberate hydrogen gas.
Question 88.
What is meant by denatured alcohol?
Answer:
Unfit for human consumption by adding one or more chemicals.
![]()
Question 89.
Complete the following equation.
CH4 + 2O2 →
Answer:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 1H2O
Question 90.
![]()
i) In the above substance, what is the hybridisation of 3rd carbon?
Answer:
sp²
ii) What is the hybridisation of 4th carbon?
Answer:
sp³
Question 91.
What is the main misuse of Ethanol?
Answer:
Drinking.
![]()
Question 92.
What is gasohol?
Answer:
10% Ethyl alcohol with gasoline.
Question 93.
Write any two uses of Ethyle alcohol.
Answer:
i) Good solvent
ii) Additive to automotive gasoline.
Question 94.
Write two IUPAC name
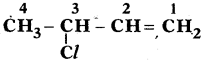
Answer:
3 – Chloro 1 – Butane
Question 95.
Name the following functional groups.
i) – COOR
ii) R – COOH
Answer:
i) – COOR (Ester)
ii) R – COOH (Carboxylic acid)
Question 96.
Name the crystalline allotrope of carbon which conducts electricity.
Answer:
Graphite.
Question 97.
Ravi gets confused while understanding the between R – COOH and R – OH functional groups, ask him one question to classify it.
Answer:
i) What is carboxylic acid?
ii) What is Alcohol?
Question 98.
Formic acid (HCOOH)
Farmaldehyde (HCHO)
Methanol (CH3OH), then answer the following questions.
i) Which is present in ants?
Answer:
HCOOH (Formic acid).
ii) Which is used to preservation of dead bodies?
Answer:
HCHO (Farmaldehyde).
Question 99.
Write the symbolic representation showing the functional groups.
i) amine
ii) amide
Answer:
i) R – NH2
ii) R – CONH2
![]()
Question 100.
How many sigma and pi-bonds present in Acetylene?
Answer:
\(\mathrm{HC} \equiv \mathrm{CH}\) ; σ bonds – 3 ; π bonds – 2
Question 101.
Which of the following will give substitution reactions?
CH4, C3H6, C3H4, C5H12, C4H8
Answer:
CH4, C5 H12
Question 102.
Which of the following will give addition reactions?
CH4, C3H6, C3H4, C5H12, C4H10
Answer:
C3H6, C3H4
Question 103.
What is a homologous series?
Answer:
Same functional group, difference between successive members is a simple structural unit – CH2.
Question 104.
Name the hydrocarbon which is used in the artificial ripening of fruits?
Answer:
C2H4
Question 105.
Define fermentation process.
Answer:
Chemical break down of a substance by bacteria, yeast or other microorganisms.
Question 106.
Define functional group.
Answer:
They are specific substituents within molecules that are responsible for die characteristic chemical reactions.
Question 107.
Which hydrocarbons participate in sp² hybridisation?
Answer:
C2H4
Question 108.
Name the following compounds,
i) CH3 – CH2 – Br
Answer:
1 – Bromo Ethane
ii)
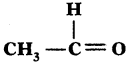
Answer:
Ethanol
iii)
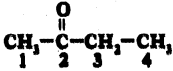
Answer:
2 – Butanone
iv)
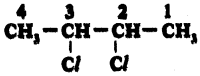
Answer:
2, 3 – dichloro Butane
Question 109.
Which constituents are present in tincture Iodine?
Answer:
i) Iodine
ii) Alcohol.
Question 110.
Write the uses of esters in daily life.
Answer:
i) Solvents
ii) Plasticizers
Question 111.
Name the gas evolved when acetic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Answer:
The gas liberated is carbon dioxide.
![]()
Question 112.
Name the organic acid present in vinegar. Write its chemical formula.
Answer:
The acid present in vinegar is acetic acid. Its formula is CH3COOH.
Question 113.
Why is graphite a good conductors’of electricity?
Answer:
Graphite has free electrons.
Question 114.
Why does carbon form compounds mainly by covalent bonding?
Answer:
Tbtravalency.
Question 115.
Why are alkanes called as paraffins?
Answer:
Low reactivity.
Question 116.
Draw two possible structures with formula C3HgO and what they are called?
Answer:
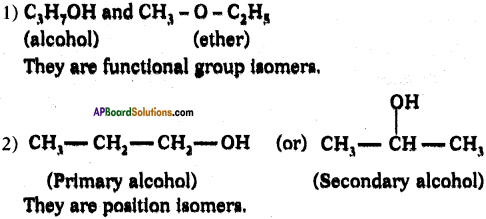
Question 117.
Draw structure of 3 – methyl pentan-3-ol.
Answer:
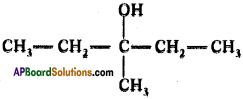
Question 118.
Draw the shape of soap molecule.
Answer:
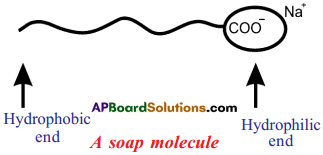
Question 119.
Draw the shape of Micelle.
Answer:
Question 120.
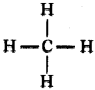
Draw the shape of methane.
Answer:
Question 121.
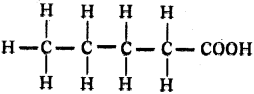
Draw the structure of pentanoic acid.
Answer:
Question 122.
How do you appreciate the role of diamond in space probes?
Answer:
Since it has the ability to filter out harmful radiations, it is used in making protective windows for space probes.
![]()
Question 123.
How do you appreciate the role of acetic acid as a preservative?
Answer:
- Dilute acetic acid is used as a food preservative in the preparation of pickles and sauces,
- As vinegar, it is also used as an appetiser for dressing food dishes.
Question 124.
How do you appreciate the role of diamond in surgery?
Answer:
A sharp edged diamond is used as a tool to remove cataract in eye surgery.
10th Class Chemistry 14th Lesson Carbon and its Compounds 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Draw the simple figure of a soap molecule. (AP March 2016)
Answer:
Structure of soap molecule :

Question 2.
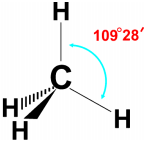
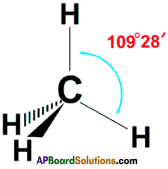
Draw the structure of the methane molecule. Write its bond angle. (TS June 2015)
Answer:
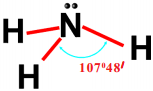
The bend angle in methane is 109°2 8′.
Question 3.
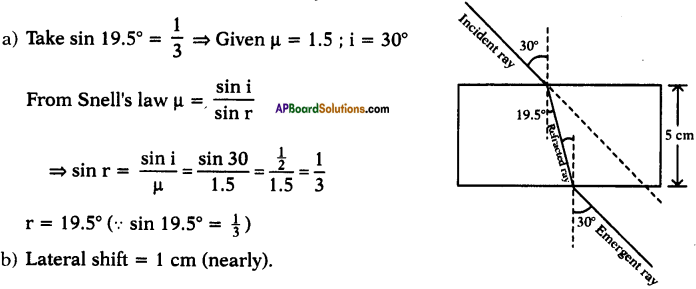
a) Why are vegetable oils healthy as compared to vegetable ghee? (TS March 2015)
b) Write the IUPAC name of
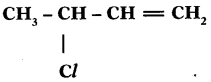
Answer:
a) Because vegetable oils contain unsaturated fatty acids or vegetable oils are easily digestible.
b) 3 – Mono chloro butene (or) 3 Chloro butene
Question 4.
What are alkenes? Write the general formula of alkenes. Give an example for alkenes. (TS June 2017)
Answer:
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons those are having carbon * carbon double bond are known as alkenes.
- The general formula of Alkenes is CHH2h.
- Example : Ethelene (C2H4).
Question 5.
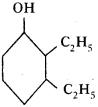
Based on the diagram, answer the following.
1) Write the name of the compound.
2) Write the name of functional group in the structure. (AP March 2019)
Answer:
- The compound is 2, 3-di ethyl-cycle hexan-1-ol.
- Alcohol (OH) is the functional group in the structure.
Question 6.
Identify the functional groups in the following compounds and write IUPAC names.
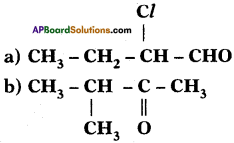
Answer:

The IUPAC name of the compound Is 2 – Chloro-Butan 1-ol.

The IUPAC name of the compound is 3 – Methyl-2-Butan-one.
Question 7.
Draw the structure of butanoic acid C3H7COOH.
Answer:
Formula of butanoic acid is C4H5O2.
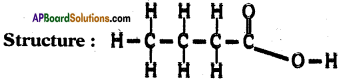
Question 8.
What is ‘Isomerism’?
Answer:
Compounds having same molecular formula but different structures are called isomers, and the phenomenon is called isomerism.
Ex: C4H10 exists an n-hutane and iso-butane.

Question 9.
How do you detect leakage in the cylinder?
Answer:
- To detect any leakage of gas from die cylinder, a strong-smelling substance like ethyl mercaptan (C2H5 SH) is added to die gas.
- Then the leakage can be easily detected by the foul smell of die ethyl mercaptan.
Question 10.
How is LPG gas useful for environment?
Answer:
- Because of its heat producing capacity (calorific value), it is considered to be a good fuel.
- It bums without producing smoke. Hence, it does not cause any pollution.
- It is a dean fuel and can be conveniently handled.
![]()
Question 11.
How is ethanol useful in pharmaceutical industry?
Answer:
- Solutions in ethanol are often prepared in pharmaceutical industry, these solutions are known as tinctures.
- For example, a solution of Iodine and potassium iodide in ethanol is called tincture of iodine.
- It is also used as an important raw material for the synthesis of many organic compounds, for example, ethanol, ethanoic acid, ethanoie anhydride, esters, chloroform, etc.
Question 12.
How are synthetic detergents harmful for environment?
Answer:
- Some synthetic detergents resist biodegradation, i.e. they are not decomposed by micro-organisms such as bacteria.
- Hence, they cause water pollution in lakes and rivers.
- They tend to persist for a long time, making the water unfit for aquatic life.
Question 13.
Explain about allotropic forms of carbon.
Answer:
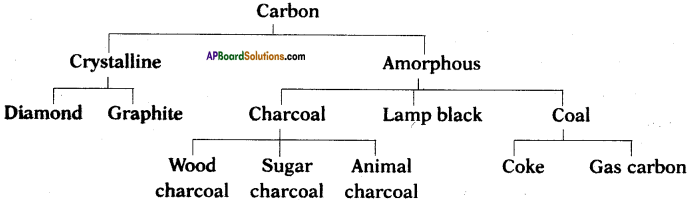
Question 14.
Diamond is considered to be the purest form of carbon. How can we prove it?
Answer:
When diamond is heated in oxygen alone, it bums at about 800° C and forms carbon dioxide leaving no residue. This proves that diamond to be the purest form of carbon.
Question 15.
Why does carbon not form C4+? Why?
Answer:
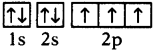
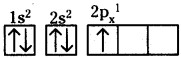
- Electronic configuration of carbon is 1s²2s²2p².
- If carbon loses four electrons from the outer shell, it will form C4+ ions.
- This requires huge amount of energy which is not available normally.
- Therefore C4+ formation is not possible.
Question 16.
Why does carbon form compounds mainly by covalent bonding?
Answer:
Carbon is unable to form C4+ ion as well as C4- ion. So carbon has to satisfy its tetra- valency by sharing electrons with other atoms. So it mainly forms covalent bonding.
![]()
Question 17.
Define Allotropy. What are the allotropic forms of carbon?
Answer:
The property of an element to exist in two or more physical forms having more or less similar chemical properties but different physical properties is called allotropy. The allotropic forms of carbon are graphite, diamond, etc.
Question 18.
Identify the unsaturated compounds of the following.
a) CH3 – CH2 – CH2
b) CH3 – CH = CH3
c)
Answer:
a) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 saturated compound.
b) CH3 – CH = CH3 unsaturated compound.
c)

Question 19.
Define Isomers. Write structural formula of isomers of butane.
Answer:
Compounds having same molecular formula but different properties are called isomers.
Isomers of butane :
1) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3
Butane

Question 20.
What happens when a small piece of sodium is dropped into ethanol?
Answer:
When a small piece of sodium is dropped into ethanol it releases hydrogen gas and forms sodium ethoxide.
2C2H5OH + 2 Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2
Question 21.
What type of reaction takes place between ethane and chlorine?
Answer:
Substitution reaction takes place between ethane and chlorine in die presence erf sunlight
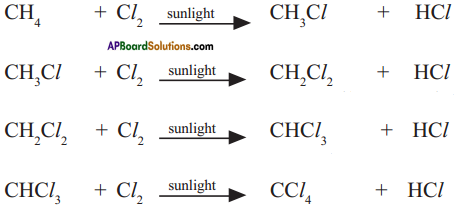
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
CH3Cl +Cl2 → CH2Cl2 + HCl
CH2Cl2 + Cl2 → CHCl3 + HCl
CHCl3 + Cl2 → CCl4 + HCl
Question 22.
What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Answer:
- Catenation
- Isomerism.
Question 23.
How could you name the following compounds?
a) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – Br
b) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2
Answer:
a) Bromo propane
b) Hexyne
Question 24.
Give examples for primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Answer:
Primary amine – CH3NH2
Secondary amine – CH3 – NH – CH3
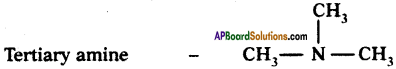
Question 25.
Write the following conversions.
1) Ethanol to Ethene
2) Ethene to Ethanol
3) Methane to carbon tetra chloride.
Answer:
1) Ethanol reacts with cone. H2SO4 at about 170°C to give ethene.
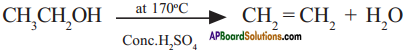
2) Ethanol is prepared from ethene by the addition of water vapour in the presence of catalyst P2O5.

3) Methane reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight. Hydrogen atoms of CH4 are replaced by chlorine at![]()
Question 26.
Name the following compounds and which one is saturated among them.
a) CH3 – \(\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{H}\) – CH3
b) CH3 – CH = CH – CH3
c) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3
Answer:
a) 2-Butyne
b) 2 – Butene
c) Butane
Butane does not show any double or triple bonds. Its valency is completely satisfied with formation of single bond. So it is a saturated compound.
![]()
Question 27.
How do you identify the given organic compound contains carboxylic acid functional group?
Answer:
- On adding carbonates and bicarbonates the compound containing carboxylic acid group evolves carbon dioxide gas.
- When warmed with alcohol and cone. H2SO4 a pleasant fruity smell is produced due to formation of ester.
Question 28.
Explain briefly about the structure of “Diamond”.
Answer:
- In a diamond, each carbon atom is surrounded by four other carbon atoms.
- In these carbon atoms, each carbon atom undergoes in its excited state sp3 hybridisation.
- These are placed at the four corners of a regular tetrahedron.
- This results in a 3-dimensional network of carbon atoms.
- So diamond is in three dimensional structure.
Question 29.
Explain briefly about the structure of “Graphite”.
Answer:
- In graphite, each ‘C’ is surrounded by three other ‘C’ atoms.
- The ‘C’ atoms are arranged in layers.
- In the layer structure, the carbon atoms are in trigonal planar environment.
- Each layer consists of a 2-dimensional hexagonal network.
Question 30.
Diamond is an extremely bad conductor of electricity.” Why?
Answer:
1) In diamond, each carbon atom is covalently bonded with four other carbon atoms.
2) So, the four outermost electrons of a carbon atom are engaged or trapped in the covalent bonds, having no free electrons making it a bad conductor of electricity.
Question 31.
Why is diamond hard but graphite is smooth and slippery?
Answer:
Diamond has sp³ hybridisation with tetrahedral environment. As C – C bonds are very strong any attempt to distort the diamond structure requires large amount of energy. Hence diamond is one of the hardest material.
Whereas graphite has sp² hybridisation with layer structure with trigonal planar environment. The layers tend to slide on one another. So graphite is smooth and slippery.
Question 32.
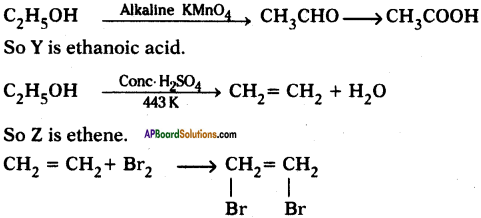
An organic compound X with a molecular formula C2H6O undergoes oxidation within presence of alkaline KMnO4 to form a compound Y. X on heating in presence of con. H2SO4 at 443 K gives Z. Which on reaction with Br2 and decolorizes it? Identify X, Y, and Z and write the reactions involved.
Answer:
X is ethanol.
Question 33.
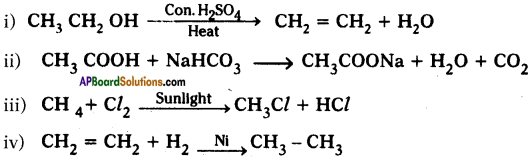
Complete the following reactions.
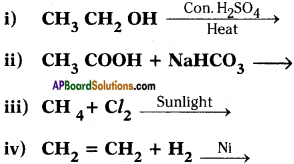
Answer:
Question 34.
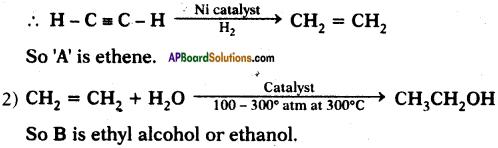
![]()
What are A and B?
Answer:
1) Alkynes undergo addition reaction in the presence of nickel catalyst and hydrogen to form Alkene.
Question 35.
Draw the structure for the following compounds.
a) Propanoic acid
b) Chlorobutane
c) Hexanone
d) Pentanal
Answer:
a) CH3CH2COOH
b) CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl
c) CH3CH2CH2CH2COCH3
d) CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO
![]()
Question 36.
Give IUPAC names of the following compounds. If more than one compound is possible, name all of them.
i) A chloride derived from butane.
ii) A ketone derived from pentane.
Answer:
i) The following chlorides are possible for butane.

ii) The following ketones are possible for pentane.
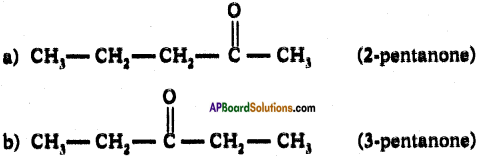
Question 37.
a) What are the various possible structural formulae of a compound having molecular formula C3H6?
b) Give IUPAC names of the above possible compounds and represent them in structure.
c) What is the difference between those
Answer:

b) The IUPAC names of compounds are propene and cycle propane.
c) The main difference Is that the first compound Is alkene-an unsaturated compound and second is cyclo alkane-a saturated compound.
Question 38.
Draw isomeric forms of C6H14.
Answer:
Isomers of hexane :
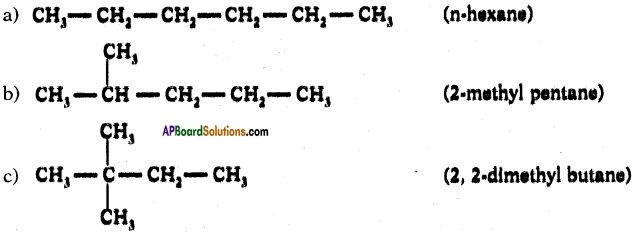
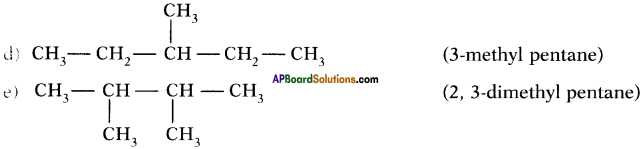
Question 39.
How do you appreciate the role of carbon in everyday life?
Answer:
- Major components of our daily food have carbohydrates, proteins, fats, etc. which are all made up of carbon compounds.
- The fibres of cloth are made up of cellulose and other types of materials, which are all carbon compounds.
- Cement and steel form the core of any of the modern buildings. Carbon bestows steel with hardness, while limestone (CaCO3) a major constituent of cement also contains carbon.
Question 40.
How do you appreciate the role of oxygen in combustion process?
Answer:
- When the oxygen supply is insufficient, the fuels burn incompletely producing mainly a yellow flame.
- When the oxygen supply is sufficient, the fuels burn completely producing a blue flame.
Question 41.
How do you appreciate the role of Ethanol as a fuel?
Answer:
- A material which is burnt to obtain heat is called a fuel. Since ethanol burns with a clear flame giving a lot of heat, it is used as a fuel.
- Some countries add ethanol to petrol to be used as a fuel in cars. Thus ethanol is used as an additive in petrol.
- Ethanol alone can also be used as a fuel for cars.
![]()
Question 42.
What are the uses of fullerenes?
Answer:
Fullerenes are under study for potential medical use such as specific antibiotics to target resistant bacteria and even target cancer cells such as melanoma.
Question 43.
Write the HJPAC names of the following compounds.
i) CH3 – CH0 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2OH
ii) CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH- CH2 – \(\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{CH}\)
iii) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CHO
iv) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – COOH
Answer:
- nananol
- 4- ene – 1 heptyne
- pentanal
- pentanoic acid
Question 44.
What are the uses of alcohol?
Answer:
- Alcohols are goods solvent for resin and gums.
- Ethanol is used in the thermometers because of its low freezing point.
- One of the products of ethyl alcohol is chloroform, which is used as an aesthetic.
- 10% ethanol in gasoline is a good motor fuel.
- It is used in medicines such as tincture iodine, cough syrups and many tonics.
Question 45.
What are the uses of acetic acid?
Answer:
- 5 to 8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar and is used widely as a preservative in pickles.
- Used as a laboratory reagent.
- Used in the production of perfumes, dyes, esters, etc.
- Used in medicine.
10th Class Chemistry 14th Lesson Carbon and its Compounds 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write IUPAC names for the following carbon compounds.
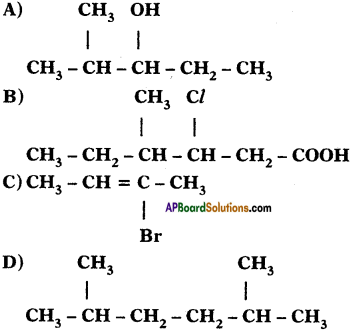
Answer:
A) 2 – methyle pentane – 3 – ol
B) 3 – chloro, 4 – Methyle hexanoic acid
C) 2 Bromo – Bute – 2 – ene
D) 2, 5 Dimethyle hexane
Question 2.
 (AP June 2017)
(AP June 2017)
Observe the given carbon compound and answer the following questions.
a) Give numbering to the carbons in the given compound according to IUPAC rules.
b) Name the functional group present in the given compound.
c) Name the word root for the given carbon compound.
d) Write the IUPAC name of the given compound.
Answer:
a)

b) The given compound contains functional group – OH. It is an alcohol.
c) Word root: The number of carbon atoms present in the molecules is called word root. Here the word root is (C5) – pent.
d) IUPAC name of the given compound is pent 4 – ene 2 – ol.
Question 3.
Alkanes are considered as Paraffins. So, they undergo substitution reactions but not addition reactions. Explain with suitable example. (AP March 2017)
Answer:
Question 4.
Observe the structure and answer the following.
a) Write the name of principal functional group present in the compound.
b) Identify the parental chain in the compound.
c) What are the substituents in the above compound?
d) Name the above compound as per IUPAC nomenclature. (AP June 2018)
Answer:
a) Ketone
b)
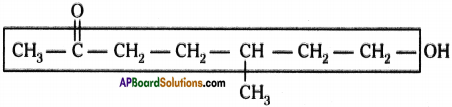
c) Methyl group ; Hydroxy group
d) 7 – hydroxy – S – methyl heptan – 2 – one
Question 5.
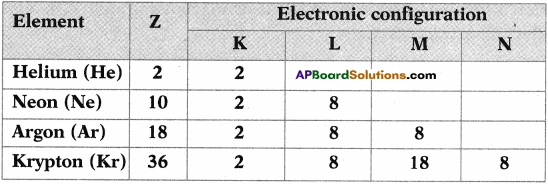
In the table given below, fill the information in the empty boxes and give answers to the following questions. (TS June 2015)
a Write the general formula of alkanes from the table.
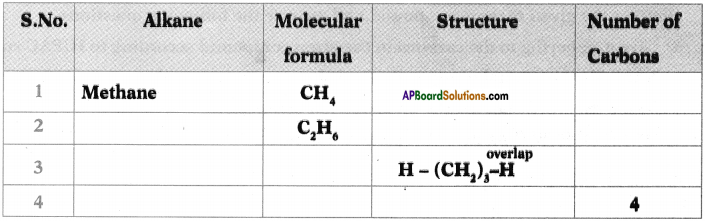
b) How many a bonds are there in C3H6?
c) What sequential order did you notice in the molecular formulae?
d) There exist single bonds between carbon atoms of alkanes. Do you agree with this statement? Give reasons.
Answer:
a) The general formula of Alkanes is CnH2n+2
b) The number of o bonds in C2H6 are 7.
c) Two successive alkanes are differed by – CH2 group.
d) Except Methane all other alkanes have single bonds between carbon atmos because it is a saturated hydro carbon.
![]()
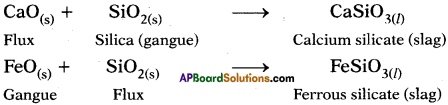
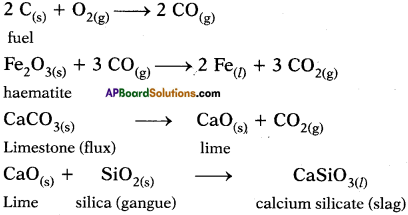
Question 6.
Why do we call alkanes as paraffins? Explain the substitution reactions of alkanes. (TS June 2016)
Answer:
a) 1. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with least reactivity.
2. Therefore they are called paraffins.
3. Parum = little and affins = affinity.
b) 1. A reaction in which one atom or a group of atoms in a given compound is replaced by other atom or group of atoms is called a substitution reaction.
2. Alkanes have single bonds and undergo substitution reactions.
3. For example :
Methane (CH4) reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight.
Question 7.
Write the types of Allotropes of Carbon. Give any three examples of each. (TS March 2016)
Answer:
The allotropes of carbon are classified into two types. They are
i) Amorphous forms,
ii) Crystalline forms.
Examples :
Amorphous forms :
Coal, coke, wood charcoal, animal charcoal, lamp black, gas carbon, petroleum coke, sugar charcoal, etc.
Crystalline forms :
Diamond, graphite, and buckminsterfullerene.
Question 8.
Write any 4 characteristic features of homologous series of Organic compounds. (TS March 2016)
Answer:
Homologous series :
The series of carbon compounds in which two successive compounds differ by – CH2 unit is called homologous series.
Characteristic features of homologous series :
- They have one general formula.
Ex : Alkane (C4H2n + 2), Alkene (C4H2n), Alkyne (C4H2n-2) - Successive compounds in their series possess a difference of (- CH2) unit.
- They possess similar chemical properties due to the same functional group.
- They show a regular gradation in their physical properties.
Question 9.
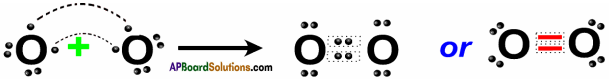
List out the materials required to conduct the experiment to understand the esterification reaction. Explain the procedure of the experiment. How can you identify that an ester is formed in this reaction?(TS March 2017)
Answer:
Required Material :
Test tube, beaker, tripod* burner, water, wire guage, ethanol (absolute alcohol), glacial acetic acid, concentrated sulphuric acid.
Procedure :
- Take 1 ml of ethanol and 1 ml of glacial acetic acid along with a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid in the test tube.
- Warm it in a water bath or in a beaker containing water for atleast five (5) minutes.
- Pour the warm contents into a beaker containing 20-50 ml of water and observe the odour of the resulting mixture.
If we smell sweet odour from the beaker, we can confirm that ester is formed.
Question 10.
Explain the Isomerism and Catenation properties of carbon. (TS March 2018)
Answer:
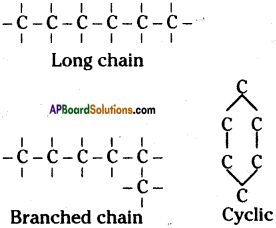
Catenation properties of carbon :
i) Carbon has ability to form longest chains with its own atoms. This special property of carbon is called catenation.
ii) Due to catenation property of carbon it can form largest chain containing millions of carbon atoms, branches and cyclic compounds.
Isomerism of carbon :
The phenomenon of possessing some molecular formula but different properties by the compounds is known as isomerism.
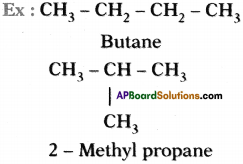
Molecular formula of above two molecules is C4 H10 but they have different structure. These two are isomers.
By there two special properties of carbon it can make number of compounds.
Question 11.

Observe the above table and answer the following questions. (TS March 2019)
1) Write the general formula of Alkanes.
2) Mention the names of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
3) Write the homologous series of Alkynes.
4) Write the formula of Hexyne.
Answer:
1) General formula for Alkanes : CnH2n+2.
2) Unsaturated Hydrocarbons in the list are :
Propene C3H6, Butene C4H6, Pentyne C5H8, Hexyne C6H10.
3) Homologous series of Alkynes is C2H2 (Ethyne), C3H4 (Propyne), C4H6 (Butyne), C5H8 (Pentyne), C6H10 (Hexyne).
4) Formula of Hexyne is C6H10.
Question 12.
Complete the following table based on functional groups of organic compounds, their structural formulas and respective suffixes. (AP SCERT: 2019-20)
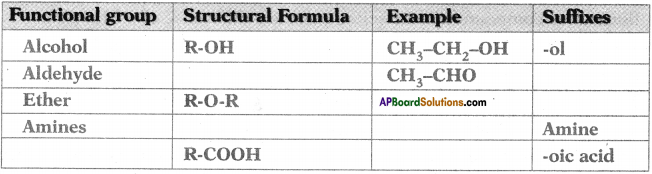
Answer:
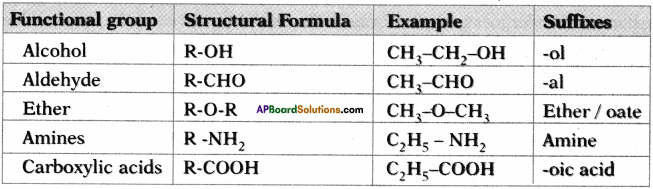
Question 13.
Explain the occurrence of carbon.
Answer:
Carbon occurs in nature in free state as well as in combined state.

Question 14.
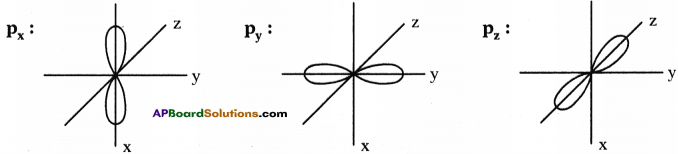
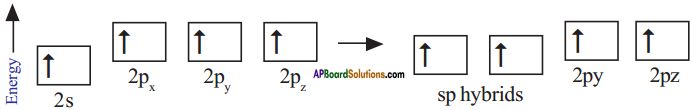
What is sp hybridisation? Explain.
Answer:
- Each carbon is only joining to two other atoms rather than four or three.
- Here the carbon atoms hybridise their outer orbitals before forming bonds, this time they only hybridise two of the orbitals.
- They use the ‘s’ orbital (2s) and one of the 2p orbitals, but leave the other 2p orbitals unchanged.
- The new hybrid orbitals formed are called sp-hybrid orbitals, because they are made by an s-orbital and a p-orbital reorganizing themselves.
![]()
Question 15.
Write the characteristics of homologous series of organic compounds.
Answer:
Characteristics of homologous series :
- They have one general formula.
e.g.: Alkanes (CnH2n+2) - Successive compounds in the series possess a difference of – CH2 unit.
- They possess similar chemical properties due to same functional group.
e.g.: C – OH - They show a regular gradation in their physical properties.
Question 16.
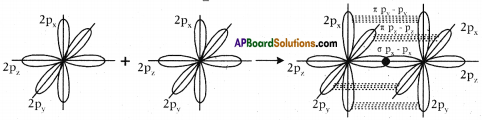
What is sp³ hybridisation with diagram? Explain.
Answer:
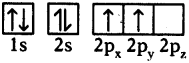
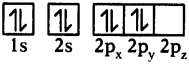
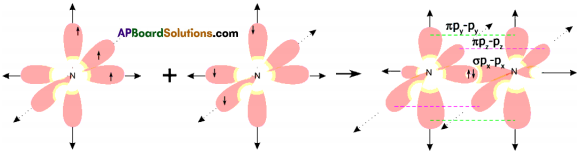
The excited carbon atom allows its one s-orbital (2s) and three p-orbitals (2px, 2py, 2pz) to intermix and reshuffle into four identical orbitals known as sp³ orbitals. Thus, carbon atom undergoes sp³ hybridization. The four electrons enter the new four identical hybrid orbitals known as sp³ hybrid orbitals, one each as per Hu nd’s rule.
1) Since carbon has four unpaired electrons, it is capable of forming bonds with four other atoms.
2) When carbon reacts with hydrogen, four hydrogen atoms allow their ‘s’ orbitals containing one electron each to overlap with four sp³ orbitals of carbon atom which are oriented at an angle of 109°. 28’.
3) Four orbitals of an atom in the outer shell orient along the four corners of a tetrahedron to have minimum repulsion between their electrons. ‘The nucleus of the atom is at the centre of the tetrahedron.
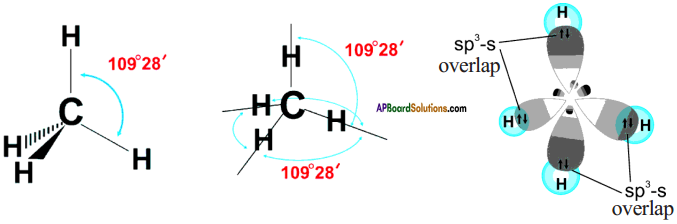
4) This leads to form four sp³ – s sigma bonds between carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms, All these bonds are of equal energy,
Question 17.
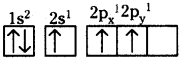
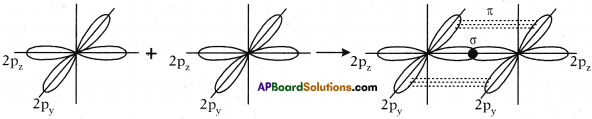
What is sp² hybridisation? Explain.
Answer:
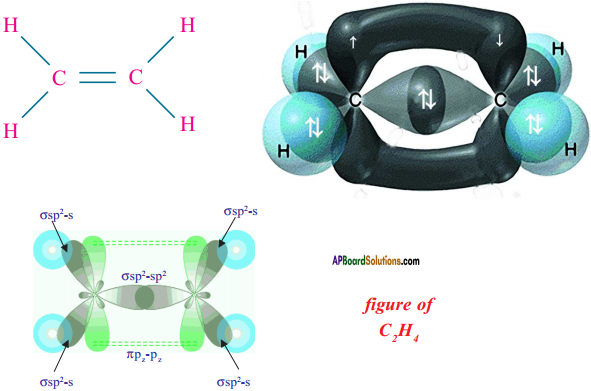
Consider ethene molecule
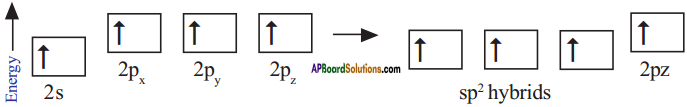
- In the formation of CH2 – CH2 each carbon atom in its excited state undergoes sp² hybridisation by intermixing one s-orbital (2s) and two p-orbitals (say 2px and 2py) and reshuffling to form three sp² orbitals.
- Mow each carbon atom is left with one ‘p’ orbital (say 2pz) unhybridised,
- The three sp² orbitals having one electron each get separated around the nucleus of carbon atoms at an angle of 120°.
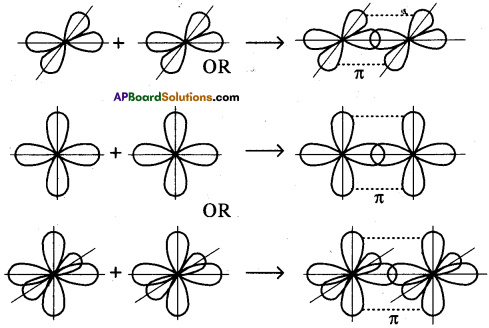
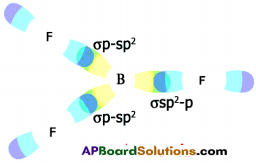
- When carbon is ready to form bonds one sp² orbital of one carbon atom overlaps the sp² orbital of the other carbon atom to form sp² – sp² sigma (σ) bond,
- The remaining two sp² orbitals of each carbon atom get overlapped by ‘s’ orbitals of two hydrogen atoms containing unpaired electrons.
- The unhybridised pz orbitals on the two carbon atoms overlap laterally as shown in figure to form a π (pi) bond.
- Hence, there exist a sigma (σ) bond and a pi π (pi) bond between two carbon atoms in ethene molecule. Hence, the molecule ethene (C2H4) is
Question 18.
The list of some organic compounds is given below.
Ethanol, ethane, methanol, methane, ethyne and ethene.
From the above list name the compound …………..
a) formed by the dehydration of ethanol by cone. H2SO4.
b) which forms methanoic acid on oxidation?
c) which forms chloroform on halogination in the presence of light?
d) which are unsaturated compounds?
e) which have compounds containing alcohol group?
Answer:
a) Dehydration ethanol in the presence of Cone. H2SO4 forms ethene,
b) Methanol on oxidation turns to methanoic acid,
c) Methane in the presence of light forms chloroform,
d) Unsaturated compounds are ethene and ethyne.
e) The compounds containing alcohol group are methanol, ethanol,
Question 19.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
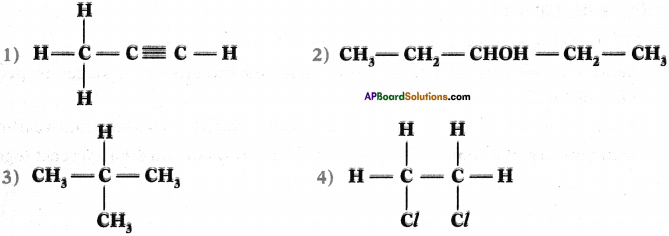
Answer:
- 1 – propyne
- 3 – pentanel (or) pentamSml
- 2 – methyl propane
- 1, 2 dichloro ethane
Question 20.
Give one example of each of the following.
i) Saturated hydrocarbon
ii) Cyclic compounds
iii) Unsaturated hydrocarbon
iv) Functional group
v) Homologous series
Answer:
i) Saturated hydrocarbons are Alkanes, So the examples are methane (CH4), Ethane, (C2H6).
ii) Cyclic compounds are cycle alkanes, eg : Cyclo propane (C3H6), Cycle butane (C4H6).
iii) Unsaturated hydrocarbons are Aikynes, eg : Ethene (C2H4), Propene
iv) The examples for functional groups are ‘ 1. Aldehyde – CHO, 2. Alcohol = OH
v) A series of carbon compounds that differ by – CH2 with similar chemical properties is called homologous series.
eg: 1, Alkane, 2, Alkene
![]()
Question 21.
Write the differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Answer:
| Saturated hydrocarbons | Unsaturated hydrocarbons |
| 1) All the four valencies of each carbon atom are satisfied by forming single covalent bonds with carbon and hydrogen atoms, | 1) The valencies of at least two carbon atoms are not fully satisfied by the hydrogen atoms. |
| 2) Carbon atoms are joined only by single bonds. | 2) Carbon atoms are joined by at least one double bond or by a triple bond. |
| 3) They are less reactive due to nonavailability of electrons in the single covalent bond therefore they undergo substitution reactions, | 3) They are more reactive because of the presence of electrons in the double or triple bond and therefore undergo addition reactions. |
Question 22.
Answer the following.
a) What are the first three members of carboxylic acid series?
b) Name the compounds which can be oxidised directly or in stages to produce ethanoic acid.
c) Write one equation each when acetic acid reacts with a metal, a base, and a carbonate.
d) Name the organic compound formed when acetic acid and ethanol react together.
Answer:
a) The first three members of carboxylic acids are :
i) Methanoic acid – HCOOH
ii) Ethanoic acid – CH3COOH
iii) Propanoic acid – CH3CH2COOH
b) Ethanol in stages oxidises to acetic acid whereas ethanol directly oxidises to ethanoic acid.
c) i) 2 CH3COOH + 2 Na → 2CH3COONa + H2
ii) CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
iii) CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
d) When ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid it forms an ester namely ethyl acetate.
Question 23.
What are the rules to be followed to name a carbon compound?
Answer:
Rules to be followed
i) Longest carbon chain is selected,
ii) Chain is numbered in such a way that the branched chain or substituent gets the smallest number,
iii) If the functional group is present, it is given the. lowest number,
iv) Substituents are named in the alphabetical order,
v) The position of substituents are prefixed with hyphen,
vi) Multiple substituents are written with numerical prefixes such as di or tri,
Question 24.
Write suffixes and prefixes for some important characteristic functional group in a tabular form.
Answer:
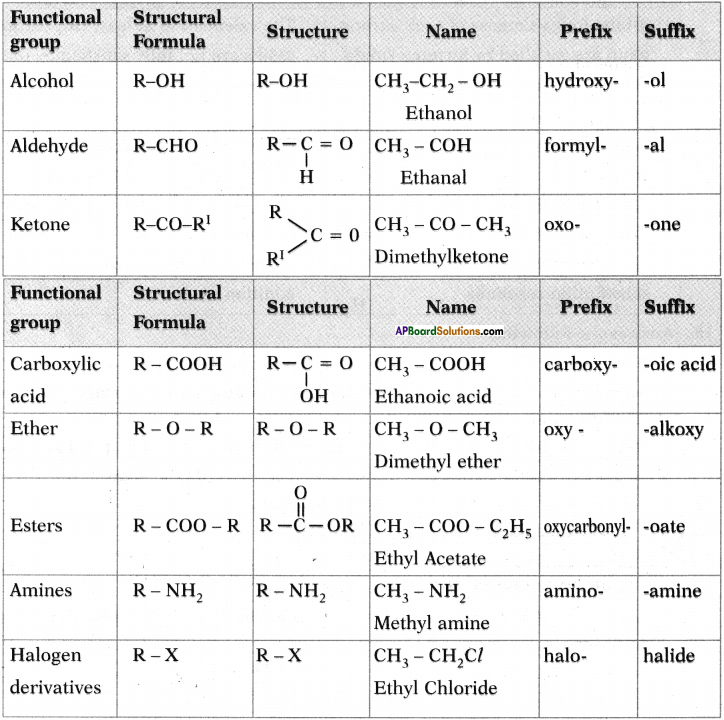
Question 25.
Correct the following statements.
1) Alkenes undergo substitution reactions.
2) Alkanes are polar in nature.
3) When sodium piece is added to ethanol oxygen gas liberates.
4) On complete combustion of carbon compound it gives carbon monoxide and water.
Answer:
- Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. So they undergo addition reactions.
- Alkanes are covalent compounds. So they are non-polar in nature.
- When sodium piece is added to ethanol it releases hydrogen gas.
- On complete combustion of carbon compound it forms carbon dioxide and water.
Question 26.
Copy and complete the following table which relates to three homologous series of hydrocarbons.
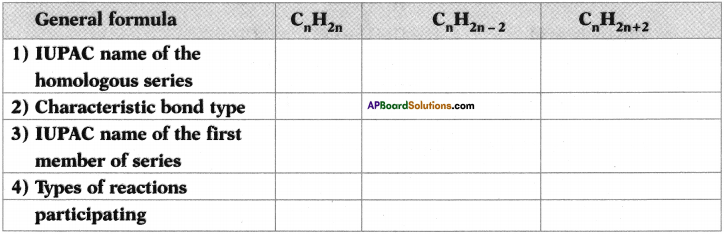
Answer:
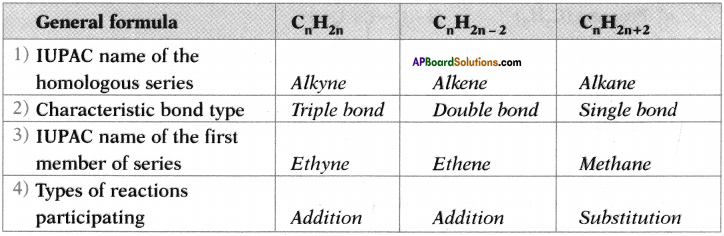
Question 27.
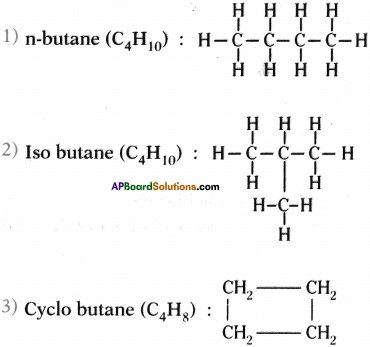
Draw the structures of isomers of butane.
Answer:
Isomers of butane are n-butane, iso butane and cyclo butane :
Structures :
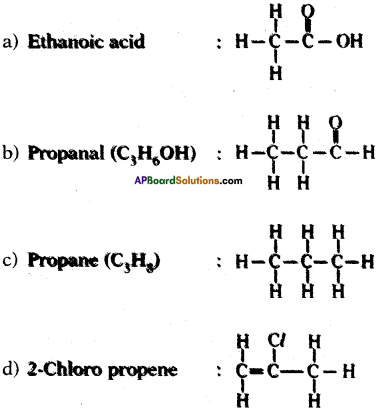
Question 28.
Draw the structures of the following.
a) Ethanoic acid
b) Propanal
c) Propene
d) Chloro propene
Answer:
Structures:
Question 29.
Draw the structures of the following compounds
a) 2 – bromo pentane
b) 2 – methyl propane
c) butanal
d) 1 – hexyne
Answer:
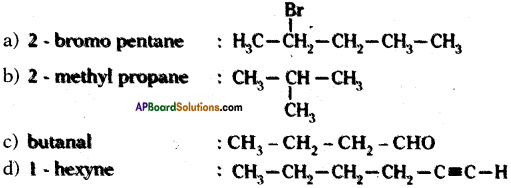
Question 30.
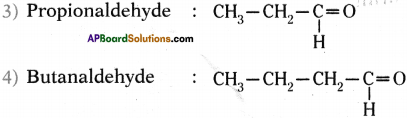
Write the molecular formula of the first four compounds of the homologous series of aldehydes.
Answer:
Homologous series of aldehydes ate Formaldehyde, Acetaldehyde, Propionaldehyde and Butanaldehyde.

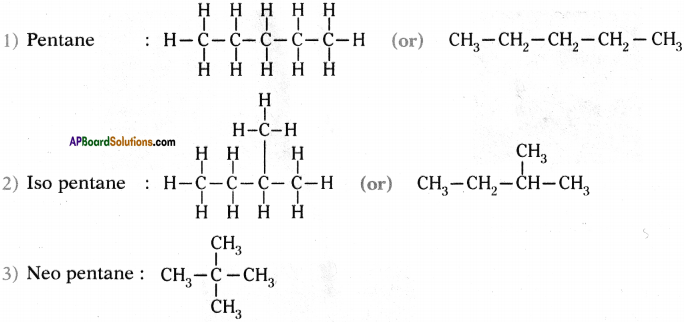
Question 31.
How many isomers can be drawn for pentane with molecular formula C-H(2? What are they? Draw their structures and mention theii common names.
Answer:
Isomers of pentane are three. These are
1) Pentane
2) Iso pentane
3) Neo pentane.
Structures :
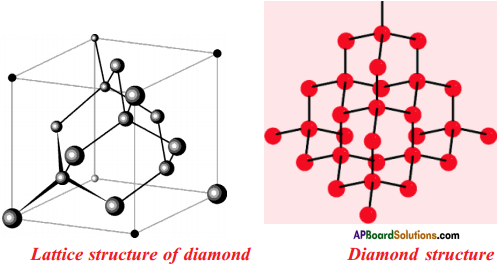
Question 32.
Draw the Allotropes of Carbon. Diamond
Answer:
Question 33.
Draw the Graphite.
Answer:
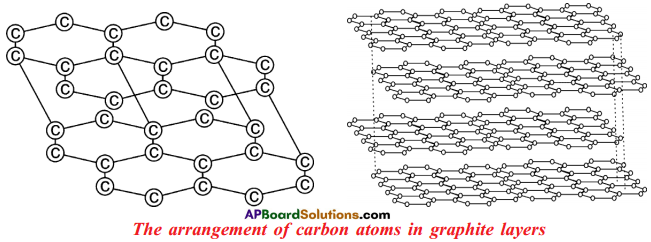
Question 34.
Draw the Buckminsterfullerene (60C).
Answer:
Question 35.
Draw the Nanotubes. A.
Answer:
Question 36.
Draw the structures of Methane :
Answer:
Methane :

Question 37.
Draw the structures of Ethyne :
Answer:
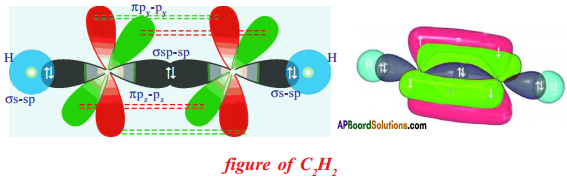
Question 38.
Draw structures of the Ethane and electron dot structure of Chlorine.
Answer:
Ethane:

Chlorine:
![]()
Question 39.
Draw the electron dot structures of Ethanoic acid arid Ethyne (Acetylene).
Answer:
Ethanoic acid (Acetic acid) :
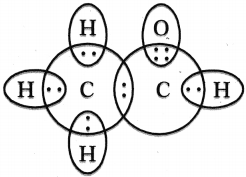
Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene) :

Question 40.
Draw the electronic dot structure of ethane molecule.
Answer:
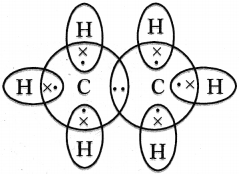
Question 41.
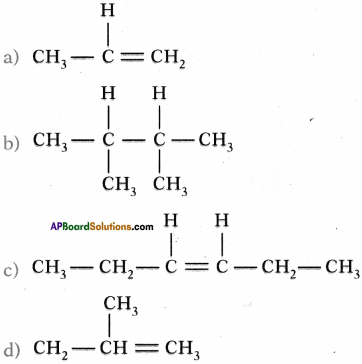
Write the structures of the following compounds.
a) prop-l-ene
b) 2, 3-dimethyl butane
c) 3-hexene
d) 2-methyl prop-l-ene
Answer:
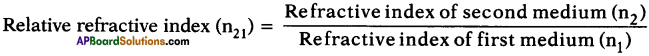

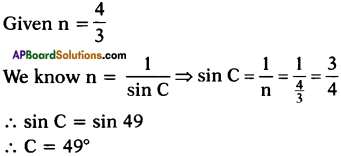
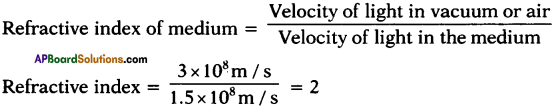
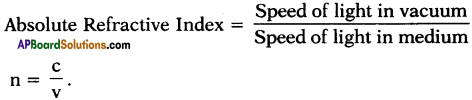



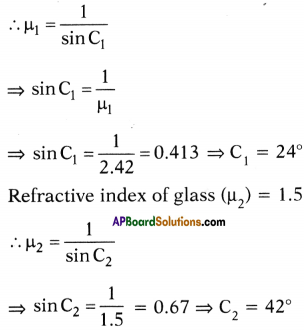
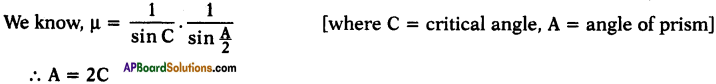
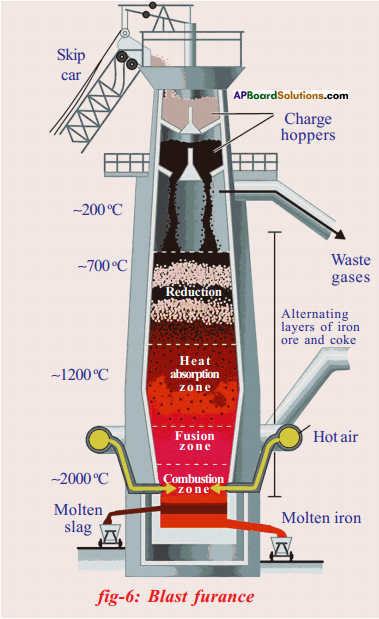
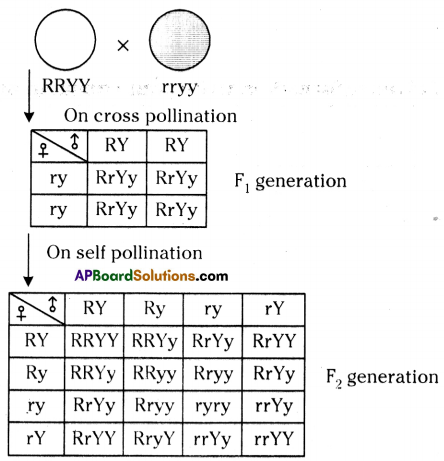

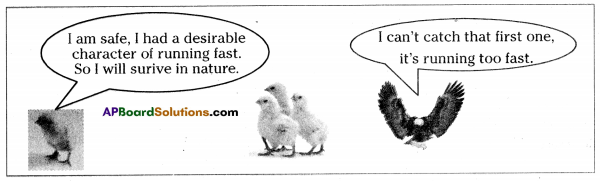

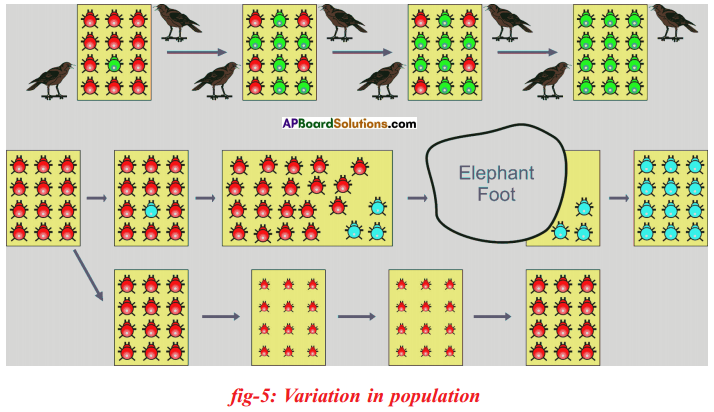 Let us consider a group of twelve beetles. They live in bushes on green leaves. Their population will grow by sexual reproduction. So they were able to generate variations in population. Let us assume crows eat these red beetles. If the crows eat more Red beetles, their population is slowly reduced. Let us discuss the above three different situations in detail.
Let us consider a group of twelve beetles. They live in bushes on green leaves. Their population will grow by sexual reproduction. So they were able to generate variations in population. Let us assume crows eat these red beetles. If the crows eat more Red beetles, their population is slowly reduced. Let us discuss the above three different situations in detail.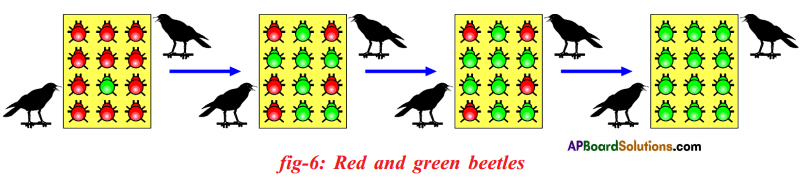 Moreover, this green coloured beetle passes its colour to Its offspring (Progeny). So that all its progeny are green. Crows cannot see the green coloured beetles on green leaves of the bushes and therefore crows cannot eat them. But crows can see the red beetles and eat them. As a result there are more and more green beetles than red ones which decrease in their number.
Moreover, this green coloured beetle passes its colour to Its offspring (Progeny). So that all its progeny are green. Crows cannot see the green coloured beetles on green leaves of the bushes and therefore crows cannot eat them. But crows can see the red beetles and eat them. As a result there are more and more green beetles than red ones which decrease in their number.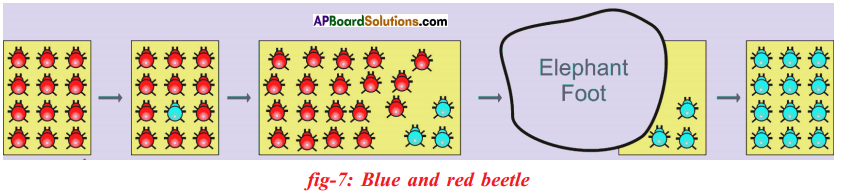 Crows can see blue coloured beetles on the green leaves of the bushes and the red ones as well. And therefore crows can eat both red and blue coloured beetles. In this case there is no survival advantage for blue coloured beetles as we have seen in case of green coloured beetles.
Crows can see blue coloured beetles on the green leaves of the bushes and the red ones as well. And therefore crows can eat both red and blue coloured beetles. In this case there is no survival advantage for blue coloured beetles as we have seen in case of green coloured beetles.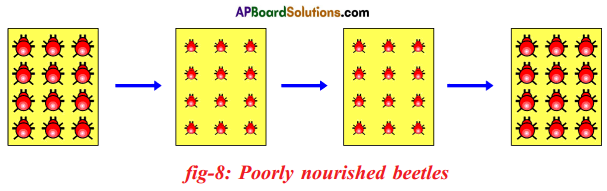 So beetles are poorly nourished. So the weight of beetles decrease but no changes take place in their genetic material (DNA). After a few years the plant disease are eliminated. Bushes are healthy with plenty of leaves.
So beetles are poorly nourished. So the weight of beetles decrease but no changes take place in their genetic material (DNA). After a few years the plant disease are eliminated. Bushes are healthy with plenty of leaves.
 Answer:
Answer: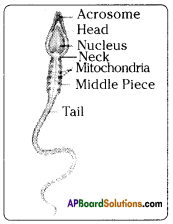
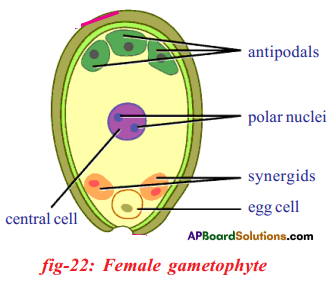
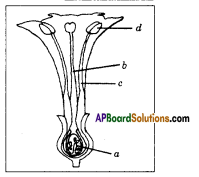
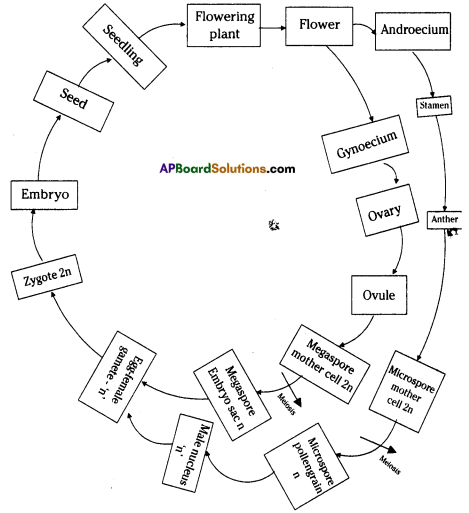
 i) Name male and female reproductive parts of the above figure.
i) Name male and female reproductive parts of the above figure.
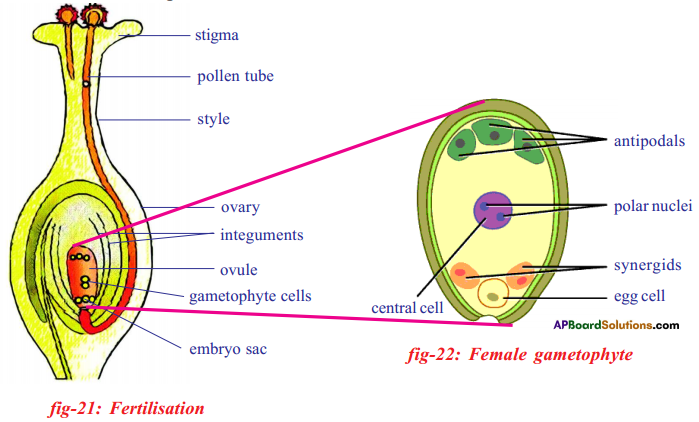
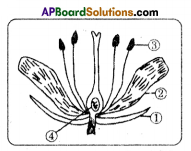
 i) What are the four main parts of a flower?
i) What are the four main parts of a flower?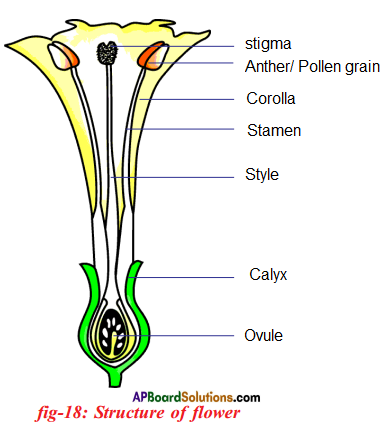 ii) A. Androecium or Stamen
ii) A. Androecium or Stamen
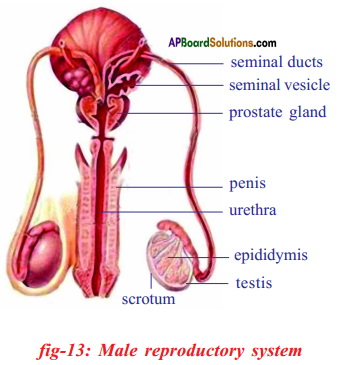 ii) The function of testosterone hormone is maintaining of secondary sexual chracters in males.
ii) The function of testosterone hormone is maintaining of secondary sexual chracters in males.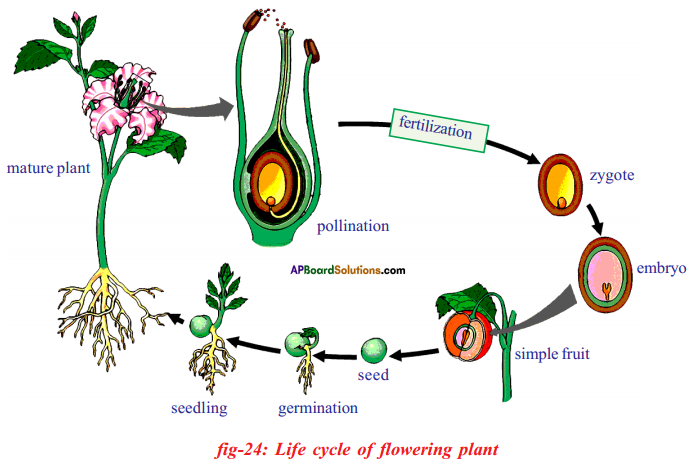
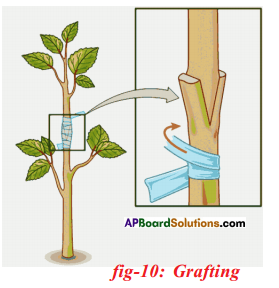
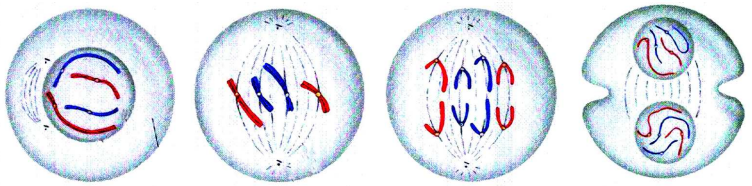 Answer:
Answer: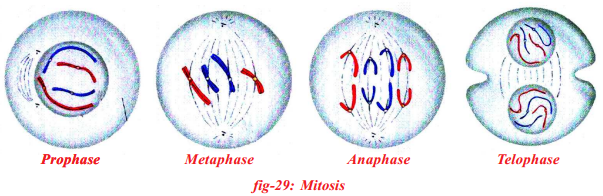
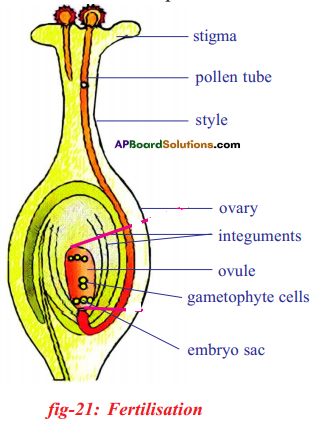
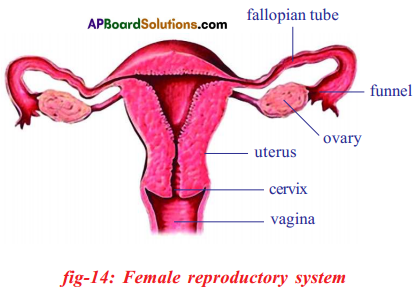 b) If fallopian tubes are closed the sperm can not reach the ova, fertilization will not happen and zygote will not form.
b) If fallopian tubes are closed the sperm can not reach the ova, fertilization will not happen and zygote will not form.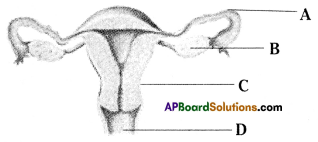
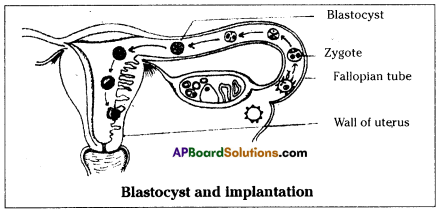
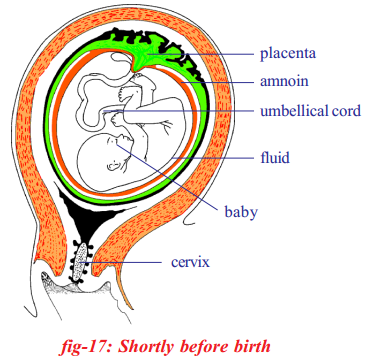
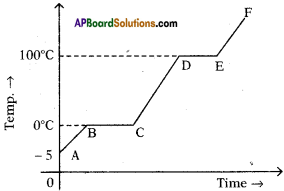










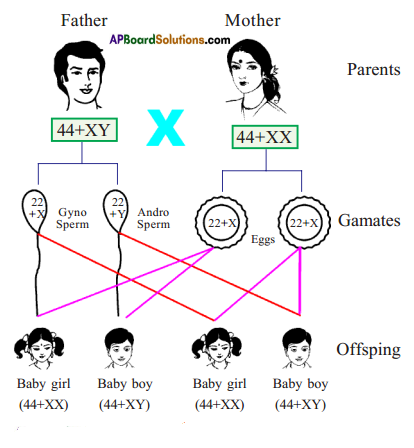
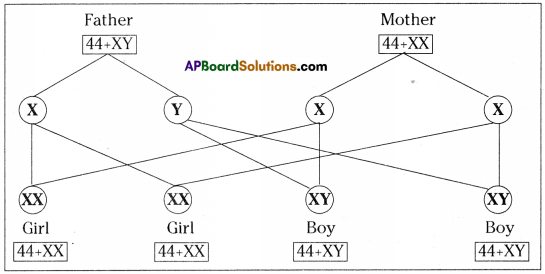
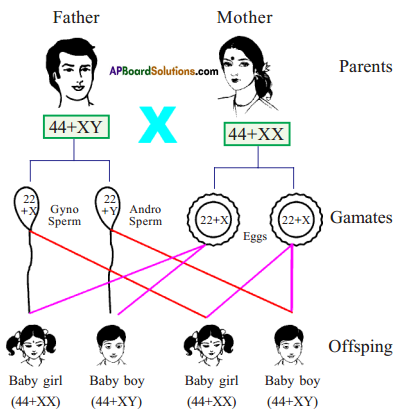
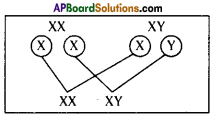 Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?
Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?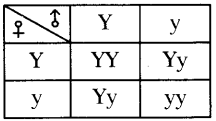 (OR)
(OR)

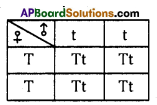
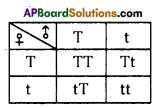
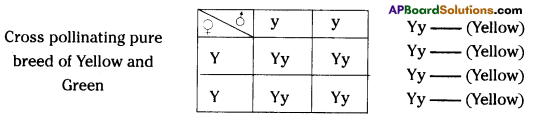
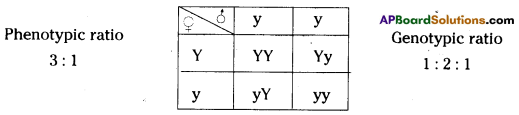
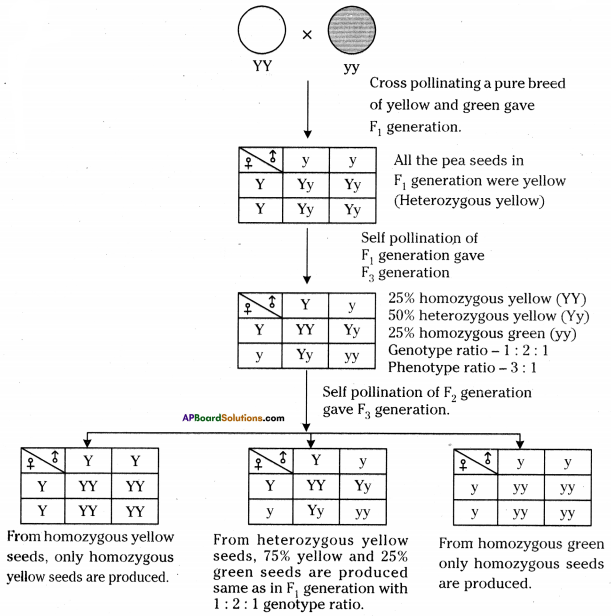
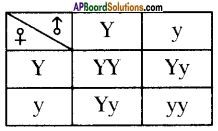 i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.
i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.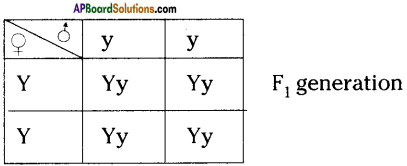 All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.
All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.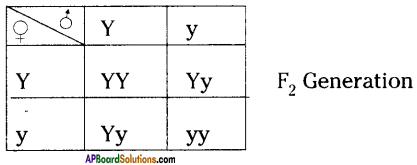 In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.
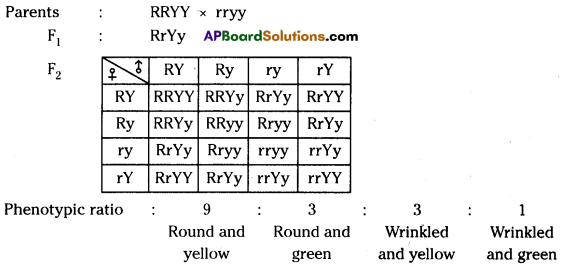
In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.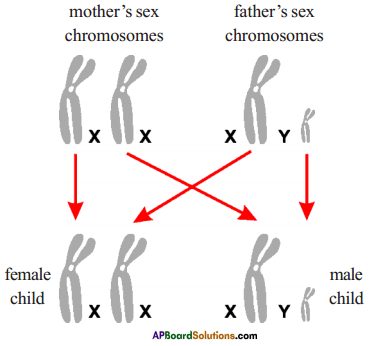 Answer:
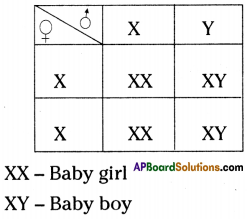
Answer: a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.
a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.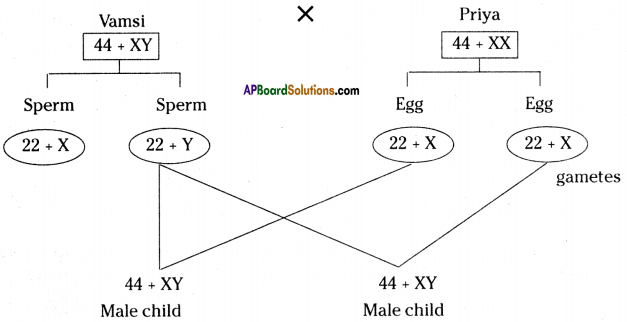 b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?
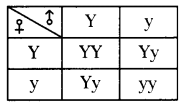
b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?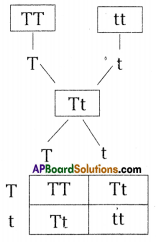 i) What does the flow – chart represent?
i) What does the flow – chart represent?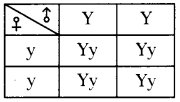
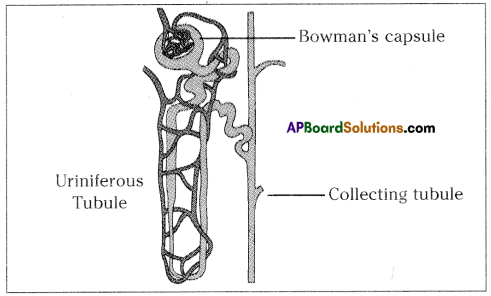
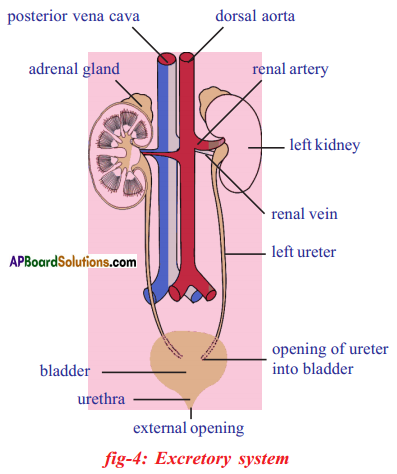
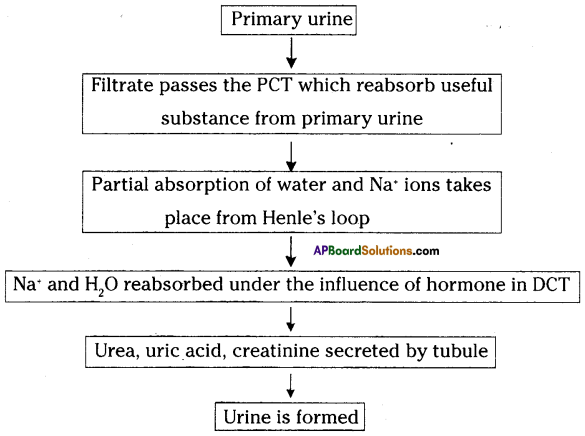
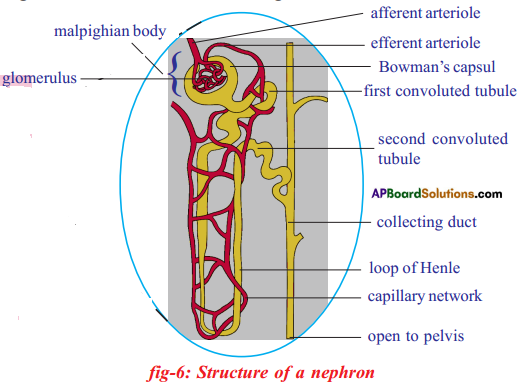
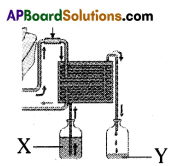 The above is a procedure of haemodialysis in a hospital.
The above is a procedure of haemodialysis in a hospital.