AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 8 Heredity.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions 8th Lesson Heredity
10th Class Biology 8th Lesson Heredity 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How did you get the characters from your parents and grandparents?
Answer:
By Genes
![]()
Question 2.
Why man is called a moving museum of vestigial organs?
Answer:
- The organs which are not useful in animals are called ‘vestigial organs’. There are nearly 180 vestigial organs in human beings,
- Hence, human being is said to be a moving museum of vestigial organs.
Question 3.
Observe the given Flow-chart and answer the question.
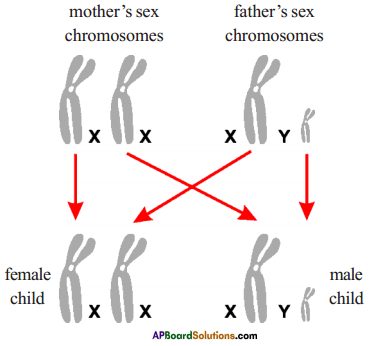
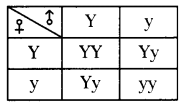
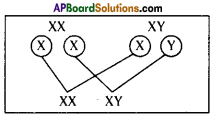 Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?
Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?
Answer:
Father decides the sex of the baby.
Mother has XX chromosomes. Father has ‘XY’ chromosomes. Y chromosome is determining factor. So father is responsible.
Question 4.
What examples you will give to prove that Lamarckism is not correct?
Answer:
August Weismann, tested the theory proposed by Lamarck by experiments on rats. He removed tails of parental rats. He observed for twenty two generations but still off springs are normal with tails.
Question 5.
Which chromosomes determine the sex in human beings?
Answer:
Allosomes or Sex chromosomes. They are xx (girls) and xy (boys).
![]()
Question 6.
Why do we call appendix as a vestigial organ?
Answer:
- Vestigial organ is the organ of our body which is smaller and simpler than those in related species they have lost their original function.
- Appendix is highly developed in ruminants which helps in the digestion of cellulose. But, in human beings the cellulose is eliminated as undigested food. Hence in human beings appendix has no role in cellulose digestion. So, we call it as a vestigial organ.
Question 7.
What are variations?
Answer:
Differences in characters within very closely related groups of organisms are referred to as variations.
Question 8.
Who is known as father of genetics?
Answer:
Gregor Johann Mendel is known as father of genetics.
Question 9.
Why Mendel has chosen garden pea plant as material for his experiments?
Answer:
Pea plant has following advantages.
- Well defined characters
- Bisexual flowers
- Predominently self fertilization
- Early hybridization
- Annual plant.
Question 10.
What are the vitamins present in pea plant?
Answer:
The vitamins present in pea plant are ‘A, C, E, K and B’.
Question 11.
What is F3 generation?
Answer:
F3 generation represents the offsprings produced from the individuals of F2 generation.
Question 12.
What is a factor?
Answer:
The determining agent responsible for each trait is called a factor.
Question 13.
WTiat is law of dominance?
Answer:
According to Mendel, among a pair of alleles for a character, only one expresses itself in the first generation as one of the allele is dominant over the other. This is known as law of dominance.
![]()
Question 14.
What is phenotype ratio?
Answer:
The characters which can be seen is known as phenotype and their ratio is called phenotype ratio.
Question 15.
What is the phenotype ratio in F1 generation of monohybrid cross?
Answer:
The phenotype ratio in F1 generation of monohybrid cross is 3 : 1.
Question 16.
What is genotype ratio?
Answer:
The genetic makeup of an individual with reference to a specific character under consideration is called genotype and their ratio is called genotype ratio.
Question 17.
What is the genotype ratio in F2 generation of monohybrid cross?
Answer:
The genotype ratio in F2 generation of monohybrid cross is 1 : 2 : 1.
Question 18.
What are genes?
Answer:
Genes are the factors which are responsible for characters or traits of an organism. These are the units of heredity that are transferred from a parent to offspring. These are small segments of DNA on a chromosome.
Question 19.
What is an allele?
Answer:
The pair of genes which are responsible for character is called allele.
Question 20.
What are homozygous alleles?
Answer:
If an organism has two copies of the same allele for example TT or tt it is homozygous for that trait.
Question 21.
What are heterozygous allele?
Answer:
If an organism has one copy of two different alleles for example Tt, then it is heterozygous.
![]()
Question 22.
What is law of independent assortment?
Answer:
In the inheritance of more than one pair of characters (traits), the factors for each pair of characters assorted independently of the other pair. This is known as “Law of independent assortment”.
Question 23.
Wliat is the law of segregation?
Answer:
The law of segregation states that every individual possesses a pair of alleles for any particular trait and that each parent passes a randomly selected copy of only one of these to its offspring.
Question 24.
What are heritable traits?
Answer:
Traits that may be passed on from one generation to the next are called as heritable traits.
Question 25.
What is heredity?
Answer:
The process of acquiring characters or traits from parents is called heredity.
Question 26.
What is inheritance?
Answer:
The process in which traits are passed from one generation to another generation is called inheritance.
Question 27.
What is genetic drift?
Answer:
Change in the frequency of genes in small populations is called genetic drift.
Question 28.
Who was the first person to propose the theory of evolution?
Answer:
Jean Baptist Lamarck was the first person to propose the theory of evolution.
Question 29.
What are acquired characters?
Answer:
The characters developed during the lifetime of an organism are called acquired characters.
![]()
Question 30.
What is inheritance of acquired characters?
Answer:
Lamarck proposed that the acquired characters are passed to its offsprings i.e., to next generation. This is known as inheritance of acquired characters.
Question 31.
Who wrote the book “principles of geology” of evolution?
Answer:
The book “principles of geology” of evolution was written by Charles Lyell.
Question 32.
What is micro evolution?
Answer:
Small changes within the species is known as micro evolution.
Question 33.
What is macro evolution or speciation?
Answer:
The process of evolution through which new species are going to be formed is known as speciation or macro evolution.
Question 34.
The double helix structure of DNA was discovered by?
Answer:
James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the double helix structure of DNA.
Question 35.
What are autosomes?
Answer:
Chromosomes whose number and morophology do not differ between males and females of a species are called autosomes.
Question 36.
What are allosomes?
Answer:
The chromosomes that determine sex of the organism are called allosomes.
Question 37.
What is meant by survival of the fittest?
Answer:
According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, nature only selects or decides which organism should survive or perish in nature. This is the meaning of survival of the fittest.
Question 38.
Write the expanded form of DNA.
Answer:
The expanded form of DNA is Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid.
![]()
Question 39.
What is the basis of evolution?
Answer:
Selection of variants by environmental factors forms the basis of evolution.
Question 40.
What are analogous organs?
Answer:
The organs which have similar appearance and functions but have different structure and origin. Ex : Wings of a butterfly, bat and a bird.
Question 41.
What is embryology?
Answer:
Embryology is the study of the development of an organism from egg to adult stage.
Question 42.
What is Palaeontology?
Answer:
The study of fossil is called Palaeontology.
Question 43.
How palaeontologists determine the age of fossil?
Answer:
Palaeontologists determine the age of fossil by using carbon dating method.
Question 44.
Where do scientists collected fossil of dinosaurs?
Answer:
Scientists collected fossils of dinosaurs from Yamanapalli in Adilabad district in Telangana State.
Question 45.
What are connecting links?
A. The organisms which bear the characters of two different groups are called connecting links.
Question 46.
Which organism is recognised as the connecting link between aves and reptiles?
Answer:
Archeopteryx is recognised as the connecting link between aves and reptiles.
Question 47.
What is human evolution?
Answer:
Human evolution is the evolutionary process leading upto the appearance of modern human beings.
![]()
Question 48.
How do variations occur?
Answer:
Variations develop during reproduction in organisms. Sexual reproduction and errors in DNA copying lead to variations in offspring in a population.
Question 49.
What is divergent evolution?
Answer:
The evolutionary process through which homologous organs develop is called divergent evolution.
Question 50.
What is convergent evolution?
Answer:
The evolutionary process through which analogous organs develop is called convergent evolution.
Question 51.
What are vestigial organs?
Answer:
Organs which are not useful in animal are called vestigial organs.
Question 52.
Who proposed the theory of inheritance of acquired characters?
Answer:
Jean Baptist Lamarck proposed the theory of inheritance of acquired characters.
Question 53.
Who proved that the bodily changes which may occur due to environment won’t be passed to its offsprings?
Answer:
Augustus Weisemann proved that the bodily changes which may occur due to environment won’t be passed to its offsprings.
Question 54.
How the study of fossil is considered significant?
Answer:
The study of fossil is considered significant because
- Fossils provide direct evidence of past life and
- Fossils provide convincing proof of organic evolution.
Question 55.
What are the nitrogen bases present in DNA?
Answer:
The nitrogen bases present in DNA are adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine.
![]()
Question 56.
How do embryological studies provide evidence for evolution?
Answer:
The similarities in embryonic development reinforce the idea of evolution from common ancestors. The sequence of embryonic development in different vertebrates shows similarities.
Question 57.
Why Mendel selected garden pea plant for his experiments? Give a reason.
Answer:
Mendel selected garden pea plant for his experiments as these can be self pollinated.
Question 58.
What is the evolutionary significance of the fossil archaeopteryx?
Answer:
Archaeopteryx serves as a connecting link between birds and reptiles. It is the fossil evidence to show that birds have evolved from reptiles.
Question 59.
How does the creation of variation in a species ensure survival?
Answer:
The creation of variations in a species enable them to adapt according to the changes and the new needs thus they will enable the survival of the species.
Question 60.
Define evolution.
Answer:
Evolution is the sequence of gradual changes which takes place in the primitive organisms over millions of years in which new species are produced.
10th Class Biology 8th Lesson Heredity 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
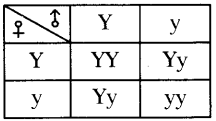
Question 1.
Write Phenotypic and Genotypic ratio of table given at side.
 (OR)
(OR)
Write the Phenotypic and Genotypic ratio when heterogygous (Yy) pea plant is hybridised with the same kind of plant.
(OR)
Write the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of Mendel’s cross-pollination experiments in pea plants with heterozygous yellow seeds (Yy) with that of the same type, i.e., Yy.
Answer:
Phenotypic ratio -3:1
Genotypic ratio -1:2:1
![]()
Question 2.
Define and explain Variations with examples.
Answer:
Variations: Differences in characters within very closely related groups of organisms are referred to as variations.
(OR)
Differences among living beings are called variations.
Ex:
- Earlobes in some humans are free and in others attached.
- Colour of eyes (cornea) in some people are blue and in others black.
- Colour of skin is black or white.
Question 3.
“Human being is said to be a moving museum of vestigial organs”. How can you support this statement?
Answer:
- During the course of evolution, some organs remain in organisms. For example, appendix in the digestive system.
- In human beings it has no role to play in the process of digestion.
- But in herbivores like rabbit appendix play important role.
- Such type of organs which are not useful in animal are called vestigial organs.
- There are nearly 18 vestigial organs in human beings.
- For example pinna, hair on skin, mammary glands in man, etc.
- That’s why human being is said to be a moving museum of vestigial organs.
Question 4.
Fill the given table and write the genotypic ratio basing on table.

Answer:

The genotypic ratio is 1: 2: 1
![]()
Question 5.
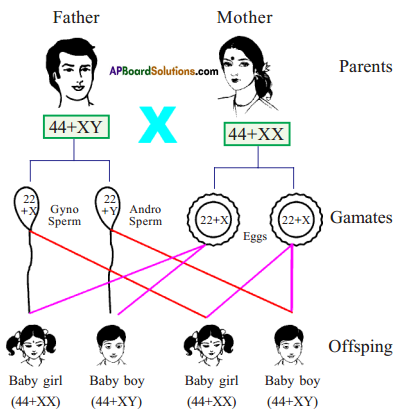
Who decides the sex of the baby, mother or father? Explain with a flow chart.
(OR)
Draw a flow-chart showing the sex determination in human beings.
Answer:
Father decides the sex of the baby.
Question 6.
Define the terms phenotype and genotype.
Answer:
Phenotype: The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype and the environment. These characters can be seen.
Genotype: The genotype is the genetic make-up an individual usually with reference to a specific characteristic consideration.
Question 7.
What questions you will ask a palaeontologist about fossils?
Answer:
- What are fossils?
- How do they preserve?
- What can be the actual remains?
- How do they form?
- What do we call the study of fossil?
- Can you tell some examples of fossils?
- How do the palaeontologists determine the age of fossils?
- What are dinosaurs and ketosaurs? In which years they belong?
- Where did they collect the fossil of dinosaurs? What is the length of this fossil?
- Where did they preserve the fossil of dinosaurs?
![]()
Question 8.
How does the embryological evidences support that Evolution has taken place?
Answer:
Evidences:
- Remarkable similarities in the Embryos of different animals from fish to man.
- Tadpole of frog resembles the fish more than the frog.
- Life history of every individual exhibits the structural features of their ancestors.
- The resemblance is so close at an early stage, it is difficulty to distinguish one embryo from other.
Question 9.
Observe the checker board and answer the following questions.
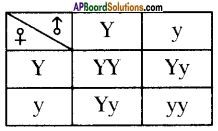 i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.
i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.
ii) How many heterozygous plants are present in the checker board?
Answer:
i) Phenotypic ratio 3 : 1
ii) Two heterozygous plants – (Yy, yY)
Question 10.
What happens if there is no evolution?
Answer:
- Evolution is a continuous and comprehensive process.
- If it does not take place, there is no formation of new species.
- Variations do not take place and hence desirable traits are not developed.
- All the Earth would be with the primitive species without any changes.
Question 11.
If you cross a plant with pure yellow seeds (YY) with a plant with pure green seeds (yy), what would be the colour of the seeds in F2 generation? Show in a checker board.
Answer:
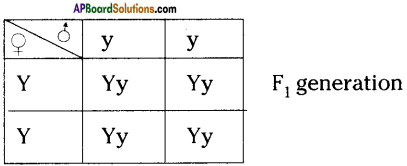 All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.
All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.
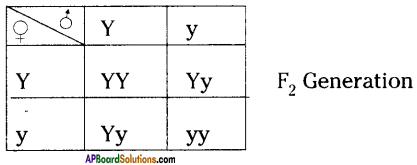 In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.
In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.
Hence the phenotypic ratio is 3 : 1 the genotypic ratio is 1 : 2 : 1
![]()
Question 12.
If you meet a historian to clarify your doubt on ‘Man has first born in African conti¬nent’, what type of questions will you ask him / her?
Answer:
- What is human evolution?
- When were early man like forms appeared on land?
- When did the fossil of the homosapiens appeared on earth?
- Where did the early man lived?
- Where can we trace the earliest members of the human race homosapiens?
- When do some of our ancestors left Africa?
- How the residents of Africa migrated to other places?
- Why did the residents of Africa migrated to other places?
- Are all humans evolved from single ancestor?
Question 13.
What is the difference between Phenotype and Genotype?
Answer:
| Phenotype | Genotype |
| 1. The characters which can be seen is known as phenotype. | 1. The genetic make up of an individual is known as genotype. |
| 2. We can’t determine the internal factors by phenotype. | 2. Genotype itself is the indication of internal factors. |
| 3. It tells about only the dominating characters which express externally. | 3. It tells about both dominant and recessive characters present within. |
| 4. The phenotype ratio in monohybrid cross is 3 : 1. | 4. The genotype ratio in mono-hybrid cross is 1 :2 : 1. |
Question 14.
What are the differences between homozygous and heterozygous ?
Answer:
| Homozygous | Heterozygous |
| 1. It refers to having two identical alleles for a single trait. | 1. It refers to having two different alleles for a single trait. |
| 2. For example, for long pea plant homozygous combination is ‘TT’ | 2. For example, for long pea plant heterozygous combination is ‘Tt’ |
| 3. On self pollination homozygous plants produce homozygous plants only. | 3. On self pollination heterozygous plants produce homozygous dominant, heterozygous dominant and homozygous recessive plants in 1: 2 :1 ratio respectively. |
![]()
Question 15.
How do traits get expressed according to Mendel?
Answer:
- Mendel hypothesised that each character or trait is expressed due to a pair of factors or alleles.
- Now these alleles are known as genes.
- Gene is made up of a segment of DNA which provide information of protein.
- Protein is needed for biochemical process.
- If the proteins work efficiently, the traits get expressed in better way.
- Thus genes control the traits or characters.
Question 16.
What is speciation? How it occurs?
Answer:
- Origin of new species from existing one is called speciation.
- It may occur due to a) mutations and b) natural selection.
Question 17.
What is sex chromosome? Name the two types of sex chromosomes. Mention the chromosomes present in male and female?
Answer:
- The chromosome which determine the sex of a person is called sex chromosome.
- The two types of sex chromosomes are X chromosome and Y chromosome.
- Sex chromosomes in male is XY.
- Sex chromosomes in female is XX.
Question 18.
Write a short notes on the law of “inheritance of acquired characters”.
Answer:
- Law of inheritance of acquired characters was proposed by Jean Baptist Lamarck.
- He thought that the characters acquired by an organism in its life time are passed to its offsprings.
- He thought that at same point of time in the history, the size of giraffe was equal to that of deer.
- Due to shortage of food material on the ground and lower branches of trees giraffes started stretching their necks.
- Because of continuous usage of neck, after several generations giraffes obtained longer necks.
- Such characters that are developed during the lifetime of an organism are called acquired characters.
![]()
Question 19.
Write a short notes on the theory of “Natural selection”.
Answer:
- The theory of natural selection was proposed by Charles Darwin.
- This theory states that nature only selects or decides which organism should survive or perish in nature.
- The organisms with useful traits will survive.
- The organisms having harmful traits are going to be perished or eliminated from its environment.
Question 20.
Write briefly about “Survival of the fittest”.
Answer:
- Variations which are useful are retained, while those which are harmful are removed.
- In a population where there is a struggle, the “fittest” will be survived.
- Nature favours only useful variations.
- Each species tends to produce large number of offspring.
- They compete with each other for food, space, mating and other species.
- In this struggle for existence, only the fittest can survive. This is called survival of the fittest.
- Over long period of time this leads to formation of new species.
Question 21.
How are new species evolved?
Answer:
- Sexual reproduction and errors in DNA copying leads to variations in offspring in a population.
- Organisms contain variations that help to adapt to its environment going to be survived more efficiently.
- But in the same population, the organisms which contain the trait which may not help to adapt in its environment may be perished or eliminated slowly.
- These small changes within the population due to variations is called micro evolution.
- When organisms of the same species with variations are separated by some cause for long years, lot of variations may take place in these species.
- These accumulated variations make them unable to mate and produce new offsprings.
- Thus new species form and this is known as speciation or macro evolution.
![]()
Question 22.
Write a brief note on homologous organs.
Answer:
- Homologous organs are the organs which perform different functions but have similar structure and origin.
- For example forelimb of a whale (swimmer), bat (flyer), horse (runner), mole (digger) and man (grasping).
- If we carefully observe the anatomy of all these animals, they have a common pattern in the arrangement of bones.
- Even though their external form and functions are different, they are similar internally.
- Thus it indicates that all the vertebrates have evolved from a common ancestor.
Question 23.
What are fossils? Write a short note on their formation.
Answer:
- Fossils are evidence of ancient life forms or ancient habitats which have been preserved by natural processes.
- Fossil evidence is typically preserved within sediments deposited beneath water and land.
- They can be actual remains of once lived such as bones or seeds or even traces of past event such as dinosaurs foot print or ripple marks on a pre-historic shore.
- Usually when organisms die, their bodies will be decomposed and lost.
- But sometimes the body or at least some parts may be in an environment that does not let it decompose completely.
- For example if a dead insect get caught in mud, it will not decompose quickly and the mud will eventually harden and retain the impression of the body parts of insect.
- All such preserved traces of living organisms are called fossils.
Question 24.
How would you appreciate Jean Baptist Lamarck for his contribution to the biology?
Answer:
- Jean Baptist Lamarck was the first person to propose the theory of evolution.
- He proposed that the acquired characters are passed to its offspring i.e., to next generation.
- This is known as inheritance of acquired characters.
- For example elongation of neck and forelimbs in giraffe.
- Even though this theory was disproved, his contribution to biology was appreciable because it changed the belief of the people of olden days that the organisms on the earth have not undergone any change.
![]()
Question 25.
How did August Weisemann disprove the theory of “Inheritance of acquired characters” proposed by Lamarck? (OR)
What example will you give to prove that Lamarckism is not correct?
Answer:
- August Weisemann, tested the theory of “Inheritance of acquired characters” proposed by Lamarck by an experiment on rats.
- He removed tails of parental rats.
- He observed its offsprings which have normal tails.
- He has done it again for twenty two generations but still offsprings are normal with tails.
- He proved that the bodily changes are not inherited. So they won’t be passed to its offspring.
- Thus he disproved the theory of “Inheritance of acquired characters”.
Question 26.
Some organisms or species adapt better and survive in a community of organisms. Why do you think this may happen?
Answer:
- This may happen due to the variations posessed by the organisms which are suitable to that habitat.
- The variations that help the organism to collect food to escape from their enemies, increase the chance of survival for the organism than the other organisms.
- In general, variations come during sexual reproduction or mutation.
- If the variations are useful, that organisms can adapt better and survive.
- These organisms can be selected by the nature.
![]()
Question 27.
What do you understand about pure breeds?
Answer:
- Pure breed is that expresses the selected character over several generations.
- A pure breed will have both the factors of the same type.
- It means all the pure breeds are homozygous.
- All the gamates produced by them will have same type of factor.
- Pure breed on self pollination will give pure breed again.
Question 28.
What do you understand about F1 generation?
Answer:
- F1 generation or first filial is the offspring of first generation parents.
- Cross pollination of pure breeds will give F1 generation.
- All the individuals produced in F1 generation are heterozygous.
- Only the dominant characters are expressed in this generation.
Question 29.
What are the differences between F1 generation and F2 generation of mono hybrid cross?
Answer:
| F1 generation | F2 generation |
| 1) F1 generation or first filial is the offspring of first generation parents.
2) Cross pollination of pure breeds will give F1 generation. 3) All the individuals produced in F1 generation are heterozygous. 4) Only the dominant characters are expressed in this generation. 5) All the individuals produced in F1 generation are same, both phenotypically or genotypically. |
1) F2 generation is the offspring of second generation parents.
2) Self or cross-pollination of F1 generation will give F2 generation. 3) Individuals produced in F2 generation may be homozygous or heterozygous. 4) Homozygous recessive plants express recessive characters. 5) In F2 generation individuals, the phenotype ratio is 3:1 and the genotype ratio is 1 : 2 : 1. |
![]()
Question 30.
What are the differences between monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross ?
Answer:
| Monohybrid cross | Dihybrid cross |
| 1) In monohybrid cross only one pair of contrasting characters are taken into consideration.
2) In monohybrid cross, the phenotype ratio of F2 generation individuals is 3:1. 3) In monohybrid cross, the genotype ratio of F2 generation individuals is 1:2:1. |
1) In dihybrid cross two pairs of contrasting characters are taken into consideration.
2) In dihybrid cross, the phenotype ratio of F2 generation individual is 1:2: 1. 3) In dihybrid cross, the genotype ratio of F2 generation individuals is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. |
Question 31.
Write a short note on fossils of dinosaurs, ketosaurs collected in Telangana state.
Answer:
- A rare and magnificient fossil of the dinosaurs, ketosaurs were collected in Yamanapalli in Adilabad district of Telangana district.
- They belong to the lower jurassic age going back to about 160 million years.
- This fossil has 14 meters length and 5 meters height.
- This fossil is preserved in BM Birla Science Centre. Hyderabad.
Question 32.
Write a short notes on vestigial organs.
Answer:
- During the course of evolution some organs remain in organisms, even though they don’t have any work to do.
- For example appendix in the digestive system of human beings has no role to play in the process of digestion.
- But in herbivores like rabbit appendix plays important role.
- Such type of organs which are not useful in animal are called “vestigial organs”.
- There are nearly 180 vestigial organs in human beings such as pinna, hair on skin, mammary glands in human, etc.
- That’s why human being is said to be a moving museum of vestigial organs.
![]()
10th Class Biology 8th Lesson Heredity 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fossils are the precious evidences preserved by the nature to help us knowing about ancient life forms. Write the information you collected about fossils.
Answer:
- Fossils are the evidences of ancient life forms or ancient habitates which have been preserved by natural processes.
- Fossils provide information about what lived in the past.
- Palentologists determine the age of fossils by using carbon-dating method.
- They convey us about genetic condition, heredity characters through inactive chromosomes which are present in them.
- They give a detailed information about their diet, life styles, shape of body, etc.
- Fossils provide the information about how species have changed across long periods of the earth history.
![]()
Question 2.
a) If a sperm with ‘X’ chromosome fertilizes with an ovum with ‘X’ chromosome, what will be the gender of the baby?
b) Who determines the sex/gender of the baby, mother or father?
c) Is it correct to blame the mother for giving birth to a baby girl?
d) Are all our characters resembles our parents?
 Answer:
Answer:
a) Female
b) Father
c) Not correct
d) No, some variations occur.
Question 3.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions. Vamsi and Priya are newly married couple. They want to give birth to a male child.
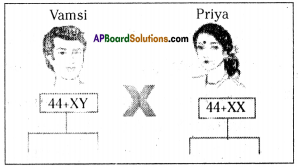 a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.
a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.
Answer:
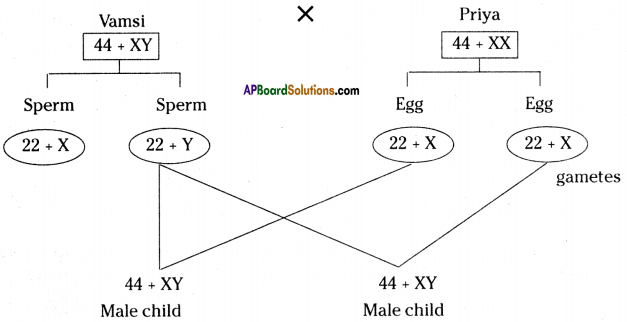 b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?
b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?
Answer:
Father (Vamsi) determines the sex of the baby. Because the chromosome ‘Y’ that determines male sex is present in males.
![]()
Question 4.


i) What does the given flow chart indicate?
Answer:
Sex determination in human beings
ii) What will happen if the sperm containing ‘X’ chromosomes fertilises the ovum?
Answer:
Baby will be a girl
iii) Who decides the sex of the baby – Mother or Father?
Answer:
Father
iv) How many pairs of chromosomes are present in off-spring?
Answer:
23 pairs
![]()
Question 5.
Write a brief note on Homologous and Analogous organs.
Answer:
Homologous organs: Organs which are structurally similar but functionally different are known as “Homologous organs”.
Forelimbs of a whale – swimming
Wings of a bat – flying
Forelegs of cheetah – running
Analogous: Organs which are structurally different but functionally similar are known as “Analogous organs”.
Eg : Wings of a bird – flying
Wings of a bat – flying
Question 6.
Observe the flow – chart and answer the following.
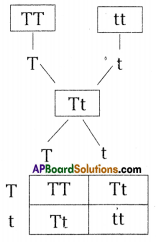 i) What does the flow – chart represent?
i) What does the flow – chart represent?
Answer:
The flow – chart represents a monohybrid hybridisation between a pure breed Tall (T) and a pure breed dwarf (t) plants resulting first filial generation. On self pollinating with F1 generation the new breed have any combinations of T, t came in F2 generation.
ii) What is the phenotype characters in F1 generation?
Answer:
In the phenotypic characters in F1 generation all are dominant that is (T) Tall,
iii) What is the Genotype, Phenotype ratio of F2 generation?
Answer:
Genotype ratio in F2 generation is 1 : 2 : 1
Phenotype ratio in F2 generation is 3 : 1
iv) What laws of inheritance did you understand by this flow – chart?
Answer:
understand that i) the law of dominance ii) law of segregation proposed by Mendel.
![]()
Question 7.
Write the Darwin’s theory of evolution in a nutshell.
Answer:
- Any group of population of an organism has variations and all members of group are not identical.
- Variations maybe passed from parent to offspring through heredity.
- The natural selection over abundance of offspring leads to a constant struggle for their survival in any population.
- Individuals with variations that help them to survive and reproduce tend to live longer and have more offsprings than organisms with less useful features.
- The offsprings of survivors inherit the useful variations, and the same process happens with every new generation until the variation becomes a common feature.
- As the environment changes, the organism within the environment adapt and changes to the new living conditions.
- Over a long period of time, each species of organism can accumulate so many changes that it becomes a new species, similar to but distinctly different from the original species. All species on the earth arise in this way.
- Evolution is a slow and continuous process that involves several thousands of generations.
Question 8.
What are Mendel’s laws of inheritance? What are the reasons to choose pea plant for his experiment?
Answer:
Mendel’s Laws of inheritance:
- Law of Dominance : Among a pair of closely related ‘alleles’ or factors, only one expresses itself. In the first generation as one of the allele is dominant over the other. This is called as Mendel’s Law of dominance.
- Law of Segregation : The law of segregation states that every individual possesses a pair of alleles for any particular trait that each parent posses a randomly selected copy only one of these to its off-spring.
- Law of Independent assortment : In the inheritance of more than one pair of characters (traits), the factors for each pair of characters assort independently of the other pairs. This is known as ‘Law of Independent assortment’.
Mendel has chosen garden pea as material for his experiment because:
- It has well developed characters.
- It is a bisexual flower.
- Predominently self pollinating.
- Suitable for cross pollination.
- It is an annual plant.
![]()
Question 9.
What is Phenotype and Genotype? Explain them with the help of Mendel’s Monohybrid cross.
Answer:
Phenotype: Expression of visible character of an individual is called phenotype.
Genotype: Genetic constitution of an individual for any character is called Genotype or Probable nature of factors is known as genotype.
Cross Pollinating a pure breed of yellow coloured pea seeds (YY) and green coloured pea seeds (yy) give F1 generation. All pea seeds were yellow in F1 generation. So, yellow colour is phenotype. ‘Yy’ is genotype of all pea seeds in F1 generation.
F2 Generation : Self pollination of F1 pea plants (Yy)
Phenotype Ratio is 3:1 Genotype Ratio is 1:2:1.
Question 10.
Explain in brief any two evidences of Evolution.
Answer:
Some of the evidences of evolution are
- Homologous and analogous organs
- Evidences from embryology and
- Evidences from fossils.
I. Homologous and analogous organs :
- Organs which have common fundamental anatomical plan and similar embryonic origin, whatever varied functions they may perform are regarded as homologous organs.
- For example forelimb of a whale, wing of bat, leg of leopord, claw of mole and hand of man.
- They indicate that all the vertebrates are evolved from common ancestor.
- Organs which are structurally different but functionally similar are known as “Analogous organs”.
- For example wings of bats and wings of birds.
- The designs of the two wings, their structure and components are different but they look similar because they have a common use for flying but their origin is not common.
II. Evidences from embryology:
- There are remarkable similarities in the embryos of different animals from fish to man.
- The resemblance is so close that at an early stage even an experienced embryologist would find difficulty to distinguish one embryo from the other.
- This strengthens the view of the existence of a common ancestor from which all these have evolved.
III. Evidences from fossils:
- Fossils are evidences of ancient life forms or ancient habitats which have been preserved by natural processes.
- Palaeontologists determine the age of fossils by using carbon dating method.
- These fossils provide evidences of presence of extinct animals like dinosaurs and how the evolution occurred on the earth, etc.
![]()
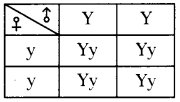
Question 11.
Observe the given flow-chart and answer the following questions:


i) Name the chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual.
Answer:
Y Chromosome of father.
ii) Show given information in the form of Checker Board.
Answer:
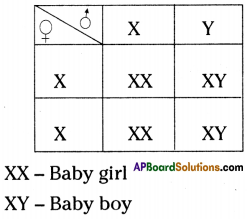
iii) In this situation, which principle of Mendel is applicable?
Answer:
Law of dominance
iv) “Mother determines the sex of the baby”. Is this statement correct or not? Why?
Answer:
The statement is not correct. Because the sperm of father that carries Y chromosome fertilize with ovum of mother that contains X chromosome the resultant will be XY – Male baby.
![]()
Question 12.
Keep in mind Mendel’s experiments and write what you know about the following concepts?
a) Pure breed b) Phenotype c) Genotype d) Alleles
Answer:
a) Pure breed: These are the plants that expresses a selected character over several generations. Such plants according to Mendel were pure breed for that character.
b) Phenotype: The characters which can be seen is known as phenotype. We cannot determine the internal factors by phenotype. It tells about only the dominating char-acters which express externally. The phenotype ratio in monohybrid cross is 3 : 1.
c) Genotype: The genetic make up of an individual is known as genotype. Genotype itself is the indication of internal factors. It tells about both dominant and recessive characters present within. The genotype ratio in monohybrid cross is 1 : 2: 1.
d) Alleles: Alleles are corresponding pairs of genes located at specific positions in chromosomes. Together they determine the genotype of their host organism. Every individual possesses a pair of alleles for any particular trait and that each parent passes a rondomly selected copy of only one of these to an offspring. The offspring then receives its own pair of alleles for that trait one each from both parents.
Question 13.
Competition among organisms, variations, natural selection survival of the fittest.
Which theory explains all these aspects? Describe them in a orderly manner.
Answer:
- Competition: Every living organism in this world reproduces itself. The rate of multiplication and existence of organisms are more or less common for all living things. But the food supply and space remain unchanged, in other words they are limited. Under these conditions, there is a competition among the organisms to fulfil their needs of food and space. This is known as struggle for existence. It may be interspecific, intraspecific and the environment factors.
- Variations: Every organism has its own specific characteristic and relationship with its environment. The variability caused by variations may be large or small. Large variations are known as macro variation and small variations called micro variations. Variations may be favourable or harmful. Those with useful variations survive while the others perish.
- Natural selection: The organism with favourable variations are best adapted to the environment in which they live. They have a better chance of survival and perpetuation of race. This principle is called natural selections.
- Survival of the fittest: Variations which are useful are retained, while those are harmful are lost. In a population where there is a struggle, the fittest will be survived and the less adjusted will be perished. This is known as the elimination of the unfit.
![]()
Question 14.
What is genetic drift? Explain how it provides diversity in the population.
Answer:
- Changes in the frequency of genes in small populations, due to accidents is known as “Genetic drift”.’
- Let us consider a colour variation occurred in red colour beetles which are living on green coloured leaves of bushes.
- It results in “blue” colour beetles instead of ‘red’ colour beetles and passed its colour to its progeny.
- Initially in the population, there are few blue beetles, but most are red.
- Imagine at this point, an elephant comes by and stamps on the bushes where the beetles live.
- This kills most of the beetles but by chance a few beetles survived are mostly blue.
- Again the beetle population slowly increases, but in the beetle population most of them are in blue colour.
- Thus genetic drift provides diversity in the population.
Question 15.
Have the apparent groups of human beings (races) evolved differently?
Answer:
- No, there is no biological basis to the notion of human races. All humans are a single species.
- Regardless of where we have lived for the past few thousand years, we all came from Africa.
- The earliest members of human species, Homosapiens, can be traced there.
- Our genetic footprints can be traced back to our African roots.
- A couple of hundred thousand years ago, some of our ancestors left Africa while others stayed on.
- While the residents spread across Africa, the migrants slowly spread across the planet.
- They did not go in a single line. They went forwards and backwards, with groups, sometimes separating from each other, even moving in and out of Africa.
- Like all other species on planet, they had come into being as an accident of evolution, and were trying to live their lives the best they could.
Question 16.
How would you appreciate Gregor Johann Mendel’s contribution to the genetics?
(OR)
Why Gregor Johann Mendel is considered as the father of genetics?
Answer:
- Gregor Johann Mendel worked on the problem of how variations were passed from one generation to the other.
- As he was a monk, he did his experiments with interest in the garden of the monastery.
- He worked for over seven years after which he presented conclusions from his experimental data in a form of a detailed research paper.
- Mendel made many careful observations of pea plants and asked himself questions about what he observed and then planned and designed experiments to find the answers.
- He had worked on nearly 10,000 pea plants of 34 different varieties choosing 7 distinguishing forms of characters.
- His experimental outcomes gave the idea how the variations were passed on from one generation to another.
- He was an exemplary person for his observation, planning, patience and experimental skills.
- His efforts to know the secrets of nature was really appreciable.
![]()
Question 17.
What are the hypothesis assumptions and outcomes of Mendel’s experiments with pea plants?
Answer:
Regarding his experiments with pea plants, Mendel hypothesised that
- Characters were carried as traits and an organism always carried a pair of factors for a character.
- The distinguishing traits of the same character were present in the population of an organism.
- The traits shown by the pea plants must be in the seeds that produced them.
- The seeds must have obtained by the traits from the parent plants.
His assumptions made to explain his observations are:
Assumption 1: Every pea plant has two ‘factors’ which are responsible for producing a particular property or trait.
Assumption 2: During reproduction one ‘factor’ from each parent is taken to form a new pair in the progeny.
Assumption 3: One of these will always dominate the other if mixed together.
Laws made from his experiments:
- Law of Dominance: Among a pair of alleles for a character, only one expresses itself in the first generation as one of the allele is dominant over the other.
- Law of Segregation: Every individual possesses a pair of alleles for any particular trait and that each parent passes a randomly selected copy of only one of these to its offspring.
- Law of Independent Assortment: In the inheritance of more than one pair of characters the factors for each pair of characters assorts independently of the other pairs.
![]()