AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Biology Solutions Chapter 7 Coordination in Life Processes Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Biology Solutions 7th Lesson Coordination in Life Processes
10th Class Biology 7th Lesson Coordination in Life Processes Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve your learning
Question 1.
What do you mean by hunger pangs?
Answer:
- When glucose levels in the blood fall, hunger pangs occur in the stomach.
- Ghrelin hormone is secreted in the stomach when it goes empty.
- Ghrelin is secreted from certain cell walls of the stomach.
- Hunger contractions (hunger pangs) start to occur in the stomach due to secretion of ghrelin hormone.
- Hunger pangs continue up to 30 – 45 minutes.
- An increase in Ghrelin levels results in sensation of hunger and motivation to consume food.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the organ systems involved in the digestion of food which we eat?
Answer:
The organ systems involved in the digestion of food are:
- endocrine system,
- nervous system,
- muscular system,
- circulatory system and
- excretory system.
Question 3.
Rafi said smell also increases our appetite. Can you support this statement ? How?
Answer:
- Yes. I support the statement made by Rafi that smell also increases our appetite.
- When we smell, the air borne substances get dissolved in the watery film of nasal mucus.
- The chemoreceptors which are otherwise called olfactory receptors present in the nose trigger signals in the form of nerve impulses to the brain where the smell is detected.
- However interactions between the senses of taste and smell enhance our appetite.
Question 4.
Write a note on peristalsis and sphincter function in the stomach.
Answer:
A) Peristalsis functions in stomach:
- Contraction and relaxation of the muscles present in the stomach bring in a wave-like motion called peristalsis.
- The contraction of the stomach muscles squeeze and mix the food with the acids and juices of the stomach.
- Mechanical mixing of food in stomach occurs by peristalsis. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.
- Peristalsis in stomach is involuntary and under the control of the autonomous nervous system.
B) Sphincter functions in the stomach:
- Pyloric sphincter is present at the opening of the stomach into the duodenum (small intestine).
- The pyloric sphincter allows only small quantities of food into duodenum at a time.
![]()
Question 5.
Observe the given part of the digestive system. What is it ? What is it’s role during digestion ?
Answer:
- The given part is the LARGE INTESTINE in the human digestive system:
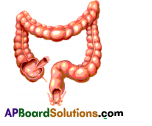
- If creates peristaltic waves to send waste material called stool or faeces into the rectum.
- In the large intestine water and mineral salts are absorbed from the waste material.
- The faecal matter containing indigested food material, bile pigments and dead bacteria is formed in the large intestine.
- It is stored in the rectum and expelled out of the body through the Anus.
Question 6.
Give reasons.
a) If we press the tongue against the palate, we can recognize taste easily.
Answer:
Reason :
- When the tongue is pressed against the palate, the food substance is pressed against the opening of the taste bud letting it to reach the taste cells and triggering taste signals.
- Finally, the taste is recognized in the brain.
b) We can’t identify taste when food is very hot.
Answer:
Reason:
- Most of the taste buds on the tongue are killed when the food is hot.
- This prevents the person from identifying the taste.
- The perception of taste decreases when the temperature of the food rises beyond 35°C.
- But we don’t pay attention to it because we become worried about the burning feeling.
c) If glucose level falls in blood, we feel hungry. (OR) €EI June 2015
We feel hungry if the blood glucose level falls down. 03 June 2019
Answer:
Reason :
- When glucose levels in the blood fall, we get hunger pangs in stomach.
- Hungry feeling start to occur in the stomach due to hunger generating signals that the brain from the stomach due to the secretion of the hormone ‘Ghrelin’.
d) Small intestine is similar to a coiled pipe. (OR)
Why is the small intestine long and coiled?
Answer:
Reason :
- The length of small intestine is 7 meters long.
- It is coiled so as to fit in the human body.
- It is coiled to increase surface area and maximum nutrient absorption when food passes through it.
e) Urination increases when we take lot of fluids.
Answer:
Reason:
- When we take lot of fluids, the kidneys will efficiently throw the water out by forming more urine than usual.
- When there is excess water in the body, the brain usually produces less of a hormone called vasopressin.
- This in turn causes the kidneys to produce a lot of dilute urine, until excess water is removed.
f) The process of digestion goes on in a person whose central nervous system has been largerly affected.
Answer:
Reason :
- The enteric nervous system embedded in the walls of the long tube of our gut or alimentary canal control gut functions often independently of the brain.
- The mass of neural tissue of enteric nervous system filled with important neurotransmitters reveals that it does much more than merely handle digestion.
![]()
Question 7.
Write differences between the following:
a) Bolus – Chyme
b) Small intestine – Large intestine
c) Mastication – Rumination
d) Propulsion – Retropulsion
Answer:
a) Bolus – Chyme:
| Bolus | Chyme |
| 1. Food that is masticated in the mouth. | 1. It is the partially digested food in the stomach. |
| 2. Alkaline in nature. | 2. Acidic in nature. |
| 3. Teeth and saliva turn food into bolus. | 3. Stomach turn food by peristalsis into chyme. |
| 4. Soft round ball of food that has been chewed. | 4. It is the liquified part of food. |
| 5. Food goes from mouth to stomach. | 5. Food goes from stomach to small intestine. |
b) Small intestine – Large intestine:
| Small intestine | Large intestine |
| 1. It is longer and has small width. | 1. It is shorter and has broad width. |
| 2. It is in between the stomach and large intestine. | 2. It is the last part of the digestive system. |
| 3. Digestive juices release from liver, pancreas. | 3. Digestive juices are not released into large intestine. |
| 4. Food is completely digested in it. | 4. Absorption of water from the undigested food takes place in it. |
| 5. It has three parts – duodenum, jejunum and ileum. | 5. It has four parts – caecum, colon, rectum and anal canal. |
| 6. Villi helps in absorption of digested food. | 6. Villi are absent in large intestine. |
c) Mastication – Rumination:
| Mastication | Rumination |
| 1. Grinding, chewing and shredding of food in the mouth by teeth is called mastication. | 1. It is the chewing of cud that come from a part near the stomach of the animal to its mouth. |
| 2. Mastication occurs only one time in the oral cavity. | 2. Rumination allows food to undergo mastication more than once. |
| 3. This is also known as chewing the food. | 3. This is also known as chewing the cud. |
| 4. It makes the food particles to tiny particles. Does not involve nutrient absorption. | 4. It allows greater nutrients to be extracted and absorbed from the food particles. |
| 5. It occurs in most of the animals (mammals), eg: Human being | 5. It occurs only in ruminate animals. eg: Cow |
d) Propulsion – Retropulsion:
| Propulsion | Retropulsion |
| 1. It is a means of creating force leading to movement of food. | 1. It is a situation in which something (food) is pushed or forced backwards. |
| 2. Peristaltic waves move food from one part to the other. | 2. Small amount of chyme is pushed into duodenum, simultaneously forcing most of it back into the stomach. |
![]()
Question 8.
How can you say that mouth is a munching machine?
Answer:
- Mouth plays a major role in changing the texture of food.
- The circular muscles of the mouth enable the food to be pushed into the oral cavity and to be moved around.
- The teeth grind, chew and shred the food.
- The surface muscles of the jaw help in biting and chewing actions, while the deep muscles of the jaw move up, down, forward and backward during food mastication.
- The teeth help in cutting and grinding while tongue movements evenly spread out the food and help in mixing it with saliva.
- The muscles of the mouth enable the food to be pushed in the oral cavity and to be moved around.
- By all this we can say that mouth is a munching machine.
Question 9.
What is mastication? Explain the role of different sets of teeth in this process.
Answer:
Mastication: Food can not be swallowed directly. So it must be grinded, chewed and shred. This process of grinding, chewing and shredding is called ’MASTICATION’.
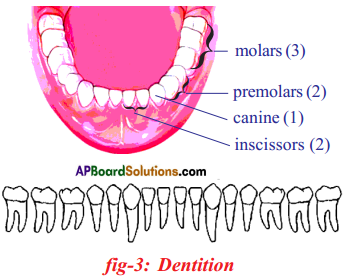 Role of different sets of teeth in mastication:
Role of different sets of teeth in mastication:
- In the oral cavity of human beings, 32 teeth and they are 4 different types to perform different functions.
- They are a) Inscisors b) Canines c) Premolars d) Molars
a) Inscisors: These are eight in number and have chisel shape. They have sharp edges and are specialized for cutting and biting the food.
b) Canines: These are four in number and are with pointed edges- These are designed for piercing and tearing food.
c) Premolars: These are eight in number and are also called cheek teeth. These are designed for crushing and grinding food.
d) Molars: These are 12 in number. They are designed for crushing and grinding food.
![]()
Question 10.
During the journey of food from the mouth to stomach through oesophagus, how does muscular system coordinate in this process?
Answer:
Movement of food (bolus) from mouth to stomach through oesophagus is influenced by the coordination between muscular system and nervous system.
Muscular movement in mouth:
- The circular muscles of the mouth enable the food to be pushed into the oral cavity and to be moved around.
- The surface muscles of the jaw help in biting and chewing actions while the deep muscles move the jaw up and down, forward and backward during mastication.
Muscular movement in oesophagus:
- The wall of the oesophagus is made up of two kinds of smooth muscles.
- The inner layer consists of circular muscles and the outer layer is of longitudinal muscles.
- Contraction of circular muscles lead to narrowing of the oesophagus behind the bolus. So the food is squeezed downwards.
- Contraction of the longitudinal muscles in front of the bolus widens the tube, results in shortening of particular part of oesophagus.
- In this way food moves easily and enters the stomach. ,
- Contraction and relaxation of oesophagus muscles bring peristaltic movements.
Question 11.
Is there any reason for the intestine to be coiled with many folds ? In what way it is helpful during the process of digestion? (OR)
Small intestine is similar to a coiled pipe. Give reason.
Answer:
- Yes, there is a reason for the intestine to be coiled with many folds.
- The coiled and folded nature of intestine slows down the passage of food along the intestine and afford an increased surface area for absorption.
- It also increases the surface area for the intestine to increase the absorption of nutrients through finger-like projections villi.
- The folded and coiled intestine absorbs nutrients and water more than they breakdown.
Question 12.
What is the function of peristalsis in these parts?
a) Oesophagus b) Stomach c) Small intestine d) Large intestine
Answer:
a) Oesophagus:
Peristalsis helps in pushing the food, down the oesophagus into the stomach.
b) Stomach:
- Peristalsis helps in storing food, breaking down food down and mixing it with juices secreted by stomach lining.
- Peristalsis in stomach helps in partial digestion of food.
c) Small intestine:
- Peristalsis pushes the digesting food through small intestine.
- It helps to mix the chyme to help in the digestive process.
- Peristalsis also helps in absorbing nutrients from the digesting food into the blood.
d) Large intestine:
Peristaltic movements help to propel feces along the large intestine through colon, to the rectum for expulsion from the body.
![]()
Question 13.
How can you justify the enteric nervous system as the second brain of the gut?
(OR)
Write about the nervous system present beneath the digestive system.
Answer:
- The enteric nervous system, the second brain consists of sheaths of neurons embedded in the walls of the long tube of our gut, or alimentary canal.
- The second brain measures about nine meters to end from the oesophagus to the anus.
- The second brain contains some 100 million neurons, more than in either the spinal cord or the peripheral nervous system.
- This multitude of neurons in the enteric nervous system enables us to “feel” the inner world of our gut and its contents.
- Enteric nervous system contains mass of neural tissue filled with important neurotransmitters.
- This reveals that it does much more than merely handling digestion or inflict the occasional nervous pang of hunger.
- Enteric nervous system stimulates and coordinates the breaking down of food, absorbing nutrients and expelling of waste.
Thus equipped with its own reflexes and senses, the second brain can control several gut functions often independently of the brain. - Several scientists also believe that the enteric nervous system is a way too complicated to have evolved only to make sure things move through and out of our gut smoothly.
- Hence we can justify that the enteric nervous system as the second brain of the gut.
Question 14.
Rajesh feels hungry upon seeing food. Sheela says no more food as she is not hungry. What makes Rajesh hungry and what suppresses Sheela’s hunger?
Answer:
- When glucose levels in the blood fall, we get hunger pangs in the stomach. Feeling hungry lies in the physiology of blood circulation.
- The secretion of the hormone GHRELIN starts in the stomach when it goes empty.
- Hunger contractions start to occur in the stomach due to hunger generating signals that reach the brain from the stomach due to ghrelin.
- So Rajesh effected with secretion of ghrelin in his stomach and he felt hungry when he saw food.
- Sheela was not affected with secretion of ghrelin in her stomach. She felt that her stomach is full.
- When we feel the stomach is full and there is no need of food any more, another hormone LEPTIN is secreted that supresses hunger.
Question 15.
How are taste and smell related?
(OR)
What is the relationship between taste and smell?
Answer:
- Taste and smell are closely related.
- This close relationship is most readily seen in how we perceive the flavours of food.
- Anyone with severe cough and cold cannot make out the difference in the taste of certain food items.
- Actually, what is really being affected is the flavour of the food , or the combination of taste and smell.
- That is because not only the taste but also the food odours are being defected.
- However, interactions between the senses of taste and smell enhance our perceptions of the foods we eat.
- Smell of the food flavour gives a similar taste to food.
Question 16.
List out the sphincter muscles of the food canal you have observed and give a brief description.
(OR)
What are the different types of sphincter muscles present in the digestive canal?
Answer:
There are different sphincter “muscles in the food canal. They are :
- Esophageal sphincter
- Cardiac sphincter
- Pyloric sphincter
- Anal sphincter and
- Ileocecal value or sphincter.
1. Esophageal sphincter:
- This allows entry of bolus into the oesophagus,
- It also reduces back flow from the oesophagus to pharynx.
2. Cardiac sphincter:
- It is present where oesophagus meets the stomach,
- It’s location is almost directly in front of the heart,
- It allows food from oesophagus into the stomach.
3. Pyloric sphincter:
- It is present at the opening called pylorus, located at the end of the stomach,
- Pyloric sphincter allows only small quantities of food into duodenum at a time.
4) Anal sphincter:
- It is located at the anus, the end of the digestive system,
- The release of waste is controlled partly, voluntarily by anal sphincter.
5) Ileocecal value:
- It is situated at the junction of the small intestine (ileum) and the large intestine (colon),
- It’s function is to limit the colonic contents into the ileum.
![]()
Question 17.
What happens if salivary ducts are closed?
(OR)
What happens if saliva is not produced by salivary glands?
Answer:
If salivary ducts are closed the following consequences may occur:
- If salivary ducts are closed saliva will not release into the mouth, the mouth becomes dry.
- We can’t taste the food.
- Saliva secretes an enzyme called salivary amylase which breaks down the carbohydrates in food into dextrose and maltose sugar.
- If saliva is not secreted in the mouth carbohydrates remains unchanged digestion will not completed.
- Due to absence of saliva food will not get moistened, chewing and swallowing becomes difficult.
- If salivary ducts are closed, the salivary glands become swollen and it leads to pain.
Question 18.
If size and shape of small intestine is like oesophagus what will happen?
Answer:
- If size and shape of small intestine is like oesophagus the height of the person should be more than 22 feet as the length of the small intestine is about 22 feet. So it will not fit in the human body.
- For the complete digestion of the food to occur, it has to stay in small intestine for 3 to 4 hours.
- Otherwise digestion will not be completed and nutrients are not absorbed into blood . in the small intestine.
- The tube like nature of small intestine as that of oesophagus will not provide increased surface area for complete absorption of nutrients.
Question 19.
Prepare a questionnaire to understand nervous coordination in the digestion process.
(OR)
What are the questions you are going to ask your teacher about nervous coordination in the digestion process?
(OR)
Prepare a questionnaire for an interview with a doctor to understand the nervous coordination in the digestion process.
Answer:
- What is enteric nervous system?
- Why the enteric nervous system is known as second brain?
- How nervous system plays an important role in digestion of food?
- Which nervous system controls the release of saliva from salivary glands?
- Which cranial nerve controls the movement of muscles in the jaw?
- The mechanism for swallowing is under the control of?
![]()
Question 20.
What experiment do you perform to understand action of saliva on flour? Explain it’s procedure and apparatus that you followed.
(Activity – 7)
(OR)
i) Explain the procedure followed in the experiment conducted to understand the action of saliva on starch.
ii) What apparatus and chemicals are used to do this experiment?
(OR)
Write the experiment you have performed in your school laboratory to know the action of Saliva on flour. How did you test the pH of Saliva?
(OR)
Explain the experiment conducted by your teacher in your class to show the action of saliva on the starch.
Answer:
Aim: To understand the action of saliva on flour.
Apparatus:
- Two test tubes
- Water
- Ata flour
- Water glass and
- Iodine solution.
Procedure:
- A test tube is taken and half of the test tube is filled with water.
- A pinch of flour is added.
- To mix flour with water, test tube as shaken.
- Few drops of flour mixture is taken in a watch glass and test for the presence of starch by putting a drop of diluted tincture Iodine in it.
- A blue black colour confirms the presence of starch.
- Divide the mixture into two equal halves by transferring it to another test tube.
- Both the test tubes have the same amount of solution.
- Add a teaspoon of saliva to one of the test tube and mark it.
- Do not add anything in the other test tube.
- After 45 minutes add a drop of dilute Tincture Iodine solution to test tubes containing the solutions.
Observation:
- Saliva containing flour mixture becomes slurry. It doesn’t show any change.
- But in the second test tube with only flour mixture turns blue colour.
Conclusion:
- Saliva in the test tube converts flour into sugar. So no change is observe here.
- In the second test tube containing only flour mixture turns blue black.
(OR)
i) Answer:
- Add a spoon of starch to the water taken in a test tube to make starch solution. Starch solution is divided into two equal parts in two test tubes.
- Add a little saliva to one of the above test tube and the other without adding saliva and keep them a side for some time.
- Add a drop of dilute iodine to both the test tubes. The test tube added with saliva doesn’t turns to blue black because the starch is broken down into smaller units called sugar by the saliva.
- The other part which is not added with saliva turns into blue black, as it has starch without any change.
So this experiment proves saliva converts complex carbohydrates into simple sugars.
ii) Answer:
Test tubes, water glass, flour, iodine, saliva.
![]()
Question 21.
Suggest a simple experiment to prove the role of palate in recognizing taste.
(OR)
How do you prove that palate has a role in recognizing taste?
(OR)
“Taste is connected to the tongue and palate”. Write an activity to prove it and write your observations.
Answer:
Experiment to prove the role of palate in recognizing taste
Aim: To prove the role of palate in recognizing taste.
Apparatus: Sugar crystals, Stop watch.
Procedure:
- Place some sugar crystals on the tongue.
- Keep mouth opened and see that tongue does not touch the palate.
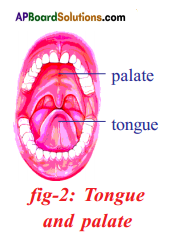
- Record the time from the moment we placed the crystals on the tongue till we get the taste by using stop watch.
- Now repeat the test by placing the sugar crystals on the tongue pressing it against the palate.
- Record the time from placing sugar crystals to getting the taste.
Observation: From the above activity we know that taste can be identified easily when the tongue is pressed against the palate.
Result: We can easily identify the taste of the substance we can identify the taste of it in lesser time.
Question 22.
Collect information related to feeling hunger from your school library and prepare a note on it.
Answer:
- Generally we feel hunger when our stomach goes empty.
- When our stomach goes empty Ghrelin hormone is released and it causes the feeling of hunger.
- As well leptin hormone also released, but it causes the feeling of suppression of hunger.
- Not only these, when we saw a colourful and good smelling food, automatically we feel hunger. So, the sight of seeing a good food also causes feeling of hunger.
- If the food doesn’t have good colour, texture, good smell we can’t eat, even though it is a good food.
- All the feelings towards food are recieved by our eyes, nose, tongue.
- From these, information is sent to brain, from there signals are sent to stomach and causes feelings either positive or negative.
- Hormones are also responsible for most of the feelings of hunger.
![]()
Question 23.
Draw the block diagram of showing sensation of taste from food material to brain.
Answer:
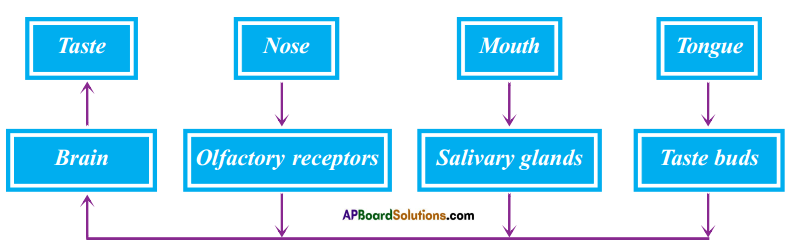
Question 24.
Draw a neatly labelled diagram showing a peristaltic movement in oesophagus Explain the importance of mucus on the walls of food pipe.
(OR)
In the food pipe, the food bolus is propelled into the stomach by peristaltic movement Represent this action with a diagram.
Answer:
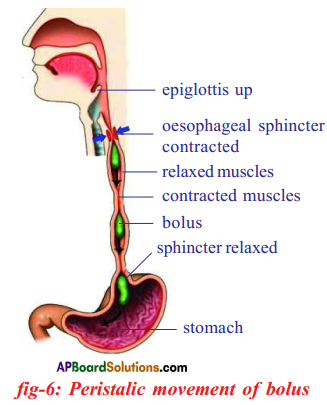 Importance of mucus on the walls of food pipe :
Importance of mucus on the walls of food pipe :
- The walls of the food pipe secrete a slippery substance called mucus.
- Mucus lubricates and protects the oesophgeal walls from damage.
- This helps the food bolus to slide down easily.
- Besides this the saliva in the bolus also helps in easy movement.
![]()
Question 25.
Draw a schematic diagram of villus in small intestinp. Explain how digestive system coordinates with circulatory system.
(OR)
Draw the diagram of villi in small intestine and lable its parts.
Answer:
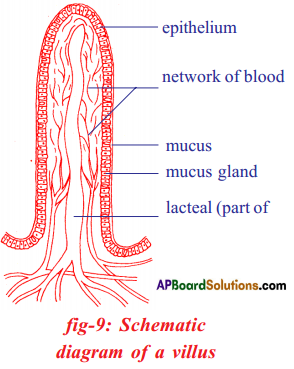 Coordination of digestive system with circulatory system :
Coordination of digestive system with circulatory system :
- After the completion of digestion in small intestine, it enters into the blood through villi.
- In blood the digested food gets oxidised after that energy is released.
- Releasing of energy from fot^d occur only when it enter into the blood.
- So, there is a great coordination between digestive and
Question 26.
The mere smell or sight of food stimulates hunger . Describe the process through a neat diagram.
Answer:
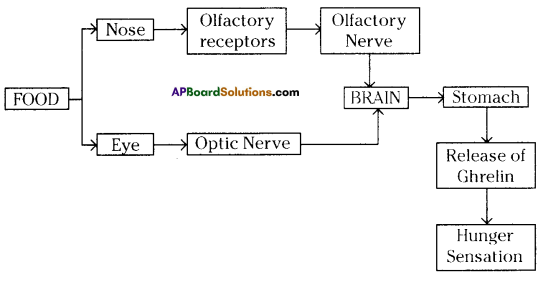
- The mere smell even the mere sight of delicious food stimulates the hunger.
- When we smell, the air borne substances get dissolved in the watery film of nasal mucus.
- The chemoreceptors in nose are otherwise called olfactory receptors which trigger signals in the form of nerve impulses to the brain where smell is defected.
- The amount of the neurosecretory protein hormone ghrelin in the blood increases as a result of visual stimulation images of food.
- Hunger contractions start to occur in the stomach due to hunger generating signals that reach the brain.
- It is believed that the diencephalon in fore brain and vagus nerve (10th cranial nerve) plays an important role in carrying these signals to brain.
- Hunger pangs continue up to 30-45 minutes.
- Increase ¡n ghrelin levels results in sensation of hunger and motivation to consume food.
Question 27.
With the help of a diagram show the movement of food from mouth to the stomach. What muscles and nerves are involved in the movement of food and what is this action called as ? (OR)
Draw a diagram of peristaltic movement of food in oesophagus of elementary canal. Write how it performs.
Answer:
 The muscles involved in movement of food from mouth to stomach :
The muscles involved in movement of food from mouth to stomach :
- The circular muscles of the mouth enable the food to be pushed into the oral cavity and to be moved around.
- The surface muscles of the jaw help in biting and chewing actions and move the jaw up, down, forward and backward.
- Contraction and relaxation of circular and longitudinal muscles in the oesophagus bring in a wave like motion that propels the bolus into stomach by the action called peristalsis.
- As the food approaches the closed ring of pyloric sphincter the surrounding muscles relax and allow the food to pass.
- The muscles of the upper part of the stomach have to relax and accept large volumes of swallowed material.
Nerves involved in the movement of food:
- The fifth cranial nerve has been found to control the movement of muscles in the jaw.
- Peristalsis in oesophagus is under the control of autonomous nervous system.
![]()
Question 28.
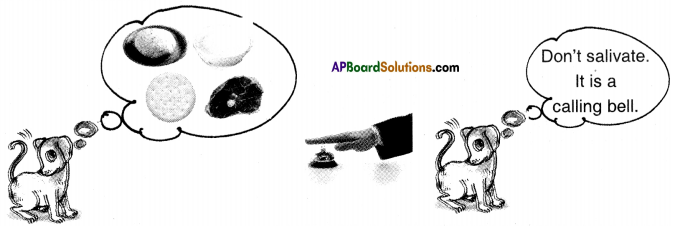
Prepare a cartoon on Pavlov’s experiment with a suitable caption.
Answer:
Question 29.
How do you appreciate stomach as a churning machine? How does this coordination
Answer:
- The stomach acts like a churning machine, churning the food around to break it into even smaller pieces.
- Mechanical mixing of food in stomach occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall.
- This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.
- Due to churning of food in stomach, a mixture that resembles thick cream called chyme is formed.
- All the muscles in the stomach works with such a great coordination.
- Hence we can call stomach as a churning machine.
Question 30.
There is a great variety in diversified life processes, express your feelings in the form of a poem.
Answer:
POEM
Life is a process of discomfort and pain.
Learn to handle it all with courage and sane
Remember the bliss waiting for you
Nutrition, excretion, respiration all are essential in our life.
Reproduction makes our species go on and on forever.
Autotrophs and heterophs are brothers.
Depend on each other In a systematic way.
So have courage to learn more tricks.
Search for happiness.
In life that survive.
![]()
Question 31.
Suggest any two important habitual actions to your friend while eating food, keeping in view of this chapter.
Answer:
- Masticate the food thoroughly in the mouth.
- Do not swallow food without chewing properly or do not eat in hurry.
- Eat small quantities of food at regular intervals for efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients.
- Eat the food that emit good smell and has good taste to eat.
- Do not eat too hot and too cold items.
Fill in the blanks.
- 3:2:1:2 is the ratio of our dentition. Here 1 represents ———–.
- Large protein molecules are broken down in ———– of digestive tract.
- ———– is the strong acid which is secreted during digestion.
- Olfactory receptors present in ———– triggering signals to brain.
- pH of saliva is ———– in nature.
Answer:
- Canine
- Stomach
- HCl
- Nose
- Alkaline nature
Fill in the blanks with suitable words given below.
Fluctuations of hormone —–(i)—– levels results in sensation of hunger and motivation of consuming food. When you feel your stomach is full and there is no need of food any more. Another hormone —–(ii)—– that gets secreted suppresses hunger. When we take food into the mouth it has to be chewed thoroughly. For this purpose the —–(iii)—– muscles help in chewing actions, while the —–(iv)—– muscles of the jaw moves the jaw up,down, forward and backward during food mastication. The —–(v)—– nerve controls the muscles of the jaw. Under the action of —–(vi)—– nervous system Saliva is released by the salivary glands moistens the food to make chewing and swallowing easier. The salivary —–(vii)—– in the saliva breaks down the starch into sugars. As a result of chewing the food is transported into the oesophagus by the action of swallowing which is coordinated by the swallowing centre in the —–(viii)—– and the —–(ix)—–. The tongue which is gustatory recognizes the taste and —–(x)—– nerve plays an important role in sensation of taste.
Choose the right ones.
i) leptin, ghrelin, gastrin, secretin.
ii) ghrelin, leptin, secretin, gastrin.
iii) deep muscles, surface muscles, circu lar muscles, striated muscles.
iv) surface muscles, deep muscles, neck muscles, long muscles.
v) fifth cranial nerve, second cranial nerve, fifth facial nerve, spinal nerve.
vi) central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, autonomous nervous system.
vii) lipase, sucrase, galactase, amylase.
viii) medulla oblongata, cerebrum, 8th spinal nerve, cranial nerve, 7th cranial nerve.
ix) Pons varoli, brain stem, medulla oblongata, mid brain.
x) 6th cranial nerve, 5th cranial nerve, 10th cranial nerve, optic nerve.
Answer:
i) ghrelin
ii) leptin
iii) surface
iv) deep
v) fifth cranial
vi) autonomous
vii) amylase
viii) medulla oblongata
ix) brain stem
x) fifth cranial nerve
![]()
Choose the correct answer.
- In which of the following situations you can taste quickly? [ ]
A) Put sugar cristals on tongue
B) Put sugar solution on tongue
C) Press the tongue slowly against the palate
D) Swallow directly without grinding and shredding
Answer: C - Peristalsis is because of [ ]
A) Contraction of longitudinal muscles
B) Contraction of circular muscles
C) Under control of autonomous nervous system
D) Digestive secretions
Answer: C - Sphincter that helps in opening of stomach into duodenum [ ]
A) Cardiac
B) Pyloric
C) Anal
D) Gastric
Answer: B - Glucose and amino acids are absorbed through the following part of villus [ ]
A) epithelial cells
B) blood capillary
C) lymphatic vessel
D) all
Answer: A - The region in brain portion that controls hunger signals [ ]
A) medulla
B) diencephalon
C) cerebrum
D) mid brain
Answer: B - Human organism is an internal combustion machine because of …. [ ]
(OR)
Human being is an “Internal combustion machine” because he/she
A) assimilation of energy from food
B) liberate CO2 during respiration
C) expel waste food at the end state of digestion
D) secrete powerful digestive juices
Answer: A
10th Class Biology 7th Lesson Coordination in Life Processes InText Questions and Answers
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 145
Question 1.
How do we know that we need food?
Answer:
When we feel hungry then we know that we need food.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 146
![]()
Question 2.
What plays a major role to identify stale food?
Answer:
Smell or odour plays a major role to identify stale food.
Question 3.
If you are having a tasty dish do you think the smell of it increases your appetite?
(OR)
Do the smell of tasty dish increases our appetite?
Answer:
Yes, the smell of tasty dish increases our appetite.
Question 4.
What are your observations after chewing cumin, sounf, potato and apple?
Answer:
If we chew cumin, sounf, potato and apple we observe in order to taste the food material the food should dissolve in saliva.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 148
Question 5.
Are there any other sensation that affect taste?
Answer:
Temperature (hotness), coldness are the sensations that affect taste.
Question 6.
What happens to your taste sensation while sipping hot milk or tea?
Answer:
We find something more tasty while we sipping hot milk or tea.
Question 7.
What do you think could be the range of temperature for us to relish food items?
Answer:
30°C to 35°C could be the range of temperature for us to relish food items.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 149
Question 8.
What do you think that would happen if the salivary glands did not function in our mouth?
Answer:
- If the salivary glands do not function in our mouth, saliva will not release and the food do not get moistened and chewing it is difficult.
- The taste of the food cannot be identified.
- Carbohydrates in the food cannot be broken down and changed to dextrose and maltose molecules.
Question 9.
Suppose your taste buds were affected what would happen to your interest in haying food?
Answer:
If my taste buds were affected I cannot identify the taste of food and also loose interest in having food.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 151
Question 10.
Does the level of saliva secretion change due to presence of food in the mouth?
Answer:
Yes, the level of saliva increases due to the presence of food in the mouth.
Question 11.
Can the process of chewing go on in the absence of saliva?
Answer:
Yes, the process of chewing go on in the absence of saliva. But it is very difficult to chew food and swallow it.
![]()
Question 12.
Does the saliva have any other roles to play?
Answer:
The enzyme present in saliva that is salivary amylase converts large molecules of carbohydrates into small molecules of sugar like maltose and dextrose.
Question 13.
What is the use of such an increase in surface area of food?
Answer:
It helps in more surface area for the enzyme to act.
Question 14.
What about the nature of medium for salivary amylase to act on food component?
Answer:
The nature of medium for salivary amylase to act on food component is alkaline.
Question 15.
If we swallow food material directly without mastication what will happen?
Answer:
If we swallow food material directly without mastication, the food will not get digest easily and completely.
Question 16.
Do you think the pH of our mouth changes?
Answer:
Yes, the pH of our mouth changes from acidic to alkaline by the release of saliva from salivary glands.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 152
![]()
Question 17.
What are the different systems that contribute to the proper functioning of digestion in the mouth?
Answer:
Endocrine, muscular, nervous systems contribute to the proper functioning of digestion in the mouth.
Question 18.
After the digestive process in the mouth where does the food move to?
Answer:
After the digestion in the mouth the food move to oesophagus.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 153
Question 19.
What are the systems that come into play for swallowing food?
Answer:
Skeletal system, nervous system and digestive systems come into play for swallowing food.
Question 20.
What does the schematic diagram tell us about the oesophagus?
Answer:
The schematic diagram of the oesophagus tells about its structure, secretion and function.
Question 21.
What kind of the tube is oesophagus?
Answer:
Oesophagus is a muscular and an elastic tube.
Question 22.
How does mucus help in passage of food?
Answer:
Mucus helps in lubricating and protecting the oesophageal wall and helps the bolus to slide down easily in the oesophagus.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 154
![]()
Question 23.
What makes the movement of the food bolus in the oesophagus easy?
Answer:
- Mucus helps the food bolus to slide down easily.
- Peristaltic movements of the walls of oesophagus also make the movement food bolus in the oesophagus easy.
Question 24.
Why do you think the stomach is structured like a bag rather than a tube like an oesophagus?
(OR)
Why stomach is structured like a bag rather than like a tube?
Answer:
- The food taken has to remain in the stomach for a long time for proper digestion with digestive juices and enzymes.
- Different kinds of muscles churns the food by contraction and relaxation to form chyme.
- If it was like a tube the food would just pass down without under going much changes and cannot remain in the stomach for long time.
Question 25.
What sets such processes into action?
Answer:
- When the food is in the oral cavity, the nerves in the cheek and tongue are stimulated.
- These carry messages in the form of nerve impulses to the brain.
- They messages are transmitted from the brain, to the wall of the stomach, and stimulate the gastric glands to produce gastric juice.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 155
Question 26.
What stimulates stomach muscle into action?
Answer:
The nervous system stimulates stomach muscle into action.
Question 27.
What causes the stomach to churn and mix the food?
Answer:
The contractions of the stomach muscles squeeze and mix the food with the acids and juices of the stomach.
![]()
Question 28.
Why should only a small quantity of food be passed from stomach to duodenum?
Answer:
For the complete digestion of chyme, only a small quantity of it be passed from stomach to duodenum.
Question 29.
What is involved in bringing about peristalsis?
Answer:
Contraction and relaxation of the muscles present in various parts of gut bring about peristalsis.
Question 30.
What is the direction of peristalsis? Which end of the gut does it begin?
Answer:
The direction of peristalsis is forward direction that is from mouth to anus.
Question 31.
What happens if the direction of peristalsis is reversed?
Answer:
If the direction of peristalsis is reversed the food present in the gut moves backwards.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 157
Question 32.
Why do you think small intestine is long and coiled?
Answer:
The small intestine is long and coiled because the food has to stay for more time for complete digestion and absorption.
Question 33.
What process is involved in this process of absorption?
Answer:
Selective absorption of nutrients by the villi of small intestine is involved in absorption.
Question 34.
What is the relation between finger-like structures and paper folds?
Answer:
- Finger-like structures increase the surface area.
- The space inside the paper folds is very much high. So area is increased.
- So increase in surface area is the relation between finger-like structures and paper folds.
Question 35.
What systems do you think are working together?
Answer:
The digestive system and circulatory system are working together.
![]()
Question 36.
Do you think those systems work together in the whole length of the digestive canal? Why / Why not?
Answer:
No, these systems are not working together in the whole length of the digestive canal. The digested food material is absorbed only in the small intestine but not elsewhere in the gut.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 158
Question 37.
Often you may have experienced that if you have tension for some reason you start having loose motions. What does this show us?
Answer:
If we are tensed for some reason, the enteric nervous system or second brain loses control over the gut. Hence without our intervention, loose motions occur.
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 159
Question 38.
What moves out of the gut?
Answer:
The indigested food material moves out of the gut.
Question 39.
Two major pathways of waste expulsion are shown above. Which of the two do you think happens exclusively through the gut?
Answer:
Indigested food matter is expelled in the form of stool from the gut.
Question 40.
What controls the exit of stools from the body?
Answer:
The two muscular layers present In the anal sphincter control the exit of stools from the body.
Question 41.
Do you think the control is voluntary? Why / Why not?
Answer:
Yes, the control is voluntary in adults and it is involuntary in infants.
![]()
Question 42.
Did we have a sphincter in any other part of the digestive canal? Where was it?
Answer:
Yes. We have a sphincter at the opening where stomach opens into duodenum (small intestine).
10th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 160
Question 43.
What is the fate of the digested substances that move into blood from the intestine?
Answer:
The digested substances reach each cell of the body through circulatory system. There it gets oxidised and release energy.
Question 44.
Where is the energy stored?
Answer:
The energy is stored in the cells as ATP.
Question 45.
Which system do you think will remove the excess salts from our body?
Answer:
The excretory system remove the excess salts from our body.
Question 46.
What would be the path of salt removed from gut to the outside of our body?
Answer:
- The digested food containing salts will be absorbed into the blood stream in small intestine.
- The circulatory system supplies this to kidney through renal artery.
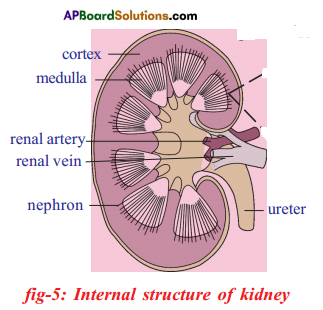
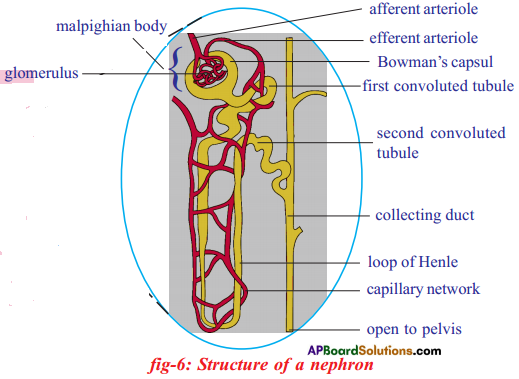
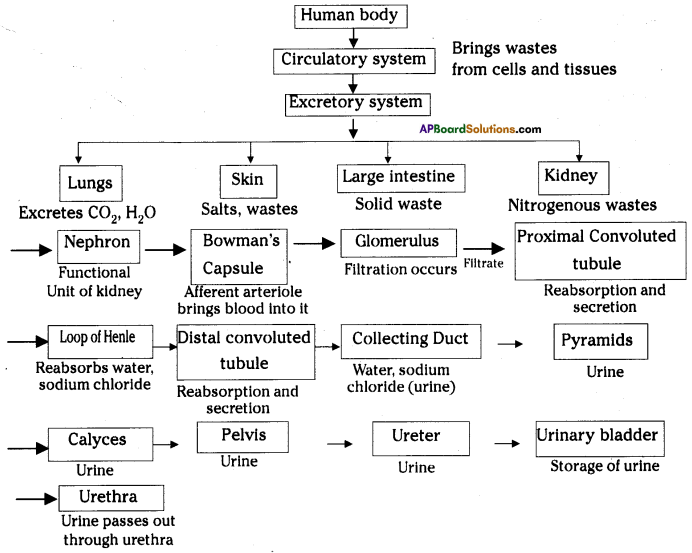
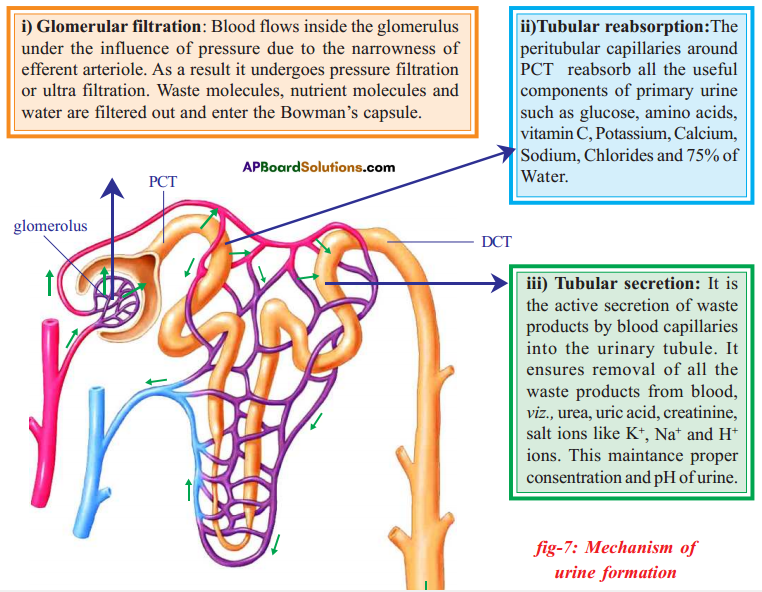
- In the kidney salts are filtered and sent out of the body along with urine.
- Some of the salts also supplied to the skin. They will be sent out of the body in the form of sweat.
10th Class Biology 7th Lesson Coordination in Life Processes Activities
Activity – 1
Observe the following table, identify and tick those options that you think makes you feel hungry.
Table
| Smell of food | Taste of food | Sight of food | Being tired and exhausted | Need of food | Thought of food |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
i) What stimulates hunger?
Answer:
Smell of food, sight of food and need of food stimulates hunger.
ii) What would be the result of stimulation of hunger?
Answer:
Hunger pangs occur in the stomach.
iii) Which system do you think would send the signals to make us realize that we are hungry?
Answer:
Nervous system.
iv) What kinds of controls are exercised during sensation of hunger? Are they hormonal or nervous or both?
Answer:
They are both hormonal and nervous.
v) Can you suggest any four systems involved in the process of generating hunger sensation?
Answer:
Digestive system, Endocrine system, Circulatory system and Nervous system.
![]()
Activity – 2
Observation of how our taste is affected by the sense of smell. (OK) How our taste is affected by the sense of smell?
- First, close your nose with your fingers.
- Pop in some zeera in your mouth and chew it for some time.
- After that chew some sounf.
- Could you recognise the taste?
- How long it taken to know the taste?
- After sometime wash your mouth and repeat the activity by chewing a piece of an apple followed by a potato (remember to close your nose)
Could you know the taste of both or did it taste the same? Why?
Answer:
No, because taste buds couldn’t send the taste signals to brain.
Observation :
- We can taste the food that is in the form of liquid only.
- Only after the dissolved food enters into the cup like taste buds, the sense of taste is carried to the brain for analysis. Then only we will know the taste of food material.
- Similarly olfactory receptors which trigger signals in the form of nerve impulses to the brain where smell is detected.
i) What happens when we put a food material in our mouth?
Answer:
Our mouth salivates.
ii) Name the parts in the mouth that help us to taste food.
Answer:
Papillae (taste buds), palate.
Activity – 3
- Take a pinch of asafoetida powder/garlic and rub it on hand kerchief/tissue paper.
- Close your eyes and smell it.
- Then try to identify taste of different types of food materials with the help of your friend.
i) Does garlic have a stronger scent than apple? How do you think the stronger scent affect your sensation of taste?
Answer:
Yes, garlic have a stronger scent than apple. The stronger scent motivate us to eat different types of foods.
ii) How many food materials you have identified correctly?
Answer:
Seven.
iii) Write a few lines on the relation between smell and taste.
Answer:
- Taste and smell are intimately entwined. This close relationship is most apparent in how we perceive the flavour of food.
- Taste itself is focussed on distinguishing chemicals that have sweet, salty, sour, bitter or umami taste.
- However interactions between the senses of taste and smell enhance our perceptions of the foods, we eat.
iv) Have you ever felt that a particular food is tasty just by looking at it?
Answer:
I felt so many times. In general, we prefer the food material, which is attractive to our eyes and flavour to nose, then we taste it.
![]()
Activity – 4
What is the role of different parts of the mouth in helping us to taste keeping sugar crystals over the tongue?
- Place some sugar crystals on the tongue and keep mouth opened and see that your tongue dosen’t touch the palate.
- Record the time from the moment you placed the crystals on your tongue till you got the taste by using stop watch.
- Now repeat the test by placing the sugar crystals on the tongue and pressing it against the palate.
- Record the time from placing sugar crystals to getting the taste. Or put a drop of sugar solution on your tongue using a dropper.
Observation :
Based on the above activity we know that taste can be identified easily when the tongue is pressed against the palate.
i) Can we taste on dry tongue?
Answer:
No. We can’t taste on dry tongue.
ii) Which way helped you taste faster? Why?
Answer:
Taste can be identified faster when the tongue is pressed against the palate.
When the tongue is pressed against the palate the food substance is pressed against the opening of the taste bud letting it reach taste celjs triggering taste signals. Finally the taste is recognised in the brain.
Activity – 5
How do you show that the breakdown of food by using the model of chalk piece kept in vinegar?
- Break a piece of chalk into two halves.
- Crush one half to tiny pieces leaving the other as it is.
- Take two small mineral wafer bottles QA ltr bottle) cut them into two equal halves and discard the upper portion.
- Now we have two beakers from the lower cut portion.
- Fill them half with vinegar and add the crushed chalk to one beaker and the other uncrushed half chalk to the other.
- Observe them after half-an-hour or so.
i) Which one dissolved faster the crushed chalk or the whole one?
Answer:
Beaker with crushed chalk dissolved faster than the whole one.
This experiment tells us the need of mechanical crushing of food the mouth to increase surface area for action of substances that aid in digestion.
ii) How does this process of mechanical crushing go on in the mouth?
Answer:
Mechanical crushing of food goes in the mouth by chewing.
iii) Which parts in the mouth are involved in this?
Answer:
Teeth and tongue.
iv) What are the systems involved in this process?
Answer:
Digestive system, Nervous system, Muscular system.
![]()
Activity – 6
Observe the diagram and answer the questions and fill the table.
 i) Observe the model or chart of jaw, on the basis of the figure try to guess what are the functions molars could be?
i) Observe the model or chart of jaw, on the basis of the figure try to guess what are the functions molars could be?
Answer:
Chewing and grinding.
ii) What do you think could be the function of inscisors?
Answer:
The function of inscisors is biting the food.
iii) Which set of teeth helps in grinding food?
Answer:
Premolars and molars.
iv) Which set helps in tearing food?
Answer:
Canines help in tearing food.
v) What is your dental formula?
Answer:
![]() is the dental formula.
is the dental formula.
Table
| Name of teeth | Number | Shape | Function |
| Incisors | 8 | Chisel, sharp edges | Biting |
| Canines | 4 | Sharp, pointed edges | Tearing |
| Premolars | 8 | Diamond shape blunt and flat | Chewing and grinding |
| Molars | 12 | Rectangular, blunt and flat | Chewing and grinding |
![]()
Activity – 7
Testing pH of mouth at intervals of one hour.
- Collect a strip of pH paper with a colour chart from a chemistry teacher.
- Take a small piece of the pH paper and touch it to your tongue.
- Match the colour with the colour chart and note the pH.
- Take some readings after having your food at lunch break.
- Compare your readings with that of your friend.
- Take at least 4 readings.
Table
| S.No. | Name of the Student | pH value before lunch | pH value after lunch | pH value after an hour | pH value after 2 hrs |
| 1. | Sagar | 7.4 | 6.8 | 7.0 | 7.4 |
| 2. | San jay | 7.4 | 6.8 | 7.0 | 7.4 |
| 3. | Raju | 7.1 | 6.9 | 7.0 | 7.1 |
| 4. | Krishna | 7.3 | 6.8 | 7.0 | 7.3 |
| 5. | Kiran | 7.4 | 6.8 | 7.0 | 7.4 |
| 6. | Yadav | 7.2 | 6.7 | 7.0 | 7.2 |
i) What is the usual range of pH of your mouth Acidic (or) Basic
Answer:
The usual range of pH of our mouth is more or less 6.5. At low level the saliva is acidic and at high level it is basic.
ii) Did you observe any change in pH after eating? What may have caused the change?
Answer:
Yes, 1 observed the change in pH. Bicarbonates in saliva changed that into basic.
iii) In what kind of pH do you think salivary amylase acts well?
Answer:
In the pH range 7.2 to 7.4 it acts well in alkaline medium.
iv) Does this type of food have any role to play on the pH of our mouth?
Answer:
If the food that enters is acidic it will be converted into basic stuff and then it is swallowed.
Based on the above tests we know that salival secreted causes the medium to change to alkaline as it aids in action salivary amylase.
Activity – 8
Making a model of oesophagus to observe how bolus moves forward.
- Take a piece of waste cycle tube and insert one or two potatoes into it.
- Lubricate the inner side of the tube with oil.
- In the same way smear oil over potatoes.
- Insert oil coated potatoes in the tube.
- Now try to push the potatoes by squeezing the tube.
i) How do you squeeze the tube to make the potatoes pass through?
Answer:
By pushing the potato from behind.
ii) Do you think that the muscles in the wall of the oesophagus have to do something like this?
Answer:
Yes.
iii) How did oil help you in pushing the potatoes through the pipe?
Answer:
Oil acted as a lubricant to push the potato easily in the forward direction.
![]()
Activity – 9
How is the stomach protected from the secretions of its own acids?
- Take two similar green leaves.
- Grease one leaf with petroleum jelly, leave the other free.
- Add 1 or 2 drops of some weak acids on both the leaves.
- Observe them after half-an-hour or so and write your observations.
i) Which leaf was effected by the acid?
Answer:
The leaf to which petroleum jelly was not applied.
ii) What kind of change did you observe in the leaves?
Answer:
The colour of the leaf changes.
iii) What saved the other leaf from the effect of acid?
Answer:
Petroleum jelly.
From the above activity we can conclude that mucus secreted by the walls of stomach protects stomach from the harmful effects of hydrochloric acid.
Activity – 10
Paper tube and folded papers.
- Provide students with a piece of paper.
- Let them calculate the area of one side of the paper and make a roll of it.
- Try to fill the tube by inserting few folded papers as much as possible in it.
- Pull out the papers from the tube, unfold them and find out the whole area of the papers.
i) Compare the area of the folded papers with that of the roll. Do you find any increase in the area ? If so try to find out the reasons?
Answer:
Area is increased. The space inside the folded papers is very much high. So we can insert as many folded papers as we could.
From the above activity we can infer that the inner surface of the small intestine contains thousands of finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area of absorption of nutrients in small intestine.

 Functions of flower parts:
Functions of flower parts:
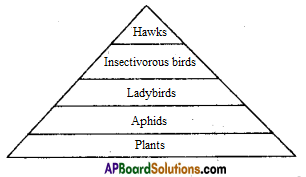
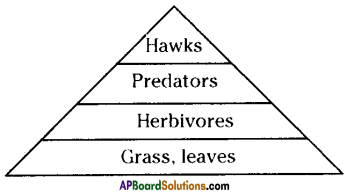
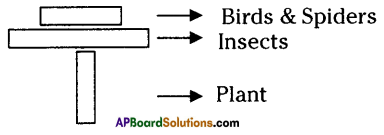
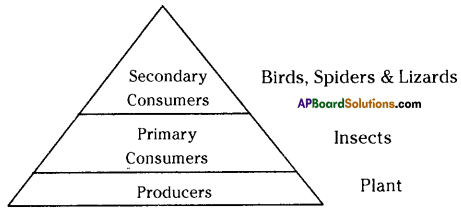


 Legend:
Legend: