SCERT AP Board 9th Class Social Solutions 16th Lesson Social Protest Movements Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Social Studies Solutions 16th Social Protest Movements
9th Class Social Studies 16th Lesson Social Protest Movements Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Which of the following statements about lives of industrial workers are correct? And correct the false statements.
a) Workers controlled the industries.
b) Living conditions of the workers were comfortable.
c) Low wages was ones of the reasons for discontent among the workers.
d) During the phase of industrialization there was emphasis on emotions and feelings.
e) Romantic writers and artists tried to highlight values of closeness to nature as described in the folk tales and folk songs.
Answer:
a) False
b) False
c) True
d) False
e) True
Correction of false statements :
a) Workers did not control the industries.
b) Living conditions of the workers were not comfortable.
d) Duringthe phase of industrialization there was no emphasis on emotions and feelings.
Question 2.
List some of the problems faced by workers of those times. Discuss if such problems exist in our times too.
Answer:
- The workers were under the control of unsympathetic foreman and managers.
- There was no security for their lives and they lost their jobs. Working hours were long and unbroken.
- Wages were meagre and frequently owners tried to cut down wages or retrench workers or increase work load on them.
- The lifespan of the workers decreased.
- Workers were prone to accidents and no compensations were given.
- Workers used to live in slums and deaths were caused by spread of diseases.
- Children were taken as child labour in risky coal mines.
Present condition of workers :
- Salaries or wages are regularized.
- Factory regulation act prohibited children in coal mines. Later child labour is now prohibited.
- Working conditions are improved.
- Compensations are paid for accidents or deaths but it is very less.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a paragraph comparing the ideas of capitalism and socialism. How were they similar or different?
(OR)
Distinguish between socialism and capitalism.
(OR)
Compare and contrast between Socialism and Capitalism.
(OR)
What are the differences between captalism and socialism?
Answer:
| Capitalism | Socialism |
| 1. Capitalism is based on private ownership of means of production. | 1. Undersocialism the means of production are under the control of the government. |
| 2. Supply and demand forces determine the prices. | 2. There will be centralized planning mechanism. |
| 3. The objective of production is profit maximisation. | 3. The objective of production is welfare of the state and people. |
| 4. Concentration of power or wealth will be in few hands. | 4. Socialism opposes concentration of power or wealth. |
| 5. The resources are controlled by the capitalists. | 5. Social control of resources is seen here. |
| 6. There is no individual freedom or equality of opportunities. | 6. The individual freedom and equality of opportunities are given high priority. |
| 7. Eg : West Europe and North America. | 7. Eg : Eastern European countries and China. |
Question 4.
How was the idea of equality being similar or differently challenged by women and workers movements?
Answer:
- Workers demands regarding equality –
a) Equality of opportunities, status, etc., irrespective of birth status.
b) Opposed discrimination of any sort. - The idea of equality challenged by women –
a) Equality of opportunities to all public dignities, offices and employments.
b) They demanded equal access to property.
c) They demanded equal access to civil rights such as voting …. etc.
Question 5.
Draw a poster to illustrate the ideas of “liberty, equality and justice” with in the context of workers and women. Identify occasions where these idea are being violated.
Answer:

In the following occasions the ideas are violated.
- Still the wages given to women labour are low when compared with men.
- Even domestic violence against women is still not able to be controlled.
- Assaults against women are seen everywhere.
- Certain job opportunities are available only for men.
![]()
Question 6.
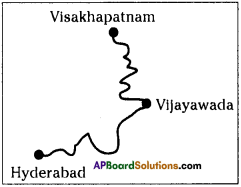
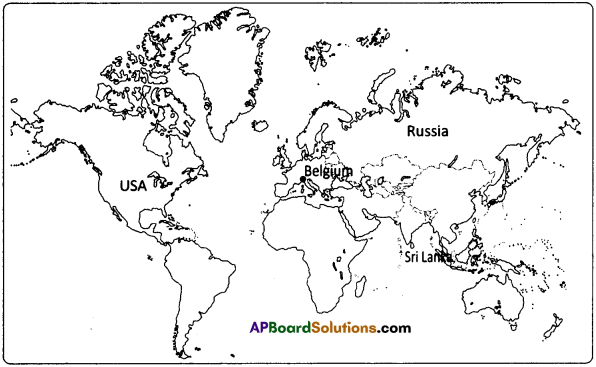
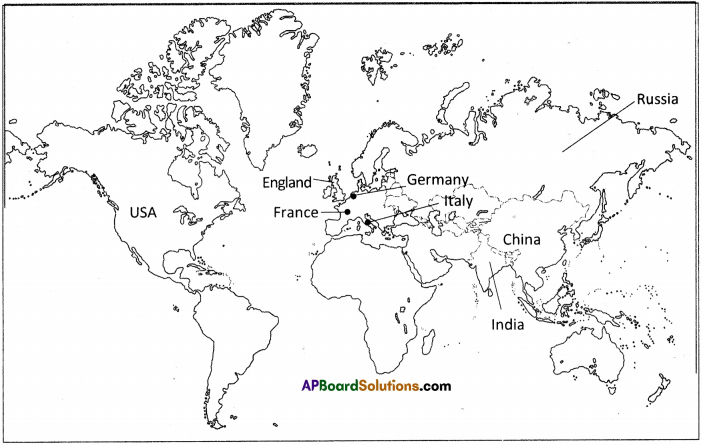
Locate the countries in the world map in which the protest movements took place.
Answer:
The protest movements took place in the following countries.
- USA
- England
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- India
- China
- Russia
Question 7.
Read the last paragraph of page 203 and first paragraph of page 204 and comment on them.
| You would have read about the struggles of social reformers in 19th century India to end practices like Sati, killing of girl children at birth, enforced widowhood for life etc. and also to extend modern education to women. The growth of education among women enabled many women to take part in public life and organise other women like themselves. This gave rise to women’s movement in India too.
Women participated in the national movement and leaders like Gandhiji specially emphasised the importance of women in the movement. Thousands of women joined the freedom movement and helped to shape the ideas of the nationalists. As a result when India became independent women were given complete legal equality vis a vis men. It also sought to end discriminations against them in property laws etc. |
Answer:
- The status of women in India has been subject to many great changes over the past few millenia.
- From equal status with men in ancient times though the low points of the medieval period, to the promotion of equal rights by many reformers, the history of women in India has been eventful.
- In modern India women have held high offices including that of the President, Prime Minister, Speaker, etc.
![]()
Question 8.
Do you find any social protest movements around you? Interview with the leaders of that movement and prepare a report and present in your class.
Answer:
Yes I found a social movement in my surrounding Area. That is “Prohibition”.
Students : Good morning Madam
Leader (Lady) : Good morning Children
Students : Madam, why did you start the movement on prohibition?
Leader : Because to protect the human beings.
Students : How did you protect them?
Leader : If we start a movement against the liquor, then the government will stop the production.
Students : Why did the government to stop the production of liquor.
Leader : Liquor it is the harmness to the health of the consumer. And how much the worker earn half ofthe amount they spend on liquor. Not spend for his family.
Students : Is it known to the government or not.
Leader : Yes, it is known by government. But they did not take any steps. That’s why we started movement for the safe of families.
Students : How far this movement is helpful to families?
Leader : Children, 90% of our families in India are poor. They are not able to fulfill they proper basic needs also. But they addict to liquor and spoil their life and health and they did not take care about families and education of their children. Gradually, the families become a poor, due to the movement they stop the use of liquor, and use the money for the welfare ofthe family and live happily.
Students : Very good Madam, how did you raise the movement?
Leader : I create awarness among the family members who affected these and gathered and maintain a group and started the movement.
Students : Did you successful any?
Leader : Yes, due to the movement government ban on “cheap liquor”. That’s why we continue our movements to “complete prohibition.”
Students : Very good Madam, you are doing a great job for society. So, we also participated in this movement.
9th Class Social Studies 16th Lesson Social Protest Movements InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In what ways do you think ideas of liberty, equality and fraternity wouid have helped to inspire protest movements? (Text Book Page No. 198)
- Industrialization deeply affected the working class.
- Human values were lost.
- There was less scope for dignity and security of life.
- Workers started protesting against their conditions.
- The spread of new political ideas of “liberty”, “equality” and “fraternity” pioneered by the French Revolution gave boost to the protest movements.
- The workers inspired by these ideas demanded
a) “Liberty” from the bonds of capitalists.
b) “Equality” of opportunities irrespective of social status.
c) “Fraternity” inspired them to fight for their dignity.
Question 2.
The government passed a law which provided capital punishment to those who broke machines. Do you think this was justified? (Text Book Page No. 199)
Answer:
No. Giving capital punishment for these who broke machines was not justifiable.
Question 3.
In what way did Marx’s Socialism disagree with Luddism? (Text Book Page No. 202)
Answer:
- Luddism is social protest movement.
- It demanded minimum wages, control over the labour of women and children.
- Demanded work for those who lost jobs because of coming of machines.
- It also demanded right to form trade unions.
Socialism as profounded by Karl Marx
- He wanted production to be an all-society affair rather than a matter of one family.
- He gave importance to collective interest.
- He forced workers not only to fight for better wages but for ending the capital system itself.
- He argued that workers should organize themselves and throughout the capitalists.
![]()
Question 4.
Why did Marx consider factory production as superior and desirable? (Text Book Page No. 202)
Answer:
- Marx believed that industrial production is progressive because it has made possible the industrial transformation of the world.
- Marx believed that industrial production made it possible for people to live and earn their livelihood.
- Factory production enabled us to work on small scale too.
Question 5.
What was the main difference between Marx and the earlier socialists? (Text Book Page No. 202)
Answer:
Marx asserts that revolution, which is a political action, is the only way to achieve socialism.
But according to early socialist, reforms and peaceful means are the best way to achieve socialism.
That was the main difference.
Question 6.
Do you think people have achieved ideas of “liberty, equality and fraternity” in the 21st century? (Text Book Page No. 198)
Answer:
- Modern states are welfare states.
- They always provide their people with the ideas of liberty.
- These ideas are included in the constitution itself.
- Now the people have
a) Liberty of thought and expression.
b) Equality irrespective of caste, sex, religion and race.
c) “Fraternity” which protects their dignity.
Question 7.
In India too such laws which protected our farmers from competition from import of cheap agricultural products are being ended. Do you think such imports will benefit the poor people in India? (Text Book Page No. 198)
Answer:
No. I do not think so. Such imports will not benefit poor people in Inaienjecauseney may cause damage to our production also.
![]()
Question 8.
Why do you think workers would have supported the ending of the ComLawsandwhy do you think the landowners supported them? (Text Book Page No. 198)
Answer:
The artificially high corn prices encouraged by the Corn Laws meant tnatuiewomng class had to spend the bulk of their income on corn just to survive. Since they had no income. Left over for other purchases, they could not afford manufactured goods. Thus the economical spiral worsened for everyone involved. So the workers would have supported the ending of the Corn Laws.
The beneficiaries of the Corn Laws were the nobility and the other large land holders. Landowners had vested interest in seeing the Corn Laws remain in force. The voting members of parliament had no interest in repeating the Corn Laws. So the landowners supported them.
Question 9.
To what extent do you think breaking the machines helped the workers? (Text Book Page No. 199)
Answer:
- The breakingof machines did not give any direct and immediate benefit to the workers.
- Rather they were given punishments like death sentence or life imprisonment.
- Of course it had long term benefit like their right against exploitation, right to express their views and right to job security were recognized.
Question 10.
Do you see any social movements which are still inspired by these idea round you? (Text Book Page No. 198)
Answer:
A) Yes, so many social movements are inspired by the ideas of “liberty, equality and fraternity”. Some of them are-
- Social movement of protection of tribals rights is based on the principles of equality.
- “SC”s demands of equality of opportunity is one of the social movements.
- “Assault” against “women” in Delhi has led to a mass social movement. That has resulted in the enactment of ‘Nirbhay Act”.
- “Prohibition of children in factories or any other work” is also based on these ideas.
![]()
Question 11.
When new machines are brought in a factory, some workers are usually rendered jobless. Why do you think this happens ? Can there be ways of improving technology without creating unemployment for workers? (Text Book Page No. 199)
Answer:
- A machine can perform the work of 100 workers in lesser time.
- Hence when new machines are brought in a factory, some workers usually rendered jobless.
- When new technology is introduced new jobs are created.
- Therefore, workers should be given propertrainingin “technical know how” to get new job opportunities.