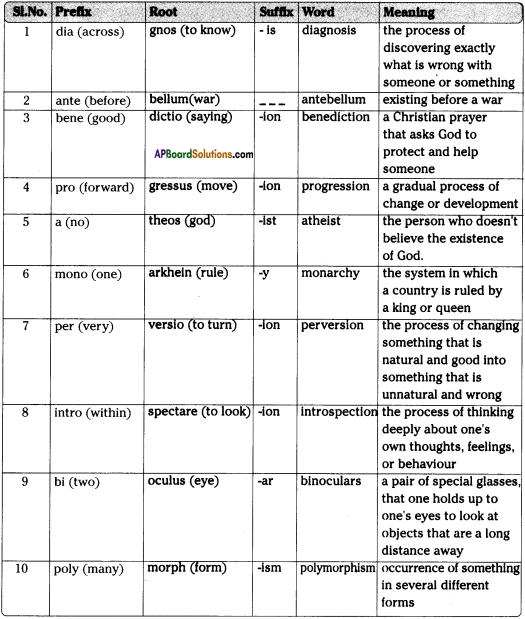
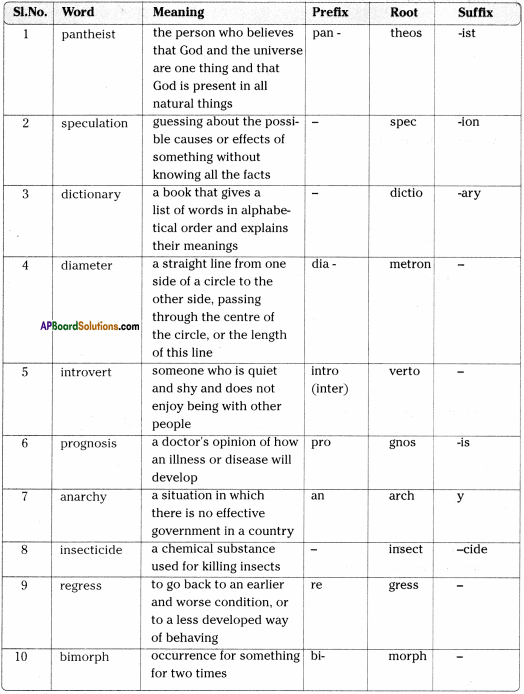
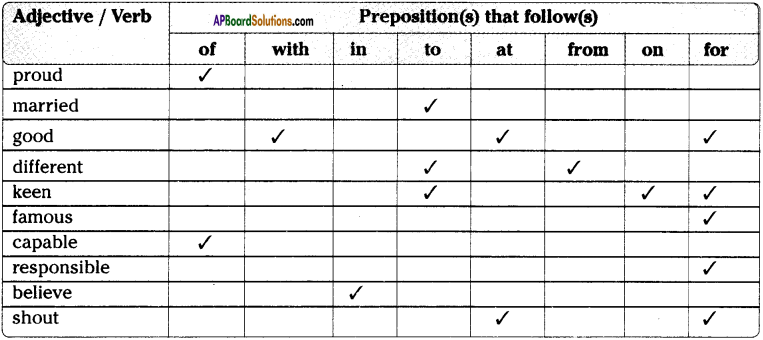
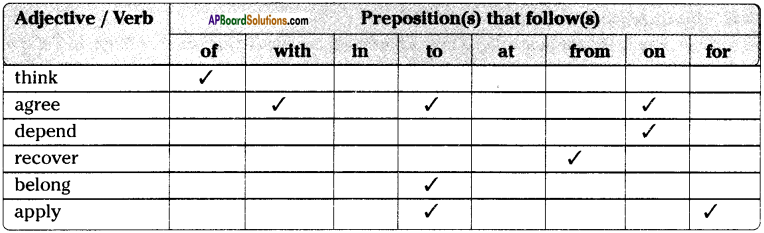
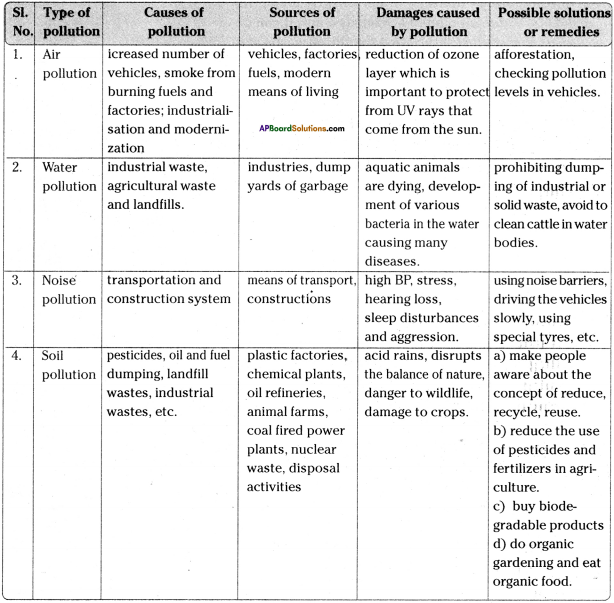
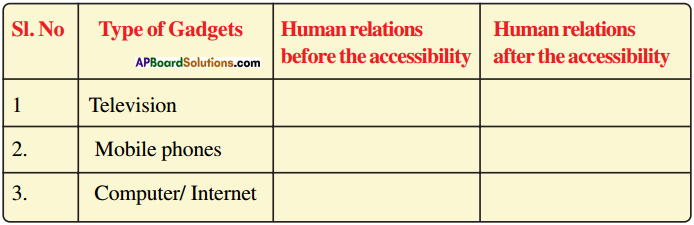
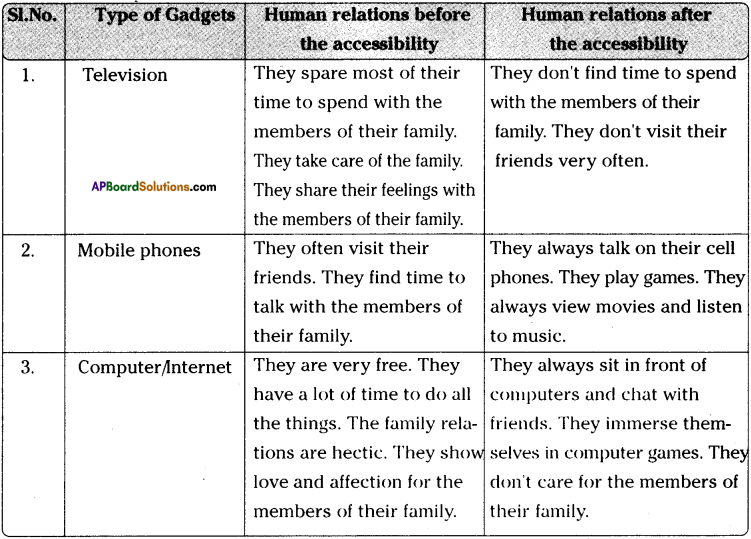
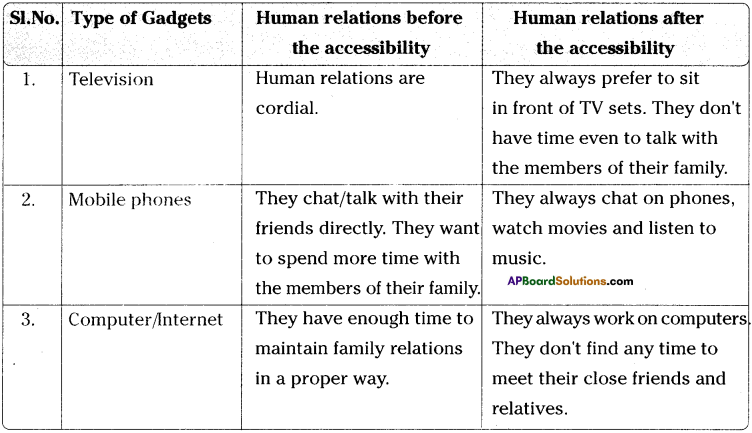
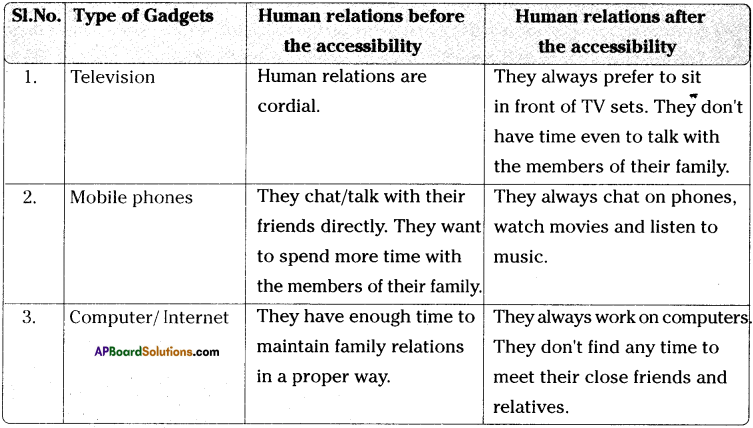
Andhra Pradesh SCERT AP State Board Syllabus 9th Class Social Studies Study Material Guide Pdf free download, 9th Class Social Textbook Solutions in English Medium and Telugu Medium are part of AP Board 9th Class Textbook Solutions.
Students can also go through AP Board 9th Class Social Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Students can also read AP 9th Class Social Important Questions for exam preparation.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Social Studies Guide Study Material Pdf Free Download
AP 9th Class Social Studies Study Material Pdf Download English Medium
- Chapter 1 Our Earth
- Chapter 2 The Natural Realms of the Earth
- Chapter 3 Hydrosphere
- Chapter 4 Atmosphere
- Chapter 5 Biosphere
- Chapter 6 Agriculture in India
- Chapter 7 Industries in India
- Chapter 8 Service Activities in India
- Chapter 9 Credit in the Financial System
- Chapter 10 Prices and Cost of Living
- Chapter 11 The Government Budget and Taxation
- Chapter 12 Changing Cultural Traditions in Europe 1300-1800
- Chapter 13 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 17th and 18th Centuries
- Chapter 14 Democratic and Nationalist Revolutions 19th Century
- Chapter 15 Industrialisation and Social Change
- Chapter 16 Social Protest Movements
- Chapter 17 Colonialism in Latin America, Asia and Africa
- Chapter 18 Impact of Colonialism in India
- Chapter 19 Expansion of Democracy
- Chapter 20 Democracy: An Evolving Idea
- Chapter 21 Human Rights and Fundamental Rights
- Chapter 22 Women Protection Acts
- Chapter 23 Disaster Management
- Chapter 24 Traffic Education
AP 9th Class Social Studies Guide Pdf Download Telugu Medium
- Chapter 1 భూమి – మనం
- Chapter 2 భూమి – ఆవరణములు
- Chapter 3 జలావరణం
- Chapter 4 వాతావరణం
- Chapter 5 జీవావరణం
- Chapter 6 భారతదేశంలో వ్యవసాయం
- Chapter 7 భారతదేశంలో పరిశ్రమలు
- Chapter 8 భారతదేశంలో సేవా కార్యకలాపాలు
- Chapter 9 ద్రవ్య వ్యవస్థ – ఋణం
- Chapter 10 ధరలు – జీవనవ్యయం
- Chapter 11 ప్రభుత్వ బడ్జెట్ – పన్నులు
- Chapter 12 యూరప్లో మారుతున్న సాంస్కృతిక సంప్రదాయాలు: 1300-1800
- Chapter 13 17, 18వ శతాబ్దాలలో ప్రజాస్వామిక, జాతీయవాద విప్లవాలు
- Chapter 14 19వ శతాబ్దంలో ప్రజాస్వామిక, జాతీయవాద విప్లవాలు
- Chapter 15 పారిశ్రామికీకరణ, సామాజిక మార్పు
- Chapter 16 సామాజిక నిరసనోద్యమాలు
- Chapter 17 లాటిన్ అమెరికా, ఆసియా, ఆఫ్రికాలలో వలసవాదం
- Chapter 18 భారతదేశంపై వలసవాద ప్రభావం
- Chapter 19 విస్తరిస్తున్న ప్రజాస్వామ్యం
- Chapter 20 ప్రజాస్వామ్యం – రూపుదిద్దుకుంటున్న భావన
- Chapter 21 మానవహక్కులు, ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు
- Chapter 22 మహిళా రక్షణ చట్టాలు
- Chapter 23 విపత్తుల నిర్వహణ
- Chapter 24 రోడ్డు భద్రతా విద్య