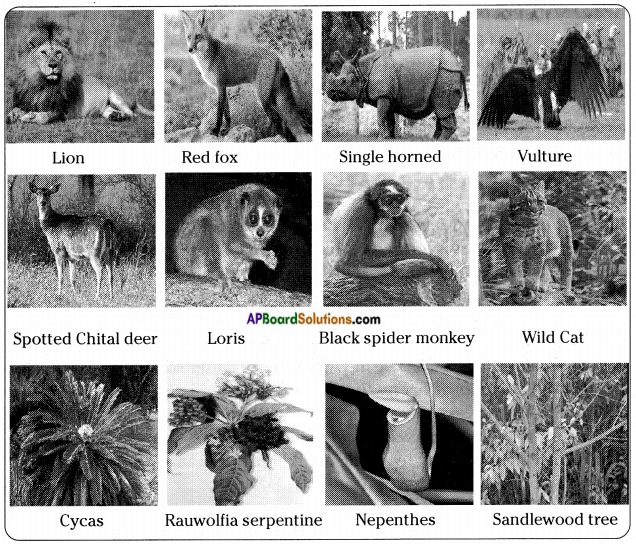
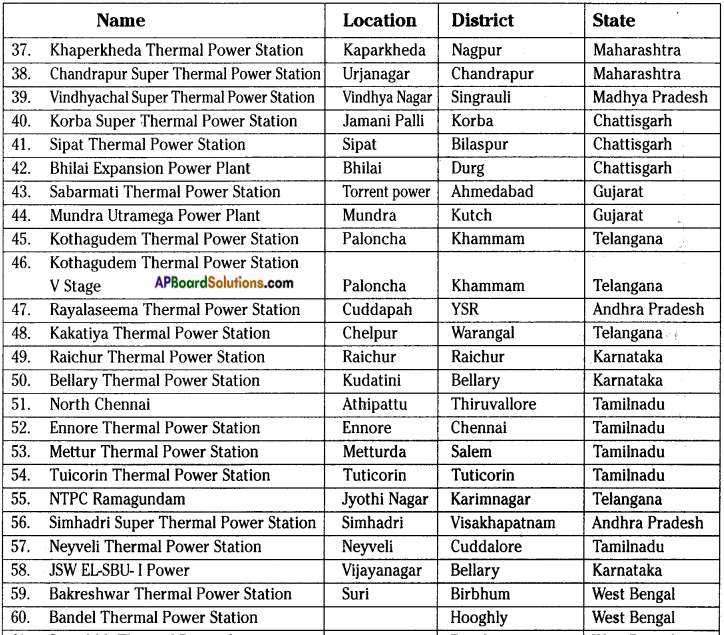
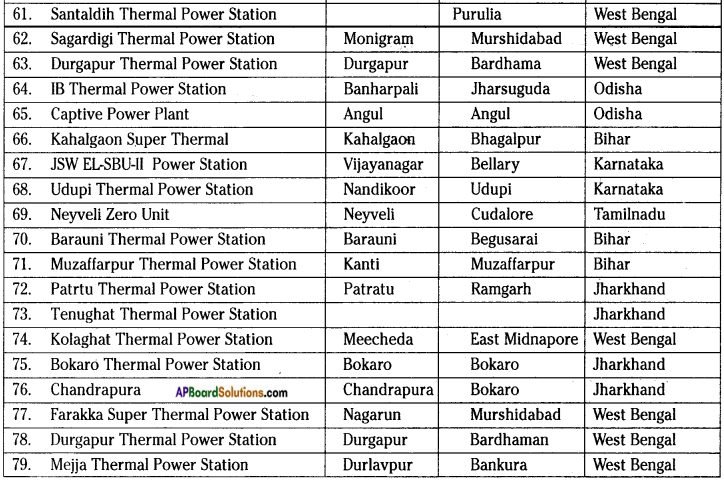
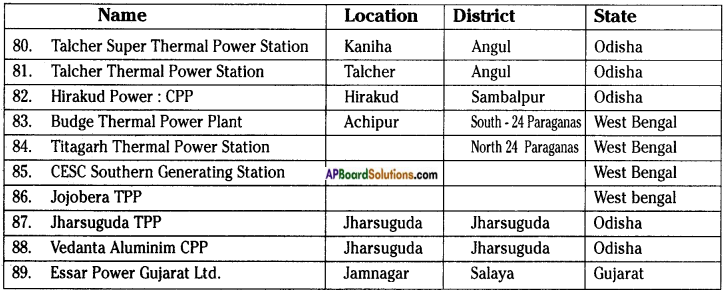
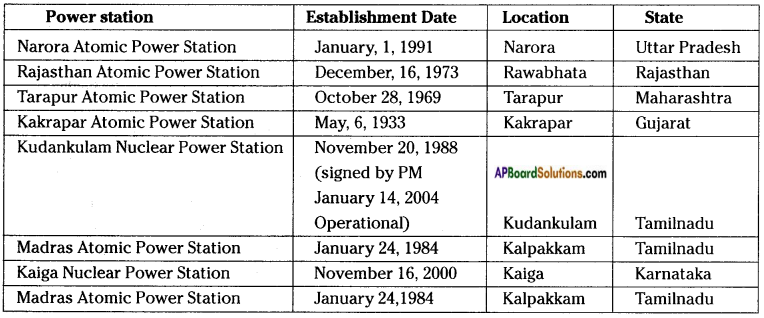
AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 7 Different Ecosystems
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Biology Important Questions 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems
8th Class Biology 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Who coined the word ecosystem at first?
Answer:
The word ecosystem was coined by a British Botanist A.G. Tansley in 1935.
Question 2.
What are the different terms used for environment?
Answer:
The different terms are habitat, biome, ecological systems.
Question 3.
What do we call the small level of ecosystem?
Answer:
The small level of ecosystem is called habitat.
![]()
Question 4.
What do we call the larger level of ecosystem?
Answer:
The larger level of ecosystem is called Biome.
Question 5.
What do we study in an ecosystem?
Answer:
In ecosystem we study about the changes occuring in the habitat like organisms moving away from the habitat or entering the habitat.
Question 6.
How is an ecosystem made up of?
Answer:
An ecosystem is made up of groups of living organisms and their environment.
Question 7.
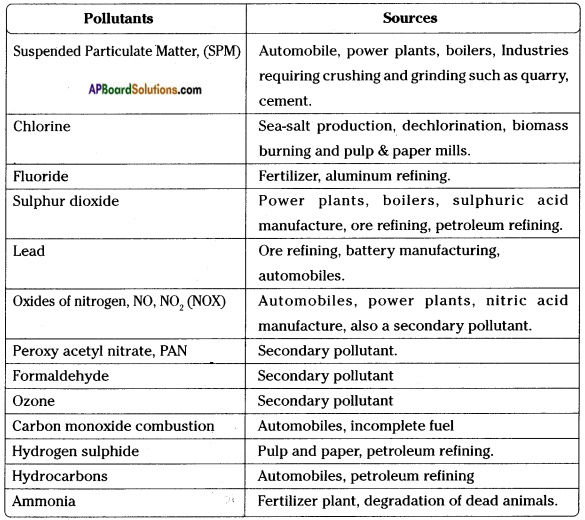
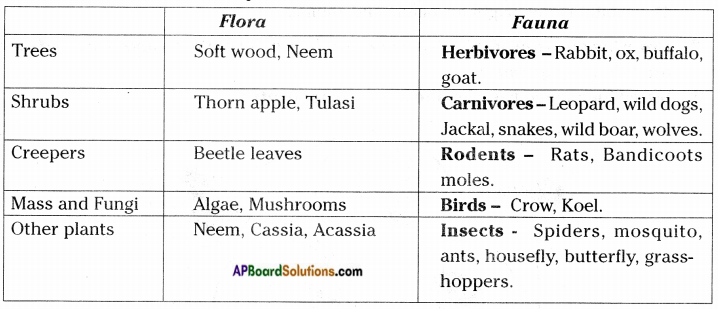
Name the biotic and the abiotic components.
Answer:
The living things like plants,animals and microorganisms are known as biotic components. Soil, water, sunlight, air, etc. are known as abiotic components.
Question 8.
What type of relationship is seen in an ecosystem?
Answer:
There is a feeding relationship between plants and animals.
Question 9.
How do plants and animals depend on one another?
Answer:
There is an interdependence between plants and animals for space, reproduction, shelter etc.
![]()
Question 10.
From where do all living things derive energy?
Answer:
All living things derive energy from sun.
Question 11.
Why are decomposers called recyclers?
Answer:
Decomposers return nutrients to the soil by decompose the dead plants and animals for the plants to use, as the cycle begins again, so they are called recyclers.
Question 12.
Where does the food web start from?
Answer:
The food web starts from the Producers.
Question 13.
What happens when plants and animals die in a food web?
Answer:
When plants and animals die in a food web, they are decayed and decomposed by decomposers like bacteria and fungi.
Question 14.
How do the changes take place in an ecosystem?
Answer:
Powerful storms, tsunami etc., destroy ecosystem and the changes take place in an ecosystem.
Question 15.
What are mangroves?
Answer:
Mangroves are one of the most productive ecosystems, deriving nourishment from terrestrial fresh water and tidal salt water.
![]()
Question 16.
Where do mangroves grow?
Answer:
Mangrove forests grow in back waters low depth areas of sea shores.
Question 17.
Where is Coringa Mangrove situated?
Answer:
Coringa Mangrove is situated South of Kakinada Bay and is about 150 km South of Visakhapatnam.
Question 18.
From which rivers C&ringa mangrove receives water?
Answer:
Coringa mangrove receives fresh water from Coringa river and Gaderu river, tributories of Gautami Godavari river.
Question 19.
Name the producers present in Coringa mangrove.
Answer:
Mangrove, spirogyra, euglena, oscilatoria, blue green algae, ulothrix etc.
Question 20.
Name the consumers present in Coringa.
Answer:
Shrimp, crab, hydra, protozoans, mussel, snails, turtle, daphnia, brittle word, tube worm, etc.
Question 21.
Name the decomposers present in Coringa.
Answer:
Detritus feeding bacteria etc.
![]()
Question 22.
In what conditions a living community lives?
Answer:
A living community lives in an environment which supplies its materials and energy requirements and provides other living conditions.
Question 23.
What is ecosystem?
Answer:
The living community together with the physical environment forms an interacting system called the ecosystem.
Question 24.
How much place is occupied by the desert on land?
Answer:
The desert occupy about 11% of the land and occur in the regions with an average rainfall of less than 23 mm per year.
Question 25.
What type of producers can be seen in deserts?
Answer:
The shrubs, bushes, grasses and some trees.
Question 26.
Why do cacti have succulent stems?
Answer:
They store water in their stems to be used during the time of water scarcity.
Question 27.
Which organisms capture energy from sun?
Answer:
The energy from the sun is captured by plants and is stored in the form of potential energy in food stuffs.
Question 28.
What are the first trophic level in the ecosystem?
Answer:
Plants are the producers and represent the first trophic level in the ecosystem.
![]()
Question 29.
What does the food chain consist of?
Answer:
The food chain consists of four steps – the producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers and tertiary consumers.
Question 30.
What are consumers? Give examples.
Answer:
The organisms which eat other living things and get their energy from them are called consumers. Ex: Animals.
Question 31.
What are decomposers? Give examples.
Answer:
The organisms which feed on wastes, debris of plants and animals or on their remains after they die. Ex : Microorganisms.
Question 32.
What is a food web?
Answer:
A food web consists of several inter linked food chains and each organism in a food web will be a member of more than one food chain.
Question 33.
What are producers? Give examples,
Answer:
Plants are the only organisms capable of carrying out photosynthesis and producing food to all living organisms in any ecosystem. For this reason plants are called Producers.
8th Class Biology 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Complete this flow chart.
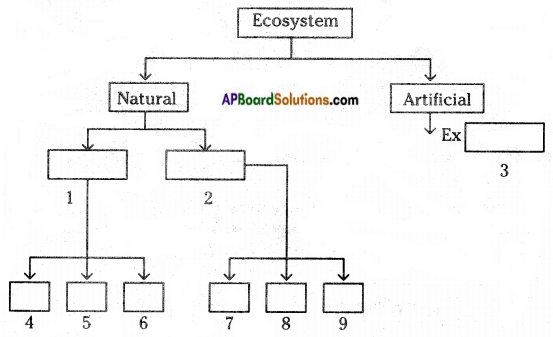
Answer:
- Terrestrial
- Aquatic
- Aquarium, Terrarium, Spaceship
- Grassland ecosystem
- Forest Ecosystem
- Desert ecosystem
- Fresh water ecosystem
- Marine water ecosystem
- Mangrove ecosystem
![]()
Question 2.
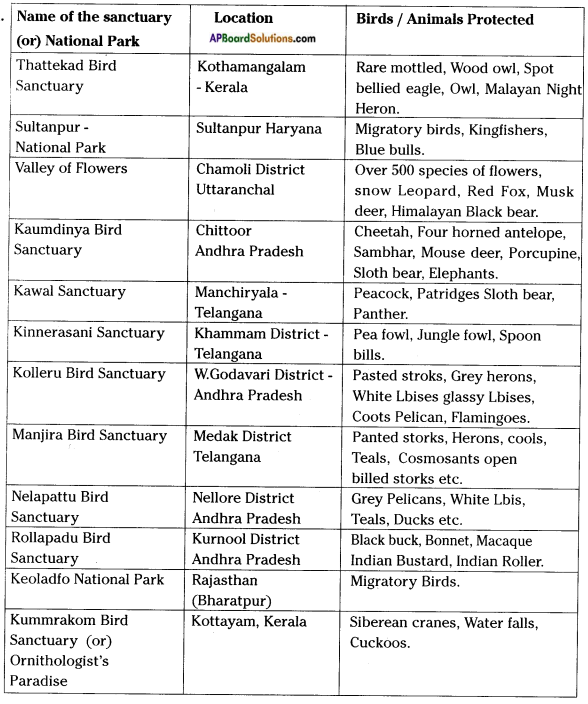
What is the significance of mangrove ecosystem?
Answer:
- Mangroves serve as important breeding grounds for a variety of commercially important organisms.
- They also serve as protective areas for endangered species.
Example: Coringa Mangrove Is situated South of Kakinada and is about 150 Km South of Vizag.
8th Class Biology 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
“The Sun is the malm source of energy for all laving things on earth”. How?
Answer:
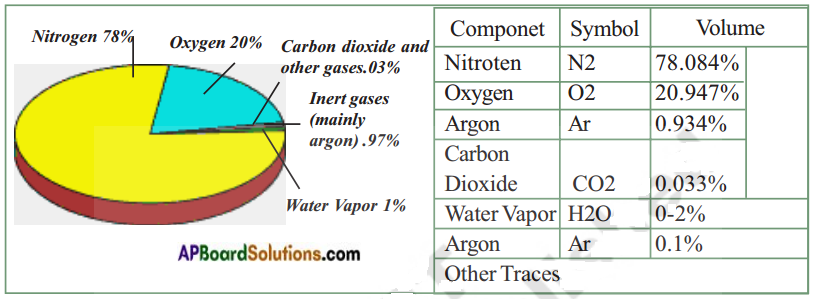
- All the organisms in an ecosystem derive energy from food to live.
- Plants trap the solar energy through photosynthesis. They convert the light energy into chemical energy.
- Animals do not get energy directly from Sun. Many animals eat plants, however which use Sunlight to make food.
- Carnivores do not eat plants still depend on the energy of the sunlight as they eat other plant eaters.
Question 2.
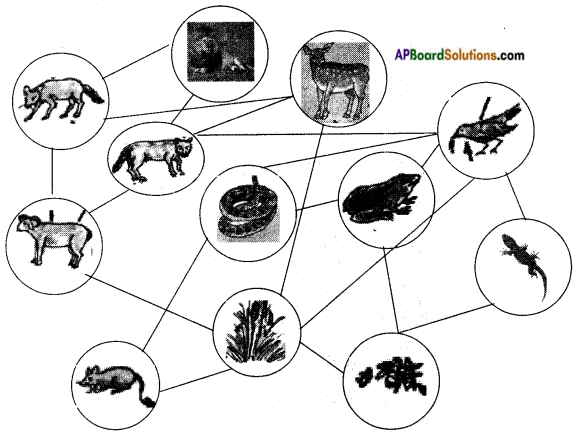
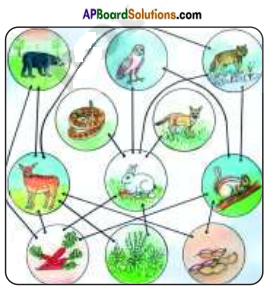
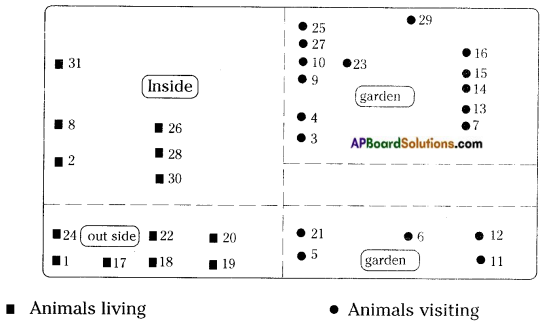
Draw and label the plants and animals present in the food web in Coringa Ecosystem.
Answer:
Diagram of the food web in Coringa Ecosystem.

![]()
Question 3.
Draw the diagram showing figure of energy flow in an ecosystem. (Annexure)
Answer:
Energy flow in an ecosystem.
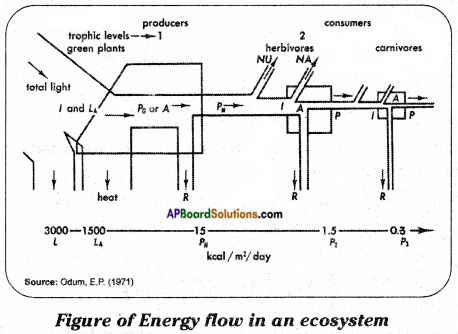
Question 4.
Classify the ecosystem on different basis. (OR)
Draw the flow chart showing different types of ecosystems. Who coined the term ecosystem?
Answer:
- Ecosystem can vary from a small plant to a dense forest. Ecologists classified ecosystem on different basis.
- Some such classifications are – artificial and natural temporary and permanent.
- Due to Abiotic factors, different ecosystems develop in different ways.
Flow chart of classification of ecosystem
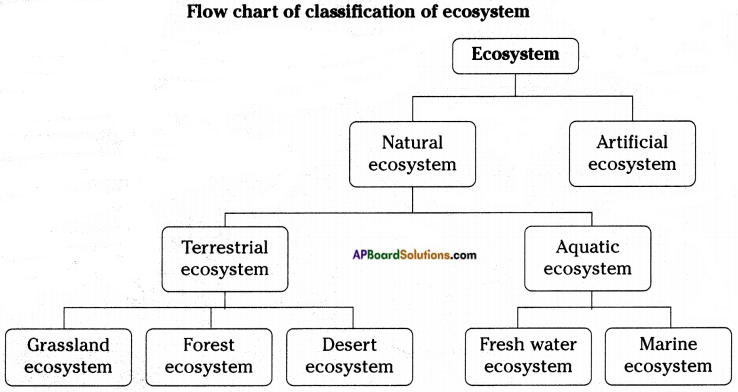
The term “Ecosystem” was coined by A.G. Tansley.
![]()
Question 5.
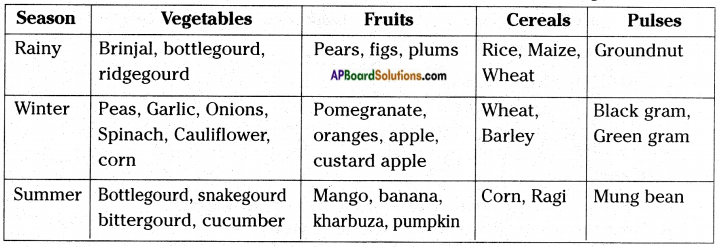
Prepare a table what are the adaptations of the desert animal take the data from your school library.
Answer:

Question 6.
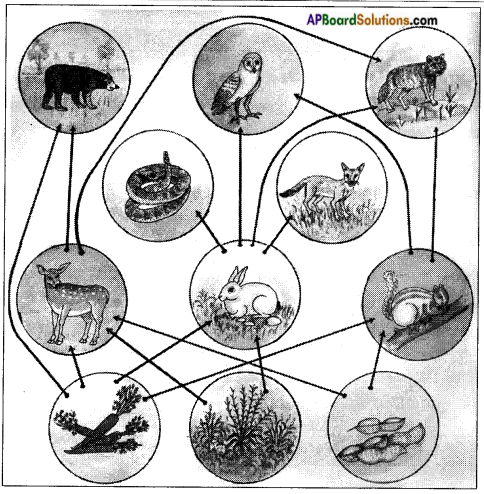
Construct the food web with the following.
Grass → Plants → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle → Goaf → Fox → Tiger → Wolf → Rabit.
Answer:
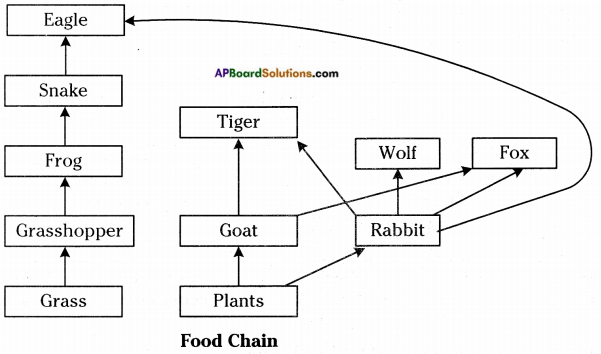
8th Class Biology 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.

Shown here is a food chain, classify each organism in the food chain as producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer or tertiary consumer.
Answer:
In the above food chain
- Leaf – producer
- Catterpillar – primary consumer
- Chameleon – secondary consumer
- Snake – tertiary consumer
- Eagle – top carnivore
![]()
Question 2.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions given below.
Several plants, algae, etc. use sunlight to make their own food are called producers. Consumers feed on producers to get energy. The last level is made of decomposers. They feed on wastes, debris of plants and animals or on their remains after they die. They are called Recyclers also.
- Which are the producers in the food web? Why are they called producers?
- What are consumers? Give some examples.
- What are recyclers? Why are they called so? Give some examples.
- How many levels should be there in a food chain? What are they?
Answer:
- Algae and plants are the producers in the given food web. They convert the solar energy into chemical energy through a process called photosynthesis.
- The animals which feed on these producers (plants) are called primary consumers. Ex : Deer, Grasshopper, Rabbit.
- Saprophytic bacteria and fungi are act as decomposers. They feed on dead plants and animals. They decompose these dead bodies and convert them into minerals. So, they are called ‘reproducers’.
- Food chain consists of 4 trophic levels.
They are 1) producers 2) primary consumers 3) secondary consumers and 4) tertiary consumers.
Question 3.
The desert occupy about 17% of the land and occur in the regions with an average rainfall of less than 23 mm per year. Due to extremes of temperature, the species composition of desert ecosystem is much varied and typical.
a) Which type of adaptations do desert animals have?
b) Write the adaptations in the desert plants.
c) Why the camel is called ship of the desert?
d) In deserts variations of animals is very less. Why?
Answer:
a) They have adaptations to prevent water loss from extreme temperatures.
b) Xerophytic plants do not have stomata. So, they prevent water loss.
c) Camel is called “desert ship” because it has so many adaptations to travel in desert.
d) Due to extremes of temperature, the species composition of desert ecosystem is varied and typical.