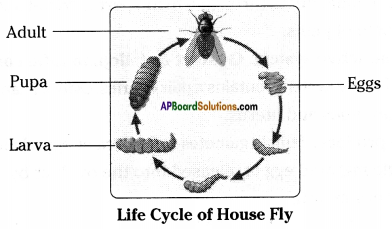
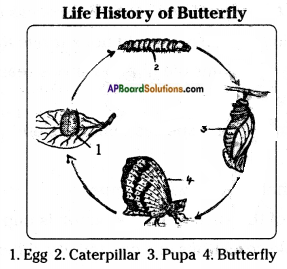
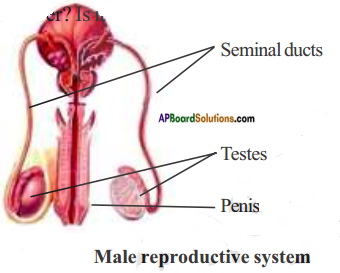
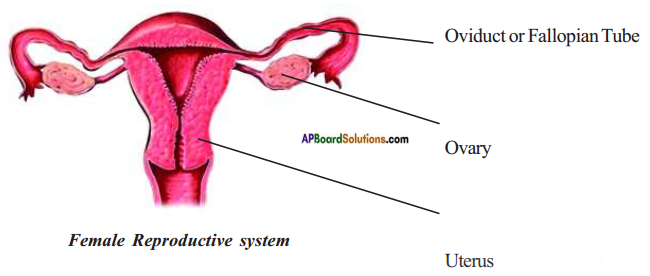
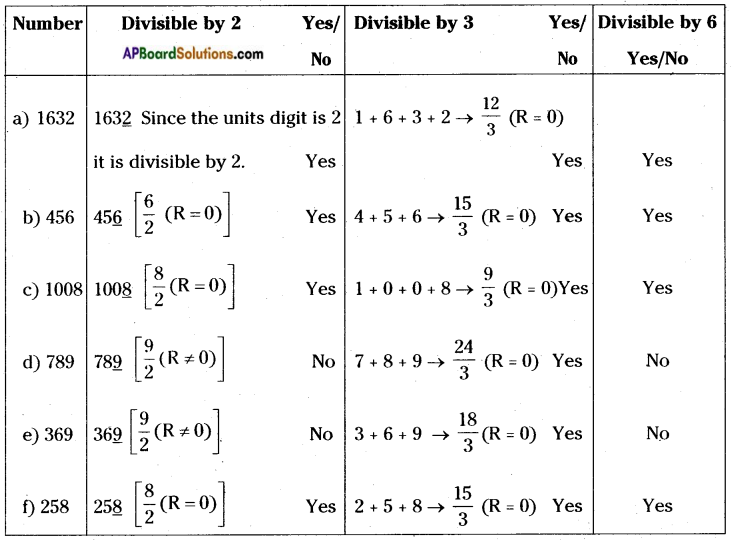
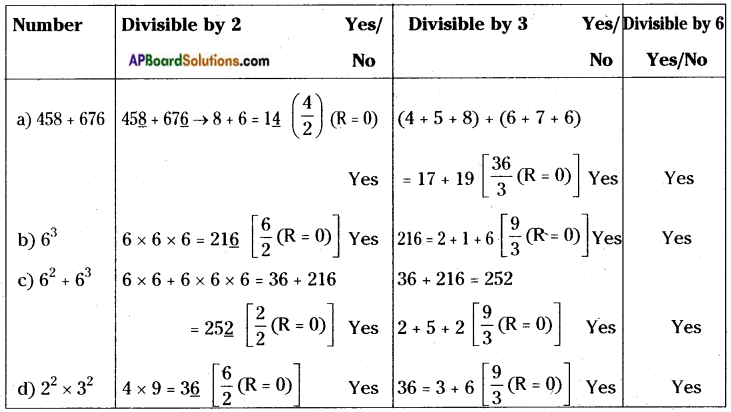
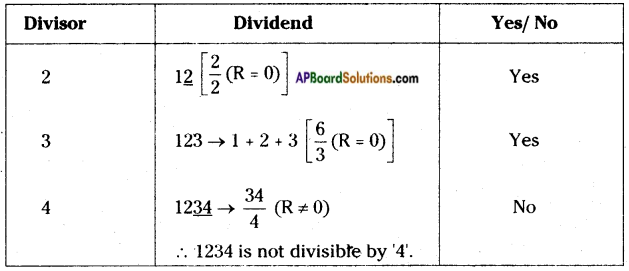
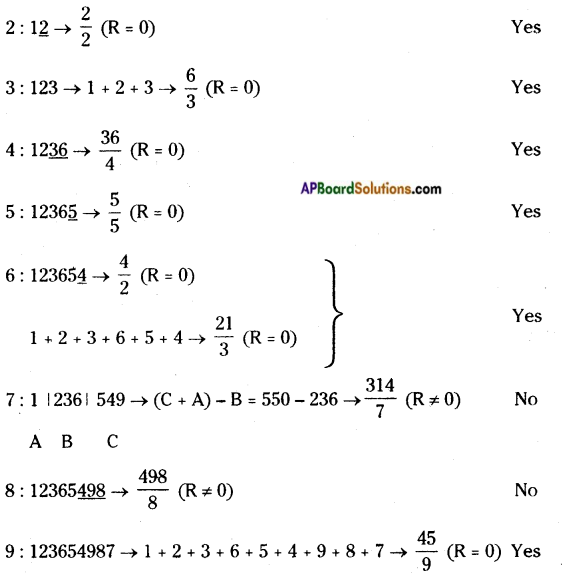
AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Biology Solutions Chapter 5 Attaining the Age of Adolescence Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Biology Solutions 5th Lesson Attaining the Age of Adolescence
8th Class Biology 5th Lesson Attaining the Age of Adolescence Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
How is adolescence different from childhood?
Answer:
| Adolescence | Childhood |
| 1. It is Independent nature and very self conscious. | 1. It depends upon parental assistance for basic needs. |
| 2. Adolescents seek company of friends to share their feelings. | 2. Children are learning through experimenting and communicating with other. |
| 3. Taking decisions by critical thinking. Don’t like the supervision of elders. | 3. Adults supervise and support the development process of child. |
| 4. Lot of Stress and strain. | 4. No stress, make new friends and gain new skills. |
| 5. Rate of growth is more | 5. Comparatively less. |
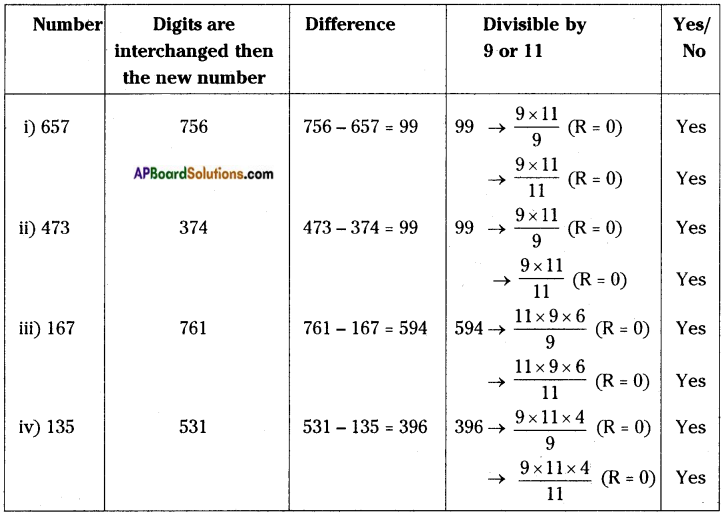
Question 2.
Write short notes on the following.
a) Secondary sexual characters
b) Adam’s Apple.
Answer:
a) Secondary Sexual characters:
- In adolescence age some external changes have seen in boys and girls.
- These are called secondary sexual characters.
- Example: in boys facial hair, moustaches and beards begin to grow. Hair starts growing on the chest of boys.
- In girls breast begin to develop.
- In both boys and girls hair grows in the arm pits.
b) Adam’s Apple:
- The Adam’s apple is actually a partial growth of our voice box or larynx.
- The larynx is made up of nine cartilages, one of which is the largest, called thyroid cartilage.
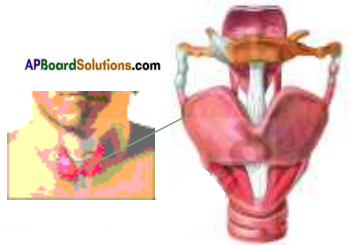
- Due to the elongation of the thyroid cartilage the Adam’s apple is formed. It protrudes out in front of the neck.
- This is caused mainly by male hormone. Testosterone during adolescence.
- As a result muscles or chords attached to the cartilage get loosened and thickened.
- When air passes through these chords a hoarse sound is produced.
- This is the reason for disturbance in voice in the stage of adolescence. At the end of this stage voice get perfect.
Question 3.
List out the changes in the body that take place at the age of adolescence.
(or)
What are the changes that could be observed in adolescence phase?
Answer:
- During this adolescence changes occur in external, internal parts of the body.
- They show interest to spend time with peers.
- Girls voice becomes soft, pimples also may appear on the face by the activation of oil and sweat glands.
- There is growth and maturity in reproductive system.
- In boys voice becomes coarse. Pimples, acne may appear on the face. Facial hair like mustache begin to grow.
Question 4.
Match the following:
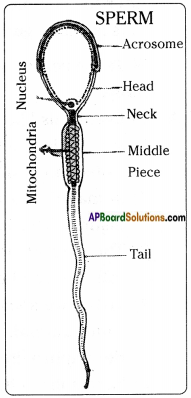
1. Testes ( ) a. Estrogen
2. Endocrine gland ( ) b. Pituitary
3. Menarche ( ) c. Sperm
4.Female hormone ( ) d. First menstruation
Answer:
1. c
2. b
3. d
4. a
Question 5.
Why acne and pimples are common in adolescents?
Answer:
- Naturally in adolescence boys and girls feel worried of their pimples and acne.
- The reason is the secretions of sweat and sebaceous glands are very active in adolescence.
- Because of increased activity of these glands in the skin, boys and girls get acne and pimples.
Question 6.
What can you suggest to your classmates to keep himself/herself clean and healthy?
Answer:
- It would better to have bath atleast twice in a day.
- All parts of the body and inner wears should be washed and cleaned every day.
- If cleanliness is not maintained, there are chances of having fungal, bacterial and other unwanted infections.
- Girls should take special care of cleanliness during the time of menstrual cycle.
- Making use of disposable napkins.
Question 7.
If you have chance to talk with a doctor, what questions you would ask about adolescent emotions and changes in the body ?
Answer:
If I have chance to talk with a doctor, I would ask about
- How to develop positive emotions like bravery, self confidence, happiness, satisfaction, appreciation gratitude, concern and forgiveness.
- And also how to over come the negative emotions like anger, bitterness, dissatisfaction, sadness, anxiety, fear, shame and guilt; which are needed in adolescence.
Question 8.
Some mobile phones have auditory meter to measure frequency of produced sound. By using this phone measure your friend’s voice frequency one from each class VI to X. Report your findings.
Answer:
| Name | Class | His/Her Voice Frequency |
| Madhavi | VI | 50 decibels |
| Kalyan | VII | 52 decibels |
| Ravi | VIII | 54 decibels |
| Hemanth | IX | 55.5 decibels |
| Jalaja | VI | 48 decibels |
| Madhu | VII | 48.5 decibels |
| Padmaja | VIII | 49 decibels |
| Sailaja | IX | 49.5 decibels |
Question 9.
Write five suggestions to improve the performance of Red Ribbon club of your school.
Answer:
- To instill life skills.
- To ensure that every college going youth is equipped with conceptual knowledge about various basic health aspects.
- To increase the capacity of educational system in teaching various basic health aspects.
- To motivate youth and build their capacity as peer educators.
- To promote voluntary blood donations.
Question 10.
Prepare a three minute speech on behavioural changes in adolescents.
Answer:
- Adolescence is the growing age where we may observe some changes in behaviour.
- They are very fast in taking decisions.
- They do not want to be forced to do any work, behave peculiarly sometimes fast and sometimes frigid.
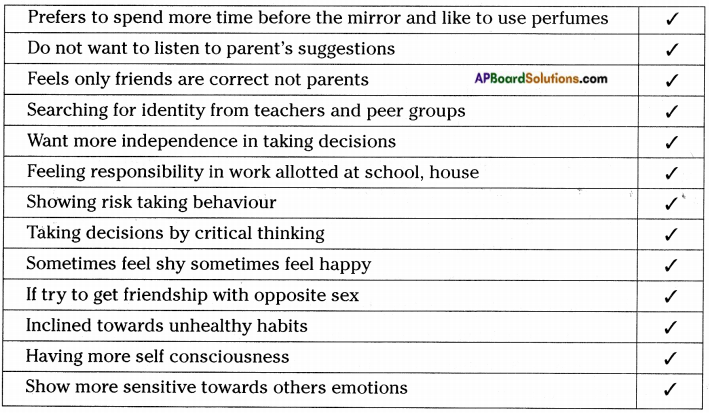
- Adolescents prefers to spend more times before the mirror and like to use perfumes.
- They do not want to listen to parents suggestions and feels friends are correct but not parents.
- They search for identify from teachers and peer groups.
- They want more independence in taking decisions.
- Sometimes they feel shy and sometimes feel happy.
- They try to get romantic relationships.
- They are more inclined towards unhealthy habits.
- The adolescents have attraction towards opposite sex.
- The mind of an adolescent is full of zealous acts and urge to find reasons for several things around.
- Emotionally they are in a turbulent state all the time they get new thoughts for their life activities.
- An adolescent feel insecure while trying to adjust to the changes in the body and the mind.
- They seek company of friends to share their feelings even if they are of opposite sex.
Question 11.
Nature prepares human body to reproduce her generations. What do you think of it?
Answer:
- In females, the reproductive phase of life begins usually around 10 to 12 years of age.
- And generally it lasts till the age of 40 – 50 years.
- The ova begin to mature with the onset of adolescence.
- One ovum matures and is released by one of the ovaries once in about 28 to 30 days.
- During this period the wall of the uterus becomes thick so as to receive a fertilized egg.
- This results in pregnancy and childs’ birth.
- If fertilization does not occur, the released egg and thickened lining of the uterus will be released with some amount of blood in woman.
- This is called menstrual cycle.
- Thus nature prepares the female human body to reproduce generation after generation to continue human life on the earth.
- This is the secret of nature and is nature’s wonderful phenomena.
Question 12.
You know that early marriage is a social taboo. Prepare some slogans to prevent this. (OR)
You know about that child-marriages are social evil. Your school students are conducting a rally to educate the society. Prepare some slogans on this.
Answer:
- Avoid child marriage – Prevent childhood.
- Let a child be a child – stop child marriage.
- Child marriage – a loosing game.
- Stop child marriage – stop child abuse
- Childhood is not for motherhood.
- Let girls be girls but not brides.
Question 13.
13 years old Swaroop always think of his height. Can he improve his height? What do you suggest him?
Answer:
The suggestion is to take nutritious food and to do body exercise regularly to improve his height.
Question 14.
Are you angry with your parents. How do you wish your parents to be?
Answer:
When insulted or threatened unfairly by parents we get angry on them. In our opinion a parent is
- to be a good advisor to give advice how to control stress and strain, which is needed by the adolescent.
- to be like a guide to give guidance how to behave with opposite sex.
- to be like a friend to give good suggestions.
- to be like a wellwisher and always stand behind us to lead us for bright future.
Question 15.
What are your expectations about your parents and teachers?
Answer:
Parents and teachers play an important role to develop the adolescents in to healthy, productive young ones to the nation. Parents feel to develop their children in to better ones than themselves. They must have good courage, confidence, boldness, and free to solve the problems. They should not be tense and worse. Parent is to be a friend and guide towards adolescents.
Teacher is not only a master is to be a captain or a leader. Every adolescent needs mental support. Teacher is the only people who give suitable suggestions to make them free from all mental stress.
8th Class Biology 5th Lesson Attaining the Age of Adolescence InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Some of you also may behave like this, Why?
Answer:
At the age of 13 – 19 years, some changes like voice becomes hoarse, not caring to follow the suggestions and advises of parents, shows restlessness and growing tall.
Because at this age children will be entering into a period which is called as Adolescence, where some changes in the behaviour is seen.
Question 2.
Have you noticed that you are growing?
Answer:
At the age of adolescence growth in height takes place about 18 years of age both boys and girls reach their maximum height.
Question 3.
Have you reached the age of“Adolescence”?
a) Is mustache growing on your upper lip?
b) Did your voice change?
c) Are hairs growing under arm pit?
d) Are there pimples or acne on your face?
e) Are you taking care of your face by applying powder and combing your hairs frequently?
f) Are you feeling shy when talking with opposite sex?
g) Are you not interested to play with opposite sex which you have done earlier?
h) Are you showing restlessness while your parents suggest to do something?
Answer:
For above all the questions the answer is ‘yes’ during adolescence changes occur in external, internal parts of the body.
8th Class Biology 5th Lesson Attaining the Age of Adolescence Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
Observing growth rate.
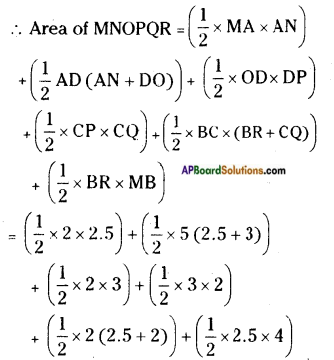
a) Observe the below table and given graph, answer the following questions.
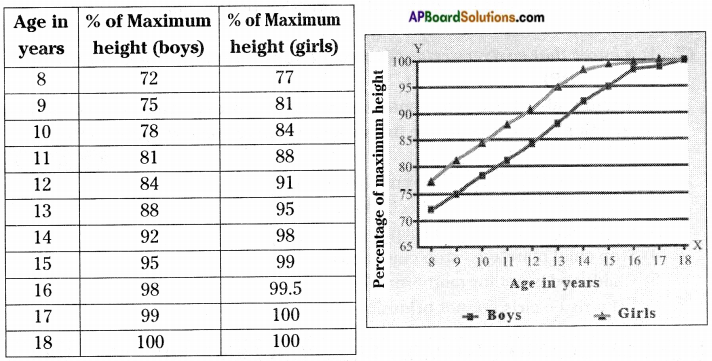
i) What have you observed from the above table?
Answer:
We have observed the height attained by boys and girls in different ages.
ii) When does growth in height nearly stop?
Answer:
In boy growth in height nearly stops at the age of 18, in girls it stops at 17 years.
iii) Which period of age according to you is the fastest growing period for girls?
Answer:
The fastest growing period for girls is between 14-17 years.
iv) Which period of age is the fastest growing period for boys?
Answer:
The fastest growing period for boys is between 16 to 18 years.
v) Who do grow faster? How can you say?
Answer:
The girls grow faster than the boys. By seeing the above graph, about 17 years of age, girls reach their maximum height.
b) Sneha is 13 years old with 125 cm tall. At the end of the growth period likely to be use the following formulae and calculate the maximum height that Sneha will reach.
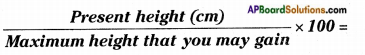
Answer:
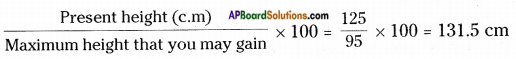
Sneha’s present height = 125 cm
At the end of the growth period Sneha is likely to be 131.5 cm.
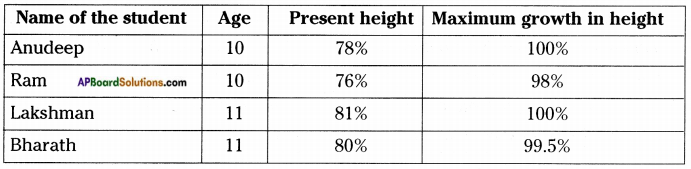
c) Table – 1 shows that girls grow faster than boys in their adolescent period. From a group with six students in your class. Measure the height and calculate the future heights in the following table:
Answer:
Activity – 2
Question 2.
Form five groups in your class. Select at least 15 students. Collect body measurement data of the selected 15 students.
Find an average body measurements for boys and girls separately.
Answer:
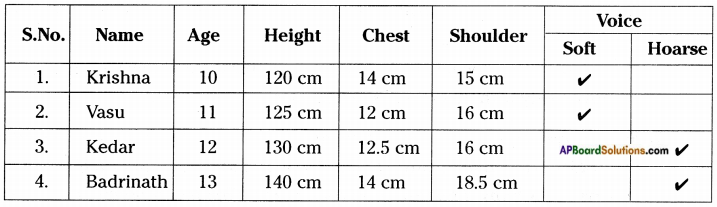
Activity – 3
Question 3.
Read the following check list. Put tick (✓) mark which points reflect your behaviour.
Answer:
Check List:
Think & Discuss
I. Read the following information and answer the following questions.
Some sections of people in our society believe that during the period of menstruation women are untouchable. So, they are asked to keep a distance from others. During this time girls may be ristricted from taking bath, cooking food or going to school. In that case they may lag behind in their studies. In some sections of the society even women are also forced to stay in the huts built at the outskirts of the village.
Question 1.
In what way this kind of discrimination is harmful for girls and women?
Answer:
- During the period of menstruation women are treated as untouchable by some sections of people in our society.
- Generally during this period they feel weak and uncomfortable physically.
- By this kind of discrimination, mentally also they get hurt and feel that why they have born as woman.
- By separation, it would be known to all by this the girl may feels shy, unable to move freely with others and she becomes dull in studies.
Question 2.
Several researches have been done to prove that all these are myths and there is no scientific reason behind these. The blood and egg that is discarded would give rise to a baby if fertilization took place. This is a biological phenomena.
So how can it be impure or unclean?
Answer:
- If fertilization took place, the uterus receives a fertilized egg and this results in pregnancy and would give rise a baby which develops in the uterus.
- If fertilization does not occur this cause bleeding in woman, which is the unwanted and waste to the uterus. So it can be treated as impure or unclean and may create some problems in uterus.
- During menstrual period proper care regarding health and hygiene is needed rather than following myths.
Question 3.
If young generation is trapped into such unhealthy habits, what will be the
future of our country ? What are its effects?
Answer:
- If young generation is trapped into unhealthy habits like consuming tobacco (gutkha, cigarettes, cigar, beedi) they addicted to such social evil.
- Todays children are tomorrows citizens so it should be avoided.
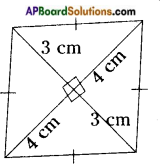
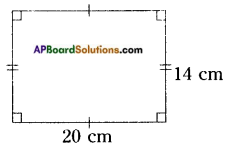
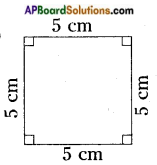
- A famous psychiatrist Stanly Hall stated that adolescence is the age of stress and strain. By getting proper guidance from teachers, parents and elders, the adolescents be able to lead a happy meaning full life and they will save the future of the country.