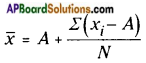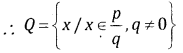Students can go through AP Board 8th Class Maths Notes Chapter 8 Exploring Geometrical Figures to understand and remember the concepts easily.
AP State Board Syllabus 8th Class Maths Notes Chapter 8 Exploring Geometrical Figures
→ Shapes are said to be congruent if they have same shape and size.
→ Shapes are said to be similar if they have same shapes but in different size.
→ If we flip, slide or turn the congruent/similar shapes their congruence/similarity remain the same.
![]()
→ Some figures may have more than one line of symmetry.
→ Symmetry is of three types namely line symmetry, rotational symmetry and point symmetry.
→ With rotational symmetry, the figure is rotated around a central point so that it appears two or more times same as original.
→ The number of times for which it appears the same is called the order.
→ The method of drawing enlarged or reduced similar figures is called Dialation.
→ The patterns formed by repeating figures to fill a plane without gaps or overlaps are called tessellations.
→ Flip: Flip is a transformation in which a plane figure is reflected across a line, creating a mirror image of the original figure.

→ After a figure is flipped or reflected, the distance between the line of reflection and each point on the original figure is the same as the distance between the line of reflection and the corresponding point on the mirror image.
![]()
→ Rotation: “Rotation “means turning around a center.
The distance from the center to any point on the shape stays the same. Every point makes a circle around the center.
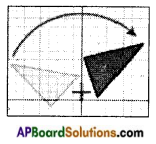
There is a central point that stays fixed and everything else moves around that point in a circle.
A “Full Rotation” is 360°.
→ Now observe the following geometrical figures.
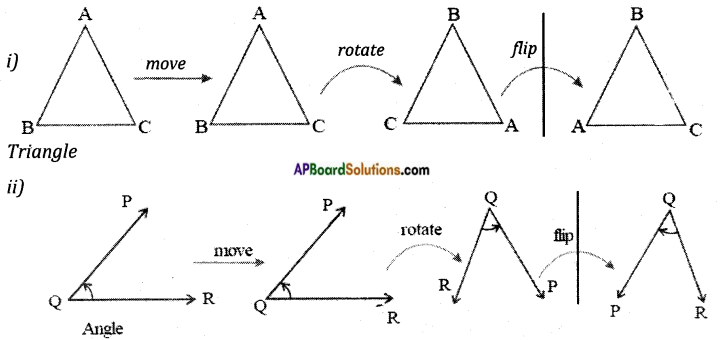
In all the cases if the first figure in the row is moved, rotated and flipped do you find any change in size and shape? No, the figures in every row are congruent they represent the same figure but oriented differently.
![]()
→ If two shapes are congruent, still they remain congruent if they are moved or rotated. The shapes would also remain congruent if we reflect the shapes by producing their mirror images.
→ We use the symbol ≅ to represent congruency.
 (short representation) where ∑xi represents the sum of all xis, where ‘i’ takes the values from 1 to n.
(short representation) where ∑xi represents the sum of all xis, where ‘i’ takes the values from 1 to n.