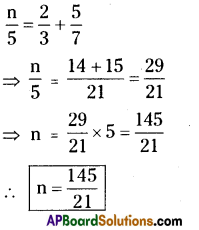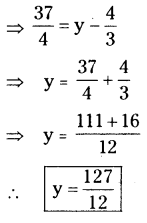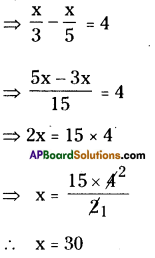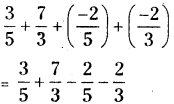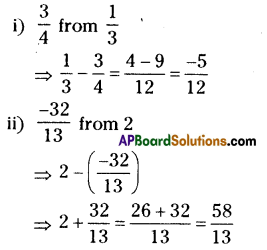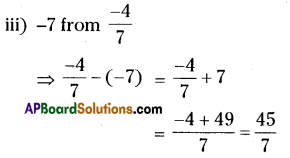AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Construction of Quadrilaterals Ex 3.1 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Maths Solutions 3rd Lesson Construction of Quadrilaterals Exercise 3.1
![]()
Construct the quadrilaterals with the measurements given below:
Question (a).
Quadrilateral ABCD with AB = 5.5 cm, BC = 3.5 cm, CD = 4 cm, AD = 5 cm and ∠A = 45°.
Solution:
In Quadrilateral ABCD with AB = 5.5 cm, BC = 3.5 cm, CD = 4 cm, AD = 5 cm and ∠A = 45°.
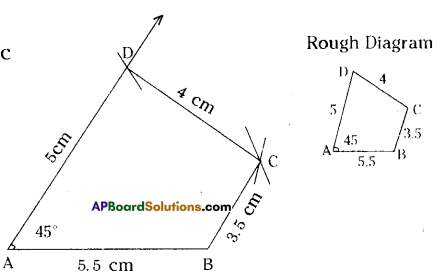
Construction Steps:
- Construct a line segment \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) with radius 5.5 cm
- With the centre A draw a ray and an arc which are equL1 to 45° and 5 cm.
- These intersecting point is keep as ‘D’.
- With centres D, B draw two arcs equal to radius 4 cm, 3.5 cm respectively.
- The intersecting point of these two arcs is keep as ‘C’.
- Join DC and BC. A F
- ∴ The required quadrilateral ABCD is formed.
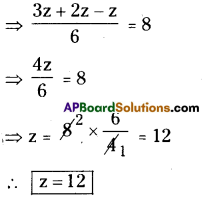
Question (b).
Quadrilateral BEST with BE = 2.9 cm, ES = 3.2 cm, ST = 2.7 cm, BT = 3.4 cm and ∠B=75°.
Solution:
In Quadrilateral BEST
BE = 2.9 cm, ES = 3.2 cm, ST = 2.7 cm, BT = 3.4 cm and ∠B=75°.
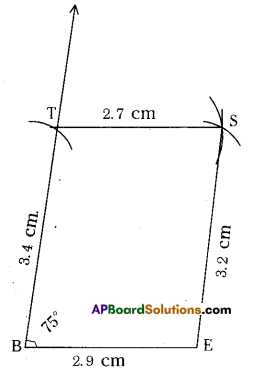
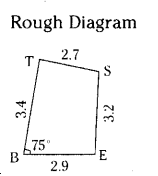
Construction Steps:
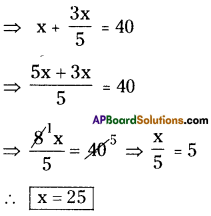
- Draw a line segment \(\overline{\mathrm{BE}}\) with radius 2.9 cm.
- With the centre B, draw a ray of 75° and draw 2.9
an arc with radius 3.4 cm, keep the intersecting point of these two as T. - With the centres T, E draw arcs with radius 2.7 cm, 3.2 cm respectively. These intersection point is keep as S’.
- Join T, S and E,S.
- ∴ The required quadrilateral BEST is formed.
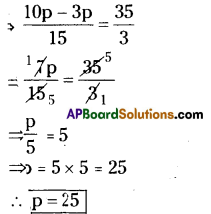
Question (c).
Parallelogram PQRS with PQ = 4.5 cm, QR =3 cm and ∠PQR = 60°.
Solution:
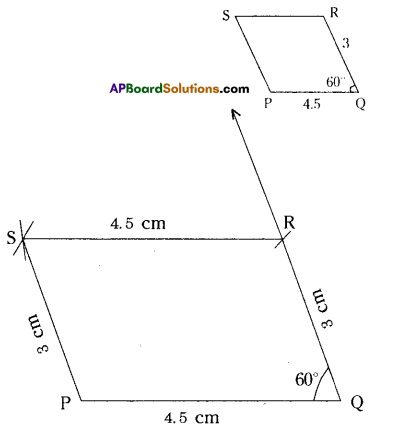
In a parallelogram PQRS
PQ = 4.5 cm, QR = 3 cm, ZPQR = 60°.
=RS4.5cmzPS=3crn
[: Opposite sides of a I)aralielograrn are equal]
Construction Steps:
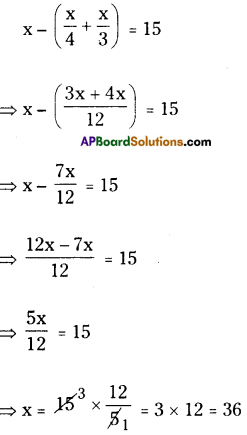
- Draw a line segment ¡i with radius 4.5 cm.
- With the centre Q draw a ray and an arc equal to 60° and 3 cm.
- The intersecting point of these two keep as R’.
- With the centres R, P draw arcs with 4.5 cm, 3 cm respectively. Keep ‘S’ as the intersecting point of these two arcs.
- Join P, S and R, S.
- ∴ The required parallelogram PQRS is formed.
Question (d).
Rhombus MATH with AT =4 cm, ∠MAT =120°.
Solution:
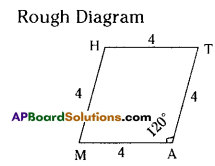
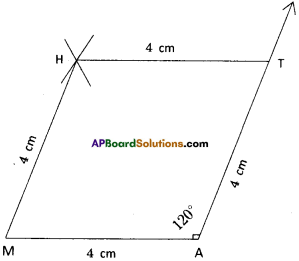
Construction Steps:
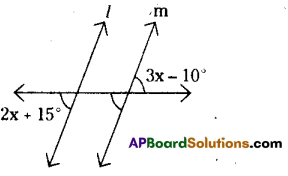
- Draw a line segment \(\overline{\mathrm{MA}}\) with radius 4 cm.
- With the centre A draw a ray and an arc equal to 120°, 4 cm. These two intersecting point be keep as T.
- With the centres M, T draw arcs equal to 4 cms.
These two arcs intersected at the point ‘H’. - Join M, H and T, H.
- ∴ The required rhombus MATH is formed.
Question (e).
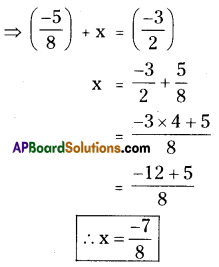
Rectangle FLAT with FL =5 cm, LA= 3 cm.
Solution:
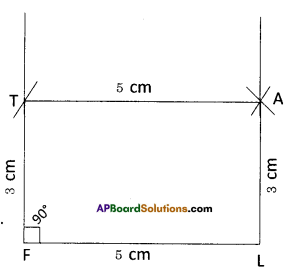
In a rectangle FLAT
FL=AT=5cm, LA = TF = 3cm, ∠F = ∠L = ∠A = ∠T = 90°
Construction Steps:
- Draw a line segment \(\overline{\mathrm{FL}}\) with radius 5 cm.
- With the centre F draw a ray and an arc equal to 900, 3 cm.
These to meet at point T. - With the centres T, L draw arcs equal to 5 cm, 3 cm respectively.
- These two arcs meet at the point ‘A’.
- Join T, A and L, A.
- ∴ The required rectangle FLAT is formed.
Question (f).
Square LUDO with LU = 4.5 cm.
Solution:
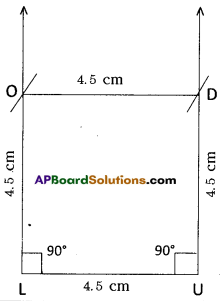
In a square LUDO
LU = UD = DO = OL = 4.5 cm
∠L = ∠U = ∠D = ∠O = 90°
Construction Steps: 45
- Draw a line segment \(\overline{\mathrm{LU}}\) with radius 4.5 cm.
- With the centre ‘L’, draw a ray of 90° and an arc with radius 4.5 cm. These two meet at the point ‘O’.
- Now with the centre U’, draw another ray of 90° and an arc with radius 4.5 cm. These two meet at the point “D”.
- Join O, D.
- ∴ The required square LUDO is formed.