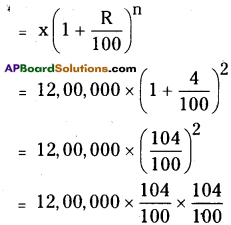
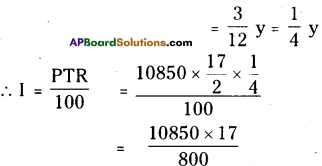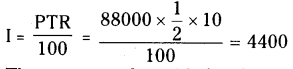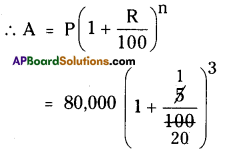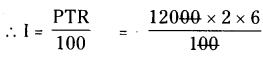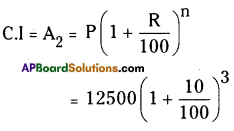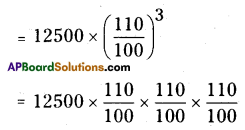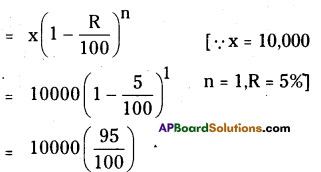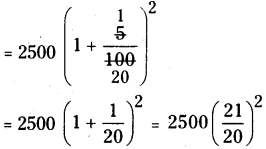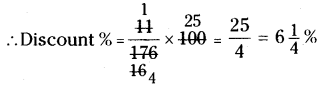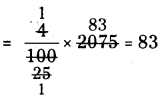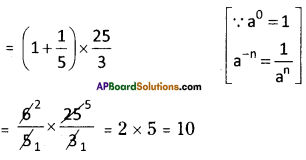AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 6 Square Roots and Cube Roots Ex 6.5 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Maths Solutions 6th Lesson Square Roots and Cube Roots Exercise 6.5
![]()
Question 1.
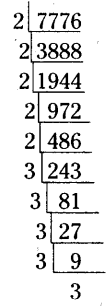
Find the cube root of the following numbers by prime factorization method.
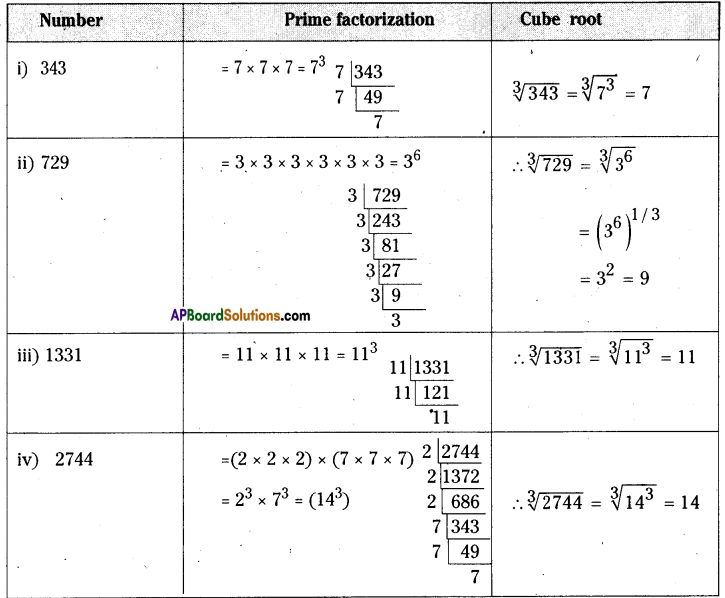
(i) 343
(ii) 729
(iii) 1331
(iv) 2744
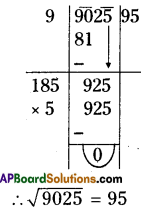
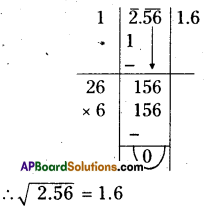
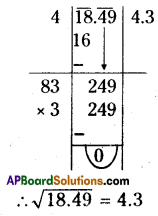
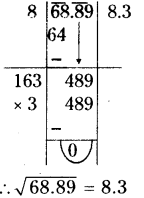
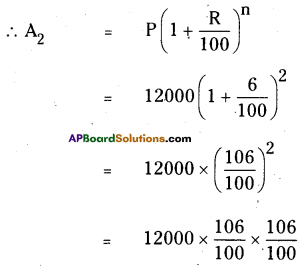
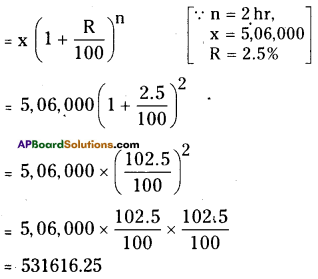
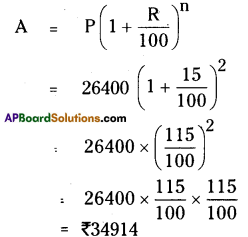
Solution:
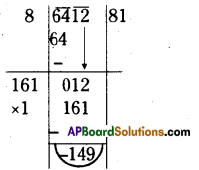
Question 2.
Find the cube root of the following numbers through estimation’?
(i) 512
(ii) 2197
(iii) 3375
(iv) 5832
Solution:
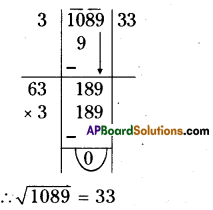
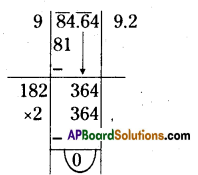
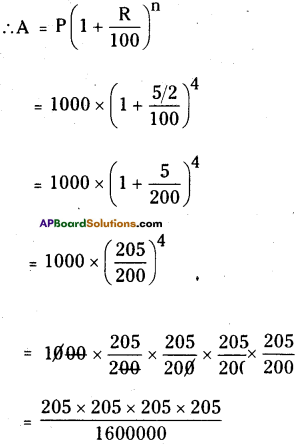
Step 1: Start making groups of three digits starting from the unit place.
i.e, \(\overline{512}\) First group is 512
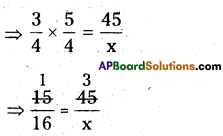
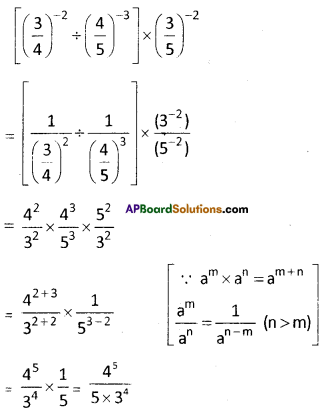
Step 2: First group i.e 512 will give us the units digit of the cube root. As 512 ends with 2, then its cube root ends with 8 (2 x 2 x 2) So the units place of the cube root will be 8.
Step 3: Now take the second group i.e. 0. Which is 03 < 1 < 23.
So the least number is ‘0′.
∴ Tens digit of a cube root of a number be 0.
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{512}\) = 08 = 8
![]()
(ii) 2197
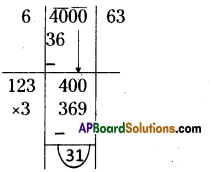
Step 1: Start making groups of three digits starting from the unit place.

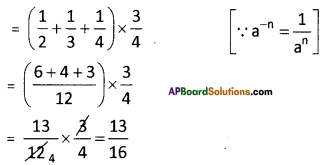
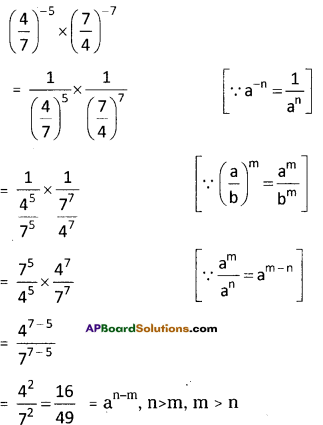
Step 2: First group i.e., 197 will give us the units digit of the cube root.
As 197 ends with 7, its cube root ends with 3. ‘
[∵ 3 x 3 x 3 = 27]
∴ Its units digit is 7.
Step 3: Now take the second group i.e.,2
We know that i3 < 2 < 2
∴ The least number be 1.
∴ The required number is 13.
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{2197}=\sqrt[3]{13 \times 13 \times 13}=\sqrt[\not]]{(13)^{8}}\)
= 13
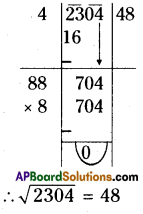
(iii) 3375
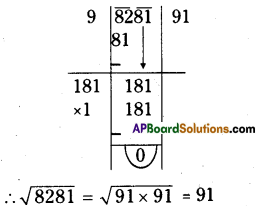
Step 1: Start making groups of three digits starting from the unit place.
i.e.;

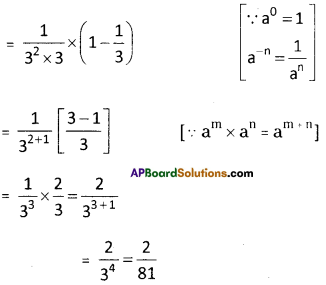
Step 2: First group is 375. Its units digit is 5.
∴ The cube root is also ends with 5.
∴ The units place of the cube root will be 5.
Step 3: Now take the second group,
i.e., 3 we know that 13 < 33 <23
∴ The least number is 1.
∴ The tens digit of a cube root will be 1.
∴ The required number = 15
\(\sqrt[3]{3375}=\sqrt[3]{15 \times 15 \times 15}=\sqrt[\not]{15^{\not 3}}=15\)
![]()
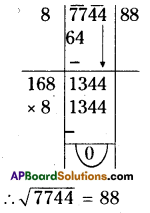
(iv) 5832
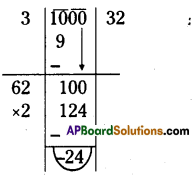
Step 1: Start making groups of three digits starting from the unit place.

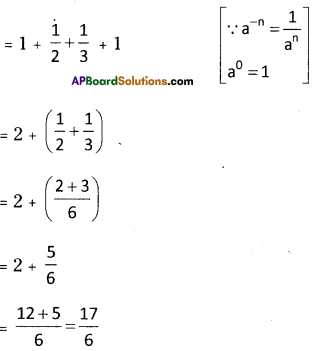
Step 2: The units digit of 832 is 2.
∴ The cube root of the number ends with units digit 8.
[∵ 8 x 8 x 8 = 512]
Step 3: In the second group i.e., 5 lie between 1 and 6
i.e., 13 < 5 < 23
∴ The tens digit of a number will bel.
∴ The required number is 18.
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{5832}=\sqrt[3]{18 \times 18 \times 18}=\sqrt[3]{(18)^{3}}\)
= 18
![]()
Question 3.
State true or false?
(i) Cube of an even number is an odd number
(ii) A perfect cube may end with two zeros
(iii) If a number ends with 5, then its cube ends with 5
(iv) Cube of a number ending with zero has three zeros at its right
(v) The cube of a single digit number may be a single digit number.
(vi) There is no perfect cube which ends with 8
(vii) The cube of a two digit number may be a three digit number.
Solution:
(i) Cube of an even number is an odd number (F)
(ii) A perfect cube may end with two zeros (F)
(iii) If a number ends with 5, then its cube ends with 5. (T)
(iv) Cube of a number ending with zero has three zeros at its right. (T)
(v) The cube of a single digit number may be a single digit number. (F)
(vi) There is no perfect cube which ends with 8(F)
(vii) The cube of a two digit number may be a three digit number. (F)
![]()
Question 4.
Find the two digit number which is a square number and also a cubic number.
Solution:
The two digited square and cubic
number is 64
∴ 64 = 8 x 8 = 82 ⇒ \(\sqrt{64}\) = 8
64 = 4 x 4 x 4 = 43 ⇒ \(\sqrt[3]{64}\) = 4