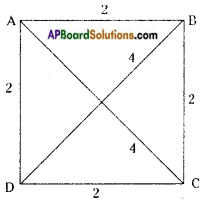
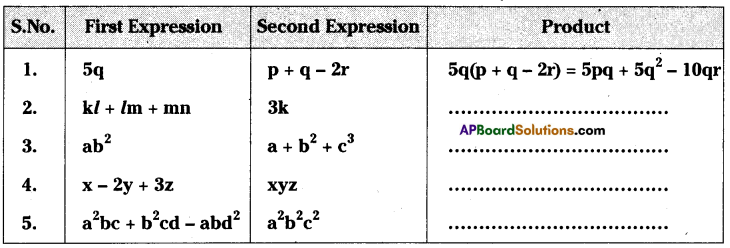
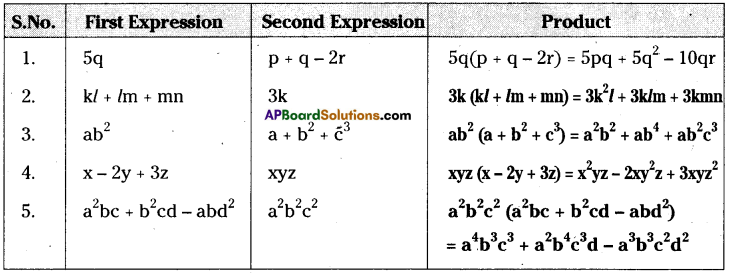
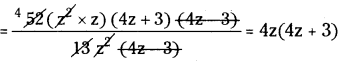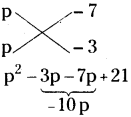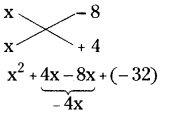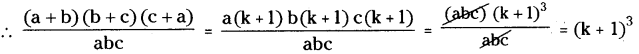AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 12 Factorisation Ex 12.3 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Maths Solutions 12th Lesson Factorisation Exercise 12.3
![]()
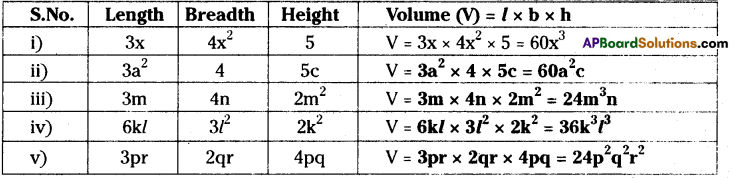
Question 1.
Carry out the following divisions
(i) 48a3 by 6a
(ii) 14x3 by 42x3
(iii) 72a3b4c5 by 8ab2c3
(iv) 11xy2z3 by 55xyz
(v) -54l4m3n2 by 9l2m2n2
Solution:
(i) 48a3 by 6a
48a3 ÷ 6a
= \(\frac{6 \times 8 \times a \times a^{2}}{6 \times a}\)
= 8a2
(ii) 14x3 by 42x3
= 14x3 ÷ 42x3
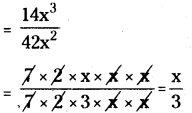
![]()
(iii) 72a3b4c5 by 8ab2c3
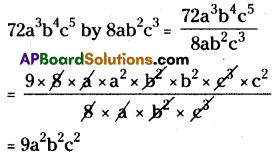
(iv) 11xy2z3 by 55xyz
11xy2z3 ÷ 55xyz
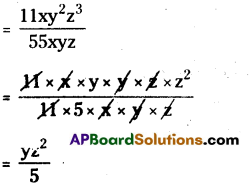
(v) -54l4m3n2 by 9l2m2n2
-54l4m3n2 ÷ 9l2m2n2

= -6l2m
Question 2.
Divide the given polynomial by the given monomial
(i) (3x2 – 2x) ÷ x
(ii) (5a3b – 7ab3) ÷ ab
(iii) (25x5 – 15x4) ÷ 5x3
(iv) (4l5 – 6l4 + 8l3) ÷ 2l2
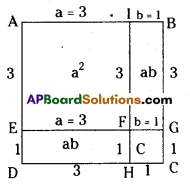
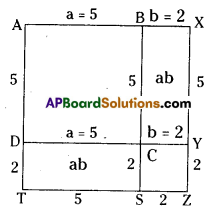
(v) 15 (a3b2c2 – a2b3c2 + a2b2c3 ) ÷ 3abc
(vi) 3p3– 9p2q – 6pq2) ÷ (-3p)
(vii) (\(\frac{2}{3}\) a2 b2 c2+ \(\frac{4}{3}\) a b2 c3) ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\)abc
Solution:
(i) (3x2 – 2x) ÷ x
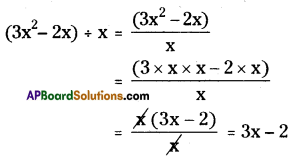
![]()
(ii) (5a3b – 7ab3) ÷ ab
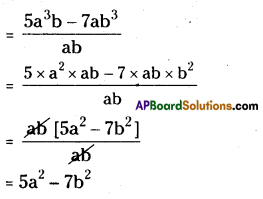
(iii) (25x5 – 15x4) ÷ 5x3
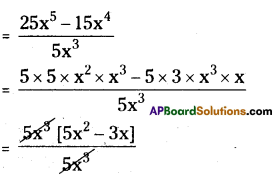
= 5x2 – 3x (or) x(5x – 3)
(iv) (4l5 – 6l4 + 8l3) ÷ 2l2
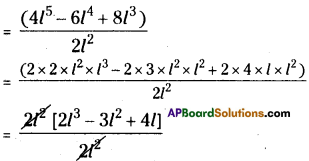
= 2l2 – 3l2 + 4l = l(2l2 – 3l + 4)
(v) 15 (a3 b2 c2 – a2 b3 c2 + a2 b2 c3 ) ÷ 3abc
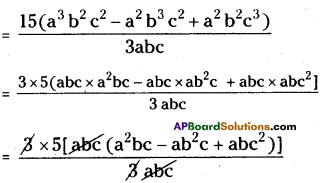
= 5[a x abc – b x abc + c x abc ]
= 5abc [a – b + c]
![]()
(vi) 3p3– 9p2q – 6pq2) ÷ (-3p)
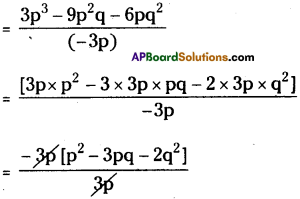
= -[p2 – 3pq – 2q2]
= 22 + 3pq – p2
(vii) (\(\frac{2}{3}\) a2b2c2+ \(\frac{4}{3}\) ab2c3) ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\)abc
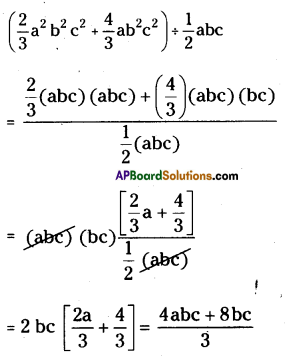
![]()
Question 3.
Workout the following divisions:
(i) (49x -63) ÷ 7
(ii) 12x (8x – 20,) ÷ 4(2x – 5)
(iii) 11a3 b3 (7c – 35) ÷ 3a2 b2 (c – 5)
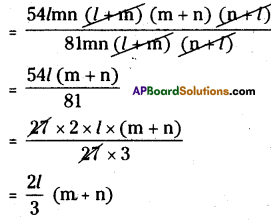
(iv) 54lmn (l + m) (m + n) (n + l) ÷ 8 lmn (l + m) (n +l)
(v) 36(x + 4)(x2 + 7x + 10) ÷ 9(x + 4)
(vi) a(a+1)(a+2)(a + 3) ÷ a(a + 3)
Solution:
(i) (49x -63) ÷ 7
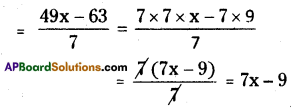
(ii) 12x (8x – 20,) ÷ 4(2x – 5)
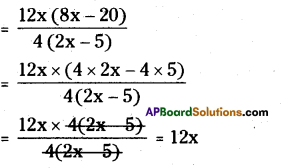
![]()
(iii) 11a3 b3 (7c – 35) ÷ 3a2 b2 (c – 5)
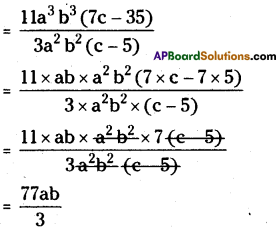
(iv) 54lmn (l + m) (m + n) (n + l) ÷ 8 lmn (l + m) (n +l)
(v) 36(x + 4)(x2 + 7x + 10) ÷ 9(x + 4)
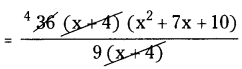
4 ( x2 + 7x + 10)
= 4 ( x2 + 5x + 2x + 10)
= 4 [x( x + 5) +2(x + 5)]
= 4( x + 5) (x + 2)
(vi) a(a+1)(a+2)(a + 3) ÷ a(a + 3)
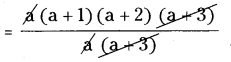
= ( a + 1)(a + 2)
![]()
Question 4.
Factorize the expressions and divide them as directed:
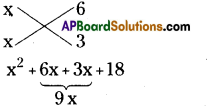
(i) (x2 + 7x + 12) ÷ (x + 3)
(ii) (x2 – 8x + 12) ÷ (x – 6)
(iii) (p2 + 5p + 4,) (p + l)
(iv) 15ab(a2 – 7a + 10) ÷ 3b(a – 2)
(v) 151m (2p2 – 2q2) ÷ 3l(p + q)
(vi) 26z3(32z2 – 18,) ÷ 13z2 (4z – 3)
Solution:
(i) (x2 + 7x + 12) ÷ (x + 3)
(x2 + 7x + 12) ÷ (x + 3)
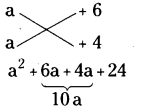
x2 + 7x + 12 = x2 + 3x + 4x + 12
= x(x + 3) + 4(x + 3)
= (x + 3) (x + 4)
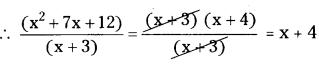
(ii) (x2 – 8x + 12) ÷ (x – 6)
(x2 – 8x + 12) ÷ (x – 6)
x2 – 8x + 12 = x2 – 6x – 2x + 12
= x(x – 6) – 2(x – 6)
= (x – 6) (x – 2)
∴ (x2 – 8x + 12) 4 (x – 6)
= \(\frac{(x-6)(x-2)}{(x-6)}\) = x – 2
![]()
(iii) (p2 + 5p + 4,) (p + 1)
p2 + 5p + 4 = p2 + p + 4p + 4
= p(p + 1) + 4(p + 1)
= (p + 1) (p + 4)
(p2 + 5p + 4) ÷ (p + 1)
= \(\frac{(p+1)(p+4)}{(p+1)}\) = p + 4
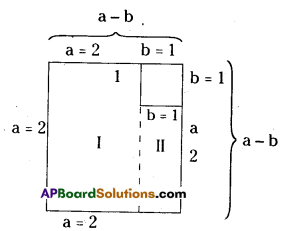
(iv) 15ab(a2 – 7a + 10) ÷ 3b(a – 2)
15ab (a2 – 7a + 10) ÷ 3b (a – 2)
15ab (a2 – 7a + 10) = 15ab (a2 – 5a – 2a + 10)
= 15ab [(a2 – 2a) – (5a -10)]
= 15ab [a(a – 2) – 5(a – 2)]
= 15ab(a – 2)(a – 5)
∴ 15ab (a2 – 7a + 10) ÷ 3b (a – 2)
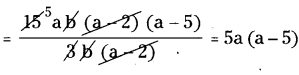
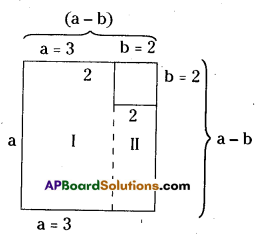
(v) 151m (2p2 – 2q2) ÷ 3l(p + q)
15lm (2p2 – 2q2) ÷ 3l (p + q)
15lm (2p2 – 2q2) = 15lm x 2(p2 – q2)
= 30lm (p + q) (p – q)
∴ 15lm(2p2 – 2q2) ÷ 3l(p + q)
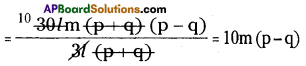
![]()
(vi) 26z3(32z2 – 18,) ÷ 13z2 (4z – 3)
26z3(32z2 – 18) ÷ 13z2 (4z – 3)
26z3(32z2 – 18) = 26z3 (2 x 16z2 – 2 x 9)
= 26z3 x 2 [16z3 – 9]
= 52z3 [(4z)3 – (3)3]
= 52z3 (4z + 3) (4z – 3)
∴ 26z3 (32z2 – 18) ÷ 13z2 (4z – 3)