AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Biology Solutions Chapter 7 Different Ecosystems Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Biology Solutions 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems
8th Class Biology 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Define an ecosystem. Explain it with a suitable example.
Answer:
- An ecosystem can be defined as a functional unit of nature, where living organisms interact among themselves and also with the surrounding physical environment.
- For example, Mangroves are one of the most productive ecosystem on earth, deriving nourishment from terrestrial fresh water and tidal salt water.
- Coringa mangrove is situated south of Kakinada Bay and is about 150 km south of Visakhapatnam.
- It is named after the river coringa. Coringa mangroves receives fresh water from coringa and Gaderu rivers and salt waters from Kakinada Bay.
- Biotic components in coringa:
Producers: Mangrove, Spirogyra, Euglena, Oscilatoria, Blue Green Algae, Ulothrix etc.
Consumers: Shrimp, crab, hydra, protozoans, mussel, snails, turtle, daphnia, brittle word, tube worm etc.
Decomposers: Detritus feeding bacteria etc. - Abiotic components: Salt and fresh water, air, sunlight, soil, etc.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain how diversity of living organisms helps in enriching any ecosystem.
Answer:
- The existence of the ecosystem depends on the continued survival of the organisms in the ecosystem.
- All organisms require energy for growth, reproduction and survival.
- This energy is obtained by the organisms from the food they consume.
- Plants are the producers producing food in any ecosystem. The animals present in the ecosystem are consumers as they consume food from plants.
- Some of the organisms in the ecosystem such as bacteria and fungi, obtained their nutritional requirements by decomposing the dead bodies of both producers and consumers.
- They retain nutrients to the soil for the plants to use. As the cycle begins again.
- Like this diversity of living organisms helps in enriching any ecosystem.
Question 3.
What happens when two animals having similar habits share one ecosystem?
Answer:
When two animals having similar habits, sharing one ecosystem , only the stronger and better equipped animal can survive, while the weaker one die or eliminated from the ecosystem. This is called ‘Survival of the fittest’.
Question 4.
What is the difference between habitat and ecosystem?
Answer:
Habitat is the natural living place of an organism or a group of organisms. Land and water are the major habitates.
An ecosystem is a Natural unit and has both Abiotic and biotic components, which interact and influence each other.
Question 5.
Who am I?
1. I am the base of food chain.
Answer:
Green plants.
2. I depend on plants for food.
Answer:
Consumers (Herbivorous Animals)
3. I break down the remains of dead plants and animals.
Answer:
Decomposers.
Ex: Bacteria, Fungi.
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following is producer and why?
а) fox b) fungus c) chicken d) grass.
Answer:
- Grass is the producer.
- All green plants produce food materials with the help of carbondioxide and water in the presence of sunlight. So plants are called producers.
- As grass is the green plant and produce food for other animals, it is called producer.
Question 7.
What do you understand by food web? Describe your own food web with the help of diagrammatic representation.
Answer:
- A food web consists of several interlinked food chains and each organism in the food web will be a member of more than one food chain.
- For example rats and insects eat seeds and other plant parts. As their food.
- Insects are eaten by frogs and lizards.
- Rats and frogs are eaten by snakes.
- Lizards and snakes are eaten by birds.
- Birds are eaten by fox, wolves. These are eaten by tigers and lions.
- Thus a single plant or an animal may become food for more than one animal.
- Similiarly an animal may consume more than one type of food depending on its taste and availability in the ecosystem.
- Thus each organism in an ecosystem may be a member of more than one food chain.
- When we looked at these relationships between various organisms for food in the ecosystem, it appears that several food chains are interlinked with each other forming a food web.
FOOD WEB
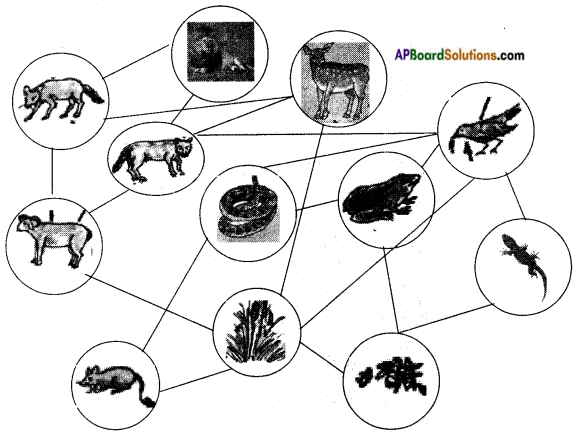
![]()
Question 8.
An ecosystem that had mice. What happens if more cats were added to it?
Answer:
- In an ecosystem if the mice and the cats were existing equally, smooth balance would be maintained. When reproduction took place in these animals, generations would be continued then the ecosystem would be maintained healthy.
- When more cats were added in that ecosystem all the mice would be eaten away by the cats it leads to the end of mice population.
- Because of lack of food, the cats, either have to leave the ecosystem or they die.
- If there is no continuity of the animals, the ecosystem would be destroyed.
Question 9.
List out producers (plants, bushes, trees), consumers (herbivores and carnivores) and decomposers that you observed in your agriculture field or school garden.
Answer:
Producers:
Plants – Grass plants, creepers like pumpkin, bottlegourd, etc.
Bushes – Rose, Jasmine, chrysanthemum, marigold.
Trees – Palm, coconut, mango, drumstick, lemon, sweet lemon, guava.
Consumers:
Herbivores – Goat, sheep, buffalo, ox, rats, butterflies, etc.
Carnivores – Crow, dogs, snakes, frogs, lizards.
Decomposers – Fungi (mushroom), Bacteria.
Question 10.
In grassland ecosystem, rabbit eats only plants. They eat plants faster than the plants can grow back. What must happen to bring the ecosystem into balance?
Answer:
The animals like fox, wolves, tigers, etc. which feed on rabbits will be introduced in that grass land ecosystem, then the rabbits will be controlled by them. Thus the ecosystem will comes into balance.
![]()
Question 11.
Plant, Tiger, Rabbit, Fox, Hawk.
Did you find any connection among the above list of things. If we remove Rabbit from the list what will happen?
Answer:
- Plant, tiger, rabbit, fox, hawk these are the animals living in an ecosystem and are interdepending one on the other, and maintaining a food web – Plants → Rabbit → Hawk → Fox → Tiger.
- A delicate balance is seen in nature between members of different species.
- Any disturbance in this balance affects the organisms in a food web.
- If we remove rabbit from the list the other animals like tiger, fox, hawk which are depending one on the other for food will die because of no food.
- All the organisms, big or small, have right to live on this planet as man. We should respect this and allow other organisms to live and share the wealth of this planet.
- “LIVE AND LET LIVE” should become our motto.
Question 12.
What do you understand by interdependency of animals and plants ? How do you appreciate ?
Answer:
- An ecosystem is made up of groups of living things and their environments.
- Living things like plants, animals and microorganisms are known as biotic components and others like soil, water, sunlight etc are called as abiotic components of the ecosystem.
- All these organisms live together and interact with one another in many ways.
- There is a feeding relationship between plants and animals. Along with this an interdependence between plants and animals for space, reproduction, shelter, etc.
- All organisms in an ecosystem derive energy from food to live.
- The sun is the main source of energy for all living things.
- Plants being autotrophic, trap this energy through a process called photosynthesis and produce food to all living organisms. They are known as Primary producers.
- Animals as they can not prepare food, they consume plants directly or indirectly and called consumers.
- Living organisms like fungi and bacteria which are called decomposers, decay and decompose the dead animals of producers and consumers, and valuable nutrients to the soil for plants to use, as the cycle begins again.
- A delicate balance is seen in nature between plants and animals by interdependence one to the other for thousands of years, which is unreachable to the human brain.
8th Class Biology 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems InText Questions and Answers
![]()
Question 1.
What is a Habitat?
Answer:
- The dwelling place for plants and animals is called habitat.
- One habitat shared by different types of plants and animals.
- Try to add more such points to your list.
- The natural home for plants and animals is called a habitat.
- Habitat is the environment of an animal or plant.
- Habitat is a suitable place for plants and animals to live.
- Habitat is the origin for plants and animals.
Question 2.
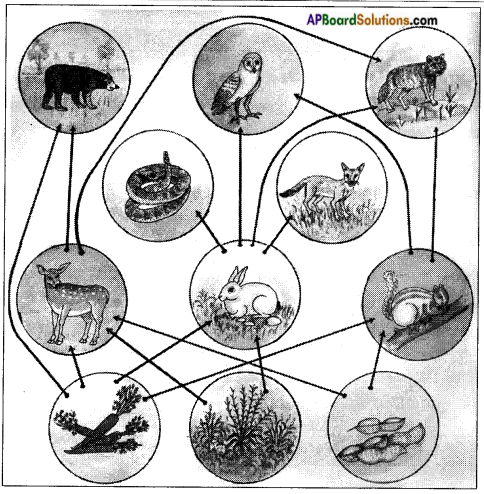
Draw the diagram of Interdependence between the biotic components and answer the following questions.
Answer:
Interdependence between the biotic components:
1. What do the arrows in the figure indicate?
Answer:
The animals are depending one on the other for food.
2. Trace the path from grass to tiger. You may trace out other paths as well.
Answer:
Grass → grass hopper → frog → snake.
Carrot and grass → rabbit → fox → tiger
Plants → deer → bear → tiger
Seeds → squirrel → eagle → tiger
3. On how many organisms is rabbit dependent? Write their names.
Answer:
Carrot, grass.
4. How many organisms depend on rabbit? Write their names.
Answer:
Snake, fox, eagle, tiger.
5. Where do plants get their food from?
Answer:
Plants are autotrophs they can prepare their food from carbondioxide and water, in the presence of sunlight.
6. What other things do animals need for their survival?
Answer:
Abiotic components like soil, water, sunlight, etc.
8th Class Biology 7th Lesson Different Ecosystems Activities
Activity – 1
![]()
Lab Activity
Answer:
Aim: Study an ecosystem at your school/ home garden to understand it’s structure. Material Required : Measuring tape string, small sticks, hand lens, hand towel.
Procedure: To know about structure of the ecosystem we have to follow the following procedure.

- Use the tape to measure a square area that is one meter long and one meter wide. It can be on grass, bare dirt or side wall.
- Mark the edges of the square with the help of string/chalk.
- Observe the study area (that has been marked). Look for the plants and animals that live there. Use the hand lens.
- Record all the living organisms you see. You can even dig to go deeper to find out other living organisms that may be present there.
Observation / Findings: We find –
- Plants like grass, herbs, shrubs, guava, neem and creepers.
- Insects like ants, grass hoppers, butterflies, mosquitoes, houseflies, locusts, etc.
- Animals like cat, dog, buffalo, frog, lizards, garden lizards, snake.
- Mushroom, algae.
- Deeper layers of soil we find earth worm, leech, rats, bandicoots, rabbits, etc.
- Birds like crow, parrot, mynah, etc.
Discussion:
1. What living things did you find in your study area? Try to count them if possible.
Answer:
Grass, creepers, shrubs, herbs, trees, herbivores, carnivores, fungi.
2. Which kind of living thing was most common in your study area?
Answer:
Plants.
3. How was your study area different from those of other student groups?
Answer:
Living conditions, food, animals and plants are different.
4. Other than the living organisms what other things can you record from your study area?
Answer:
Soil, water, sunlight (temperature) are recorded.
Activity – 2
![]()
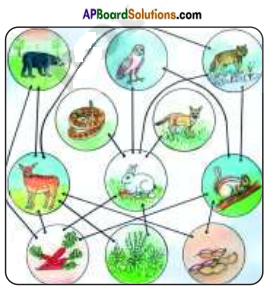
Question 2.
Observe the food web given below figure.

Answer:
The diagram showing food web.
Now answer the following Questions.
1. Which are the producers in the food web?
Answer:
Grass, rice plants, maize, bushes.
2. Which are consumers?
Answer:
Fish, frog, birds, rats, rabbit, deer, tadpole, larva ,sheep, cat, fox, tiger, crane, eagle, snake, owl, peacock, insects, lion.
3. Where does the food web start from?
Answer:
Food web starts from green plants.
4. Name the organism where the food web ends.
Answer:
Crane, eagle, owl, peacock, lion.
5. What happens when plants and animals die in a food web?
Answer:
When plants and animals die, they are decayed and decomposed by Decomposers like bacteria and fungi. They return nutrients to the soil for plants to use, as the cycle begin again. This is the reason ‘Decomposers are also called as recyclers.
Activity – 3
Question 3.
Collect the information forests of Andhra Pradesh and write the flora and fauna and fill up the following table:
Answer:
Forests of Andhra Pradesh

Name of the Forest – Kondapalli Reserve Forest
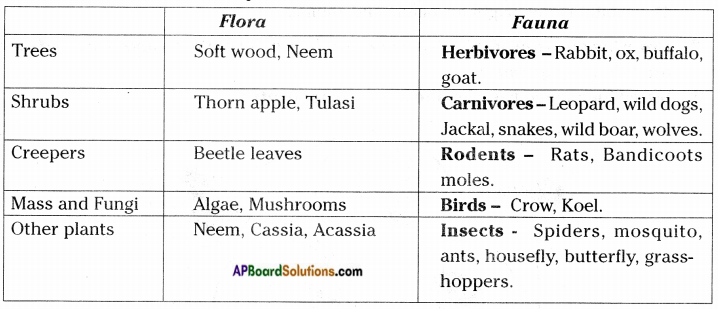
![]()
Investigations:

1. Do all the forest have same type of vegetation?
Answer:
No, there are mainly trees that show much species diversity and greater degrees stratification.
2. Are producers afforest ecosystem higher than its consumers?
Answer:
Trees are higher than consumers, besides trees shrubs and ground vegetation also there.
3. Do all the forests have same type of animals?
Answer:
No, the availability of food and environment different type of animals are present in different forest.