AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 3 Story of Microorganisms 1
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Biology Important Questions 3rd Lesson Story of Microorganisms 1
8th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Story of Microorganisms 1 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are microorganisms?
Answer:
Some organisms can be seen only with the help of a microscope. Such organisms are called ‘microorganisms’.
Question 2.
Where can we find microorganisms?
Answer:
Microorganisms can found in air, water, soil and all living organisms.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the names of some groups of microorganisms.
Answer:
Bacteria, fungi, protozoa, algae are some of the groups of microorganisms.
Question 4.
What is meant by arthropods?
Answer:
Arthropods are joint legged organisms which causes the diseases like scabies.
Question 5.
Write the names of diseases which are caused by bacteria.
Answer:
Diseases like typhoid, tuberculosis (T.B.) and septicemia (blood poisoning) are caused by bacteria.
Question 6.
Mention the diseases caused by protozoans.
Answer:
Malaria, Amoebiasis, Kala Azar, Sleeping bickness are some of the diseases caused by protozoans.
![]()
Question 7.
How do we classify the groups of microorganisms?
Answer:
Basing upon the cell structure and mode of living we can classify the microbes into 6 groups.
- Bacteria,
- Algae,
- Fungi,
- Protozoans,
- Micro orthropods and
- Viruses.
Question 8.
What are the uses of yeast?
Answer:
- Yeast cells are frequently used in the fermentation process of sugars.
- Yeast is used in the preparation of cakes and buns in bakeries.
Question 9.
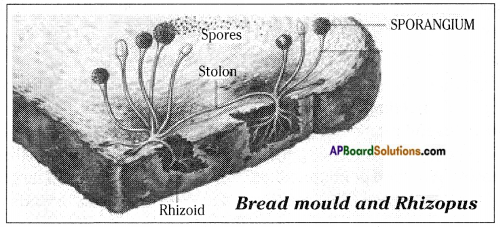
What is a “bread mould”?
Answer:
Rhizopus
Question 10.
Aspergillus reproduction takes place through a special structures. What are they?
Answer:
Conidiospores.
8th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Story of Microorganisms 1 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Prepare a model of any micro arthropod.
Answer:

![]()
Question 2.
What is Pencillin? Who discovered this?
Answer:
- ‘Antibacterium’ is prepared from a fungi called Pencillium notatum. This is called Pencillin.
- Pencillin was discovered by Dr. Alexander Flemming.
Question 3.
How do you culture protozoa?
Answer:
- Soak hay in pond water taken in a dish.
- Add rice powder or ‘Gangi’ to this solution.
- Keep the dish undisturbed for 3 – 4 days.
- You can observe several protozoans in this hay decoction.
Question 4.
How can you observe algae in your laboratory?
Answer:
- Take 2-3 drops of greenish pond water on a slide.
- Spread the scrapings having small stringe like bodies on the slide.
- Cover it with a cover slip and observe it under microscope.
- You can see algae like spirogyra, spirulina and ceratium.
Question 5.
How Microbiology helps in identifying diseases and their prevention?
Answer:
- Microbiology plays a very vital important role in identifying the cause of diseases by the discovery of several microorganisms.
- Microbiology helps in the preparation of diseases caused by microorganisms by the discovery of their transmission methods.
8th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Story of Microorganisms 1 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Collect different pictures of micro arthropods.
Answer:
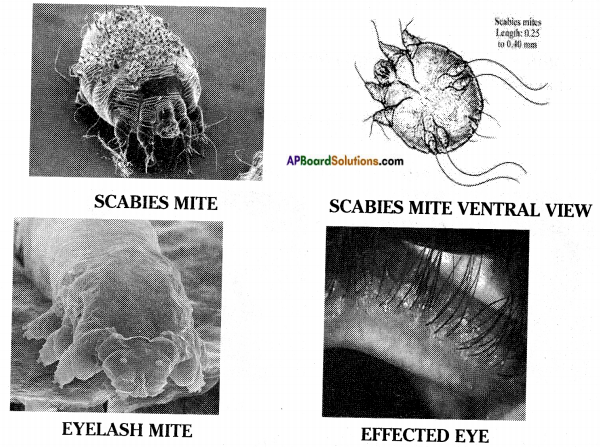
![]()
Question 2.
Make sketches of bacterial cell.
Answer:
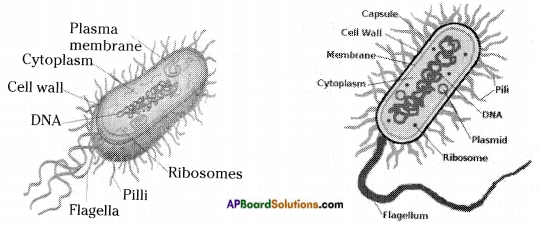
Question 3.
How can you grow protozoa practically in your school? Explain.
Answer:
To grow protozoa, soak hay in pond water to prepare a decoction of hay. After 3-4 days take one or two drops of hay or grass decoction and observe it under microscope. We can see different protozoans like amoeba, paramecium etc.

Question 4.
Identify the following diagram and Label parts.
Answer:
Question 5.
How do you appreciate the fact that some of the bacteria are useful to human?
Answer:
At birth, a baby’s digestive system is a sterile, undiscovered continent. Within minutes, microbes have started pouring in from every direction. They come from the birth canal, from the mother’s breast milk, from the fingertips of nurses and the lips of happy relatives.
There are also innumerable colonies of E. coli in biotechnology and microbiology labs around the world. Everyday pharmaceutical companies manipulate E. coli to produce human-growth hormone, insulin, vitamins, and even the rennet used to make cheese. Biologists use E. coli to map metabolic pathways. Scientists are even using E. coli try to understand why we age and die.
Nitro bacter, ammonifying bacteria etc., are more useful for decompositions and fixing of Nitrogen in the plants and soil.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain how microorganisms are important for maintaining of healthy soil and biodiversity.
Answer:
The soil is home to a large proportion of the world’s biodiversity. The top eight inches of soil of one acre area may contain as much as five and half tons of bacteria and fungi.
Soil organisms breakdown organic matter, making nutrients available for uptake by plants and other organisms. A gram of garden soil contains around one million fungi, such as yeasts and moulds. Bacteria and fungi play key roles in maintaining a healthy soil. They act as decomposers that break down organic materials to produce detritus and other breakdown products. Soil detritivores, like earthworms, ingest detritus and decompose it.
Question 7.
Collect the information about useful microorganisms from your school library.
Answer:
| Name of the microorganism | Utility |
| Yeast(Fungus) | Production of alcohol fermented foods like Idli, Dosa etc……….. |
| Pencillium notatum (Fungus) | Preparation of antibiotics |
| Nostoc, Anabina, Azatobactor | Fixation of atmospheric nitrogen. |
| Spirulina | Preparation of medicines |
| Lactobacillus | Preparation of curd, cheese, buttermilk. |
Question 8.
How do you appreciate the role of decomposers in the earth?
Answer:
- Microorganisms are the decomposers of the earth.
- They decompose the organic matter from plant parts and dead animals. They enrich the soil with organic matter again.
- Thus, they maintain the soil fertility and eliminate the wastes from the earth.
- I appreciate the role played by decomposers in scavenging the earth by decomposing the organic matter of dead bodies.
![]()
Question 9.
What are ‘bio – fertilizers’? How are they useful?
Answer:
- Microorganisms like Bacteria, Fungi which decompose the fallen plant parts, dung and vegetable peelings into simple chemical compounds.
- They form ‘useful manure’ to the plants since this manure is formed naturally from biological activity of microorganisms, they are called ‘bio – fertilizers’.
- Farmers are benefited economically. They don’t need chemical fertilizers to increase the soil fertility. Hence, Bio – fertilizers are considered as “friends of farmers”.