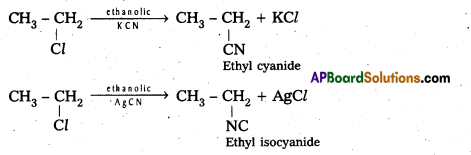
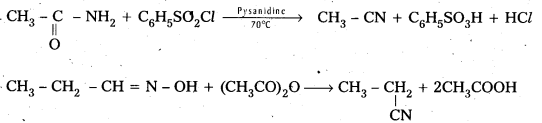
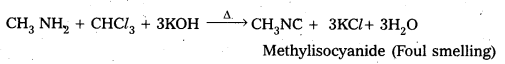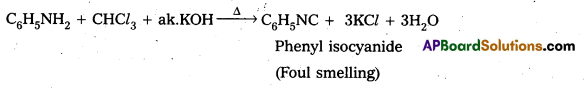Telangana & Andhra Pradesh BIEAP TS AP Intermediate Inter 1st Year Zoology Study Material Textbook Solutions Guide PDF Free Download, TS AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Blue Print Weightage 2022-2023, Telugu Academy Intermediate 1st Year Zoology Textbook Pdf Download, Questions and Answers Solutions in English Medium and Telugu Medium are part of AP Inter 1st Year Study Material Pdf.
Students can also read AP Inter 1st Year Botany Syllabus & AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
AP Intermediate 1st Year Zoology Study Material Pdf Download | Jr Inter 1st Year Zoology Textbook Solutions
- Chapter 1 Diversity of Living World
- Chapter 2 Structural Organisation in Animals
- Chapter 3 Animal Diversity-I: Invertebrate Phyla
- Chapter 4 Animal Diversity-II: Phylum Chordata
- Chapter 5 Locomotion and Reproduction in Protozoa
- Chapter 6 Biology in Human Welfare
- Chapter 7 Type Study of Periplaneta Americana (Cockroach)
- Chapter 8 Ecology and Environment
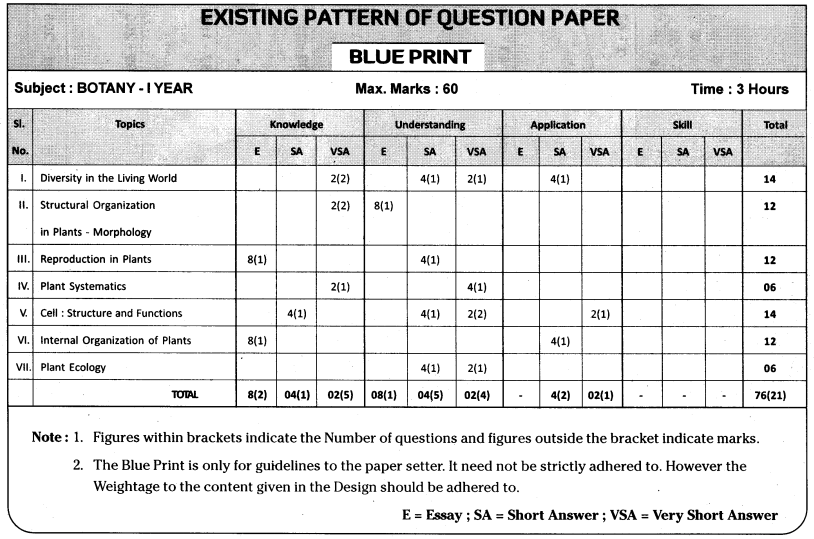
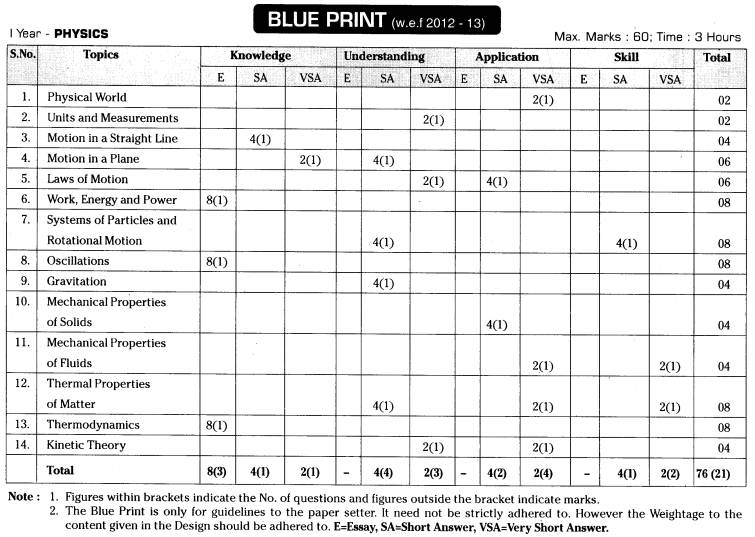
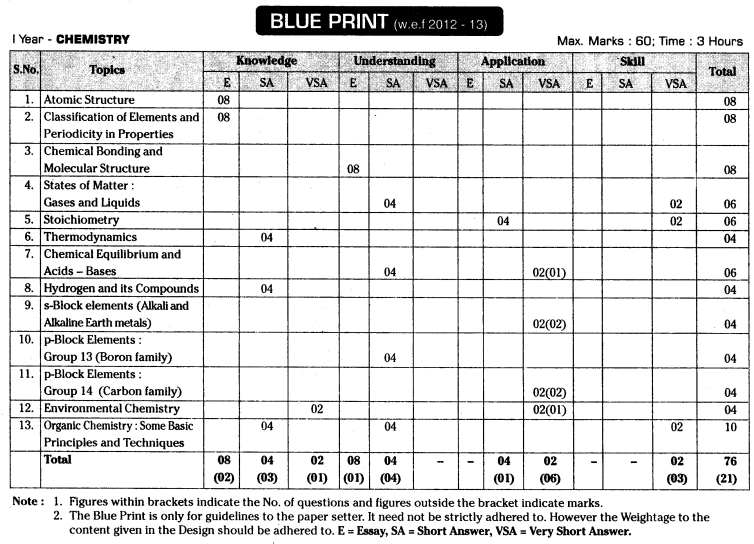
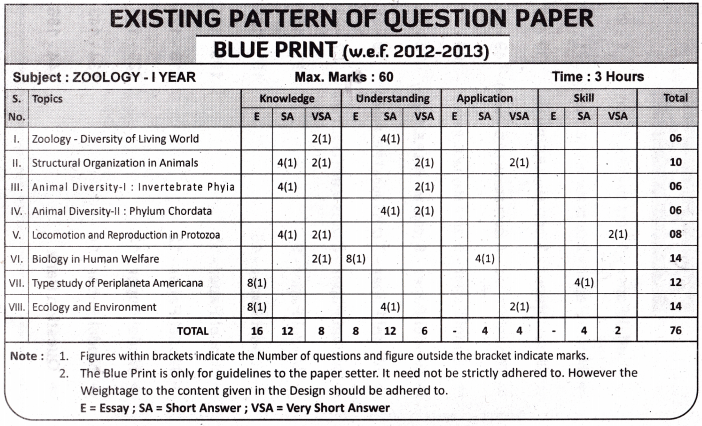
TS AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Weightage Blue Print 2022-2023
TS AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Weightage 2022-2023 | TS AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Blue Print 2022
TS AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Weightage to Objectives
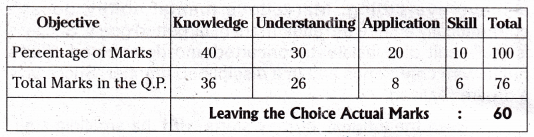
TS AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Weightage to Form of Questions
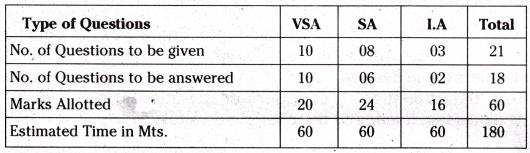
TS AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Weightage to Content: Units
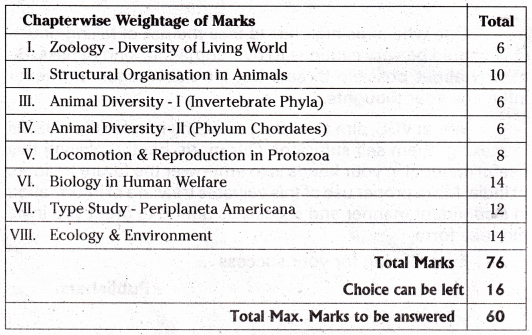
Intermediate 1st Year Zoology Syllabus
TS AP Inter 1st Year Zoology Syllabus
Unit I Zoology – Diversity of Living World
- 1.1 What is life?
- 1.2 Nature, Scope & meaning of zoology
- 1.3 Branches of Zoology
- 1.4 Need for classification- Zoos as tools for the study of taxonomy
- 1.5 Basic principles of Classification: Biological system of classification- (Phylogenetic classification only)
- 1.6 Levels of Hierarchy of classification
- 1.7 Nomenclature – Bi & Trinominal
- 1.8 Species concept
- 1.9 Kingdom Animalia
- 1.10 Biodiversity – Meaning and distribution (Genetic diversity, Species diversity, Ecosystem diversity(alpha, beta, and gamma), other attributes of biodiversity, the role of biodiversity, threats to biodiversity, methods of conservation, IUCN Red data books, Conservation of wildlife in India – Legislation, Preservation, Organisations, Threatened species.
Unit II Structural Organization in Animals
- 2.1 Levels of organization, Multicellularity: Diploblastic & Triploblastic conditions.
- 2.2 Asymmetry, Symmetry: Radial symmetry, and Bilateral symmetry (Brief account giving one example for each type from the representative phyla)
- 2.3 Acoelomates, Pseudocoelomates, and Eucoelomates: Schizo & Entero coelomates (Brief account of the formation of coelom)
- 2.4 Tissues: Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, and Nervous tissues. (make it a little more elaborative)
Unit III Animal Diversity – I: Invertebrate Phyla
General Characters – Strictly restrict to 8 salient features only
Classification up to Classes with two or three examples – Brief account only
- 3.1 Porifera
- 3.2 Cnidaria
- 3.3 Ctenophora
- 3.4 Platyhelminthes
- 3.5 Nematoda
- 3.6 Annelida (Include Earthworm as a type study strictly adhering to NCERT textbook)
- 3.7 Arthropoda
- 3.8 Mollusca
- 3.9 Echinodermata
- 3.10 Hemichordata
Unit IV Animal Diversity – II: Phylum: Chordata
General Characters – Strictly restrict to 8 points only Classification up to Classes – Brief account only with two or three examples
- 4.1 Sub phylum: Urochordata
- 4.2 Sub phylum: Cephalochordata
- 4.3 Sub phylum: Vertebrata
- 4.4 Super Class: Agnatha
- 4.4.1 Class Cyclostomata
- 4.5 Super Class: Gnathostomata
- 4.5.1 Super Class: Pisces
- 4.5.2 Class: Chondrichthyes
- 4.5.3 Class: Osteichthyes
- 4.6 Tetrapoda
- 4.6.1 Class: Amphibia (Include Frog as a type study strictly adhering to NCERT textbook)
- 4.6.2 Class: Reptilia
- 4.6.3 Class: Aves
- 4.6.4 Class: Mammalia
Unit V Locomotion & Reproduction in Protozoa
- 5.1 Locomotion: Definition, types of locomotor structures pseudopodia (basic idea of pseudopodia without going into different types), flagella & cilia (Brief account giving two examples each)
- 5.2 Flagellar & Ciliary movement – Effective & Recovery strokes in Euglena, Synchronal & Metachronal movements in Paramecium
- 5.3 Reproduction: Definition, types. Asexual Reproduction: Transverse binary fission in Paramecium & Longitudinal binary fission in Euglena. Multiple fission, Sexual Reproduction.
Unit VI Biology & Human Welfare
- 6.1 Parasitism and parasitic adaptation
- 6.2 Health and disease: introduction (follow NCERT) Life cycle, Pathogenicity, Treatment & Prevention (Brief account only)
1. Entamoeba histolytica 2. Plasmodium vivax 3. Ascaris lumbricoides 4. Wuchereria bancrofti - 6.3 A brief account of pathogenicity, treatment & prevention of Typhoid, Pneumonia, Common cold, & Ringworm.
- 6.4 Drugs and Alcohol abuse
Unit VII Type study of Periplaneta Americana
- 7.1 Habitat and habits
- 7.2 External features
- 7.3 Locomotion
- 7.4 Digestive system
- 7.5 Respiratory system
- 7.6 Circulatory system
- 7.7 Excretory system
- 7.8 Nervous system – sense organs, the structure of ommatidium.
- 7.9 Reproductive system
Unit VIII Ecology & Environment
- 8.1 Organisms and Environment: Ecology, population, communities, habitat, niche, biome, and ecosphere (definitions only)
- 8.2 Ecosystem: Elementary aspects only Abiotic factors – Light, Temperature & Water (Biological effects only), Ecological adaptations
- 8.3 Population interactions
- 8.4 Ecosystems: Types, Components, Lake ecosystem
- 8.5 Food chains, Food web, Productivity and Energy flow in Ecosystem, Ecological pyramids – Pyramids of numbers, biomass, and energy.
- 8.6 Nutrition cycling – Carbon, Nitrogen, & Phosphorous cycles (Brief account)
- 8.7 Population attributes Growth, Natality, and Mortality, Age distribution, and Population regulation.
- 8.8 Environmental issues
We hope that this Telangana & Andhra Pradesh BIEAP TS AP Intermediate Inter 1st Year Zoology Study Material Textbook Solutions Guide PDF Free Download 2022-2023 in English Medium and Telugu Medium helps the student to come out successful with flying colors in this examination. This Jr Inter 1st Year Zoology Study Material will help students to gain the right knowledge to tackle any type of questions that can be asked during the exams.