Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material 10th Lesson The p-Block Elements – Group 13 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 1st Year Chemistry Study Material 10th Lesson The p-Block Elements – Group 13
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Discuss the pattern of variation in the oxidation states of Boron to Thallium.
Answer:
- Boron exhibits – 3 oxidation state due to its small size and non-metalic nature.
- Aluminium exhibits +3 oxidation state.
- Gallium, Indium and Thallium exhibits both +1 and +3 oxidation states.
- In Thallium +1 oxidation state is more stable than +3 due to inert pair effect.
Question 2.
How do you explain higher stability of TlCl3 ?
Answer:
[TlCl3 is not stable because Tl doesnot exist in Tl3 stable state.] [TlCl is stable because of inertpair effect Tl+1 is stable].
![]()
Question 3.
Why does BF3 behave as a Lewis acid ?
Answer:
BF3 is a electron deficient molecule. It has the tendency to accept an electron pair. Electron pair acceptors are Lewis acids. Hence BF3 behave as a Lewis acid.
Question 4.
Is boric acid a protic acid ? Explain.
Answer:
Boric acid is a weak mono basic acid. In Boric acid plannar BO3 units are joined by hydrogen bonds. It has layer structure (polymeric). Hence it is not a protic acid. It does not give up a proton.
Question 5.
What happens when boric acid is heated ?
Answer:
Boric acid when heated above 370 K forms meta boric acid. This on heating forms Boric oxide.
![]()
Question 6.
Describe the shapes of BF3 and BH4–. Assign the hybridization of boron in these species.
Answer:
- Shape of BF3 molecule is Trigonal planar
Hybridisation of ‘B’ in BF3 is sp2 - Shape of BH4– molecule is Tetrahedral
Hybridisation of ‘B’ in BH4– is sp3
![]()
Question 7.
Explain why atomic radius of Ga is less than that of ‘Al’.
Answer:
In Gallium penultimate shell contains 10-d electrons. Due to this 10-d electrons shielding effect becomes poor on outer most electrons. So nuclear charge increased in Gallium. Hence atomic radius of Ga is lessthan that of ‘Al’.
Question 8.
Explain inert pair effect.
Answer:
The reluctance of ‘ns’ pair of electrons to take part in bond formation is called inert pair effect.
(or)
The occurrence of oxidation states two unit lessthan the group oxidation states is called inert pair effect.
Eg : In Group – 13 Tl exhibits +1 oxidation state instead of +3 oxidation state due to inert pair effect.
Question 9.
Write balanced equations for
a) BF3 + LiH →
b) B2H6 + H2O →
c) NaH + B2H6 →
d) H3BO3 ![]()
e) B2H6 + NH3 ![]()
Answer:
a) 2BF3 + 6LiH → B2H6 + 6 LiF
b) B2H6 + 6H2O → 2B(OH)3 + 6H2
c) B2H6 + 2NaH → 2NaBH4
d) H3BO3 ![]() HBO2
HBO2 ![]() B2O3
B2O3
e) B2H6 + 6NH3 → 3[BH2(NH3)2]+ (BH4)– ![]() 2B3N3H6 + 12H2
2B3N3H6 + 12H2
Question 10.
Why is boric acid polymeric ?
Answer:
Boric acid has layer like lattice. In this structure planar BO3 units are joined by hydrogen bonds and forms a polymeric structure.
![]()
Question 11.
What is the hybridization of B in diborane and borazine ?
Answer:
- In diborane ‘B’ hybridisation is sp3
- In Borazine ‘B’ hybridisation is sp2
Question 12.
Write the electronic configuration of group – 13 elements.
Answer:
General outer electronic configuration of Group – 13 elements is ns2np1
- B – 1s22s22p1
- Al – [Ne] 3s23p1
- Ga – [Ar] 3d104s24p1
- In – [Kr] 4d105s25p1
- Tl – [Xe] 5d10 6s26p1
Question 13.
Give the formula of borazine. What is its common name ?
Answer:
- The formula of borazine is B3N3H6.
- It’s common name is “In organic benzene” because it is – iso structural with benzene.
Question 14.
Give the formulae of
a) Borax
b) Colemanite.
Answer:
a) Formula of Borax is Na2B4O7. 10H2O
b) Formula of Colemanite is Ca2B6O11.5H2O
![]()
Question 15.
Give two uses of aluminium.
Answer:
Uses of Aluminium :
- Aluminium is used in packing.
- Aluminium is used in utensil making.
- Aluminium alloys are used in shaping of pipes, tubes, wires etc.
- Aluminium alloys are used in making air craft bodies.
Question 16.
What happens when
a) LiAlH4 and BCl3 mixture in dry ether is warmed and
b) Borax is heated with H2SO4 ?
Answer:
a) When LiAlH4 and BCl3 mixture is warmed in dry ether diborane is formed.
4BF3 + 3 LiAlH4 → 2B2H6 + 3 LiF + 3 AlF3
b) Borax is heated with H2S04 then boric acid is formed
Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 + 5H2O → Na2SO4 + 4H3BO3
Question 17.
Sketch the structure of Orthoboric acid.
Answer:
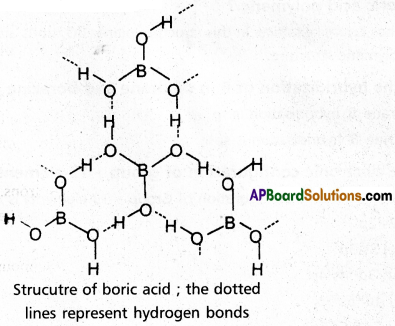
Question 18.
Write the structure of AlCl3 as a climer.
Answer:
![]()
Question 19.
Metal borides (having 10B) are used as protective shield – Why ?
Answer:
Boron – 10 (10B) has the capacity to absorb neutrons. Hence metal borides (having 10B) are used as protective shields in nuclear industry.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write reactions to justify amphoteric nature of aluminium.
Answer:
- Amphoteric nature means having acidic as well as basic nature.
- Aluminium reacts with both mineral acids as well as aqueous alkalis.
a) Reaction with mineral acid :
‘Al’ reacts with dil.HCl and liberates hydrogen gas.
2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2 ↑
b) Reaction with aqueous alkali :
‘Al’ reacts with aqueous alkali (NaOH) and liberates hydrogen gas.
2Al + 2NaOH + 6H2O → Na2[Al(OH)4] + 3H2 ↑
Question 2.
What are electron deficient compounds ? Is BCl3 an electron deficient species ? Explain.
Answer:
These are the compounds in which the available no.of valence electrons is lessthan the number required for normal covalent bond formation (or) for writting the Lewis structure of the molecule.
- These compounds are electron pair acceptors and acts as Lewis acids.
- BCl3 is an electron deficient compound.
- In BCl3 ‘B’ contains only six electrons instead of eight electrons.
- BCl3 has the tendency to accept an electron pair and acts as Lewis acid.
Eg : Formation of BCl3 . NH3 :-
BCl3 accepts an electron pair from NH3 and forms the compound BCl3.NH3 (Tetrahedral)
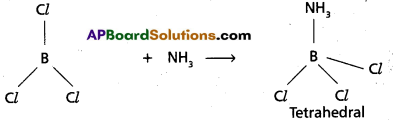
![]()
Question 3.
Suggest reasons why the B – F bond lengths in BF3 (130 pm) and BF4– (143 pm) differ.
Answer:
About BF3 :
- In BF3 the central atom ‘B’ contains three bond pairs in the valency shell.
- ‘B’ under goes sp2 hybridisation.
- Shape of the molecule is trigonal planar.
About BF4– :
- In BF4– the central atom ‘B’ contains four bond pairs in the valency shell.
- ‘B’ under goes sp3 hybridisation.
- Shape of the molecule is tetrahedral.
- The above reasons suggent that the difference in bond lengths of BF3 (130 pm) and BF4– (143 pm).
Question 4.
B – Cl bond has a bond moment. Explain why BCl3 molecule has zero dipolemoment.
Answer:
- B – Cl bond is a polar bond so it has bond moment.
- BCl3 molecule is non-polar because of its symmetrical structure. (Trigonal planar structure)
- Symmetrical molecules has zero dipole moment.
∴ Dipole moment of BCl3 (μ) = 0
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the structure of boric acid.
Answer:
- Boric acid has a layer lattice.
- In this layer lattice planar BO3 units are joined by hydrogen bonds.
- The structure of Boric acid is polymeric as shown in following figure.
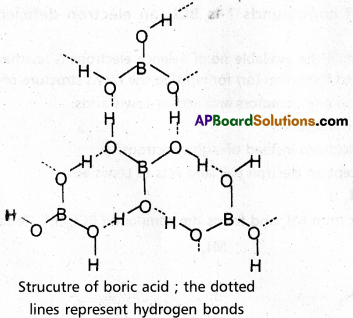
- In the above structure dotted lines represents the hydrogen bonds
Question 6.
What happens when
a) Borax is heated strongly
b) Boric acid is added to water
c) Aluminium is heated with dilute NaOH
d) BF3 is treated with ammonia
e) Hydrated alumina is treated with aq.NaOH solution.
Answer:
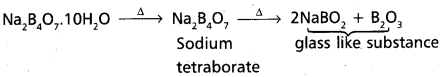
a) Borax on heating first loses water molecules and forms sodium tetraborate. This on further heating forms a mixture of sodium metaborate and boric an hydride. This mixture is solidifies into glass like substance.
b) Boric acid is added to water, boric acid accepts a hydroxyl ion from water.
B(OH)3 + 2H2O → [B(OH)4]– + H3O+
c) Aluminium is heated with dilute NaOH, sodium metaluminate is formed with the liberation of hydrogen gas.
2Al + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2 ↑
d) BF3 is treated with NH3 an addition compound BF3. NH3 is formed. BF3 accepts an electron pair from NH3 and forms a dative bond.
BF3 + ![]() → [BF3 ← NH3] → [BF3.NH3]
→ [BF3 ← NH3] → [BF3.NH3]
e) Hydrated Alumina is treated with aq.NaOH to form sodium metaluminate.
Al2O3.2H2O + 2NaOH(aq) → 2NaAlO(aq) + 3H2O
Question 7.
Give reasons
a) Conc.HNO3 can be transported in aluminium container.
b) A mixture of dil. NaOH and aluminium pieces is used to open drain.
c) Aluminium alloys are used to make aircraft body.
d) Aluminium utensils should not be kept in water overnight.
e) Aluminium wire is used to make transmission cables.
Answer:
a) Cone. HNO3 can be transported in Aluminium containers because Al is passive towards Conc.HNO3 due to the formation of thin layer of Al2O3 on the surface.
b) A mixture of dil.NaOH and aluminium pieces is used to open drain because it acts as cleaning agent.
2Al + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2
c) Aluminium alloys are used to make air craft body because it is a light metal, soft, malleable, ductile and tenacious. It shows resistance to atmosphere corrosion.
d) Aluminium utensils should not be kept in water overnight because Aluminium reacts with water and liberates hydrogen gas and heat. It makes colour dissolving and sometimes Aluminium compounds are toxic in nature.
e) Aluminium wire used to make transmission cables because of it’s good conductivity (electrical) and resistance to atmospheric corrosion.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain why the electronegativity of Ga, In and Tl will not vary very much.
Answer:
- Ga, In and Tl have the electro negativity values 1.6, 1.7 and 1.8 respectively.
- In Ga, In and Tl the d-electrons (d10) in penultimate shell do not shield the outer most electrons from nuclear attraction effectively.
- The reason for the above fact is.the shielding effect of various electrons in the orbitals follows the order
s > p > d > f. - Hence the outer electrons are held more firmly by the nucleus. Because of this, atoms with d- electrons in the penultimate shell (d10) are smaller in size. Ga, In and Tl has same number of penultimate shell electrons.
- So, Ga, In and Tl will not vary very much in their electronegativities.
Question 9.
Explain Borax bead test with a suitable example. [T.S. Mar. 16] [Mar. 13]
Answer:
Borax bend test: This test is useful in the identification of basic radicals in qualitative analysis. On heating borax swells into a white, opaque mass of anhydrous sodium tetra borate. When it is fused, borax glass is obtained. Borax glass is sodium meta borate and B203. The boric anhydride, B203, combined with metal oxides to form metal metaborates as coloured beads. The reactions are as follows :

Question 10.
Explain the structure of diborane. [A.P. Mar. 16] [A.P. & T.S. Mar. 15]
Answer:
Diborane is an electron deficient compound. It has ’12’ valency electrons for bonding purpose instead of ’14’ electrons.
In diborane each boron atom undergoes sp3 hybridization out of the four hybrid orbitals one is vacant.
Each boron forms two, σ – bonds (2 centred – 2 electron bonds) bonds with two hydrogen atoms by overlapping with their ‘1s’ orbital.
The remaining hybrid orbitals of boran used for the formation of B-H-B bridge bonds.
In the formation of B-H-B bridge, half filled sp3 hybrid ofbital of one boron atom and vacant sp3 hybrid orbital of second boron atom overlap with 1s orbital of H-atom.
These three centred two electron bonds are also called as banana bonds. These bonds are present above and below the plane of BH2 units.
Diborane contains two coplanar BH2 groups. The four hydrogen atoms are called terminal hydrogen atoms and the remaining two hydrogens are called bridge hydrogen atoms.
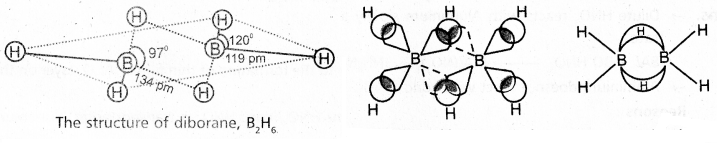
Bonding in diborane, Each B atom uses sp3 hybrids for bonding. Out of the four sp3 hybrids on each B atom, one is without an electron shown in broken lines. The terminal B-H bonds are normal 2-centre-2- electron bonds but the two bridge bonds are 3-centre-2- electron bonds. The 3-centre-2-electron bridge bonds are also referred to as banana bonds.
![]()
Question 11.
Explain the reactions of aluminium with acids.
Answer:
Reactions of ‘Al’ with adds :
i) DiS. (or) cone. HCl dissolves Al and gives H2.
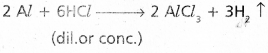
ii) a) Dil.H2SO4 liberates H2.
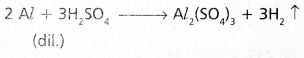
b) Cone. H2SO4 dissolves the metal ‘Al’ and gives SO2.
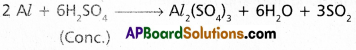
iii) a) Very dil.HNO3 is reduced to NH4 NO3 by Al.

b) Cone. HNO3 makes ‘Al’ passive due to the formation of a thin film of oxide layer on the metal surface.
Question 12.
Write a short note on the anamalous behaviour of boron in group – 13.
Answer:
- Among Group – 13 elements ‘B’ is only the non metal.
- ‘B’ forms only covalents compounds.
- ‘B’ doesnot displaces hydrogen from acids.
- ‘B’ shows diagonal relationship with ‘Si’.
- ‘B’ forms acidic oxide where as other elements of group forms amphoteric oxides and basic oxides.
- ‘B’ has only two electrons in the penultimate shell.
- ‘B’ has covalency ‘4’ where as other elements has covalency of maximum ‘6’.
![]()
Question 13.
Aluminium reacts with dil.HNO3 but not with conc.HNO3 – explain.
Answer:
- Dilute HNO3 reacts with Aluminium slowly and forms aluminium nitrate and ammonium nitrate.
8Al + 30 HNO3 → 8 Al(NO3)3 + 3NH4NO3 + 9H2O - Aluminium doesnot react with cone. HNO3.
Reasons :
- Aluminium is passive towards cone. HNO3 due to the formation of thin film of Al2O3 layer on the surface.
- Because of this passivity between Al and conc.HNO3, conc.HNO3 is transported in Aluminium containers.
Question 14.
Give two methods of preparation of diborane.
Answer:
- In industries diborane is prepared by the reaction between boron tri fluoride and lithium hydride.

- Boron trichloride and hydrogen mixture subjected to silent electric discharge at low pressure to from diborane.
2BCl3 + 6H2 → B2H6 + 6HCl - Boron trichloride undergo reduction with LiAlH4 to form diborane.
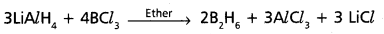
Question 15.
How does diborane react with
a) H2O
b) CO
c) N(CH3)3 ?
Answer:
a) Diborane reacts with water to form boric acid and hydrogen.
B2H6 + 6H2O → 2H3BO3 + 6H2↑
b) Diborane reacts with CO at 100° C and 20 atm. pressure to form borane carbonyl.
![]()
c) Diborane reacts with N(CH3)3 and form a adduct.
B2H6 + 2N(CH3)3 → 2BH3.N(CH3)3 (adduct)
Reactions b, c are cleavage reactions.
![]()
Question 16.
Al2O3 is amphoteric – explain with suitable reactions.
Answer:
- Amphoteric oxides are the oxides which possess both acidic as well as basic nature.
Al2O3 possess both acidic as well as basic behaviour. - Al2O3 react with both acids as well as bases to produce salts and water.
Supporting reactions for amphoteric nature of Al2O3
a) With acids:
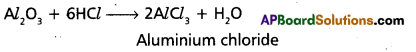
b) With bases:
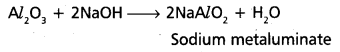
Question 17.
Na2B4O7 + Cone. H2SO4 → A ![]() > B (Green edged flame) Identify A and B
> B (Green edged flame) Identify A and B
Hint: A = H3BO3 B = (C2H5)3 BO3.
Answer:
Na2B4O7 + Cone. H2SO4 + 5H2O → 4H3BO3 A) ![]() B) 4(C2H5)3BO3
B) 4(C2H5)3BO3
- ‘A’ is H3BO3
- ‘B’ is (C2H5)3 BO3.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
How are borax and boric acid prepared ? Explain the action of heat on them.
Answer:
Preparation of Borax:
Boric acid on heating first forms tetraboric acid. This on reaction with sodium hydroxide to form borax.
![]()
Preparation of Boric acid : Borax is treated with conc.H2SO4 boric acid is formed.
Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 + 5H2O → 4H3BO3 + Na2SO4.
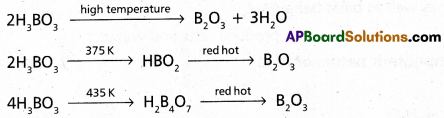
Heating of Borax :
Borax on heating first loses the water molecules and forms sodium tetraborate. This on further heating forms a mixture of sodium meta borate and boric anhydride.
Na2B4O7.10H2O ![]() Na2B4O7 imgg 2 2 NaBO2 + B2O3.
Na2B4O7 imgg 2 2 NaBO2 + B2O3.
Heating of Boric acid :
Boric acid on heating forms boric anhydride. The reaction depends on the temperature used.
Question 2.
How is diborane prepared ? Explain its structure.
Answer:
In industries diborane is prepared by the reaction between boran tri fluoride and lithium hydride.
![]()
Boron trichioride and hydrogen mixture subjected to silent electric discharge at low pressure to from diborane.
2BCl3 + 6H2 → B2H6 + 6HCl
Boron trichloride undergo reduction with LiAlH4 to form diborane.
![]()
Diborane is an electron deficient compound. It has ’12’ valency electrons for bonding purpose instead of ’14’ electrons.
In diborane each boron atom undergoes sp3 hybridization out of the four hybrid orbitals one is vacant.
Each boron forms two, σ – bonds (2 centred – 2 electron bonds) bonds with two hydrogen atoms by overlapping with their ‘1s’ orbital.
The remaining hybrid orbitals of boran used for the formation of B-H-B bridge bonds.
In the formation of B-H-B bridge, half filled sp3 hybrid ofbital of one boron atom and vacant sp3 hybrid orbital of second boron atom overlap with 1s orbital of H-atom.
These three centred two electron bonds are also called as banana bonds. These bonds are present above and below the plane of BH2 units.
Diborane contains two coplanar BH2 groups. The four hydrogen atoms are called terminal hydrogen atoms and the remaining two hydrogens are called bridge hydrogen atoms.

Bonding in diborane, Each B atom uses sp3 hybrids for bonding. Out of the four sp3 hybrids on each B atom, one is without an electron shown in broken lines. The terminal B-H bonds are normal 2-centre-2- electron bonds but the two bridge bonds are 3-centre-2- electron bonds. The 3-centre-2-electron bridge bonds are also referred to as banana bonds.
![]()
Question 3.
Write any two methods of preparation of diborane. How does it react with
a) Carbon monoxide and
b) Ammonia ?
Answer:
Preparation of diborane:
In industries diborane is prepared by the reaction between boroh tri fluoride and lithium hydride.
![]()
Boron trichloride and hydrogen mixture subjected to silent electric discharge at low pressure to from diborane.
2BCl3 + 6H2 → B2H6 + 6HCl
Boron trichloride undergo reduction with LiAlH4 to form diborane.
![]()
a) Reaction with carbon monoxide :
Diborane reacts with CO at 100° C and 20 atm. pressure to form borane carbonyl.
![]()
b) Reaction with ammonia
Diborane reacts with ammonia at 120° C first forms B2H6.2NH3 (or) [BH2(NH3)2]+[BH4]– and on further heating forms borazole (or) borazine. Which is also called as “In organic benzene”. It has iso structural with benzene. Flence it is named as “Inorganic Benzene”.
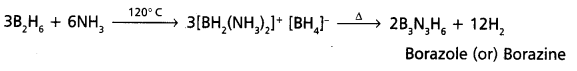
Solved Problems
Question 1.
Standard electrode potential values, EΘ for Al3+ / Al is – 1.66 V and that of Tl3+ / Tl is + 1.26 V. Predict about the formation of M3+ ion in solution and compare the electropositive character of the two metals.
Solution:
Standard electrode potential values for two half cell reactions suggest that aluminium has high tendency to make Al3+ (aq) ions, whereas Tl3+ is not only unstable in solution but is a powerful oxidising agent also. Thus Tl+ is more stable in solution than Tl3+. Aluminium being able to form +3 ions easily, is more electropositive than thallium.
Question 2.
White fumes appear around the bottle of anhydrous aluminium chloride. Give reason.
Solution:
Anhydrous aluminium chloride is partially hydrolysed with atmospheric moisture to liberate HCl gas. Moist HCl appears white in colour.
![]()
Question 3.
Boron is unable to form \(\mathrm{BF}_6^{3-}\) ion. Explain.
Solution:
Due to non – availability of d orbitals, boron is unable to expand its octet. Therefore, the maximum covalence of boron cannot exceed 4.
Question 4.
Why is boric acid considered as a weak acid ?
Solution:
Because it is not able to release H+ ions on its own. It receives OH+ ions from water molecule to complete its octet and in turn releases H+ ions.