AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Social Studies Important Questions Chapter 3 Earth Movements and Seasons.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Social Studies Important Questions 3rd Lesson Earth Movements and Seasons
Question 1.
Can you relate what are the major seasons you have seen?
Answer:
The major seasons I have seen are Summer season, Rainy season and Winter season.
Question 2.
Write any two factors that influence the order of seasons.
Answer:
The factors are:
a) The spherical shape of the Earth and the curvature of its surface.
b) Daily rotation of the Earth on its own Axis.
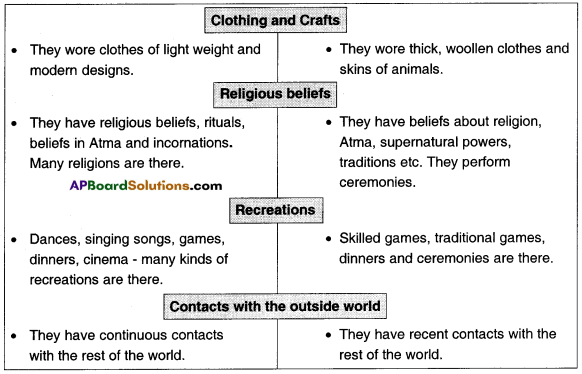
![]()
Question 3.
From where can we see the axis of the earth?
Answer:
The axis of the earth is an imaginary line. We cannot see it.
Question 4.
What are the reasons behind the formation of seasons?
Answer:
Earth’s revolution and inclination of the axis are the reasons behind it.
Question 5.
What happens if there are no seasons?
Answer:
If there are no seasons, there will be no life on the earth.
Question 6.
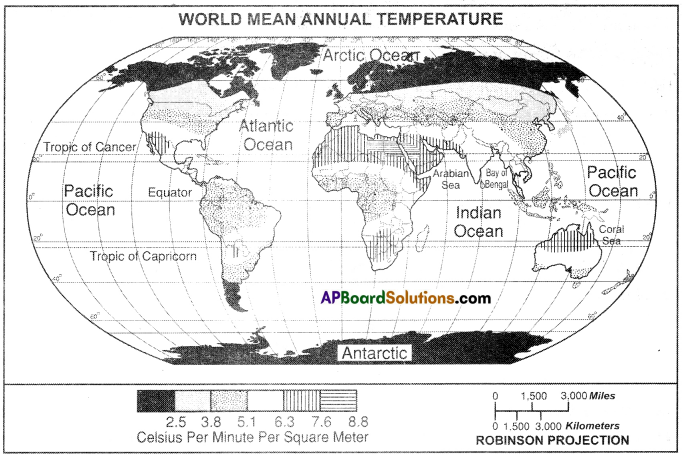
Find out if Andhra Pradesh is in the Tropical Belt or in the Temperate Beit.
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh is extended between 18°N to 79°N latitude (approximately). It is in Tropical Belt.
![]()
Question 7.
Will the Sun shine directly on our heads in Andhra Pradesh during any month? If yes, in which month?
Answer:
The Sun’s rays fall straightly on Andhra Pradesh in the month of May.
Question 8.
Find out in which belt is Delhi and if it would receive snowfall in winters.
Answer:
Delhi is located between 28°22″ N. latitude and 28°54″ N. latitude. It is in Temperate Belt. It records low temperatures but there is no snowfall.
Question 9.
The earth is rotating daily in such a high speed. But why don’t we feel this?
Answer:
The earth is rotating in such a speed with all its – atmosphere, human, animal and plant kingdoms. So we don’t feel this.
![]()
Question 10.
Appreciate the rotation and revolution.
Answer:
The Earth is rotating and revolving since her birth without any rest. If it stops for a while, the life on the Earth may get disappeared. So a lot of thanks to Mother Earth.
Question 11.
Which season is important out of all the seasons?
Answer:
All the seasons are important. The existence of all the seasons only supports the life on the earth.
Question 12.
What are the factors that influence the order of seasons?
Answer:
The factors that influence the order of seasons are:
- The spherical shape of the Earth and the curvature of its surface.
- Daily rotation of the Earth on its own Axis.
- The tilt of the Axis of rotation compared to the plane on which the Earth moves.
- The Earth’s movement around the Sun once a year (revolution).
![]()
Question 13.
From where can we see the axis of the earth?
Answer:
The axis of the earth is an imaginary line. We cannot see it.
Question 14.
The earth is rotating daily in such a high speed. But why don’t we feel this?
Answer:
The earth is rotating in such a speed with all its – atmosphere, human, animal and plant kingdoms. So we don’t feel this.
Question 15.
Appreciate the rotation and revolution.
Answer:
The Earth is rotating and revolving since her birth without any rest. If it stops for a while, the life on the Earth may get disappeared. So a lot of thanks to Mother Earth.
Question 16.
Which season is important out of all the seasons?
Answer:
All the seasons are important. The existence of all the seasons only supports the life on the earth.
![]()
Question 17.
Draw the important latitudes.
Answer:
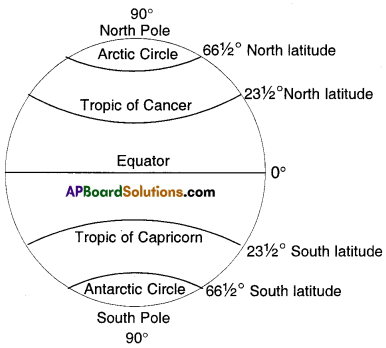
Question 18.
Draw the temperature belts on the earth.
Answer:
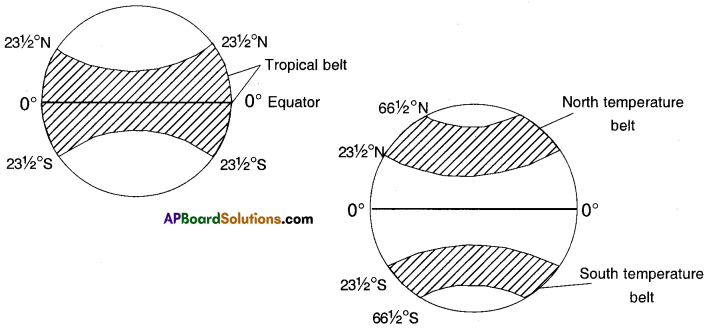
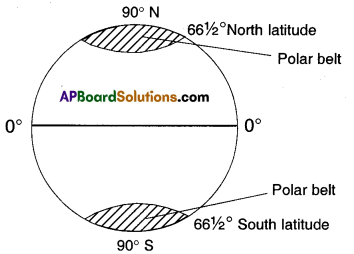
![]()
 1. What is the line to south of equator?
1. What is the line to south of equator?


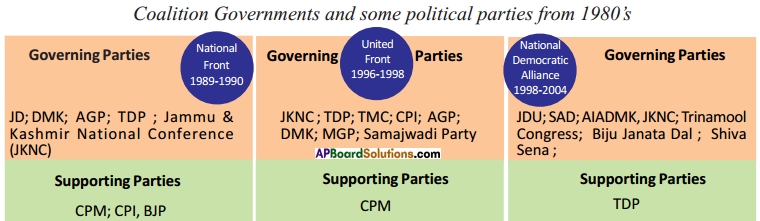
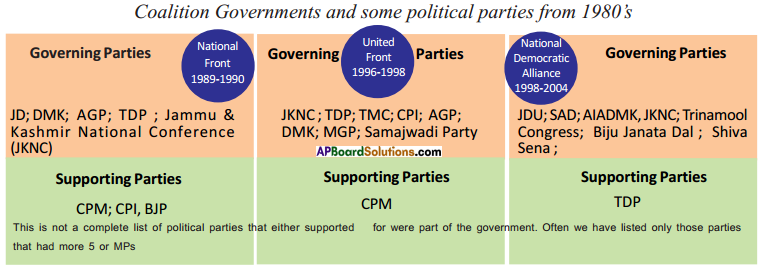
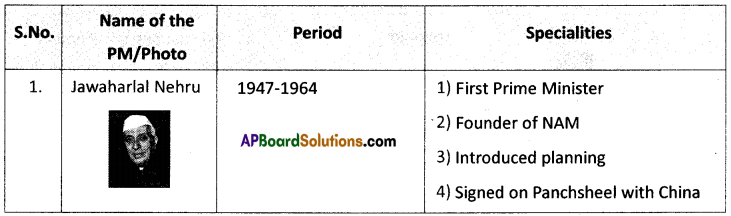
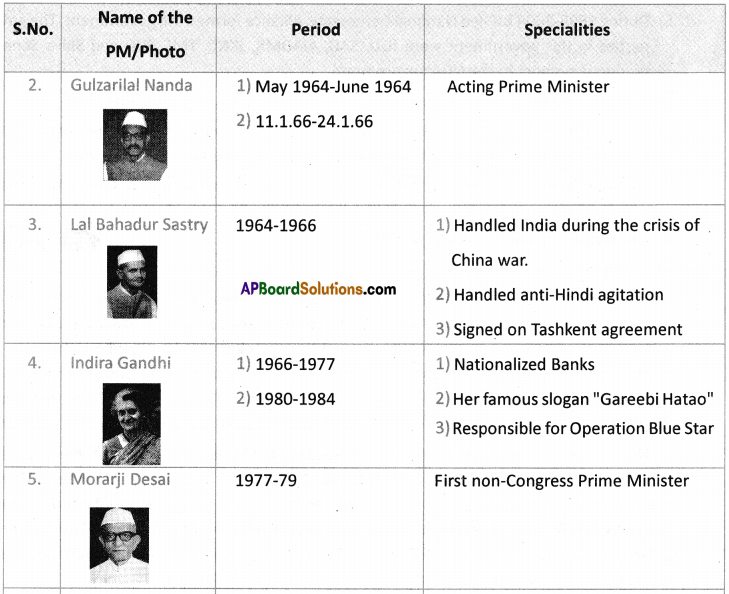
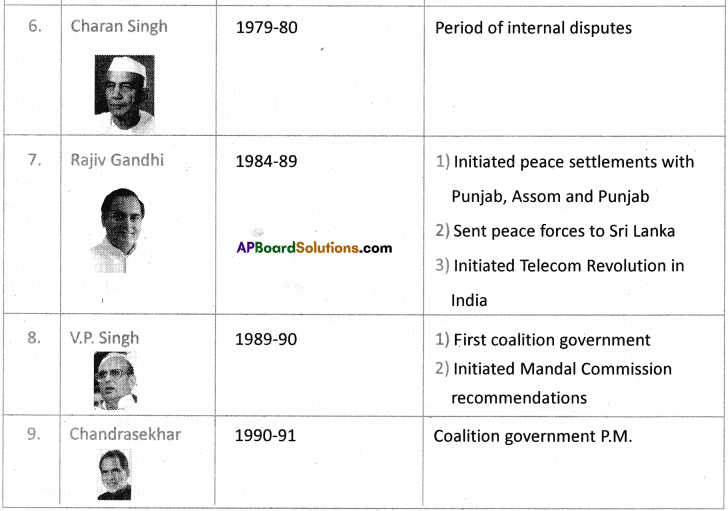
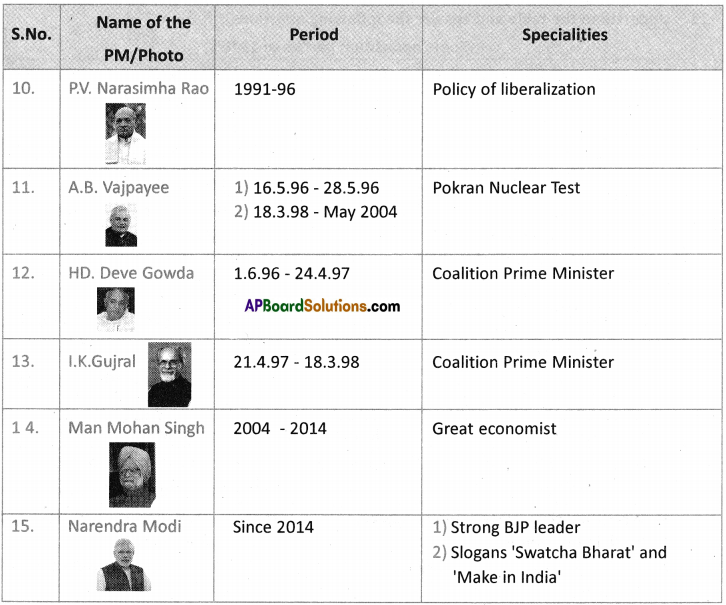
 a) Who was the Prime Minister that initiated peace agreements with Sri Lanka?
a) Who was the Prime Minister that initiated peace agreements with Sri Lanka?
 Answer:
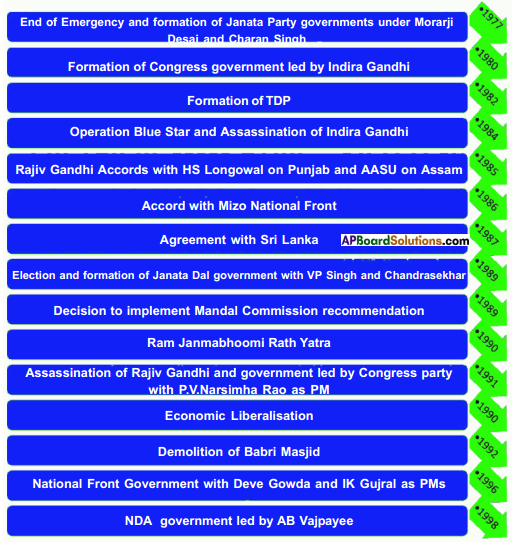
Answer: Write the suitable ENGLISH LETTER for each event listed above in the boxes against each on the timeline.
Write the suitable ENGLISH LETTER for each event listed above in the boxes against each on the timeline.