AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Social Studies Important Questions Chapter 1 India: Relief Features.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Social Studies Important Questions 1st Lesson India: Relief Features
10th Class Social 1st Lesson India: Relief Features 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
![]()
Question 1.
According to the given table below, which area is the eastern side?
| Date | Area: Imphal | Area: Dwaraka | ||
| Sunrise | Sunset | Sunrise | Sunset | |
| Jan 3 | 05.53 | 16.34 | 07.19 | 18.07 |
Answer:
According to the given table, Imphal is the eastern side.
Question 2.
What is the time In India when it is 8 am in London?
Answer:
The time is 1.30 pm in India when It is 8 am in London.
Question 3.
Which Indian islands are of volcanic origin?
Answer:
Andaman and Nicobar islands are of volcanic origin.
(OR)
Narkondam and Barren islands are of volcanic origin.
Question 4.
Give examples for Himalayan hill stations.
Answer:
Examples for the Himalayan hill stations are
- Simla
- Mussoorie
- Raniket
- Nainital
![]()
Question 5.
Read the map given and answer the questions.
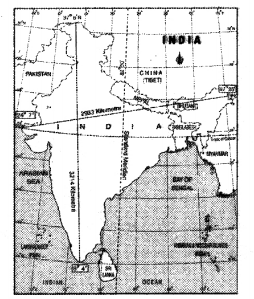
east – west extent and standard meridian
a) Name the latitude that divides India into two parts.
Answer:
Tropic of Cancer / 23°30′ Northern latitude.
b) On which longitude, is Indian Standard Time based upon?
Answer:
82°30′ Eastern longitude.
Question 6.
Mention any one difference between the physical features of the Andaman and Nicobar islands and the Lakshadweep.
Answer:
| Andaman and nicobar Islands | Lakshadweep Islands |
|
|
Question 7.
Mention any two differences between the Western and Eastern Ghats.
Answer:
| Eastern ghats | Western ghats |
| Less height | More height |
| Not continuous ranges | Continuous ranges |
| No origin of rivers | Rivers originate |
| Highest peak is Aroma Konda | Highest peak is Anaimudi |
Question 8.
Write any two unique features of Eastern Coastal Plain?
Answer:
Unique features of East Coastal Plain
- East Coastal Plains are very wide.
- The rivers which are flowing in this area are formed deltas.
- These plains are agriculturally developed.
- These Plains has lakes.
![]()
Question 9.
Name the landform from which the World originated.
Answer:
World originated from two giant lands namely Angara Land (Laurasia) and Gondwana Land.
Question 10.
What is the location of India?
Answer:
India is located between 8°4’ and 37°6′ north latitudes and 68°7′ and 97°25′ east longitudes.
Question 11.
What do you mean by “Doab”?
Answer:
The fertile land between two rivers is known as the Doab feature. ‘Do’ means two, ‘ab’ means water.
Question 12.
Name three parallel ranges of the Himalayas.
Answer:
Three parallel ranges are there in the Himalayas. They are
- the Himadri
- the Himachal
- the Shivalik.
Question 13.
Name the tributaries of Indus.
Answer:
The Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Sutlej are the tributaries of Indus.
Question 14.
Name the tributaries of the Ganga.
Answer:
The Ghaggar, the Teesta, the Sone, the Kosi and the Yamuna are the tributaries of the Ganga.
![]()
Question 15.
Expand IST.
Answer:
Indian Standard Time.
Question 16
Expand GMT.
Answer:
Greenwich Mean Time.
Question 17.
What do you mean by “Dun”? Give one example.
Answer:
The valleys lying between the lesser Himalayas and Shivalik ranges are called “Duns’’, e.g. Dehra Dun.
Question 18.
Which continents of today were part of the Gondwana land?
Answer:
India, South Africa, Australia and South America were part of the Gondwana land.
Question 19.
Name three major divisions of the Himalayas from North to South.
Answer:
- The Greater Himalayas or Himadri.
- The Lesser Himalayas or Himachal.
- The Shivaliks or Outer Himalayas.
Question 20.
Name the island group of India having a coral origin.
Answer:
Lakshadweep.
Question 21.
What is the peninsular plateau composed of?
Answer:
The peninsular plateau is composed of igneous and metamorphic rocks
![]()
Question 22.
Identify the regional division of the Northern plains.
Answer:
- Punjab plain
- Ganga plain
- Brahmaputra plain.
Question 23.
What are the relief features that are found in the Northern plains?
Answer:
- Bhabar
- Terai
- Bhangar
- Khadar
Question 24.
Which landform feature was a part of Gondwana land?
Answer:
Peninsular Plateau.
Question 25.
Which plateau lies between the Aravalis and the Vindhya range?
Answer:
Malwa Plateau.
Question 26.
Where are the Aravali hills located?
Answer:
The Aravali hills are located on the western and north-western margins of the peninsular plateau in Rajasthan.
Question 27.
What is Bhangar?
Answer:
Bhangar is the largest part of the northern plains and is formed by the oldest alluvium.
Question 28.
What is Khadar?
Answer:
The younger alluvium deposit is called Khadar.
![]()
Question 29.
What is a reef?
Answer:
A ridge of jagged rock formed from coral secretions and skeletons.
Question 30.
Name some kinds of reefs.
Answer:
Barrier reef, coral reef and fringing reef.
Question 31.
What was called Angara land?
Answer:
The northern part of Pangaea was called Angara land.
Question 32.
What are known as Purvanchal?
Answer:
The Himalayas in the north-eastern states are known as the Purvanchal hills.
Question 33.
Where is the Kanchenjunga peak?
Answer:
The Kanchenjunga peak is in Sikkim.
![]()
Question 34.
Which is the second highest peak in the Himalayas?
Answer:
K2, in the Karakoram range, is the second-highest peak after Mount Everest.
Question 35.
Name the valleys in the Himachal range.
Answer:
Kangra, Kulu and Kashmir valley.
Question 36.
What are Duns?
Answer:
The longitudinal valleys between the Lesser Himalayas and the Shivaliks are known as Duns,
e.g.: Dehradun, Patli dun and Kotli dun.
Question 37.
Where is Bhabar located?
Answer:
Bhabar is located at the foot of the Shivaliks.
Question 38.
What are the two divisions in the Peninsular Plateau?
Answer:
Central Highlands and Deccan Plateau.
Question 39.
Which is the easternmost part of the central highlands?
Answer:
The Chotanagapur Plateau is the eastern-most part of the central highlands.
Question 40.
What is the other name of Ooty?
Answer:
Udagamandalam.
![]()
Question 41.
Which is a narrow coastal plain?
Answer:
The Western coastal plain is a narrow plain.
Question 42.
Name the Peninsular rivers.
Answer:
The Godavari, the Krishna and the Cauveri.
10th Class Social 1st Lesson India: Relief Features 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Mention the major relief divisions of Indian landmass.
Answer:
The relief divisions of Indian landmass can be divided into following groups :
- The Himalayas
- The Indo-Gangetic Plain
- The Peninsular Plateau
- The Coastal Plains
- The Desert
- The Islands
![]()
Question 2.
Study the following map and answer the questions given below:
a) Name the two countries that share their land boundaries with India.
b) In between which latitudes, is India located?
Answer:
a) Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Myanmar.
b) 8°4′ – 37°6′ Northern latitudes.
Question 3.
Observe the map given below and answer the following questions.
a) What is the distance between the eastern and western most points of India?
b) Name any two countries that share their boundaries with India.
Answer:
a) The distance between the eastern and the western most points of India is 2933 kms.
b) Pakistan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Nepal, China and Bhutan.
Question 4.
Discuss the significant differences between the Himalayan Rivers and the Peninsular Rivers.
Answer:
| The Himalayan Rivers | The Peninsular Rivers |
| 1. The Himalayan Rivers are Perennial. | 1. The Peninsular rivers are seasonal in nature. |
| 2. They originated in Glaciers. | 2. They originated in Western ghats and highlands. |
| 3. Himalayan Rivers changes their way frequently. | 3. These rivers has fixed course. |
| 4. These rivers irrigate the northern plains. | 4. These rivers irrigate the Deccan Plateau. |
| 5. They made the northern plains fertile. | 5. These rivers are straight. |
Question 5.
Discuss the various islands in India.
Answer:
- There are 2 groups of islands – Andaman and Nicobar Islands stretched in Bay of Bengal and Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea.
- In Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Narkondam and Barren islands are volcanic origin.
- The southernmost tip of India found in Nicobarlsland is called Indira point which was submerged during the 2004 Tsunami.
- Lakshadweep Islands are of coral origin.
- It is famous for great variety of flora and fauna.
![]()
Question 6.
Himalayas play a vital role in India’s development. How?
Answer:
- The Himalayas affect the climate of India by blocking cold air blowing from Siberia and Central Asia.
- They are reason for the monsoon type of climate in India.
- Without the Himalayas India would have remained drier.
- The rivers originating in the glaciers of the Himalaya are perennial and caused the economic growth of the northern plains.
- The Himalayan valleys are known for the cultivation of fruits.
- The rivers of the Himalayas for the formation of fertile.
Question 7.
How are the Himalayas divided regionally or on the basis of river valleys?
Answer:
- Punjab Himalayas between rivers Indus and Sutlej.
- Kumaon Himalayas between rivers Sutlejjind Kali.
- Nepal Himalayas between rivers Kali and Teesta.
- Assam Himalayas between rivers Teesta and Brahmaputra.
Question 8.
Look at the picture and comment on it.
Answer:
It is a sketch of different levels of vegetation in the Himalayas. There are 5 levels in that vegetation.
Level I: On the top of the mountains there is no vegetation.
Level II: On the hill slopes – there is only grass.
Level III: Next to the level II – this area is covered with conifers.
Level IV: Next to level III – this area is covered with broadleaf trees.
Level V: At the feet of the mountains. It is Terai with tree cover.
![]()
Question 9.
Write a short note on the Great Indian Desert.
Answer:
The Great Indian desert lies towards the western margins of the Aravalli Hills.
The region gets scanty rainfall. Hence the climate is arid and vegetation is scanty. Luni is the only large river. Some streams appear during rainy season. Crescent-shaped duns are formed around in this area.
10th Class Social 1st Lesson India: Relief Features 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
1. Describe any four of major relief divisions of Indian land mass.
Answer:
I. Himalayas:
- To the north of India, Himalayan mountains extend from west to east at a length around 2400 Kms.
- There are three parallel ranges viz. Himadri, Himachal and Shivaliks.
II. Indo-Gangetic Plains:
- Indo-Gangetic Plain is formed with the interaction of the rivers Ganga, Indus, Brahmaputra and their tributaries.
- These fertile alluvial plains are suitable for agriculture.
III. Peninsular Plateau:
- The Indian plateau is also known as the peninsular plateau as it is surrounding by the sea on the three sides.
- It is broadly divided into two parts : Malwa plateau and Deccan plateau.
IV. Coastal Plains:
- The Western coastal plain is extended between Western Ghats and Arabian Sea. The East coastal plain is extended between Eastern Ghats and Bay of Bengal.
- These coastal plains are known locally by different names.
Eg: Coast of AP – Circar Coast
Coast of Kerala – Malabar coast etc.
V. Thar Desert:
- Thar desert lies in the rain shadow region of Aravali mountains.
- Luni is the only river in this region.
VI. Islands:
- Andaman and Nicobar islands are in Bay of Bengal. They are of volcanic origin.
- Lakshadweep islands are in Arabian Sea. They are of coral origin.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the uses of Himalayas.
Answer:
- Himalayas act as natural barriers on the northern side of India.
- They protect India from the cold winds from Central Asia during severe winter
- The Himalayas are the reason for summer rains.
- The himalayas are responsible for monsoon type of climate.
- If there are no Himalayas, India will remain as a desert.
- They are the origin for many perennial rivers.
- They attract tourists from all over the world.
- Himalayan rivers bring a lot of silt, making the northern plains very fertile.
Question 3.
Describe the Indian Islands.
Answer:
- There are two groups of islands in India.
- They are Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep Islands.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands are in Bay of Bengal.
- Lakshadweep islands are in Arabian Sea.
- In Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Narkondam and Barren islands are of volcanic origin.
- Lakshadweep islands are of coral origin.
- Indira point, the southernmost tip of India is found in Nicobar Island.
- Lakshadweep islands are famous for great variety of flora and fauna.
Question 4.
In what ways is the Indo-Gangetic plain different from the Peninsular plateau?
Answer:
| Indo – Gangetic plain | Peninsular plateau | |
| 1. This plain area was formed due to deposition of sediments brought by rivers. | 1. Plateau region was formed due to volcanic eruption. | |
| 2. It consists of alluvial soil. | 2. It is mainly composed of the old crystalline, hard igneous rocks and metamorphic rocks. | |
| 3. It has fertile alluvial soils and flat surface. | 3. It has a rugged surface. | |
| 4. It provides much irrigation facilities. | 4. It also provides much irrigation facilities. | |
| 5. Plain regions have perennial rivers. , | 5. Plateau region does not have any perennial river. | |
| 6. Plains are rich in agriculture practice. | 6. Plateau region is rich in mineral resources. | |
Question 5.
Read the following paragraph and comment on Indian climate and the Himalayas.
The formation of the Himalayas influences the climate in various ways. These act as barriers protecting the great plains of India from the cold winds of central Asia during severe winter. The Himalayas are the reason for summer rains and monsoon type of climate in regions that are beyond the Western Ghats of India. In its absence, this region would have remained drier.
Answer:
- The Himalayas affect the climate of India by blocking cold air blowing from the North that comes from Siberia.
- Without the Himalayas, India would get cold temperatures in the winter months.
- The Himalayas form a natural barrier that prevents monsoon winds from going further north.
- The Himalayas are reason for summer rains and monsoon type climate in the regions that are beyond the western ghats of India.
- In its absence this region would have remained drier.
- India would have been a tropical desert.
- The Himalayas are the birthplace of so many rivers.
- These rivers bring a lot of silt, making these plains very fertile.
![]()
Question 6.
How the Himalayas are influencing the climate of India and agriculture?
Answer:
- The Himalayas are obstructing cold winds.
- The Himalayas are reason for rains in summer.
- They are cause for seasonal climate.
- If there is no Himalayas the northern region becomes dry.
- The flow of the Himalayan rivers, making the plains very fertile.
Question 7.
Write about the similarities and differences between East Coastal Plains and West Coastal Plains.
Answer:
Similarities :
- They are the physical features of India. 2) They both lie in the southern part of India.
- They both lie near to the coast.
Differences:
| Eastern Coastal Plains | Western Coastal Plains |
| 1. Eastern coastal plains is a belt of plain region lying towards the east between Eastern Ghats and Bay of Bengal. | 1. Western coastal plains is a belt of plain region lying towards the west between Western Ghats and Arabian Sea. |
| 2. Eastern coastal plains are comparatively wider. | 2. This belt of plains is narrow in width. |
| 3. Eastern coastal plains are very fertile because rivers like Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery deposit their sediments during delta formation. | 3. Western coastal plains are less fertile because no major river is engaged in sediment deposition. |
| 4. Eastern plains receive comparatively lesser rainfall. | 4. Western plains receive more rainfall. |
| 5. From north to south, Eastern coastal plains are divided into Utkal coast, Sircar coast and Coramandal coast. | 5. From north to south, Western coastal plains are divided into Konkan coast, Canara coast and Malabar coast. |
Question 8.
Explain the differences between the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats,
Answer:
| Eastern Ghats | Western Ghats |
| 1. The Eastern Ghats start from Bhuvaneswar in Odisha. | 1. The Western Ghats start from Khandesh in Maharashtra. |
| 2. They end at Nilgiris in the south. | 2. They end at Kanyakumari. |
| 3. They run parallel to some extent in the east coast. | 3. They run parallel to the west coast. |
| 4. They are nearer to the Bay of Bengal keeping away some distance. | 4. They are nearer to the Arabian sea. |
| 5. They have more number of gaps. | 5. They have gaps. |
| 6. They are less strongly built. | 6. These are strongly built. |
| 7. The coastal plain of the Eastern Ghats is wider than that of the Western Ghats. | 7. The coastal plain of the Western Ghats is not as broad as that of the Eastern Ghats. |
| 8. There are no dense forests in the Eastern Ghats when compared to those of the Western Ghats. | 8. There are dense forests in the Western Ghats. |
| 9. There are no rivers originating in Eastern Ghats. | 9. The rivers Godavari and Krishna take origin in the Western Ghats. |
| 10. The Eastern Ghats are dissected by rivers. | 10. The Western Ghats are not dissected by rivers. |
| 11. They have structural level and uniformity. | 11. They have more rugged topography. |
| 12. In Nilgiris they join the Western Ghats. | 12. In Nilgiris they join the Eastern Ghats. |
![]()
Question 9.
Which are the major physiographic divisions of India? Contrast the relief of The Indo-Gangetic Plain with that of The Peninsular Plateau.
Answer:
The major physiographic divisions of India are :
- The Great Himalayas,
- The Northern Plains
- The Great Indian Desert
- The Peninsular Plateau
- The Eastern and Western Coastal plains and
- The Island Group
Question 10.
Prepare a table showing the particulars of different mountain ranges of the Himalayas.
Answer:
| Himalayan region | Peninsular region |
| 1. The Himalayas are located in the northern region of our country. | 1. The Peninsular region is located in the southern region of our country. |
| 2. The Himalayas are young fold mountains. | 2. The central Highlands are formed of low hills and plateaus. |
| 3. Many great perennial rivers like the Indus, the Ganges and the Brahmaputra originate from the Himalayas. | 3. Some great rivers like the Godavari, the Krishna, the Mahanadi, the Tapati and the Narmada originate from these hills. |
| 4. These are formed of the sedimentary rocks. | 4. The central highlands are formed of igneous and metamorphic rocks. |
| 5. They are formed at the edge of the Indo- Gangetic plain. | 5. They are formed at the edge of the Deccan plateau. |
| 6. Important hill stations like – Shimla, Mussorie, Darjeeling, Nainital are found on the Himalayas. | 6. Udagamandalam, Araku – Harsley hills are hill stations found in the Peninsula plateau region. |
| 7. There are three parallel ranges a) Himadri b) Himachal and c) Shivaliks. | 7. They consist of two divisions – Central high lands, Deccan plateau. |
| 8. They run in west – east direction in the form of an arch. | 8. The plateau is tilted towards east. |
Question 11.
What is the importance of the Himalayas?
Answer:
- The formation of the Himalayas influences the climate in various ways.
- These act as barriers protecting the great plains of India from the cold winds of central Asia during severe winter.
- The Himalayas are reason for summer rains and monsoon type climate in regions that are beyond the Western Ghats of India.
- The Himalayan rivers have a perennial flow since these are fed by the glaciers.
- These rivers bring a lot of silt, making these plains very fertile.
- There are famous hill stations like Simla, Mussorie, Nainital, Raniket, etc. covered by evergreen forests.
- The valleys are known for the cultivation of fruits.
- There are passes in the Himalayas which act as great exchange of culture and commerce.
Question 12.
Write about the coastal plains.
Answer:
- The southern part of the peninsular plateau is bordered by narrow coastal strips along the Arabian Sea on the west and the Bay of Bengal on the east.
- Western plain is uneven and broken by hilly terrain.
- It is divided into 3 parts.
a) Konkan coast-northern part comprising Maharashtra and Goa coast.
b) The second is Canara Coast – the middle part includes coastal plain of Karnataka.
c) The last part is Malabar coast – the southern part, mostly in the state of Kerala. - Bay of Bengal plains are wide and have large surface structure.
- It stretches from Mahanadi in Odisha to Cauvery deltas in Tamil Nadu.
- These coastal plains are known locally by different names as Utkal coast in Odisha, Circar coast in Andhra Pradesh and Coromandel coast in Tamil Nadu.
![]()
Question 13.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion on its content.
The formation of the Himalayas influences the climate in various ways. These act as hornets protecting the great plains of India from the cold winds of central Asia during severe winter. The Himalayas are the reason for summer rains and monsoon type climate in regions that are beyond the Western Ghats of India. In its absence, this region would have remained drier. The Himalayan Rivers have a perennial flow since these are fed by the glaciers and bring a fat of silt, making these plains very fertile.
Answer:
- According to the paragraph given, it is dearly understood that the Himalayas are useful to India in many ways.
- It means that because of the Himalayas only there are fertile soils, sufficient rainfall, and perennial rivers and so it is useful to agriculture which is the backbone of our economy.
- I agree with this paragraph because every point discussed here is correct.
- The Himalayas are extending in the north of our country from Jammu Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh for about 2400 kilometers.
- Automatically they stop the cold winds blowing from central Asia because our cultivable lands are in the south.
- If the Himalayas were not there, India would become dry land or a desert.
- Though we have many benefits from the Himalayas, the passes of the Himalayas caused for foreigners to invade our country and these helped in exchanging business and culture.
Question 14.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion on the condition of the area as well as people living there.
The Thar Desert is located on the leeward side afAravalis and receives very low amount of rainfall, ranging from 100 to 150 mm per year. The desert consists of an undulating sandy plain and rocky outcrops. It occupies much of western Rajasthan. It has an arid climate with very law vegetation cover. Streams appear during the rainy season and disappear soon after. ‘Luni’ is the only river in this area. These internal drainage rivers fill into the lakes and don’t reach the sea.
Answer:
- This paragraph says that much of western Rajasthan is sandy and without adequate rainfall.
- Without sufficient rainfall we can’t expect proper cultivation and production of crops.
- Though Rajasthan ranks first in the area it has maximum desert area.
- According to this paragraph, there are a few streams which can be seen during rainy season.
- The unfortunate thing of the people living there is that the area is in the leeward side of the Aravali Mountains.
- The southwest monsoons remain empty by reaching there.
- My opinion is that the people should make a few changes in their livelihoods.
- They should grow more crops during rainy season. It would be better for them to go for multiple cropping.
- They grow food crops with the help of Indira Gandhi canal water irrigation.
- Government should provide their commodities at subsidized prices.
- Along with the Indira Gandhi canal, there should be many more schemes like that till their needs are fulfilled.
![]()
Question 15.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion on the geographical location of India.
The geographical location of India provides its vast diversity in climatic conditions. This has led to a variety of vegetation and life forms along with advantages for growing many kinds of crops. Its long coastline and location in the Indian Ocean enabled trade routes as well as fishing.
Answer:
- According to this paragraph, the geographical location of India is very prosperous.
- India has ocean water on the three sides whereas the high Himalayan Mountains in the north.
- These Himalayas give birth to various perennial rivers because of glaciers so as to grow more crops and this led to a variety of vegetation.
- In my opinion, there are a few benefits as well as losses to the people living in coastal plains and hilly areas.
- The coastal people face some drastic situations when there is a tsunami or cyclones.
- The people living in hilly areas face the problem of landslides.
- Nowadays global warming is increasing. It may lead to submerge of coastal cultivable lands.
- People may face many problems.
- Along with these problems they have the opportunity of maintaining foreign trade with the help of sea routes.
- Visakhapatnam, Chennai, Mumbai and Cochin are some of the examples for the trade cen¬ters of sea routes.
Question 16.
Observe the table and answer the questions.
| Ranges | Direction | Uaiaht | Speciality |
| Himadri | The Northernmost range | Above 6100 mts |
|
| Himachal | Situated to the South of Himadri | Between 37004500 mts. |
|
| Shivalik | The Southernmost range of the Himalayas | 900-1100 mts. |
|
| Purvanchal | The Easternmost range | Act as the Eastern boundary of India |
|
Answer the following questions.
- What are the names of the three Himalayan ranges?
Answer:
The three names of the Himalayan ranges are the Greater Himalayas, the Lesser Himalayas and the Shivaliks. - Which of the ranges have hill stations?
Answer:
The hill stations are found in the Lesser Himalayan ranges. - Where do we find Dehra Dun and Patli Dun?
Answer:
We find Dehra Dun and Patli Dun in the valleys in between the Lesser Himalayas and the Shivaliks. - What is the difference in between the ranges of the Greater Himalayas and the Lesser Himalayas with regard to the composition?
Answer:
The Greater Himalayas are composed of ice and snow cover whereas the Lesser Himalayas are composed of highly compressed rocks.
![]()
Question 17.
Describe the formation and divisions of Indo-Gangetic plains.
Answer:
- The interaction of three Himalayan rivers the Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra and their tributaries resulted in the formation of great northern plain.
- In the beginning it was a shallow basin later gradually filled with alluvial soil from these rivers.
- The western part of Indo-Gangetic plains was formed by the Indus and its tributaries, the Jhelum, the Chenab, the Ravi, the Beas and the Sutlej flowing from the Himalayas.
- Doab features dominate the fertile land between the two rivers.
- The central part is known as Ganga plain extending from the rivers the Ghaggar to the Teesta. 6} The eastern part of the plain exists mostly in the Brahmaputra valley of Assom and the river
Brahmaputra is mainly responsible for its formation.
Question 18.
Describe the vairous aspects of the peninsular plateau.
Answer:
- The Indian Plateau is also known as the peninsular plateau as it is surrounded by the sea on three sides.
- Large amounts of metallic and non-metallic mineral resources are found here.
- Its topography is slightly tilted towards east.
- Its two divisions are central high lands (Malwa plateau) and the Deccan Plateau.
- The rivers here are not perennial.
- The triangular landmass to the south of Narmada is called Deccan Plateau.
- The structure of Western Ghats is continuous with a few passes as the gateways to the coastal plains.
- The Eastern Ghats are not continuous.
- One of the remarkable features of the peninsular plateau is black soils formed due to volcanic activity.
Question 19.
Write about the Thar desert.
Answer:
- The Thar Desert is located on the leeward side of Aravalisand receives very low rainfall, ranging from 100 to 150 mm per year.
- The desert consists of an undulating sandy plain and rocky outcrops.
- It occupies much of western Rajasthan.
- It has an arid climate with very low vegetation cover.
- Streams appear during rainy season and disappear soon after.
- Luni is the only river in this area.
- The internal drainage rivers fall into the lakes and don’t reach the sea.
- Indira Gandhi canal is watering part of Thar desert.
- Several hectares of desert land have been brought under cultivation.
![]()
Question 20.
Read the given map and answer the following questions.
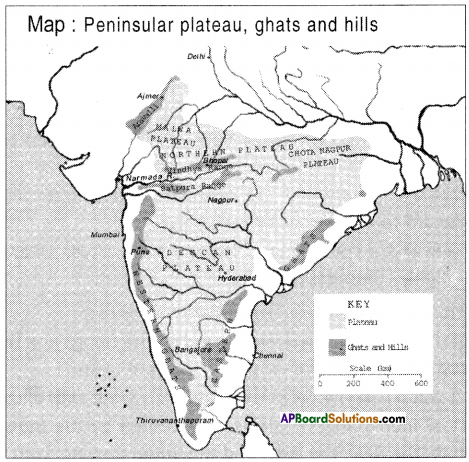
- Which hills are spread continuously from North to South?
Answer:
Western Ghats spread continuously from North to South. - Which Ghats are the birthplace of many rivers?
Answer:
Western Ghats are the birthplace of many rivers. - Which river flows westwards?
Answer:
The river which flows westwards is Narmada. (Tapti also) - Which plateau is there on the windward side of the Aravali?
Answer:
Malwa plateau is there on the windward side of the Aravali. - Where do the eastern and western Ghats join?
Answer:
The eastern and western Ghats join Nilgiris near Gudalur. - Which ocean is located in the south of India?
Answer:
The Indian Ocean is located in the south of India. - Which plateau is there in between Ms s and Chotanagpur plateau?
Answer:
Central plateau is there in between Malwa and Chotanagpur plateau.
Question 21.
Read the given map and answer the following questions.
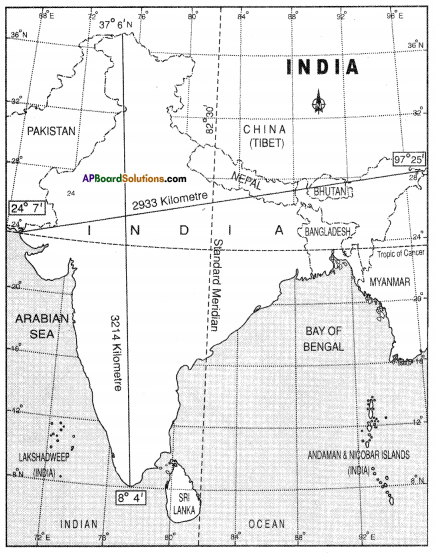
- Which is the standard meridian in India?
Answer:
82° 30′ Eastern Longitude is the standard meridian in India. - Name the latitude that moves from the centre of India.
Answer:
23% northern latitude moves from the centre of India. This is called Tropic of Cancer. - What is the distance between north and south tip of India?
The distance between north and south tips is 3214 kms. - Mention the location of India.
Answer:
India is located in between the latitudes of 8°4′ and 37°6′ N and longitudes of 68°7′ and 97°25′ E. - Name any two frontier countries of India.
Answer:
Pakistan, China, Bhutan, Myanmar, Bangladesh and Nepal. ( any two can be written) - Which islands are located in the southeast corner of India?
Answer:
Andaman Nicobar islands are located in the southeast corner of India.
![]()
Question 22.
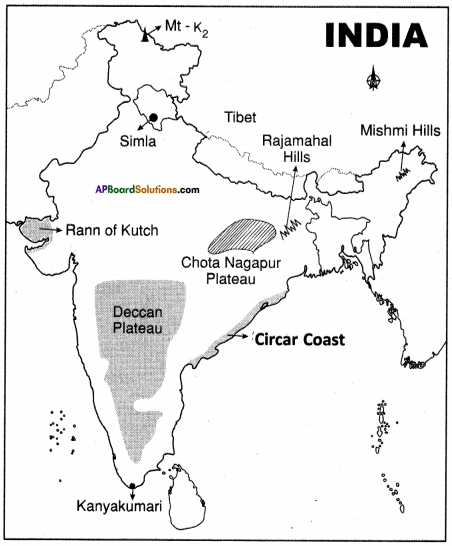
Locate the following in the given map of India.
- Locate the Highest plateau in the world.
Answer: Tibet - Capital of Himachal Pradesh.
Answer: Simla - Highest peak in India.
Answer: Mt-K2 - Locate the Hills in Arunachal Pradesh.
Answer: Mishmi Hills - This plateau has rich variety of mineral resources.
Answer:
Chotanagpur - Rajmahal hills
Triangular plateau.
Answer:
Deccan Plateau Circar Coast - The southernmost tip of India.
Answer:
Kanya Kumari - Mashy Swampy region of Gujarath.
Answer:
Rann of Kutch
 Answer:
Answer: Many people have argued for localisation of food production rather than food travelling long distances. How is localisation of food connected to the environment ? Find out more about the localisation movement in food and organise a discussion and debate in the classroom.
Many people have argued for localisation of food production rather than food travelling long distances. How is localisation of food connected to the environment ? Find out more about the localisation movement in food and organise a discussion and debate in the classroom.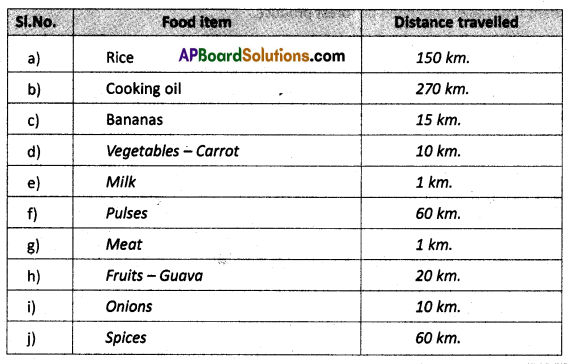
 Answer:
Answer:
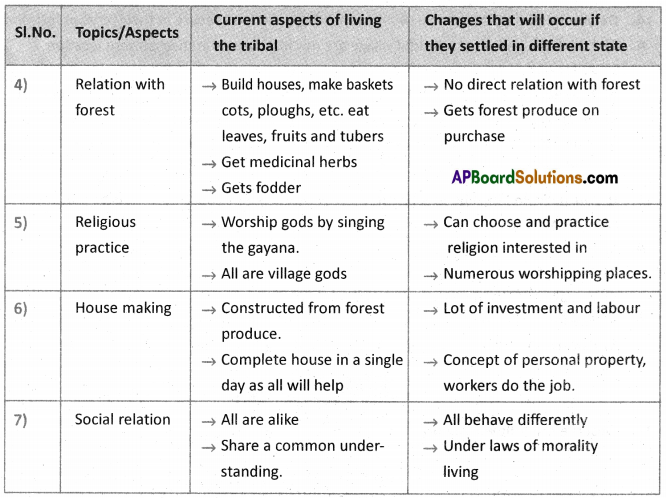
 Write your caption in the context of the environment.
Write your caption in the context of the environment. Answer:
Answer: Write your caption in the context of development.
Write your caption in the context of development. Answer:
Answer:
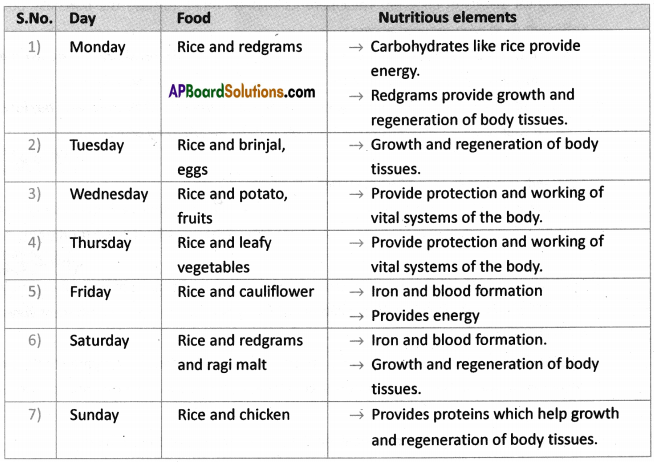
 Answer:
Answer:
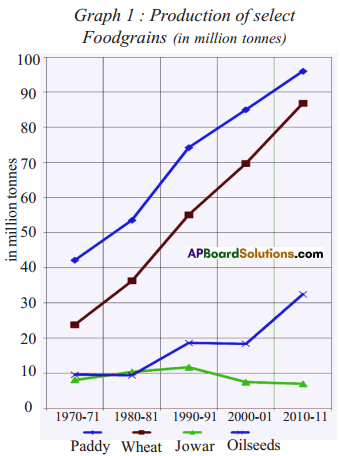 The food grains production has grown over the period 1970-71 to ——–. Paddy production increased from about 40 million tonnes in 1970-71 to about ——– million tonnes in 2010-11. Another important food crop that witnessed rapid increase in production during this 40 years period was ——–. Compared to paddy and wheat the production of ——– did not increase during 1970-2011. This could be due to ——–.
The food grains production has grown over the period 1970-71 to ——–. Paddy production increased from about 40 million tonnes in 1970-71 to about ——– million tonnes in 2010-11. Another important food crop that witnessed rapid increase in production during this 40 years period was ——–. Compared to paddy and wheat the production of ——– did not increase during 1970-2011. This could be due to ——–.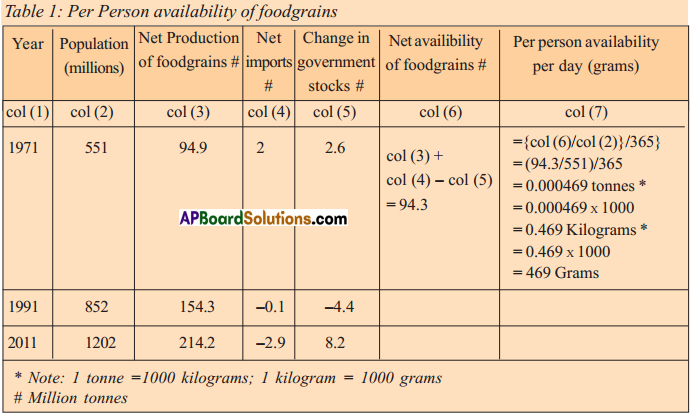 Answer:
Answer: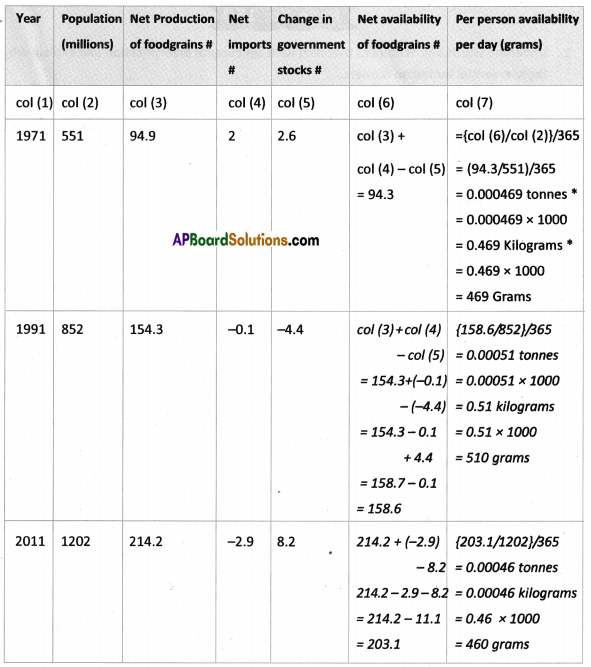
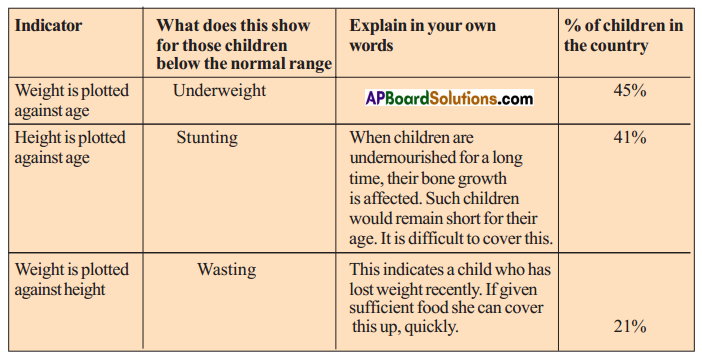
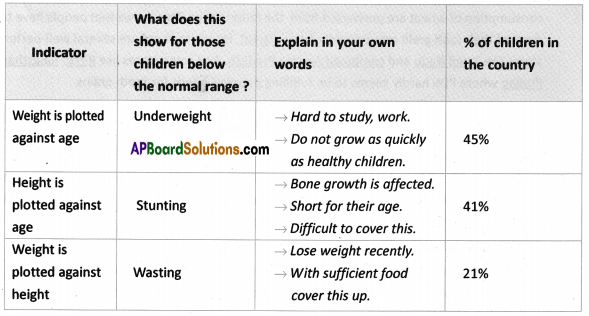 When weight is plotted against age nearly 45% of children in the country are under weight. It means that they cannot study, work or perform physical activities. They do not grow as quickly as healthy children. Their immune system is weakened. When height is plotted against age 41% of children not up to the height they have to be. It seems their growth is affected and short for their age. They are difficult to cover this. When weight is plotted against height 21% children are not with weight they are supposed to be. With sufficient food they can cover this up.
When weight is plotted against age nearly 45% of children in the country are under weight. It means that they cannot study, work or perform physical activities. They do not grow as quickly as healthy children. Their immune system is weakened. When height is plotted against age 41% of children not up to the height they have to be. It seems their growth is affected and short for their age. They are difficult to cover this. When weight is plotted against height 21% children are not with weight they are supposed to be. With sufficient food they can cover this up.

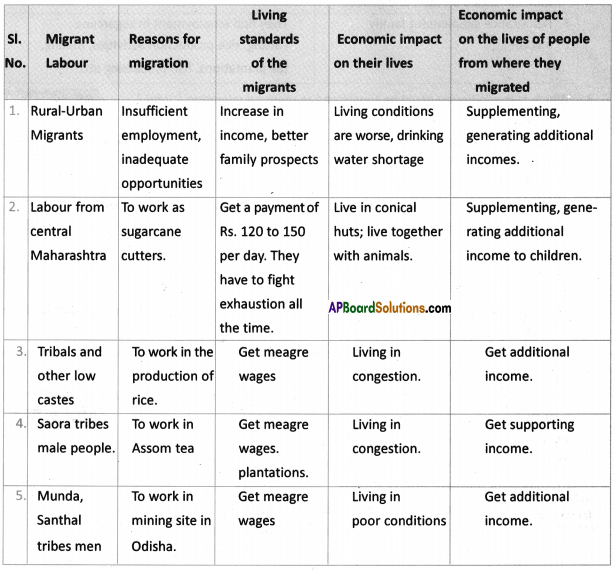
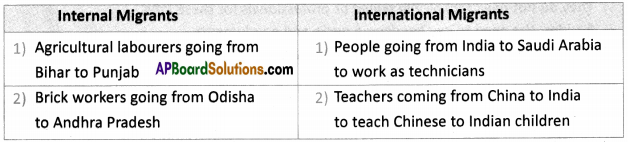
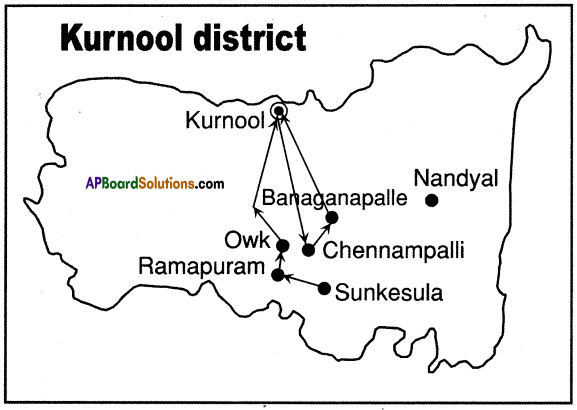
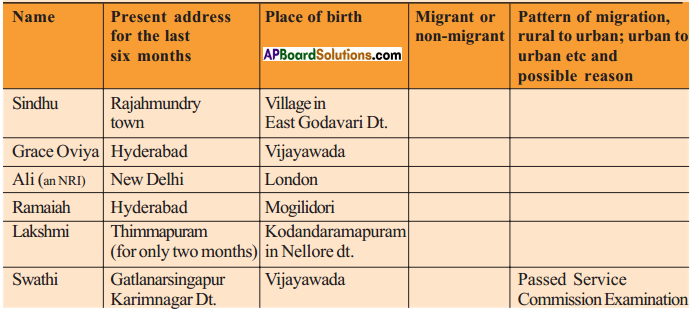 Answer:
Answer: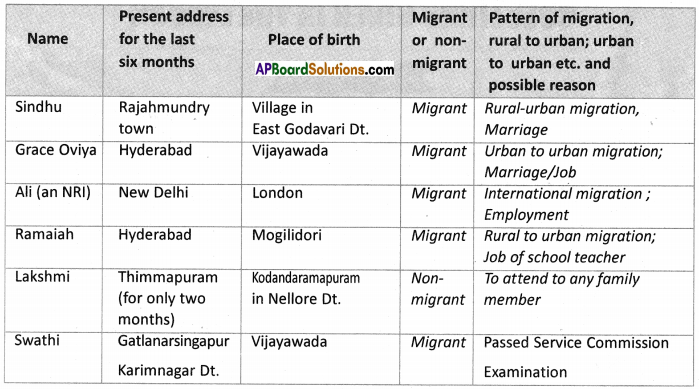
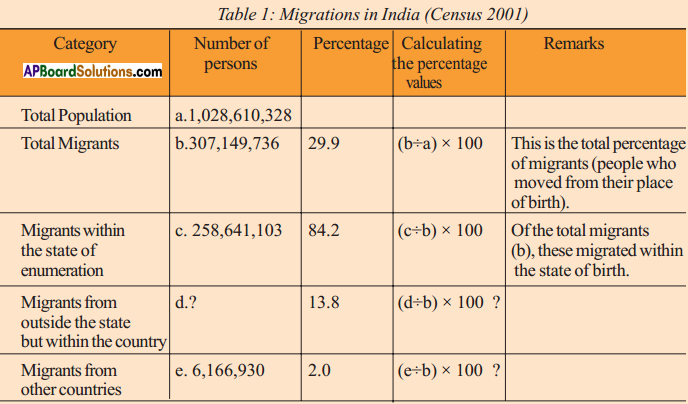 Answer:
Answer: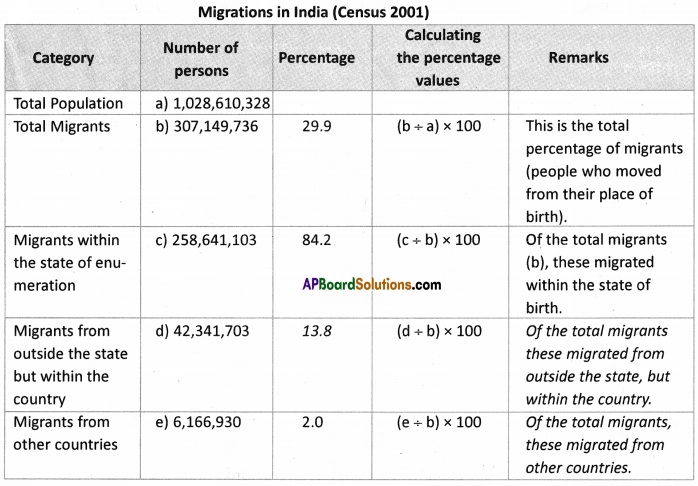
 Answer:
Answer: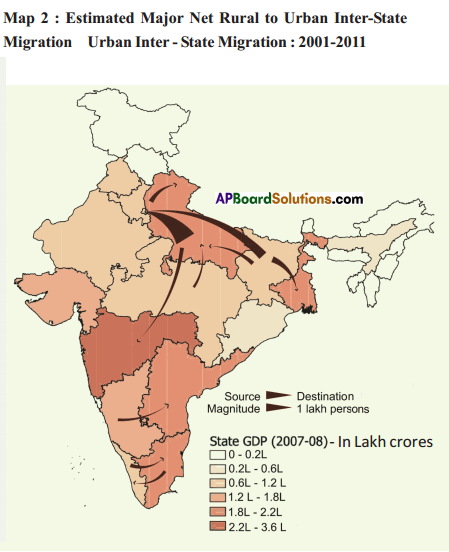 Answer:
Answer: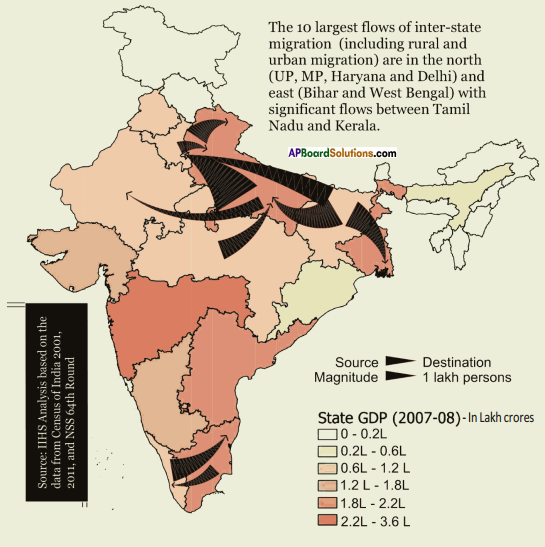 Answer:
Answer: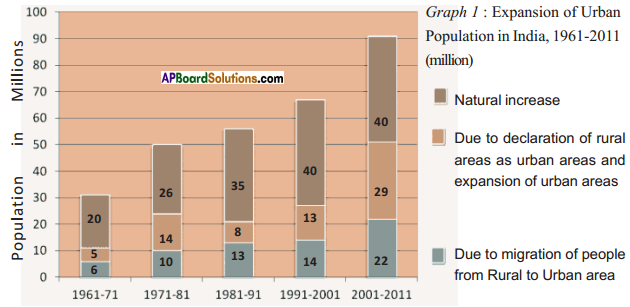 Answer:
Answer: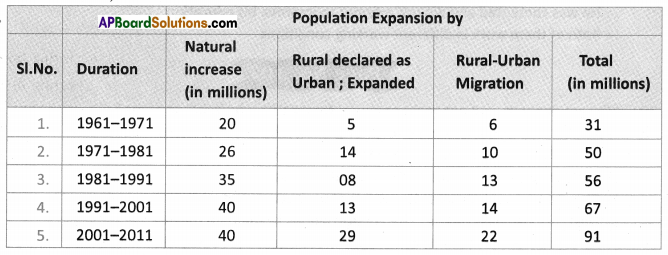
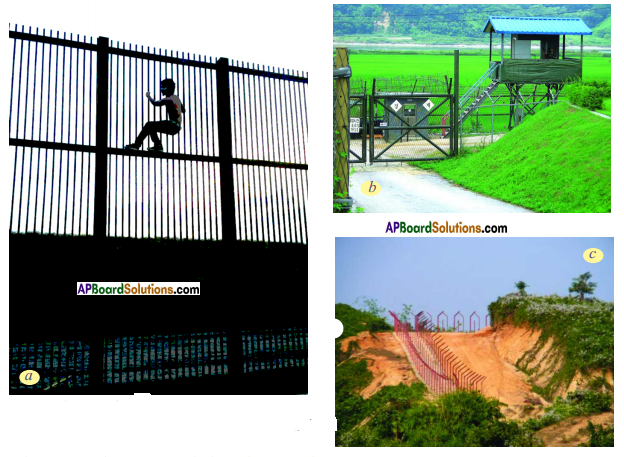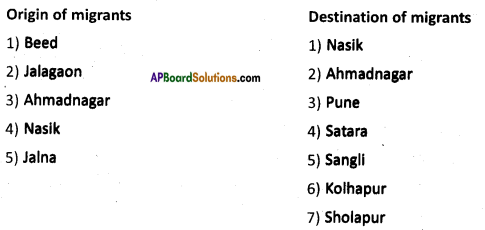
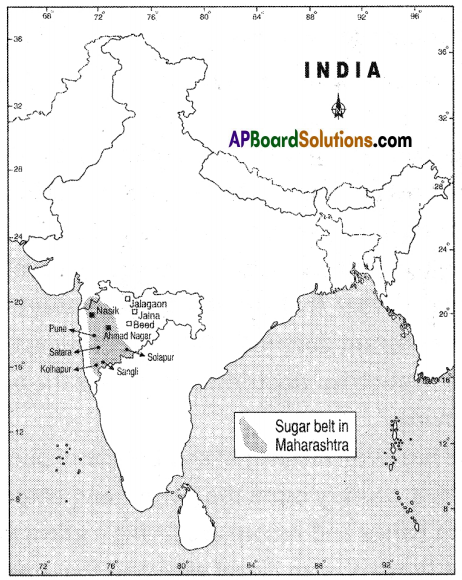
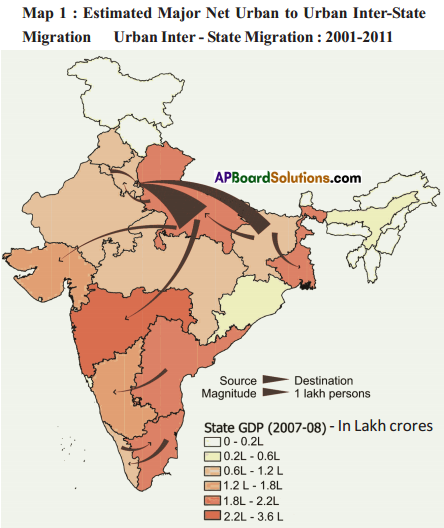
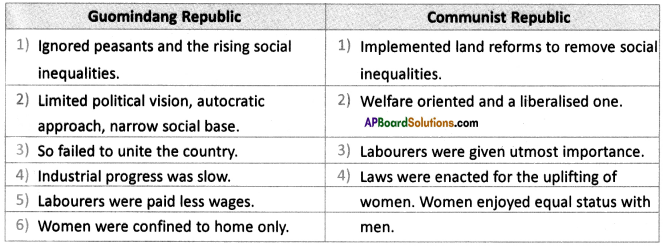
 What do you think of migrants across the border?
What do you think of migrants across the border?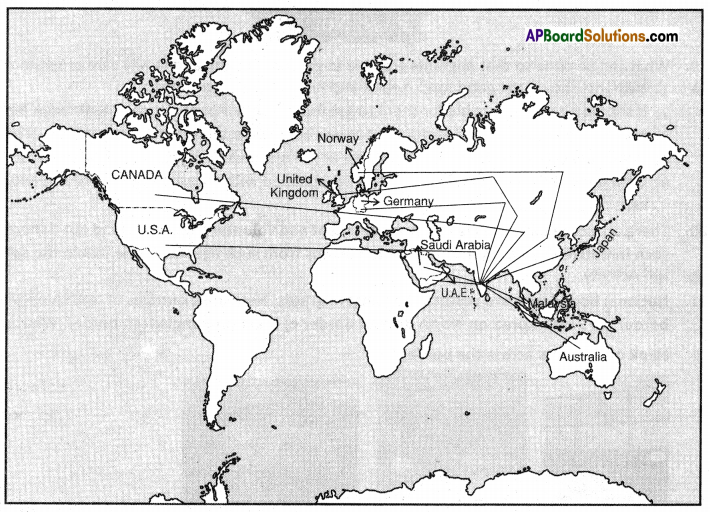






 Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: