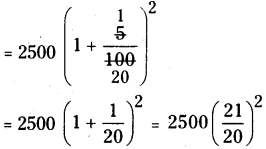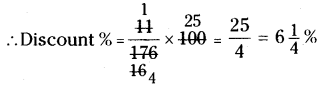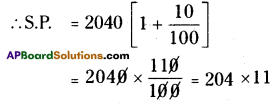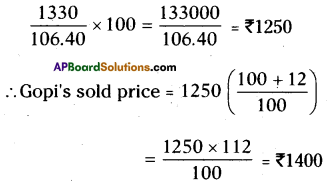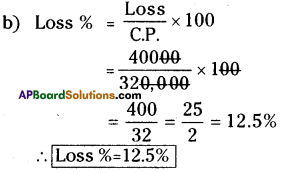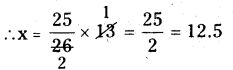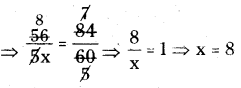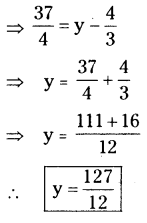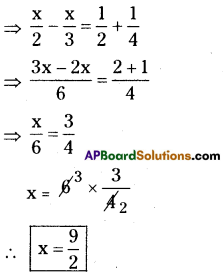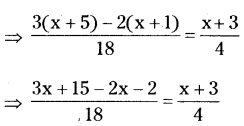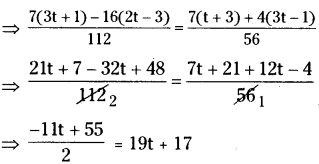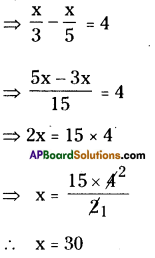AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Comparing Quantities Using Proportion Ex 5.3 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Maths Solutions 5th Lesson Comparing Quantities Using Proportion Exercise 5.3
![]()
Question 1.
Sudhakar borrows ₹ 15000 from a bank to renovate his house. He borrows the money at 9% p.a. simple interest over 8 years. What are his monthly repayments’?
Solution:
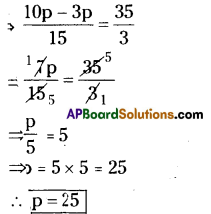
P = 15,000
R = 9%
T = 8 years
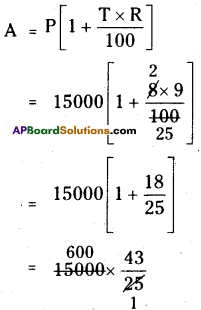
A = ₹ 25800
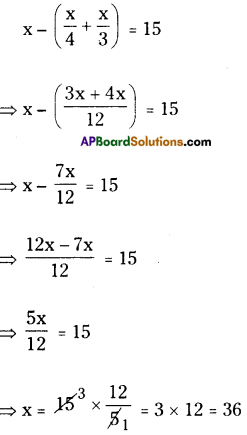
∴ His monthly payment = \(\frac{25800}{8 \times 12}\)
= ₹268.75
∴ Monthly he has to pay = ₹268.75
![]()
Question 2.
A TV was bought at a price of ₹ 21000. After 1 year the value of the TV was depreciated by 5% (Depreciation means reduction of the value due to use and age of the item). Find the value of the TV after 1 year.
Solution:
The C.P. of T.V = ₹ 21,000.
After 1 year its value
= 21000 – 5% of 21000
=21000 – \(\frac { 5 }{ 100 }\) × 21000
= 21000 – 1050
= ₹19,950
Question 3.
Find the amount and the compound interest on ₹ 8000 at 5% per annum, for 2 years
compounded annually.
Solution:
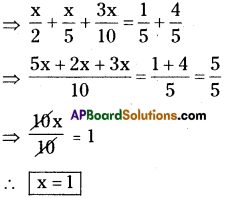
P = ₹8000
R = 5%
The interest is compounded every year.
Then 2 time periods wII be occurred.
∴ n = 2
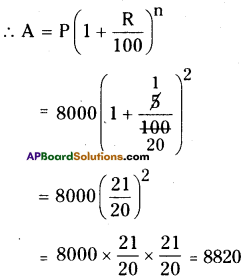
∴ Amount (A) = ₹8820
C.I = A – P
= 8820 – 8000 = ₹ 820
![]()
Question 4.
Find the amount and the compound interest on ₹ 6500 for 2 years, compounded annually, the rate of interest being 5% per annum during the first year and 6% per annum during the second year.
Solution:
P = ₹ 6500
R = 5%
T = 1 years
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{PTR}}{100}=\frac{6500 \times 5 \times 1}{100}\) = 325
∴ A = P + I = 6500 + 325 = 6825
∴ P = 6825
(At the begining of 2,id year A=P)
R = 6%
T = 1 year
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{PTR}}{100}=\frac{6825 \times 6 \times 1}{100}\) = 409.5
∴ A = P + I = 6825 + 409.5
∴ Amount = ₹ 7234.50
C.I. = A – P
= ₹ 7234.50 – 6500
= ₹734.50
Question 5.
Prathibha borrows ₹47000 from a fmance company to buy her first car. The rate of simple interest is 17% and she borrows the money over a 5 year period. Find: (a) How much
amount Prathibha should repay the finance company at the end of five years. (b) her equal
monthly repayments.
Solution:
P = ₹ 47000
R = 17%
T =5 years
∴ I = \(\frac{\mathrm{PTR}}{100}=\frac{47000 \times 5 \times 17}{100}\)
= ₹ 39,950
![]()
a) Amount to be paid
A = P + I
= 47000 + 39,950
= 86950
∴ Amount to be pay = ₹ 86950
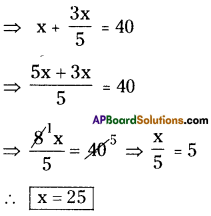
b) In monthly equal instalments she has to pay

= 149.1
= ₹ 1450 (approx)
Question 6.
The population of Hyderabad was 68,09,000 in the year 2011. If it increases at the rate of 4.7% per annum. What will be the population at the end of the year 2015.
Solution:
The population of Hyderabad
= 68,09,000
If every year increase in 4.7%.
Then the population of the city in 2015
= 68,09,000 ( 1 + \(\frac{4.7}{100}\) )4
100 J
[ ∵ P = 6809000, R = 4.7 %, n = 4(2015 -2011)]
= 68,09,000 x \(\frac{104.7}{100} \times \frac{104.7}{100} \times \frac{104.7}{100} \times \frac{104.7}{100}\)
= 81,82,199
![]()
Question 7.
Find Compound interest paid when a sum of ₹ 10000 is invested for 1 year and 3 months at 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) % per annum compounded annually.
Solution:
P = ₹10,000; R = 8\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) % = \(\frac { 17 }{ 2 }\)%
T = 1 year
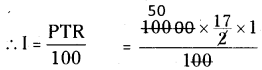
= 50 × 17 = 850
∴ I = ₹ 850
∴ A = P + I = 10,000 + 850
A = 10,850
∴ P = 10,850; R = \(\frac { 17 }{ 2 }\)% % ; T = 3 months
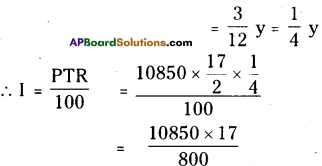
= ₹ 230.50
∴ Compound Interest
= 850 + 230.50
= ₹ 1080.50
Question 8.
Arif took a loan of ₹ 80,000 from a bank. If the rate of interest is 10% per annum, find the
difference in amounts he would be paying after 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) years, if the interest is (i) compounded annually (ii) compounded half yearly.
Solution:
P = ₹ 80,000; R = 10%;
T = 1 year
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{PTR}}{100}\) = \(\frac{80000 \times 10 \times 1}{100}\)
= ₹8000
∴ A = P + I = 80000 + 8000
= ₹ 88,000
Interest on 6 months :
P = 88,000 ; R = 10% ; T = 6 Months
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) year
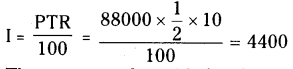
i) The amount to be paid after 1 year 6 months = P + I
= 88000 + 4400
A1 = ₹ 92,400
ii) He has to pay compounded on
every 6 months in 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) years
∴ 3 time periods will be occurred.
∴ n = 3
R = \(\frac { 10 }{ 2 }\) = 5% P = ₹ 80,000
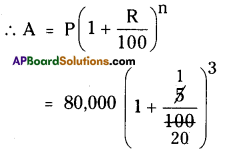
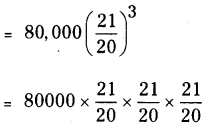
A2 = ₹ 92610
∴ Difference between the amounts = A2 – A1 = 92610 – 92400 = ₹ 210
![]()
Question 9.
I borrowed ₹ 12000 from Prasad at 6°/o per annum simple interest for 2 years. Had
I borrowed this sum at 6% per annum compounded annually, what extra amount would
I have to pay9
Solution:
Sum borrowed from Prasad
P = ₹ 12000
T = 2 years;
R = 6%
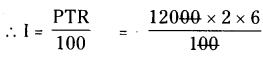
= ₹144O
A = P + I
A1 = P + I = 12000 + 1440
= ₹13440
12000 + 1440 , = ₹ 13440
∴ He has to pay the amount after 2 years at the rate of 6% on C.I.
P = ₹12,000; R = 6%; n = 2 years
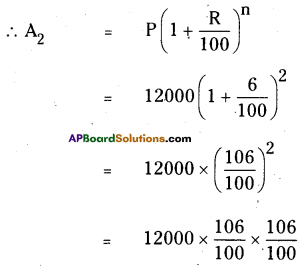
A2 = ₹13483.2
∴ The difference between the C.I and S.I = 13483.2 – 13440
= ₹ 43.20
Question 10.
In a laboratory the count of bacteria in a certain experiment was increasing at the rate of 2.5% per hour. Find the bacteria at the end of 2 hours if the count was initially 5,06,000
Solution:
No. of bacteria in a laboratory = 5,06,000
If they are increased at the rate of 2.5% per hour then their number after 2 hours
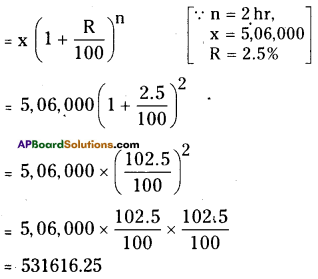
![]()
Question 11.
Kamala borrowed ₹ 26400 from a bank to buy a scooter at a rate of 15% per annum compounded yearly. What amount will she pay at the end of 2 years and 4 months to clear the loan?
Solution:
Kanala borrowed from bank = ₹ 26400
Rah of interest (R) =15%
n = 2 years
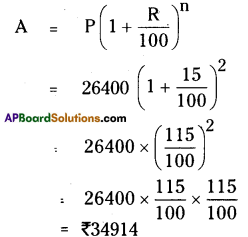
After 4 rpnths the amount will be ₹ 34914
∴ P = 34914; R = 15%; T = 4 months
T = \(\frac { 4 }{ 12 }\) year
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) year
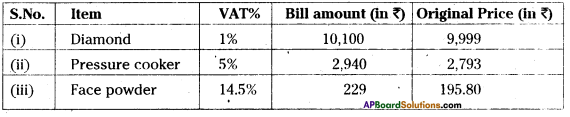
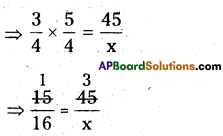
∴ \(I=\frac{P T R}{100}=\frac{34914 \times 15 \times \frac{1}{3}}{100}\)
= ₹1745.7
∴ Kamala has to pay the amount after 2 years and 4 months to the bank = 34914 + 1745.7
= ₹36659.7
![]()
Question 12.
Bharathi borrows an amount of ₹ 12500 at 12% per annum for3 years at a simple interest and Madhuri borrows the same amount for the same time period at 10% per annum, compounded annually. Who pays more interest and by how much?
Solution:
Bharathi borrowed the sum
P = ₹12500
R = 12%
T = 3 years
S. I (I) = \(\frac { PTR }{ 100 }\)
= \(\frac{12500 \times 12 \times 3}{100}\)
= 125 × 36
= 4500
After 3 years she has to pay
(A1)= P + I
= 12500 + 4500 .
A1 = ₹17,000
Madhuri has to pay the amount on
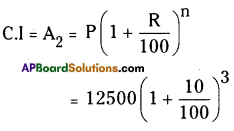
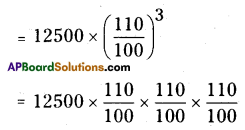
A2 = 16637.5
∴ A1 > A2
A1 – A2 = 17000 – 16637.5
= ₹ 362.5
∴ Bharathi has to pay ₹ 362.5 more than Madhuri.
![]()
Question 13.
Machinery worth ₹ 10000 depreciated by 5%. Find its value after 1 year.
Solution:
The value of machinery after 1 year on 5% depreciation
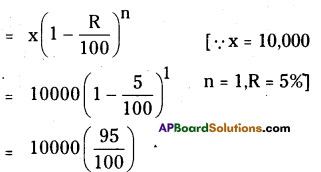
= 95 × 100
= ₹ 9500
Question 14.
Find the population of a city after 2 years which is at present 12 lakh, if the rate of increase is 4%.
Solution:
Present population of a city = 12,00,000 If its population increases at the rate of 4%, then the population after 2 years
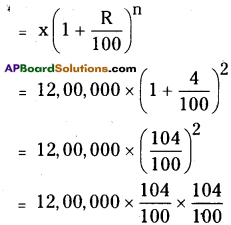
= 120 × 104 × 104
= 12,97,920
![]()
Question 15.
Calculate compound interest on ₹ 1000 over a period of 1 year at 10% per annum, if interest is compounded quarterly?
Solution:
compounded quarterly then 4 time periods will be there in 1 year.
∴ n = 4
C.I. on ₹ 1000 over a period of 1 year at
10% per annum A = P (1 + \(\frac{\mathrm{R}}{100}\) )n
P = 1000; n = 4; R = \(\frac{10}{4}=\frac{5}{2}\) %
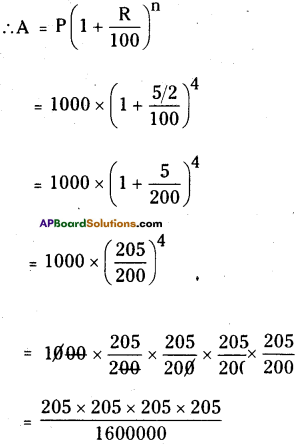
= ₹ 1103.81
A = ₹ 1103.81
C.I. for 1 year
= 1103.81 – 1000
= ₹ 10.81