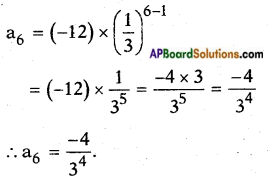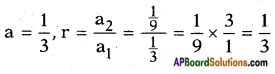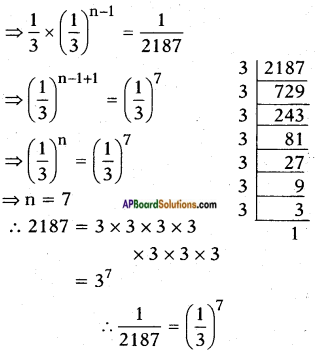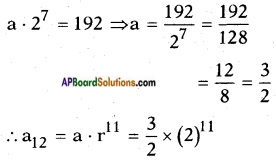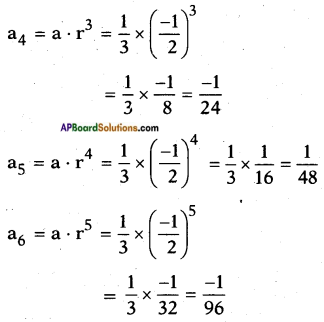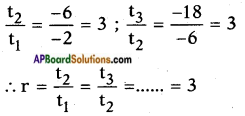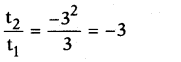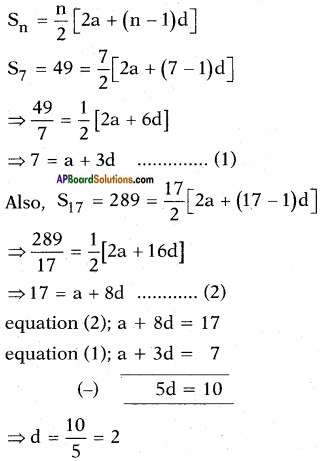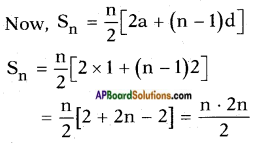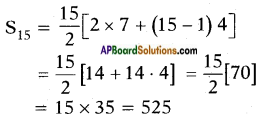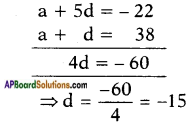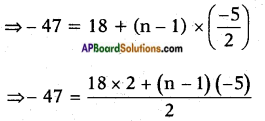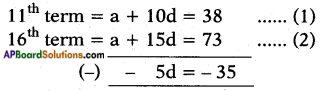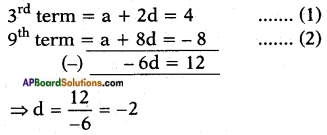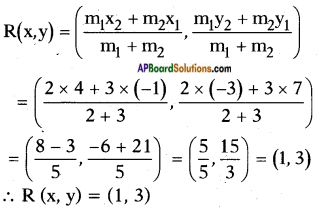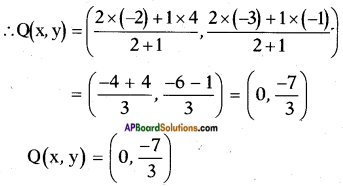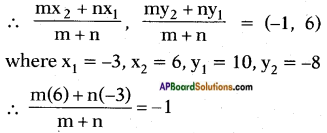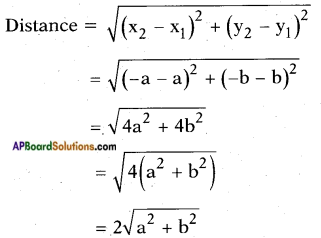AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Maths Textbook Solutions Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations Ex 5.3 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Maths Solutions 5th Lesson Quadratic Equations Exercise 5.3
10th Class Maths 5th Lesson Quadratic Equations Ex 5.3 Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations, if they exist, by the method of completing the square:
i) 2x2 + x – 4 = 0
Answer:
Given: 2x2 + x – 4 = 0
⇒ 2x2 + x = 4
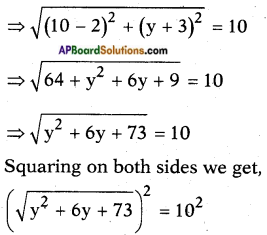
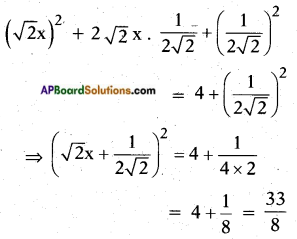
⇒ (√2x)2 + x = 4
⇒ (√2x)2 + 2.√2.x.\(\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{2}}\) = 4
Now LHS is in the form a2 + 2ab
where b = \(\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{2}}\)
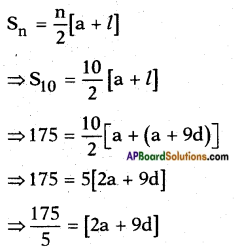
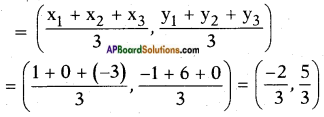
Adding b2 = \(\left(\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{2}}\right)^{2}\) on both sides we get
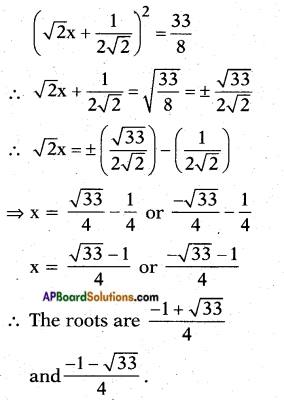
![]()
ii) 4x2 + 4√3x + 3 = 0
Answer:
Given: 4x2 + 4√3x + 3 = 0
⇒ 4x2 + 4√3x = -3
⇒ (2x)2 + 2(2x)√3 = -3
LHS is of the form a2 + 2ab where
where b = √3.
∴ Adding b2 = (√3)2 = 3 on both sides, we get
(2x)2 + 2(2x)(√3) + (√3)2 = -3 + (√3)2
⇒ (2x + √3)2 = -3 + 3 = 0
∴ (2x + √3)2 = 0
⇒ 2x + √3 = 0
⇒ 2x = -√3
⇒ x = \(\frac{-\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
∴ The roots are \(\frac{-\sqrt{3}}{2}\), \(\frac{-\sqrt{3}}{2}\).
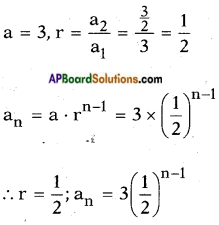
iii) 5x2 – 7x – 6 = 0
Given quardratic equation = 5x2 – 7x – 6 = 0
∴ 5x2 – 7x – 6
⇒ x2 – \(\frac{7}{5}\)x = \(\frac{6}{5}\), it can be re-written as
x2 – 2.\(\frac{7}{10}\)x = \(\frac{6}{5}\) now it is in the form
of a2 – 2ab where a = x, and b = \(\frac{7}{10}\)
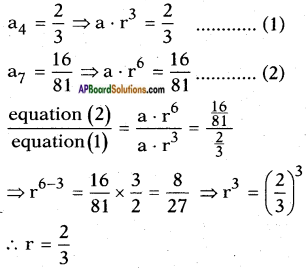
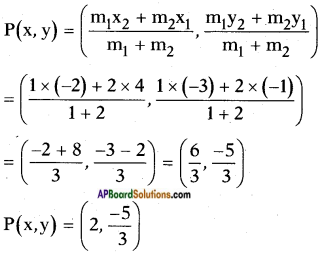
Now adding b2 = \(\left(\frac{7}{10}\right)^{2}\) on both sides, we get
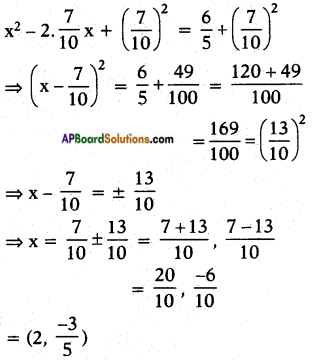
Note: If we take the Q.E. as 5x2 – 7x + 6 = 0, then we get the T.B. answer.
![]()
iv) x2 + 5 = -6x
Answer:
The given Q.E. is x2 + 5 = -6x
⇒ x2 + 6x = -5
⇒ (x)2 + 2.(x).3 = -5
Now L.H.S. is of the form a2 + 2ab where b = 3.
Adding b2 = 32 on both sides we get
x2 + 2(x)(3) + 32 = -5 + 32
(x + 3)2 = -5 + 9 = 4
∴ x + 3 = 74 = ± 2
⇒ x = +2 – 3 or – 2 – 3
= -1 or -5 are the roots of the given Q.E.
Question 2.
Find the roots of the quadratic equations given in Q.1 above by applying the quadratic formula,
i) 2x2 + x – 4 = 0
Answer:
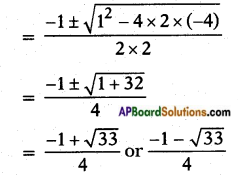
Comparing this Q.E. with ax2 + bx + c = 0
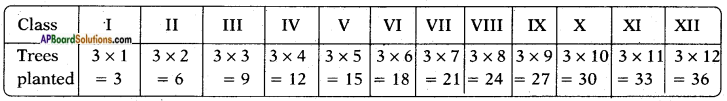
a = 2; b = 1; c = -4
x = \(\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4 a c}}{2 a}\)
ii) 4x2 + 4√3x + 3 = 0
Answer:
Given: 4x2 + 4√3x + 3 = 0
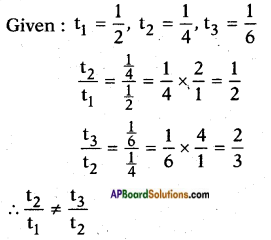
Here a = 4; b = 4√3 ; c = 3
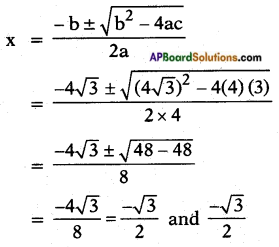
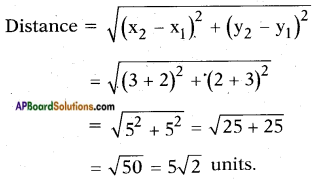
![]()
iii) 5x2 – 7x – 6 = 0
Answer:
Given: 5x2 – 7x – 6 = 0
Here a = 5; b = -7 and c = -6
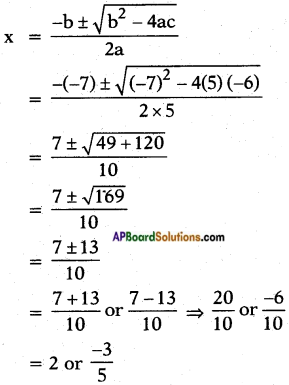
iv) x2 + 5 = -6x
Answer:
Given: x2 + 5 = -6x
⇒ x2 + 6x + 5 = 0
Here a = 1; b = 6; c = 5
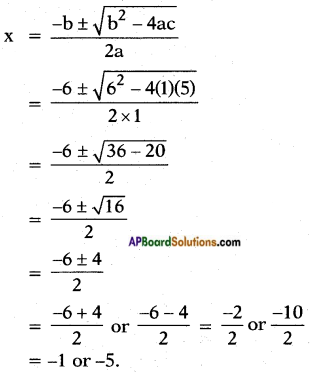
Question 3.
Find the roots of the following equations:
i) x – \(\frac{1}{x}\) = 3, x ≠ 0
Answer:
Given: x – \(\frac{1}{x}\) = 3
⇒ x2 + 6x + 5 = 0
⇒ \(\frac{x^{2}-1}{x}\) = 3
⇒ x2 – 1 = 3x
⇒ x2 – 3x – 1 = 0
Here a = 1; b = -3; c = -1

![]()
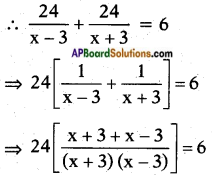
ii) \(\frac{1}{x+4}\) – \(\frac{1}{x-7}\) = \(\frac{11}{30}\), x ≠ -4, 7
Answer:
Given: \(\frac{1}{x+4}\) – \(\frac{1}{x-7}\) = \(\frac{11}{30}\)
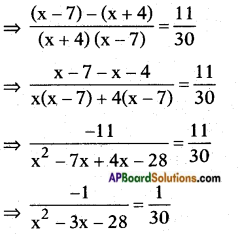
⇒ x2 – 3x – 28 = -30
⇒ x2 – 3x – 28 + 30 = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x + 2 = 0
⇒ x2 – 2x – x + 2 = 0
⇒ x(x – 2) – 1(x – 2) = 0
⇒ (x – 2) (x – 1) = 0
⇒ x – 2 = 0 (or) x – 1 = 0
⇒ x = 2 or x = 1
⇒ x = 2 or 1.
Question 4.
The sum of the reciprocals of Rehman’s ages, (in years) 3 years ago and 5 years from now is \(\frac{1}{3}\). Find his present age.
Answer:
Let the present age of Rehman be x years.
3 years ago Rehman’s age = x – 3 and its reciprocal is \(\frac{1}{x-3}\)
Rehman’s age 5 years from now = x + 5 and its reciprocal is \(\frac{1}{x+5}\)
The sum of the reciprocals
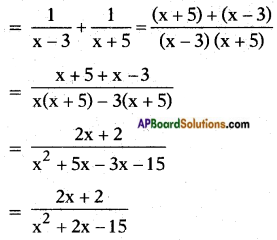
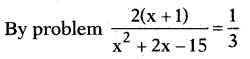
⇒ x2 + 2x – 15 = 3(2x + 2)
⇒ x2 + 2x – 15 = 6x + 6
⇒ x2 + 2x – 15 – 6x – 6 = 0
⇒ x2 – 4x – 21 =0
⇒ x2 – 7x + 3x – 21 =0
⇒ x(x – 7) + 3(x – 7) 0
⇒ (x – 7) (x + 3) = 0
⇒ x – 7 = 0 or x + 3 = 0
⇒ x = 7 or x = -3
But x can’t be negative, x = 7
i.e., Present age of Rehman = 7 years.
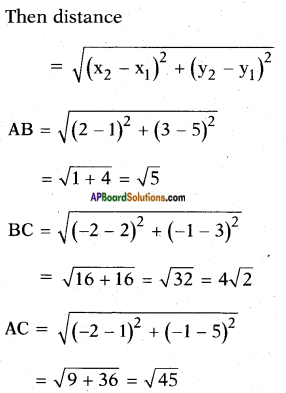
![]()
Question 5.
In a class test, the sum of Moulika’s marks in Mathematics and English is 30. If she got 2 marks more in Mathematics and 3 marks less in English, the product of her marks would have been 210. Find her marks in the two subjects.
Answer:
Sum of the marks in Mathematics and English = 30
Let Moulika’s marks in Mathematics be x Then her marks in English = 30 – x
If she got 2 more marks in Mathematics, then her marks would be x + 2.
If she got 3 marks less in English then her marks would be 30 – x – 3 = 27 – x
By problem (x + 2) (27 – x) = 210
⇒ x(27 – x) + 2(27 – x) = 210
⇒ 27x – x2 + 54 – 2x = 210
⇒ -x2 + 25x + 54 = 210
⇒ x2 – 25x – 54 + 210 = 0
⇒ x2 – 25x + 156 = 0
⇒ x2 – 12x – 13x + 156 = 0
⇒ x(x – 12) – 13(x 12) = 0
⇒ (x – 12) (x – 13) = 0
⇒ x – 12 = 0 or x – 13 = 0
⇒ x = 12 or x = 13
If x = 12, then marks in Mathematics = 12 English = 30 – 12 = 18
If x = 13, then marks in Mathematics = 13 English = 30 – 13 = 17
Question 6.
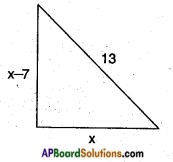
The diagonal of a rectangular field is 60 metres more than the shorter side. If the longer side is 30 metres more than the shorter side, find the sides of the field.
Answer:
Let the shorter side of the rectangular field = x m.
Then its longer side = x + 30 m.
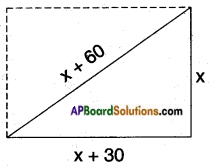
The diagonal of a rectangle is also the hypotenuse of the lower triangle Here the diagonal = x + 60
∴ By Pythagoras Theorem
(side)2 + (side)2 = (hypotenuse)2
⇒ (x + 30)2 + x2 = (x + 60)2
⇒ x2 + 60x + 900 + x2 = x2 + 120x + 3600
⇒ x2 – 60x – 2700 = 0
⇒ x2 – 90x + 30x – 2700 = 0
⇒ x(x – 90) + 30 (x – 90) = 0
⇒ (x – 90) (x + 30) = 0
⇒ x – 90 = 0 (or) x + 30 = 0
⇒ x = +90 (or) x = -30 But ‘x’ can’t be negative.
∴ x = 90 m
i.e., the shorter side x = 90 m Longer side x + 30 = 90 + 30 = 120 m.
![]()
Question 7.
The difference of squares of two numbers is 180. The square of the smaller number is 8 times the larger number. Find the two numbers.
Answer:
Let the large number be x.
8 times larger number = Square of the srnall number = 8x
Square of the larger number = x2
By problem, x2 – 8x = 180
⇒ x2 – 8x – 180 = 0
⇒ x2– 18x + 10x – 180 = 0
⇒ x(x – 18) + 10(x – 18) = 0
⇒ (x + 10)(x – 18) = 0
⇒ x + 10 = 0 (or) x – 18 = 0
⇒ x = -10 (or) x = 18
If x = 18, then larger number =18;
(small number)2 = 8 × (+18) = 144
∴ Small number = √144 = 12
The numbers are 18, 12
Note: Discard x = -10.
Question 8.
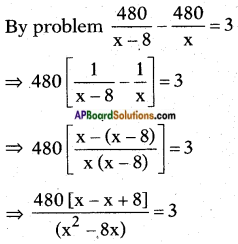
A train travels 360 km at a uniform speed. If the speed had been 5 km/h more, it would have taken 1 hour less for the same journey. Find the speed of the train.
Answer:
The distance travelled = 360 km.
Let the speed of the train = x kmph.
Time taken to complete a journey = \(\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { speed }}\)
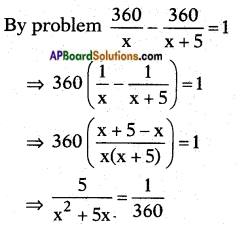
⇒ x2 + 5x = 1800
⇒ x2 + 5x – 1800 = 0
⇒ x2 + 45x – 40x – 1800 = 0
⇒ x(x + 45) – 40(x + 45) = 0
⇒ (x + 45) (x – 40) = 0
x + 45 = 0 or x -40 = 0
x = -45 or x = +40
But x can’t be negative.
∴ The speed of the train = 40 kmph.
![]()
Question 9.
Two water taps together can fill a tank in 9\(\frac{3}{8}\) hours. The tap of larger diameter takes 10 hours less than the smaller one to fill the tank separately. Find the time in which each tap can separately fill the tank.
Answer:
Let the time taken to fill the tank by smaller tap = x (hours)
So the part filled by smaller tap in
1 hour = \(\frac{1}{x}\) × \(\frac{75}{8}\) = \(\frac{75}{8x}\) ……. (1)
Again then the time taken to fill the tank by larger tap = (x – 10) hours
∴ the part of tank that can be filled by larger tap alone in one hour of time = \(\frac{1}{x-10}\)
∴ In \(\frac{75}{8}\) hours the part filled by larger tap = \(\frac{75}{8}\left(\frac{1}{x-10}\right)\)
∴ By both taps together
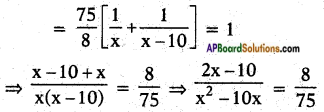
⇒ 150x – 750 = 8x2 – 80x
⇒ 8x2 – 80x – 150x + 750 = 0
⇒ 8x2 – 230x + 750 = 0
⇒ 4x2 – 115x + 375 = 0
⇒ 4x2 – 100x – 15x + 375 = 0
⇒ 4x(x – 25) – 15(x – 25) = 0
∴ (4x – 15) (x – 25) = 0 15
⇒ 4x = 15, x = \(\frac{15}{4}\) or x = 25
x = 25 hours.
then time taken to fill by larger tap = x – 10 = 25 – 10 = 15 hours
(x cannot be \(\frac{15}{4}\) since we have considered ‘x’ as time taken by smaller tap, which is to be higher one)
Question 10.
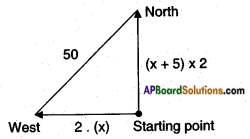
An express train takes 1 hour less than a passenger train to travel 132 km between Mysore and Bangalore (without taking into consideration the time they stop at intermediate stations). If the average speed of the express train is 11 km/hr more than that of the passenger train, find the average speed of the two trains.
Answer:
Let the speed of the passenger train = x kmph.
Then speed of the express train = x + 11 kmph.
Distance travelled = 132 km
We know that time = \(\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { speed }}\)
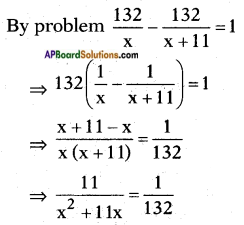
⇒ x2 + 11x = 13 × 11
⇒ x2 + 11x – 1452 = 0
⇒ x2 + 44x – 33x – 1452 = 0
⇒ x(x + 44) – 33 (x + 44) = 0
⇒ (x + 44) (x – 33) = 0
⇒ x + 44 = 0 (or) x – 33 = 0
⇒ x = -44 (or) x = 33
But x can’t be negative.
∴ Speed of the passenger train = x = 33 kmph.
Speed of the express train = x + 11 = 44 kmph.
![]()
Question 11.
Sum of the areas of two squares is 468 m2. If the difference of their perimeters is 24m, find the sides of the two squares.
(OR)
If the sum of the areas of two squares is 468 m2 and the difference of their perimeters is 24m, then find the measurements of their sides.
Answer:
Let the side of first square = x m say Then perimeter of the first square = 4x [∵ P = 4 . side]
By problem, perimeter of the second square = 4x + 24 (or) 4x – 24
∴ Side of the second square =
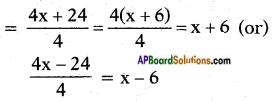
Now sum of the areas of the two squares is given as 468 m2
x2 + (x + 6)2 = 468
⇒ x2 + x2 + 12x + 36 = 468
⇒ 2x2 + 12x + 36 – 468 = 0
⇒ 2x2 + 12x – 432 = 0
⇒ x2 + 6x – 216 = 0
⇒ x2 + 18x – 12x – 216 = 0
⇒ x(x + 18)- 12(x + 18) = 0
⇒ (x + 18) (x – 12) = 0
⇒ x + 18 = 0 (or) x – 12 = 0
⇒ x = -18 (or) 12
But x can’t be negative.
∴ x = 12
i.e., side of the first square = 12
∴ Perimeter = 4 × 12 = 48
∴ Perimeter of the second square = 48 + 24 = 72
∴ Side of the second square = \(\frac{72}{4}\) = 18 m.
(or)
x2 + (x – 6)2 = 468
⇒ x2 + x2 – 12x + 36 = 468
⇒ 2x2 – 12x – 432 – 0
⇒ x2 – 6x – 216 = 0
⇒ x2 – 18x + 12x – 216 = 0
⇒ x(x-18) + 12(x-18) = 0
⇒ (x – 18) (x + 12) = 0
⇒ x – 18 = 0 (or) x + 12 = 0
⇒ x = 18 (or) – 12
But x can’t be negative.
∴ x = 18
i.e., side of the first square = 18 m
∴ Perimeter = 4 × 18 = 72
Perimeter of the second square = 72 – 24 = 48
∴ Side of the second square = \(\frac{48}{4}\) = 12 m.
i.e., In any way, the sides of the squares are 12m, 18m.
![]()
Question 12.
If a polygon of ‘n’ sides has \(\frac{1}{2}\)n(n – 3) diagonals. How many sides will a polygon having 65 diagonals? Is there a polygon with 50 diagonals?
Answer:
Given: Number of diagonals of a polygon with n-sides = \(\frac{n(n-3)}{2}\)
No. of diagonals of a given polygon = 65
i.e., \(\frac{n(n-3)}{2}\) = 65
where n is number of sides of the polygon
⇒ n2 – 3n = 2 × 65
⇒ n2 – 3n – 130 = 0
⇒ n2 – 13n + 10n – 130 = 0
⇒ n(n – 13) + 10(n – 13) = 0
⇒ (n – 13) (n + 10) = O
⇒ n – 13 = 0 (or) n + 10 = 0
⇒ n = 13 (or) n = -10
But n can’t be negative.
∴ n = 13 (i.e.) number of sides = 13.
Also to check 50 as the number of diagonals of a polygon
∴ \(\frac{n(n-3)}{2}\) = 50
⇒ n2 – 3n = 100
⇒ n2 – 3n – 100 = 0
There is no real value of n for which the above equation is satisfied.
∴ There can’t be a polygon with 50 diagonals.