AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Maths Textbook Solutions Chapter 11 Trigonometry Ex 11.3 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Maths Solutions 11th Lesson Trigonometry Exercise 11.3
10th Class Maths 11th Lesson Trigonometry Ex 11.3 Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Evaluate:
i) \(\frac{\tan 36^{\circ}}{\cot 54^{\circ}}\)
Answer:
Given that \(\frac{\tan 36^{\circ}}{\cot 54^{\circ}}\)
= \(\frac{\tan 36^{\circ}}{\cot \left(90^{\circ}-36^{\circ}\right)}\) [∵ cot (90 – θ) = tan θ]
= \(\frac{\tan 36^{\circ}}{\tan 36^{\circ}}\)
= 1
ii) cos 12° – sin 78°
Answer:
Given that cos 12° – sin 78°
= cos 12° – sin(90° – 12°) [∵ sin (90 – θ) = cos θ]
= cos 12° – cos 12° = 0
![]()
iii) cosec 31° – sec 59°
Answer:
Given that cosec 31° – sec 59°
= cosec 31° – sec (90° – 31°) [∵ sec (90 – θ) = cosec θ]
= cosec 31° – cosec 31° = 0
iv) sin 15° sec 75°
Answer:
Given that sin 15° sec 75°
= sin 15° . sec (90° – 15°)
= sin 15° . cosec 15° [∵ sec (90 – θ) = cosec θ]
= sin 15° . \(\frac{1}{\sin 15^{\circ}}\) [∵ cosec θ = \(\frac{1}{\sin \theta}\)]
= 1
v) tan 26° tan 64°
Answer:
Given that tan 26° tan 64°
= tan 26° . tan (90° – 26°)
= tan 26° . cot 26° [∵ tan (90 – θ) = cot θ]
= tan 26° . \(\frac{1}{\tan 26^{\circ}}\) [∵ cot θ = \(\frac{1}{\tan \theta}\)]
= 1
Question 2.
Show that
i) tan 48° tan 16° tan 42° tan 74° = 1
Answer:
L.H.S. = tan 48° tan 16° tan 42° tan 74°
= tan 48°. tan 16° . tan(90° – 48°) . tan(90° – 16°)
= tan 48° . tan 16° . cot 48° . cot 16° [∵ tan (90 – θ) = cot θ]
= tan 48° . tan 16° . \(\frac{1}{\tan 48^{\circ}}\) . \(\frac{1}{\tan 16^{\circ}}\) [∵ cot θ = \(\frac{1}{\tan \theta}\)]
= 1 = R.H.S.
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
ii) cos 36° cos 54° – sin 36° sin 54° = 0
Answer:
L.H.S. = cos 36° cos 54° – sin 36° sin54°
= cos (90° – 54°) . cos (90° – 36°) – sin 36° . sin 54° [∵ cos (90 – θ) = sin θ]
= sin 54° . sin 36° – sin 36° . sin 54°
= 0 = R.H.S.
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
![]()
Question 3.
If tan 2A = cot (A – 18°), where 2A is an acute angle. Find the value of A.
Answer:
Given that tan 2A = cot (A – 18°)
⇒ cot (90° – 2A) = cot (A – 18°) [∵ tan θ = cot (90 – θ)]
⇒ 90° – 2A = A – 18°
⇒ 108° = 3A
⇒ A = \(\frac{108^{\circ}}{3}\) = 36°
Hence the value of A is 36°.
Question 4.
If tan A = cot B where A and B. are acute angles, prove that A + B = 90°.
Answer:
Given that tan A = cot B
⇒ cot (90° – A) = cot B [∵ tan θ = cot (90 – θ)]
⇒ 90° – A = B
⇒ A + B = 90°
Question 5.
If A, B and C are interior angles of a triangle ABC, then show that \(\tan \left(\frac{\mathbf{A}+\mathbf{B}}{2}\right)=\cot \frac{\mathbf{C}}{2}\)
Answer:
Given A, B and C are interior angles of right angle triangle ABC then A + B + C = 180°.
On dividing the above equation by ‘2’ on both sides, we get 180°
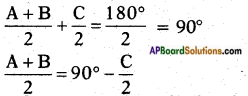
On taking tan ratio on both sides
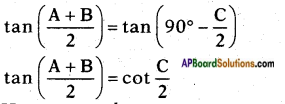
Hence proved.
![]()
Question 6.
Express sin 75° + cos 65° in terms of trigonometric ratios of angles between 0° and 45°.
Answer:
We have sin 75° + cos 65°
= sin (90° – 15°) + cos (90° – 25°)
= cos 15° + sin 25° [∵ sin (90 – θ) = cos θ and cos (90 – θ) = sin θ]


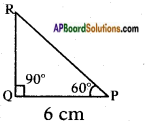
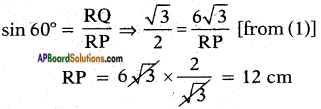
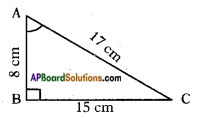
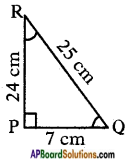
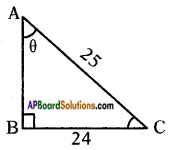
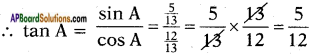
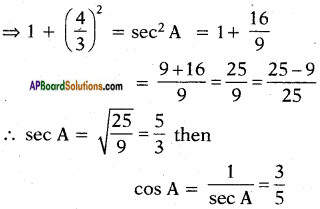

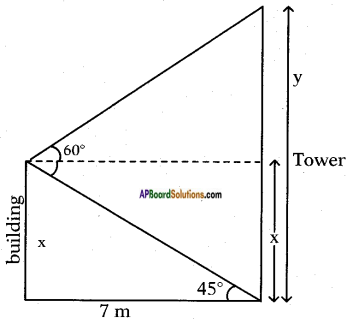
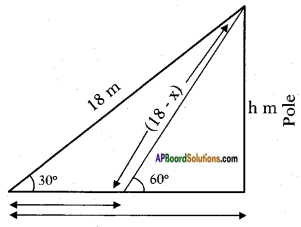
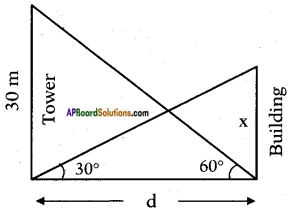
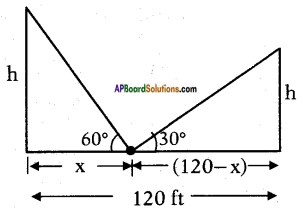
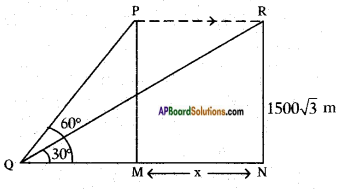
 Let the height of the tower = h m
Let the height of the tower = h m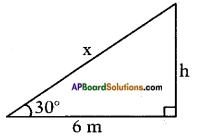 Distance between the foot of tree and the point of contact of the top of the tree on the ground = 6 cm.
Distance between the foot of tree and the point of contact of the top of the tree on the ground = 6 cm.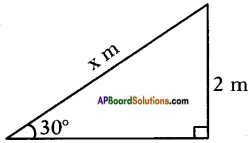 Height of slide = 2 m
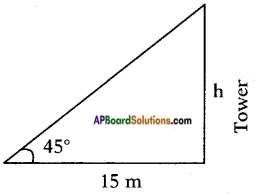
Height of slide = 2 m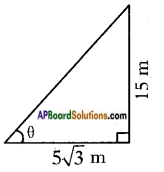 Height of the pole = 15 m
Height of the pole = 15 m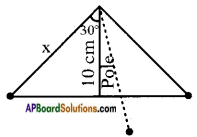
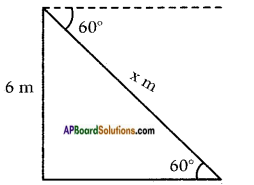 Height of the building = 6 m
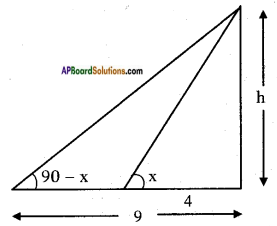
Height of the building = 6 m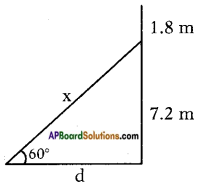 Height of the pole = 9m
Height of the pole = 9m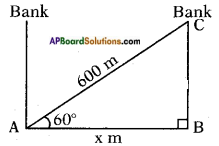 Let the width of the river = AB = x m
Let the width of the river = AB = x m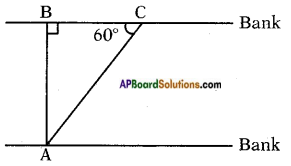 In the figure
In the figure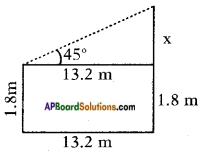 From the figure
From the figure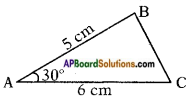 Answer:
Answer: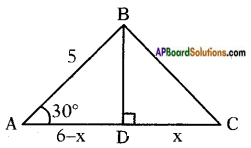 Draw a perpendicular BD to AC
Draw a perpendicular BD to AC Answer:
Answer:
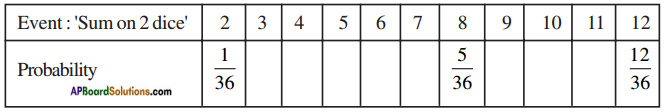
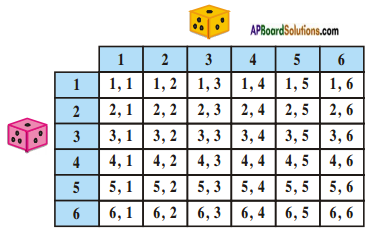 (i)
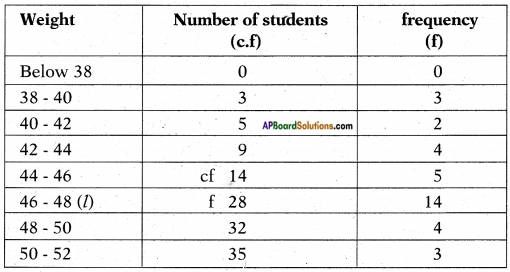
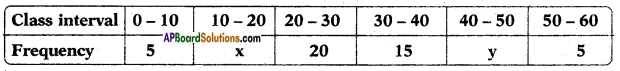
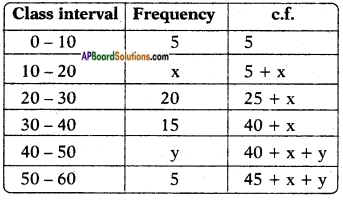
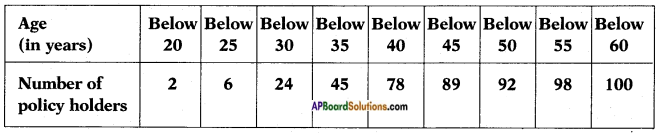
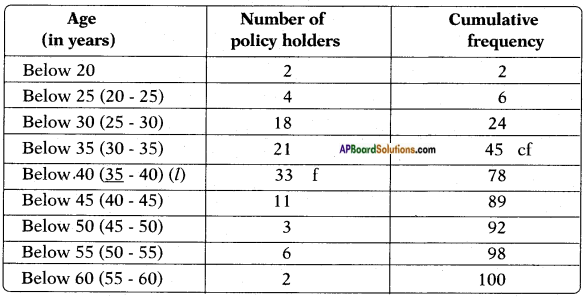
(i)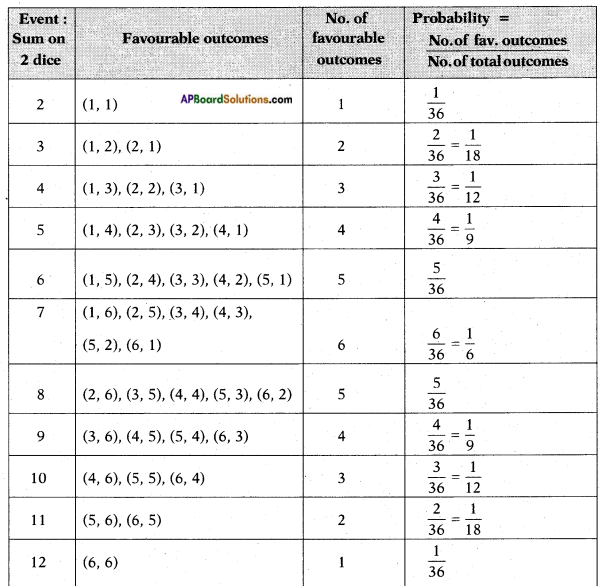 (ii) The above (given) argument is wrong [from the above table].
(ii) The above (given) argument is wrong [from the above table]. ∴ P(E) = \(\frac{\text { No. of favourable outcomes }}{\text { No. of total outcomes }}\)
∴ P(E) = \(\frac{\text { No. of favourable outcomes }}{\text { No. of total outcomes }}\)


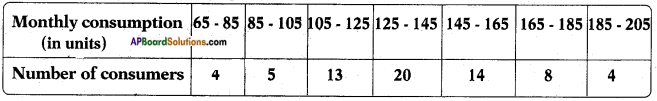
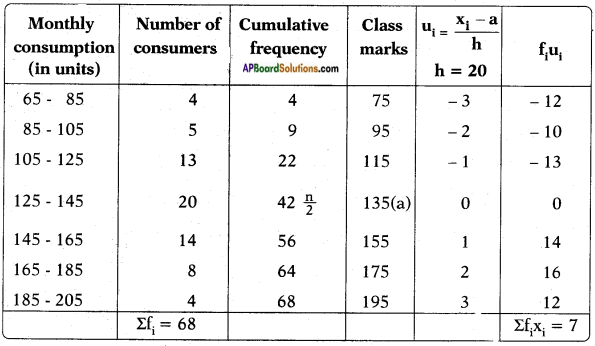





 symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.
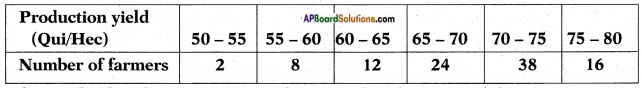
symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.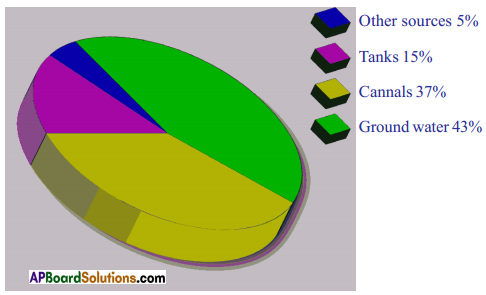 A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?
A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?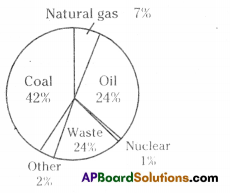 i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.
i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.