AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class English Textbook Solutions Chapter 2C V.V.S. Laxman, Very Very Special Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class English Solutions Chapter 2C V.V.S. Laxman, Very Very Special
9th Class English Chapter 2C V.V.S. Laxman, Very Very Special Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What is Laxman’s philosophy of life as per the interview you have read?
Answer:
Laxman’s philosophy of life is to work hard continuously and treat success and failure equally.
Question 2.
What role did Laxman play in making India, No. 1 test cricket team?
Answer:
Laxman says that India hadn’t become No.l all of a sudden. It was a slow and long drawn process. He was frank in saying that he did not play in the World Cup that saw India as the No. 1 team. But he was proud to be the member of the world No.l team.
![]()
On the basis of your reading of V.V.S. Laxman’s interview with Sportstar magazine complete the following table.
| Events/Incidents in his life | Your responses |
| 1. Home ground | |
| 2. Teams he represented | |
| 3. Levels he played at | |
| 4. People who influenced him | |
| 5. Things he likes /hobbies | |
| 6. Memorable events | |
| 7. His message |
Answer:
| Events/Incidents in his life | Your responses |
| 1. Home ground | Hyderabad Cricket Association – Uppal Stadium |
| 2. Teams he represented | Under 16; Under 19; Ranji Trophy – Hyderabad team; National team, One Day Internationals; T20s – IPL |
| 3. Levels he played at | Under 16; Under 19; Senior Level |
| 4. People who influenced him | Parents; Specially father Dr. V. Shantaram |
| 5. Things he likes /hobbies | Spending with members of family; reading biographies of successful individuals; listening to music. |
| 6. Memorable events | 281 against Australia in Kolkata in 2001 |
| 7. His message | Work hard continuously; treat success and failure equally |
Writing
Write persona! views and reflections on V.V.S. Laxman in a paragraph of about 75-100 words.
Discuss the following questions in groups before writing the paragraph individually.
1) What is the main idea that you wish to project?
2) What are the supporting ideas that you think of?
3) How do you organize your ideas?
4) How do you link your thoughts?
5) How do you conclude?
Answer:
V.V.S. Laxman is both an excellent cricketer and a wonderful individual. As a cricketer, he reached dizzy heights and won for him a special title ‘Very Very Special.’ But as a human being, he exhibits very noble qualities. He loves his parents, wife, and children intensely. He is thankful to all those who helped him. He is frank in admitting his weak points. He is honest in declaring his sources of inspiration. He is free to announce his hobbies, food habits, and future plans. His philosophy to treat success and failure equally is highly admirable. On the whole, V.V.S. Laxman is a very, very special model to everyone.
Project Work
Collect the information from newspapers, magazines, periodicals, and books about two famous Indian sportswomen and prepare their profiles.
Fill the details of the following information and you may use them as tips for profile writing and speaking.
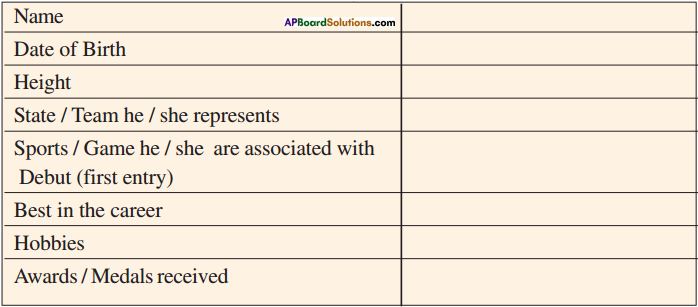
Talk about one profile in the class.
| Profile – 1: (P.T.Usha) | |
| Name | Pilavullakandi Thekkeparambil Usha |
| Date of Birth | June 27, 1964 |
| Height | 5.7″ (170 cm) |
| State/Team she represented | National Team – India |
| Sports/Game she is associated with | Running (Track & Field) |
| Debut (first entry) | At the age of 16, in 1980 in the Moscow Olympics |
| Best in the Career | At the Asian Meet in Jakarta in 1985, Usha established herself as the Asian sprint queen with five gold medals (in the 100 meters, 200m, 400m, 400m hurdles, and the 4 x 400 m relay) besides a bronze in the 100m relay, |
| Hobbies | Reading books and listening to music |
Answer:
Awards/Medals Received
- Recipient of Arjuna Award, 1984.
- Adjudged as the greatest women athlete, in 1985 Jakarta Asian Athletic Meet.
- Padma Sree in 1984.
- Best Athlete of the year Award from India Government in 1984,/85,/B6,/B7, and 89.
- In 1986 Seoul Asian Games, won the Adidas Golden Shoe Award for the best athlete by the Asian Amateur Athletics Association, Seoul Asian Games, 1986.
- Asian Amateur Athletics Association, Seoul Asian Games, 1986.
- 33 medals including 13 gold medals in Asian Games and Asian Championships.
- Won a total of 102 medals at National and International meets during her career.
- Won 1 gold and 2 silver at the 1999 SAF Games held at Kathmandu.
- Thirty International Awards, for her excellence in Athletics.
- Kerala Sports Journalists Award for the year 1999.
![]()
Profile with more details
P.T. Usha was born, as the daughter of Paithal and Lakshmi, at Payyoli, a small village in Kozhikode, on June 27, 1964. Her full name is Pilavullakandi Thekkeparambil Usha. She was the queen of Indian track and field for two decades. P.T. Usha has been associated with Indian athletics since 1979. Usha made her international debut at the Moscow Olympics in 1980 but she shone into the limelight in the 1982 Asian Games in New Delhi, winning the silver in the 100 m and 200 m event. At the Asian Meet in Jakarta in 1985, Usha established herself as the Asian sprint queen with five gold medals (in the 100meters, 200m, 400m, 400m hurdles, and the 4 x 400m relay) besides a bronze in the 100m relay.
This magnificent performance was followed by an equally brilliant spell a year later at the Asian Games at Seoul where Usha notched up four golds and a silver medal.
The finest moment in Usha’s career and also perhaps the saddest however came in a single race at the 1984 Olympics in Los Angeles. In the 400m hurdles, Usha missed winning the bronze by just 1/100th of a second. She recorded her best time of 55.42secs in that race — still an Indian national record — but lost the medal in a photo-finish. Usha said that she cried after the event because “It was difficult to believe that I had missed an Olympic medal by a whisker.”
In 1976 the Kerala State Government started a Sports School for women, and Usha was chosen to represent her district, at a cost of Rs. 250 per month paid by the state. In 1979 she participated in the National School Games, where she was noticed by O. M. Nambiar, who coached her through most of the rest of her career. India Today describes the athletic situation in 1979 as a time when ‘athletics was very much a male sport and track-suited women a rarity’.
P.T Usha started a School of Athletics to impart training to girl children from all over the country. The School, located at Koyilandi near Kozhikode in Kerala, recruits children in the 10-12 age group for its training. She likes reading books and listening to music.
Awards and Medals Received
- Recipient of Arjuna Award, 1984.
- Adjudged as the greatest women athlete, in 1985 Jakarta Asian Athletic Meet Padma Sree in 1984.
- Best Athlete of the year Award from India Government in 1984,/85,/86,/87, and 89.
- In 1986 Seoul Asian Games, won the Adidas Golden Shoe Award for the best athlete by the Asian Amateur Athletics Association, Seoul Asian Games, 1986.
- 33 medals including 13 golds in Asian Games and Asian Championships.
- Won a total of 102 medals at National and International meets during her career.
- Won 1 gold and 2 silver at the 1999 SAF Games held at Kathmandu.
- Thirty International Awards, for her .excellence in Athletics.
- In recognition of her achievements, a road at Payyoli, her home town, is named after her.
- The Kerala Government has also set up a “PT Usha Sports Council” at Central Stadium, Thiruvananthapuram.
- Kerala Sports Journalists Award for the year 1999.
![]()
Profile – 2
| Profile – 2: (Koneru Humpy) | |
| Name | Koneru Humpy |
| Date of Birth | 31 March, 1987 |
| Height | 5.6″ (165 cm) |
| State/Team she represented | National – India |
| Sports/Game she is associated with | Chess |
| Debut (first entry) | At the age of 8, in 1995 in Indian Under 8 Championship |
| Best in the Career | The second woman in the world with 2606 points in FIDE rating in July 2009 |
| Hobbies | Reading books and spending with family |
Awards and Medals Received
- Asia’s youngest International Woman Master, 1999.
- World under-14 championship, 2001, Castellan, Spain.
- India’s youngest Woman Grand Master, 2001.
- World Junior Championship, 2001, Athens.
- World’s youngest Women Grandmaster to achieve full Grand Master status.
- Arjuna Award in the year 2003.
- In 2007, she was awarded with the prestigious Padma Shri award.
- Humpy was also conferred upon the Raja Lakshmi Award in the year 2008 by Raja Lakshmi Foundation of Chennai.
- become the second-highest ranked female player in history with more than 2600 points in FIDE rating in July 2009.
Profile with more details
Koneru Humpy is a popular femaie Indian chess player, and feasibly the best woman at the chess board. She is the world second ranking among the Female Chess PIaryers,’stayed behind only by Judit Polgar, who is world number one Female Chess Player.
She was born on 31st March, 1987 at Gudivada, Andhra Pradesh. Her father is Ashok Koneru worked as a lecturer in Chemistry and he was a quite well chess player. In 1985 he won the South India Open Championship. Humpy fell in love with the game of chess when she was just 5 years of old. In fact, in orderto guide her properly and to make sure she gets the best attention for improving her skills as a chess player her father introduced her to the game at quite an early age. The little Humpy showed her outstanding performance in chess and she won the Under 8 National Chess Championship in 1995.
After proved her brilliant performance at the National level, Humpy entered the international chess circle. She clinched the World Chess titles in the Under 10, Under 12 and Under 14 age groups, later, in 1990 Humpy holds an International Master title when she was 12 years. After, she gained her 3rd Grand Master norm in the Elekes Memorial Grand Master Tournament held at Budapest, Hungary. Koneru has set up a world record by getting the International Grand Master title at the age of 15 years old. She broke Judit Polgar record to achieve the feat, and she became the youngest woman ever to have got the coveted title. Further Hou Yifan broke Humpy’s record by taking the title, when she was 14 years. Humpy has been the First Indian Woman to have achieved an International Grand Master title in the chess game.
She likes reading books and spending with her family
For showing advanced talent as a chess player and making the nation proud at many times at the International level, Humpy has been honoured with a number of awards and recognitions.
![]()
Awards & Honours
- Asia’s youngest International Woman Master, 1999.
- World under-14 championship, 2001, Castellan, Spain.
- India’s youngest Woman Grand Master, 2001.
- World Junior Championship, 2001, Athens.
- World’s youngest Women Grandmaster to achieve full Grand Master status.
- Arjuna Award in the year 2003.
- In 2007, she was awarded with the prestigious Padma Shri award.
- Humpy was also conferred upon the Raja Lakshmi Award in the year 2008 by Raja Lakshmi Foundation of Chennai.
- At Doha Asian Games 2006, Koneru Humpy bagged two Gold Medals in the Individual as well as Team event of Chess.
- In 2007, she won the International Open Chess Tournament 2007 held at Kaupthing, Luxembourg.
- Humpy scored a FIDE Elo rating of 2606 points
- Humpy has broken the world record set by Susan Polgar who had a rating of 2577 points while she was at the World No. 2 spot,
V.V.S. Laxman, Very Very Special Summary in English
Vangipurapu Venkata Sai Laxman recently retired from cricket. Sportstar interviewed this sports star on that occasion. Laxman gives us lots of details. He says his parents Dr. V Shantaram and Dr. V. Satyabhama were his inspiration and influence. He adds that the Hyderabad Cricket Association encouraged him even as a boy. He acknowledges his uncle Baba Mohan’s help and his coaches’ guidance.
He cherishes his 281 against Australia in Kolkata in 2001. He remembers his embarrassment when he collided against Sourav in an Oval ODI. He fondly recollects his association with his captains Sourav, Sachin and Dhoni. He admires John Wright’s role as a coach. He repeatedly appreciates his wonderful wife and lovely kids. He is proud of his role in making India No. 1 in cricket. He is happy to put an end to his 16 year long loving cricket career. His message to the young is to work hard and to treat success and failure with equal ease. He gratefully declares that cricket has taught him character. He plans to start a school and an academy. He is confident of his success in his future ventures too.
V.V.S. Laxman, Very Very Special Glossary
fabulous (adj) : fantastic, excellent
leap (n) (here) : progress
on the verge of : very close to
culminated (v-past tense) : resulted in; ended
integral (adj) : essential, main
crucial (adj) : valuable, important
reckoning (n) : consideration
transformation (n) : change; new form
traits (n) (plural) : qualities
amazingly (adv) : surprisingly impressive
collided (v-past tense) : dashed against
disgusted (v-past tense) : disappointed
cuisine (n) : dish