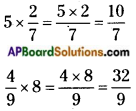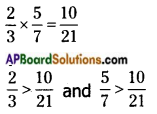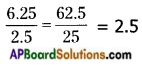Students can go through AP Board 7th Class Maths Notes Chapter 7 Data Handling to understand and remember the concepts easily.
AP State Board Syllabus 7th Class Maths Notes Chapter 7 Data Handling
→ Data: Information which is in the form of numbers or words and helps in taking decisions or drawing conclusions is called data. Tables and graphs are the ways in which data is presented.
The numerical entries in the data are called ‘observations’.
→ The average or Arithmetic Mean or Mean
A.M = \(\frac{\text { Sum of all observations }}{\text { Number of observations }}\)
→ (i.e.,) A.M. is equal to sum of all the observations of a data set divided by the number of observations. It lies between the lowest and highest values of the data.
![]()
→ Mode: An observation of data that occurs most frequently is called the mode of the data. A data may have one or more modes and sometimes none.
→ Median: Median is simply the middle observation, when all observations are arranged in ascending or descending order. In case of even number of observations median is the average of middle observations.
→ Mean, mode, median are representative values for a data set.
→ When all values of data set are increased or decreased by a certain number, the mean also increases or decreases by the same number.
→ Data can be presented in bar graphs / double bar graphs or pie chart.
→ Bar graph: Bar graph are made up of bars of uniform width which can be drawn horizontally or vertically with equal spacing between them. The length of each bar tells us the frequency of the particular item. We take convenient scale for the length of bar graph.
![]()
→ Double bar graph: It presents two observations side by side.
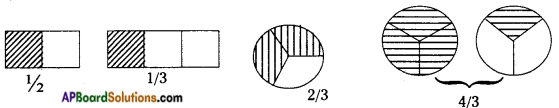
→ Pie chart: A circle is divided into sectors to represent the given data.
Angle subtended by the sector at the centre of the circle is directly proportional to each observation.