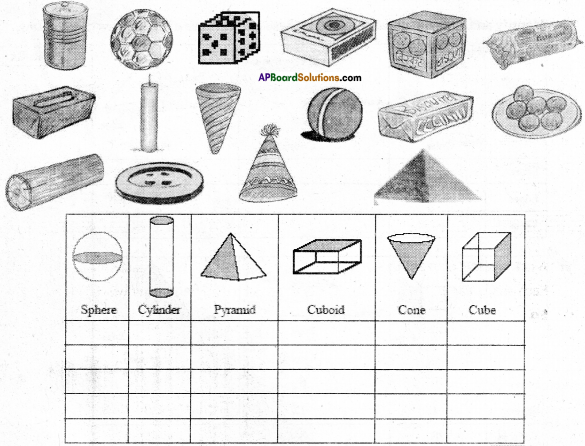
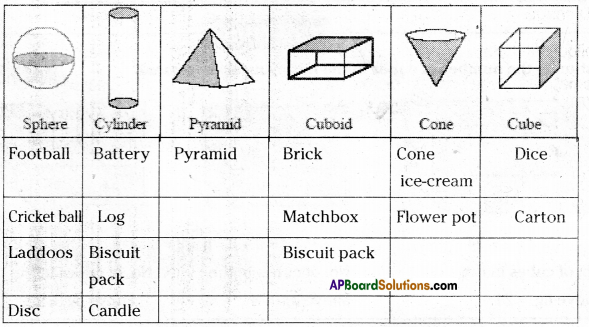
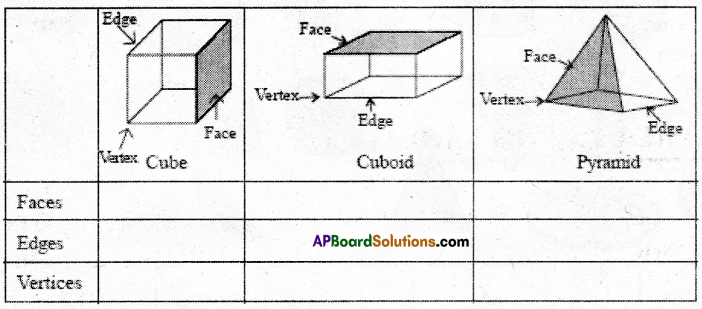
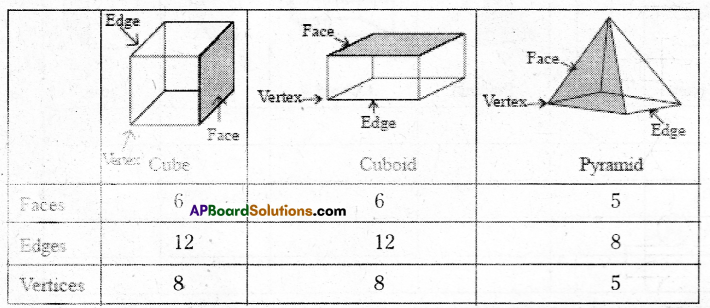
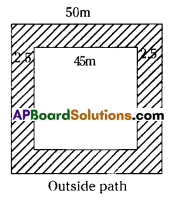
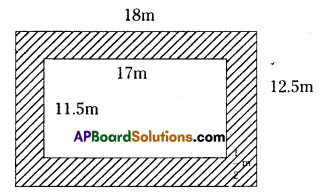
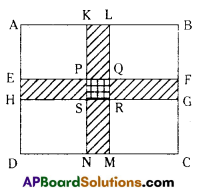
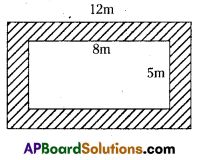
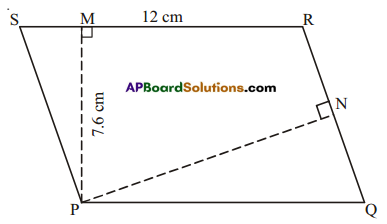
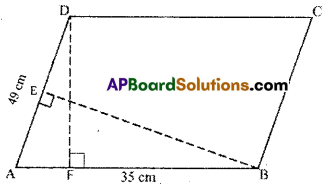
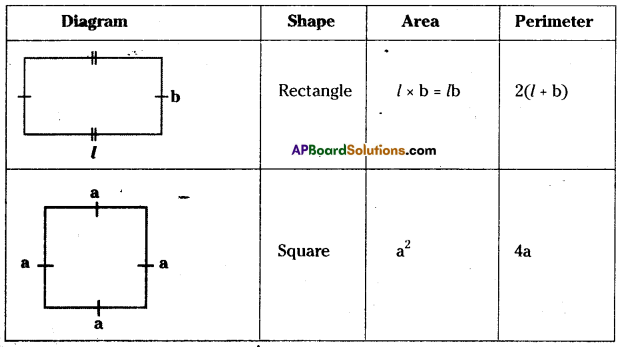
AP State Syllabus AP Board 7th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 15 Symmetry Ex 1 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Maths Solutions 15th Lesson Symmetry Exercise 1
![]()
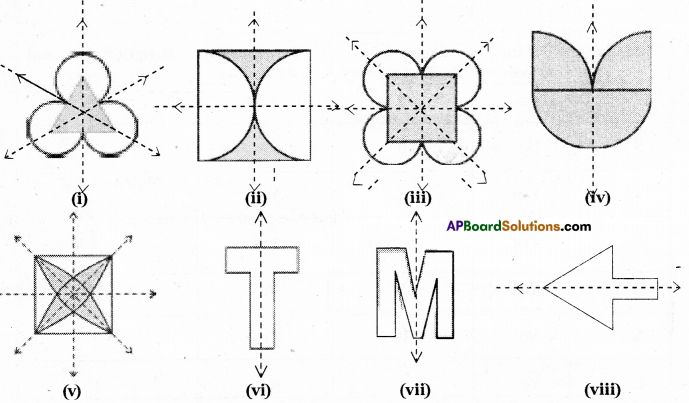
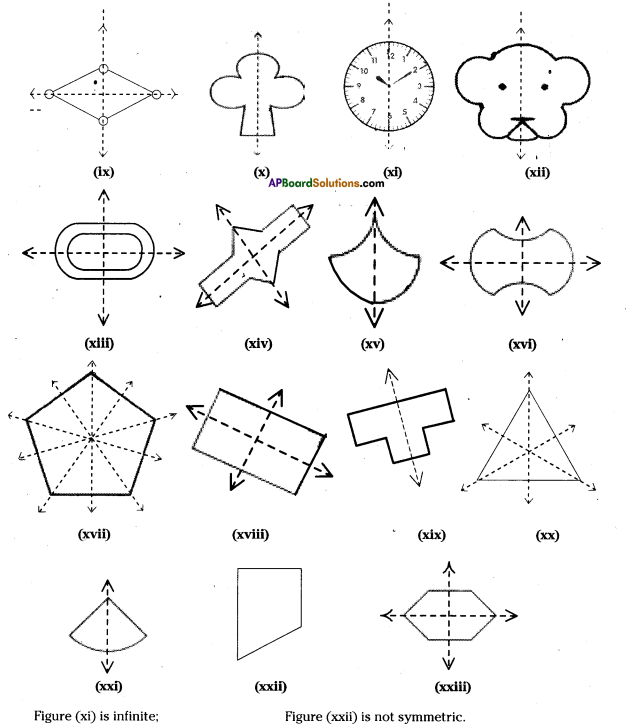
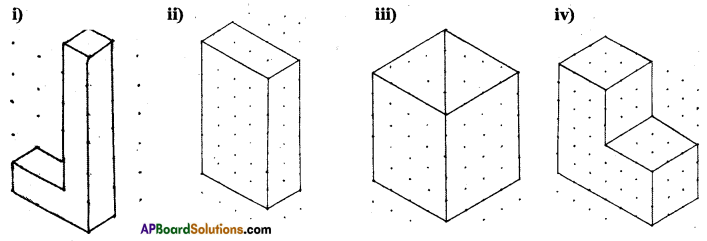
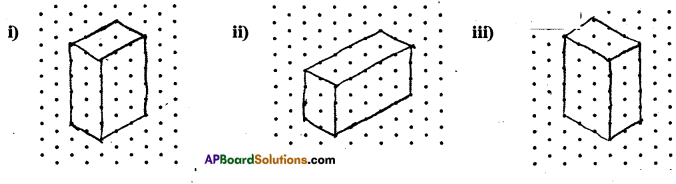
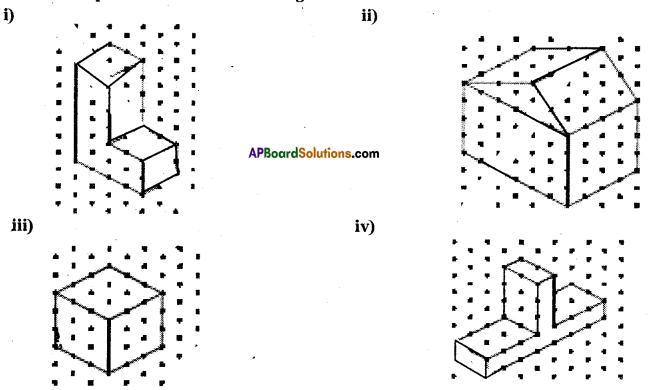
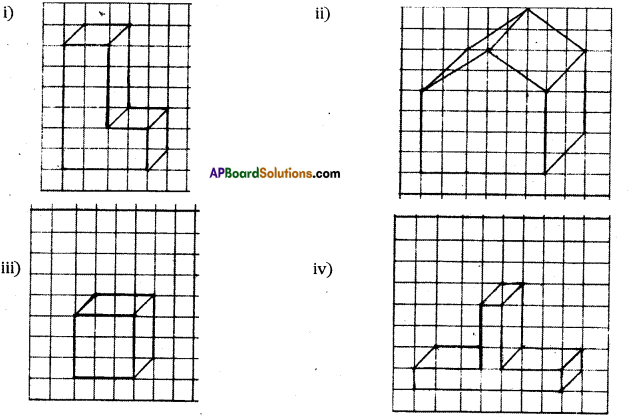
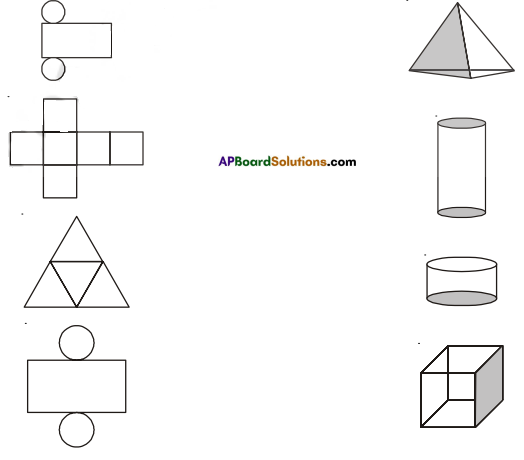
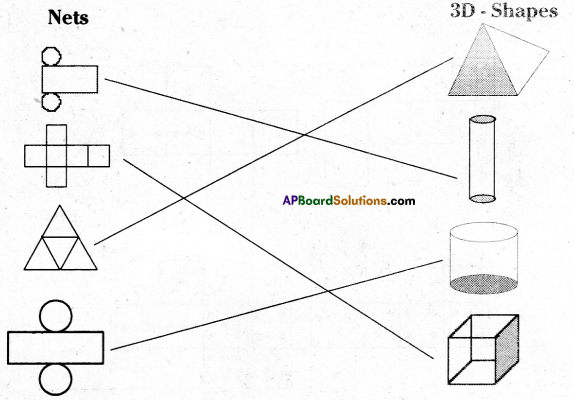
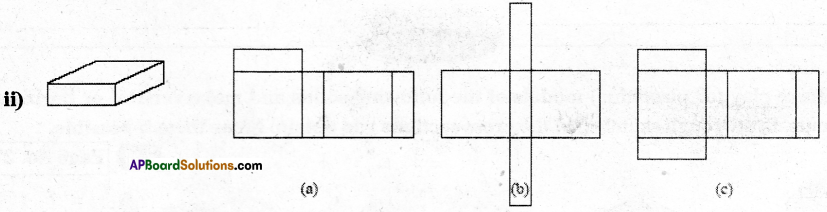
Question 1.
Given below are some fiugres. Which of them are symmetric? Draw the axes of symmetry
for the symmetric figures.
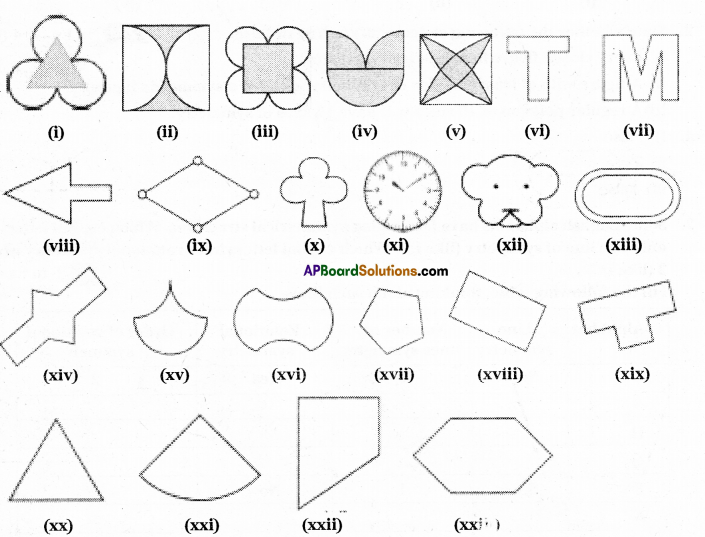
Solution: