AP State Syllabus AP Board 6th Class Science Solutions Chapter 10 Basic Electric Circuits Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 6th Class Science Solutions 10th Lesson Basic Electric Circuits
6th Class Science 10th Lesson Basic Electric Circuits Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Fill in the Blanks.
1. The flow of electricity in a circuit is called ——–.
Answer:
current
2. A ——– helps us to allow or break the flow of electricity in a circuit.
Answer:
switch
3. Substances that allow electricity to pass through them are known as ——–.
Answer:
conductors
4. The electric bulb was invented by ——–.
Answer:
Thomas Alva Edison
![]()
Choose the correct answer.
1. In a bulb the part which gives us light is
A) Metal Base
B) Glass Chamber
C) Filament
D) Terminals
Answer:
C) Filament
2. Which of the following is an insulator?
A) Hairpin
B) Iron Nail
C) Plastic Scale
D) Pencil Lead
Answer:
C) Plastic Scale
3. The metal used in making filaments of present-day bulbs is
A) Iron
B) Copper
C) Tungsten
D) Cotton
Answer:
C) Tungsten
Answer the Following Questions.
Question 1.
What is an electric circuit? Explain with a diagram.
Answer:
- An arrangement in which a cell and a bulb are connected by using wires is called a simple electric circuit.
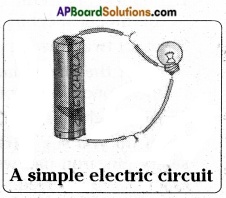
- A simple electric circuit is a path for the flow of electric current between cell and the bulb.
Question 2.
What are the parts of a torchlight?
Answer:
The parts of a torchlight are
- Hollow cylindrical barrel
- Torch cells
- Bulb
- Glass cover
- Reflector
- Switch
- Metal spring
![]()
Question 3.
Classify the following into conductors and insulators:
Water, Plastic pen, Pencil lead, Dry cotton cloth, Wet cotton cloth, Dry wood, Wet wood.
Answer:
| S.No. | Conductors | S.No. | Insulators |
| 1 | Pencil lead | 4 | Water |
| 2 | Wet cotton cloth | 5 | Plastic pen |
| 3 | Wet wood | 6 | Dry cotton cloth |
| 7 – | Dry wood |
Question 4.
What will happen if the cells in a torch are arranged as shown in the following figure? Why?

Answer:
- The bulb does not glow.
- Because two positive terminals of the cells are connected to each other which does not provide a closed path.
Question 5.
Niharika observed an electrician repairing a street light wearing gloves on his hand. She asked him some questions. What would be those questions?
Answer:
- Why do you wear gloves?
- With what the gloves are made up of?
- How do these gloves help in your work?
- What will happen if the glows are made up of cloth instead of rubber?
Question 6.
A circuit is connected with a cell, bulb, and a switch, but the bulb is not glowing. Write all possible reasons for this.
Answer:
- The cell used might have been totally discharged.
- The bulb taken might have been fused.
- The switch arranged may not be in touch with the wires as expected.
- Any breakages in the circuit cause failure.
Question 7.
How do you test the materials given to you, to know whether they are conductors or insulators?
Answer:
Aim: To test the given materials to know whether they are conductors or insulators What you need? (Materials required): a cell (power source), a bulb, connecting wires, wooden plank or thermocol sheet, two drawing pins, and the materials provided to test.
How to do? (Procedure):
- Connect a circuit on a wooden plank or on a thermocol sheet as shown in Fig.
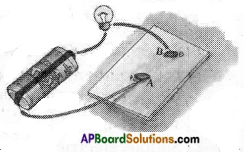
- Insert two drawing pins at A and B.
- insert the given materials in the gap between A and B one after another.
- With each insertion, check whether the bulb glows or not.
What do you see? (Observation): The bulb glows only when some materials like a safety pin, iron nail were inserted. It does not glow when the materials like paper, eraser were inserted.
What do you learn? (Result): Bulb glows only when an electric current passes through the materials. So all the materials which made the bulb glow are conductors and the remaining are insulators.
![]()
Question 8.
Draw a circuit diagram showing a cell, switch, and bulb.
Answer:
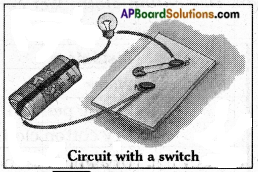
Question 9.
If you put the switch on, a light will glow, a fan will rotate, an iron box heats up etc. All these different functions will be performed by electricity. How do you feel about the comforts given by this great invention to human beings?
Answer:
- Electricity plays a key role in modern technology.
- Without electricity, most of the things could never work. (i.e. TV, Computer, bulb, etc…)
- We can’t imagine our life without electricity.
- Electricity is a gift given by scientists to human beings.
- Electricity is a basis for new inventions.
Question 10.
List the daily activities in which we use electricity.
Answer:
Following are our daily activities in which we use electricity.
- Electric bulb and fluorescent lights etc.
- Washing machine and Grinder
- Electric fan and Electric iron
- Television and Tape recorders
- Computers and Motors to lift water etc.
Activities and Projects
6th Class Science Textbook Page No. 115
Question 1.
In activity 4, we observed some situations where the torch bulb glows. Niharika challenged her friends that she could make the bulb not glow even with the cells kept in the proper position. What would she have done?
Answer:
- Niharika might have put an insulator in between the two cells.
- Or she might have used the powerless batteries.
![]()
Question 2.
Connect a circuit as shown in the given diagram.
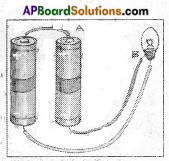
a) Does the bulb glow? Why?
b) Draw the circuit so that the bulb glows.
c) Verify it by connecting cells and bulbs as per the circuit drawn.
Answer:
a) The bulb does not glow. As the positive terminals of the two cells are connected. So current does not flow and bulb does not glow.
b)
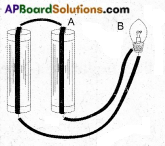
c) I have connected the circuit as shown in (b) and found the bulb glowing.
Question 3.
You have studied the story of Thomas Alva Edison. Write a note appreciating his efforts in inventing the bulb.
Answer:
- Thomas Alva Edison was a famous scientist who invented the bulb.
- He experimented with a number of different filaments.
- His goal was to find materials that would light well and last for a long time.
- Though he failed a number of times he worked hard continuously to get success.
- Without an electric bulb, we can’t imagine our life.
Question 4.
Connect circuits as shown in the following figure. Write your observation in each case.

Answer:
a) The bulb does not glow as the +ve terminals of the two cells are directly connected.
b) The bulb glows as the cells are connected correctly.
c) The bulb glows and gives dim light as only one cell is connected.
d) The bulb glows brilliantly as the three cells are connected in series and more current flows in the bulb.
6th Class Science 10th Lesson Basic Electric Circuits Activities
Activity – 1
1. Let us take a torch cell and observe it. Can you describe it? (Page No. 108)
Answer:
- The cell consists of a cylindrical metal can.
- Its heaviness suggests that it is filled with some chemicals.
- The protrusion on one end is due to a carbon rod in the centre.
- At the top of the cell, a metal cap is fixed.
- This metal cap act as the positive (+) terminal of the cell.
- Opposite to this, the bottom of the cell (metal can) act as a negative (-) terminal of the cell.
- The entire can is sealed.
- Positive and negative terminals of the cell are labelled on it as + and – respectively.
![]()
Activity – 2
Simple electric circuits (Page No. 108)
2. Take four wires of different colours, say blue, green, red and yellow, each about 15 cm long. Electric wires are often covered with plastic. First, remove about two centimetres of the plastic covering, from both ends of each wire. Now attach two wires (Blue and Green) to a bulb and two wires (Red and Yellow) to a cell with a cello-tape or cell-holder as shown in Fig. 4(a). We can use a cell holder to hold the cells and wires together tightly.
Now connect the wires in different forms as shown in Fig. 4(b) to 4(g). In each case, check whether the bulb glows or not. Record your observations in Table 1.
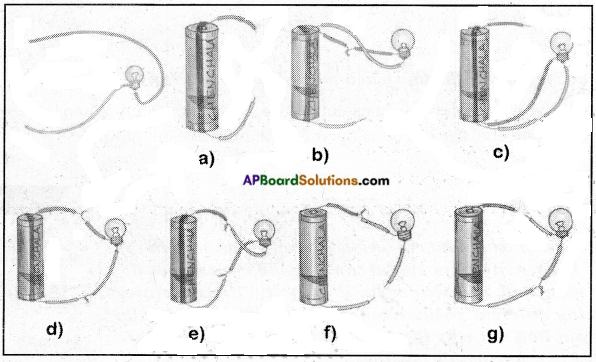
Answer:
| Connection | Does the bulb glow (Yes / No) |
| Fig (b) | No |
| Fig (c) | No |
| Fig (d) | Yes |
| Fig (e) | Yes |
| Fig (f) | No |
| Fig (g) | No |
- In which case does the bulb glow? Why?
Answer:
The bulb glows in connections shown in Fig. 4(d) and Fig. 4(e). This is because in these connections form a closed path. - In which case the bulb does not glow? Why?
Answer:
In the remaining cases means like in Figs. 4(b), 4(C), 4KO, and 4(g), bulb does not glow.
This is because there is some gap in the path. (circuit is open)
Activity – 3
Electric Switch (Page No. 110)
3. Connect a circuit on a wooden plank or on a thermocol sheet as shown in Figure. Insert two drawing pins at A and B. Insert a safety pin in between A and B. such that one end of the pin is completely in contact with B and the other end is left free. Now observe the bulb.
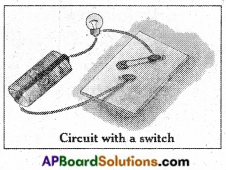
- What do you notice?
Answer:
The bulb does not glow.
Now touch the safety pin to pin A and observe the bulb again. - What happens?
Answer:
The bulb glows. - Why doesn’t the bulb glow when the safety pin is left free at one end?
Answer:
In this activity, the safety pin is used to close /open the circuit. When the safety pin is left free at one end, the circuit is open. So the bulb doesn’t glow.
![]()
Activity – 4
4. Take a torch that has two cells. Arrange the cells in the torch in as many ways as you can. In which cases does the bulb glow and in which cases it doesn’t? Draw pictures showing different positions of cells and glowing of bulb. Can you find out why the bulb glows only when cells are placed in a particular position? (Page No. 111)
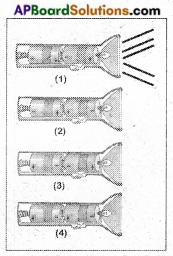
Answer:
The bulb glows only in the first position. This is because in the remaining positions the circuit is being open as the cell’s terminals are not in a proper sequence. In the first position they are in proper sequence, so the circuit is closed. As a result the bulb glows.
Activity – 5
Identifying conductors and insulators (Page No. 111)
5. Take the circuit which we used in activity-3, as shown in Figure. Remove the safety pin from the drawing pins so that you have two open terminals A and B.
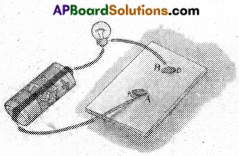
Insert different objects like a hair pin, safety pin, eraser, plastic scale, match stick, piece of a metal bangle, piece of a glass bangle, paper clip etc. in the gap between A and B. With each insertion, check whether the bulb glows or not. Record your observations in table 2 for each case.
Answer:
| S.No. | Object | Name of the Material | Does the bulb glow (Yes/No) | Conductor/Insulator |
| 1. | Hair pin | Metal | Yes | Conductor |
| 2. | Pencil lead | Lead | Yes | Conductor |
| 3. | Eraser | Rubber | No | Insulator |
| 4. | Plastic scale | Plastic | No | Insulator |
| 5. | Match stick | Wood | No | Insulator |
| 6. | Divider from geometry box | Metal | Yes | Conductor |
| 7. | Piece of paper | Paper | No | Insulator |
| 8. | Iron nail | Iron | Yes | Conductor |
| 9. | Piece of Metal bangle | Metal | Yes | Conductor |
| 10. | Piece of Glass bangle | Glass | No | Insulator |
| 11. | Paper clip | Metal | Yes | Conductor |
| 12. | Piece of chalk | Chalk | No | Insulator |
| 13. | Safety pin | Metal | Yes | Conductor |
- If you look at table 2, after recording your observations you will find that the bulb glows in some cases and does not glow in other cases. Can you guess the reason?
Answer:
Bulb glows in some cases as they allow an electric current to pass through them. They are conductors.
Bulb does not glow in other cases as they do not allow the electric current to pass through them. They are insulators. - Can you group the objects you observed in your daily life as conductors and insulators? Make a list of objects and group them as conductors and insulators and write in table-3
Answer:S.No. Conductors Insulators 1 Metals Water 2 Iron Air 3 Silver Plastic 4 Salt water Wood 5 Copper Rubber 6 Aluminium Paper