SCERT AP Board 6th Class Social Solutions 2nd Lesson Globe – Model of the Earth Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 6th Class Social Studies Solutions 2nd Lesson Globe – Model of the Earth
6th Class Social Studies 2nd Lesson Globe – Model of the Earth Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
What is a globe?
Answer:
Globe is a true model of the Earth.
Question 2.
What are the movements of the Earth?
Answer:
Rotation and Revolution are the movements of the Earth.
Question 3.
Which movement of the Earth causes Day and Night?
Answer:
Rotation of the Earth causes Day and Night.
![]()
Question 4.
What happens when the Earth rotates?
Answer:
During rotation, half portion of the Earth receives Sun’s rays and the remaining half portion remains in darkness.
Question 5.
Define the Earth’s Rotation and Revolution.
Answer:
Rotation: Planet Earth rotates around itself on its own axis. This movement is called Rotation.
Revolution: Planet Earth rotates around the Sun. This movement is called Revolution.
Question 6.
What is the true shape of the Earth?
Answer:
The Earth is round in shape. The Earth is slightly flattened at the poles and bulges in the middle or at the equator.
Question 7.
Which Latitude is known as the Tropic of Cancer?
Answer:
The latitude which is located at 23\(\frac{1}{2}\)° north of the equator is known as the Tropic of Cancer.
![]()
Question 8.
Read the Paragraph under the title ‘Equinox’ and comment on it.
On 21st March and September 23rd direct rays of the Sun fall on the equator. At this position, neither of the poles is tilted towards the Sun. So, the whole earth experiences equal days and nights. This is called an equinox.
On 23rd September, it is autumn season in the Northern Hemisphere and spring season in the Southern Hemisphere. The opposite is the case on 21st March when it is spring in the Northern Hemisphere and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere. Thus, you find days and nights and changes in the seasons because of the rotation and revolution of the earth.
Answer:
On 21st March and 23rd, September Sun’s rays fall directly on the Equator. So we experience equal day and night on both these days. This is called equinox. On 21st March it is autumn in the Northern Hemisphere and spring in the Southern Hemisphere. Because of Earth’s rotation, half portion of the Earth receives Sun’s rays and the remaining half remains in darkness. So we find changes on Earth because of Earth’s rotation and revolution.
Question 9.
Create a table and list out the similarities and differences between Latitudes and Longitudes.
Answer:
Similarities between latitudes and longitudes:
- Latitudes and longitudes are both artificial.
- Latitudes and Longitudes are both invisible lines.
- Latitude is based on the 0° latitude while longitude is based on Greenwich.
- They both help us to locate a place on earth
Differences:
| Latitudes | Longitudes |
| 1) Latitudes are the horizontal lines. | 1) Longitudes are vertical lines |
| 2) Lines of latitudes are parallel to the equator. | 2) Lines of longitude are not parallel and come to a singular point. |
| 3) Latitudes lines run in the East and West directions. | 3) Longitude lines run in the North to South direction. |
![]()
Question 10.
If India has day, it is night in America. What is the reason for this difference?
Answer:
The part of the Earth that faces the Sun gets illuminated and experiences the day. The opposite part of the earth that does not face the Sun, experiences night. As India is opposite to America the difference in day and night occurs.
Question 11.
Take a ball and draw the latitudes and longitudes on the surface.
Answer:
Project Work: Student Activity.

Question 12.
Prepare a note on the difference between a globe and an atlas.
Answer:
- A globe is a three-dimensional sphere. An atlas is two-dimensional.
- A globe represents the whole earth. An atlas represents the whole earth or a part of it.
- A globe can be used to get a broad-level picture of the world. An atlas provides more specific information about different places.
Question 13.
Find out the latest leap year and the coming leap year.
Answer:
The present year 2020 is a leap year. 2024 is the coming leap year.
Question 14.
What preparations should be taken to watch a solar eclipse safely?
Answer:
The Sun outputs more power than our eye is designed and so it damages the retina. So we should not watch the Sun or the solar eclipse directly. We should use special-purpose solar filters, such as eclipse glasses to watch Solar eclipses safely. Projecting the Sun through a box projector is another safe way to watch the solar eclipse.
![]()
Question 15.
It is difficult to understand the geographical location, time, and distance in the absence of the imaginary lines – latitudes and longitudes. Appreciate the design of the imaginary lines of latitudes and longitudes.
Answer:
- Latitudes are used to define the North-South position of a location on the planet.
The general climatic division of a place can be studied with the help of latitudes. - Longitudes are used to define the East-West position of a location on the planet. Longitudes also help us to calculate the time of a particular place.
- If the latitude and longitude are known any position on earth can be located. Even- though, longitudes and latitudes are imaginary lines they play an important role.
So we should appreciate the design of the imaginary lines of the latitudes and longitudes.
Question 16.
Venu met some children from different cities at a youth festival. They were: Geethika, John, Nihal, and Uma. Venu collected some information about their cities.
Venu has given us certain clues. Can you find out the cities with the help of an Atlas?
- Geethika – A girl from a city where 19° Northern Latitude and 72° Eastern Longitude nearly coordinates.
Find and write the city name: ……………………………………………………… - John – A boy from a city where 12° Northern Latitude and 77° Eastern Longitude nearly coordinates.
Find and write the city name: ……………………………………………………… - Nihal – A boy from a city where 28° Northern Latitude and 77° Eastern Longitude nearly coordinates.
Find and write the city name: ……………………………………………………… - Uma – A girl from a city where 22° Northern Latitude and 88° Eastern Longitude nearly coordinates.
Find and write the city name: ………………………………………………………
Answer:
- Geethika – A girl from a city where 19° Northern Latitude and 72° Eastern Longitude nearly coordinates.
Find and write the city name: ( Bombay) - John – A boy from a city where 12° Northern Latitude and 77° Eastern Longitude nearly coordinates.
Find and write the city name: (Bangalore) - Nihal – A boy from a city where 28° Northern Latitude and 77° Eastern Longitude nearly coordinates.
Find and write the city name: (Delhi) - Uma – A girl from a city where 22° Northern Latitude and 88° Eastern Longitude nearly coordinates.
Find and write the city name: (Kolkata)
![]()
Question 17.
If an astronaut from a spaceship looks down at the Earth, can he/she see the rotation of the earth?
Answer:
Yes. From a spaceship, an astronaut can see the rotation of the earth. Spaceships move around the Earth at a different speed. So the astronaut can see the Earth’s rotation.
Question 18.
Why can’t we sense the rotation and revolution of the Earth?
Answer:
The Earth is moving at a fixed speed and we are also moving along with it at the same speed. That is why we can’t sense the Earth’s spin. If Earth’s spin changes we would definitely sense it. If we are in a car that is moving at a constant speed on a smooth surface, we will not know that we are moving. However, when the car accelerates or when the brakes are applied, we will feel the motion. Another example is, we can drink coffee or tea on a moving train which is moving at a constant speed* because we are traveling by the train at the same speed. If the speed of the train changes we can’t drink. The spin of Earth doesn’t make those kinds of changes. So we can’t sense the rotation and revolution of the Earth.
Question 19.
Choose the correct answer.
i) The movement of the Earth around the Sun is known as
A) Rotation
B) Revolution
C) Inclination
D) Meridian
Answer:
B) Revolution
![]()
ii) Sun rays fall directly on the Equator on:
A) 21 March
B) 21 June
C) 22 December
D) 22 October
Answer:
A) 21 March
iii) Christmas is celebrated in summer in:
A) Japan
B) Australia
C) India
D) The USA
Answer:
B) Australia
iv) The cycle of the seasons is caused due to:
A) Rotation
B) Revolution
C) Gravitation
D) Inclination
Answer:
B) Revolution
Question 20.
Find and fill the latitudes and longitudes in the given table with the help of Atlas and Globe.
| S.No. | PLACE | LATITUDES | LONGITUDES |
| 1. | Vijayawada | ||
| 2. | Kadapa | ||
| 3. | Tirupati | ||
| 4. | Visakhapatnam | ||
| 5. | Your Village (Chittor) |
Answer:
| S.No. | PLACE | LATITUDES | LONGITUDES |
| 1. | Vijayawada | 16°50′ N | 80°64′ E |
| 2. | Kadapa | 14°46’ N | 78°82′ E |
| 3. | Tirupati | 13°62’ N | 79°41′ E |
| 4. | Visakhapatnam | 17°68′ N | 83°21′ E |
| 5. | Your Village (Ex: Chittoor) | 13°21′ N | 79°10’ E |
![]()
Question 21.
Find and fill the latitudes and longitudes extent of India and Andhra Pradesh in the given table with the help of Google Maps or Atlas.
| PLACE | LATITUDES | LONGITUDES | ||
| From | To | From | To | |
| India | ||||
| Andhra Pradesh | ||||
| Your district (Kurnool) | ||||
| Your Mandal (Nandyal) | ||||
Answer:
| PLACE | LATITUDES | LONGITUDES | ||
| From | To | From | To | |
| India | 8°4′ N | 37°6′ N | 68°7′ E | 97°25′ E |
| Andhra Pradesh | 12°41′ N | 19°07’ N | 77° E | 84°40′ E |
| Your district (Ex: Kurnool) | 15°50′ N | 4°32′ N | 78° 1′ E | 45° 71′ E |
| Your Mandal (Ex: Nandyal) | 15°28′ N | 42°84′ N | 78°28′ E | 59°13′ E |
Question 22.
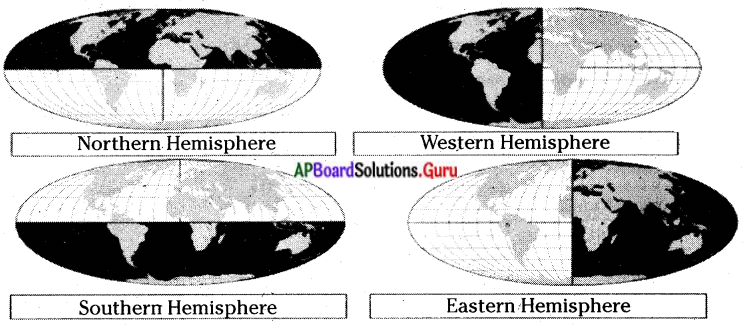
Observe the following pictures and fill the boxes with the name of the shaded hemispheres.
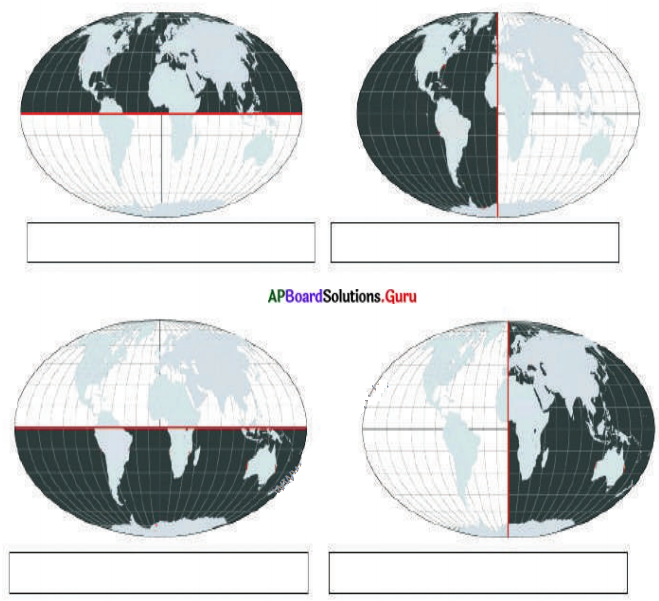
Answer:
Project Work
Draw a diagram of the globe showing the earth’s axis, the Equator, Tropic of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic Circle, and Antarctic Circle.
Answer:
Student Activity.
![]()
6th Class Social Studies 2nd Lesson Globe – Model of the Earth InText Questions and Answers
Let’s Do
(Textbook Page No. 17)
Question 1.
Take a big round apple. Pierce a cycle spoke through it. The spoke resembles the axis shown in a globe. You can now move the apple around this axis from left to right.
Answer:
Student Activity.

Think and Respond
(Textbook Page No. 16)
Question 1.
How does the earth rotate and revolve without any needle, unlike the Globe? Discuss with the teacher.
Answer:
Our Solar System formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a huge cloud of gas and dust started to collapse under its own gravity. As the cloud collapsed, it started to spin. The Solar system is made up of the Sun and everything that orbits around it includes the planets and their moons as well as numerous asteroids, meteoroids, and comets. Without any unbalanced forces acting on them, the tremendous gravity of the Sun and the planets have kept them rotating for billions of years. Either the Earth or any other planet does not have any needle to rotate or to revolve.
![]()
Question 2.
All the celestial bodies are round in shape. Why?
Answer:
A planet is round because of its gravity. Gravity pulls from the center to the edges like the spokes of a bicycle wheel. This makes the overall shape of a planet a sphere, which is a three-dimensional circle.
(Textbook Page No. 17)
Question 3.
In which hemisphere is India located?
Answer:
India is located within both the Northern and Eastern hemispheres.
Question 4.
Which hemisphere has the maximum number of continents?
Answer:
Northern Hemisphere has the maximum number of continents.
Question 5.
In which hemisphere is the continent Antarctica located?
Answer:
Antarctica is located in the Southern hemisphere.
![]()
(Textbook Page No. 17)
Question 6.
Complete the table with the help of a world map, globe, or internet.
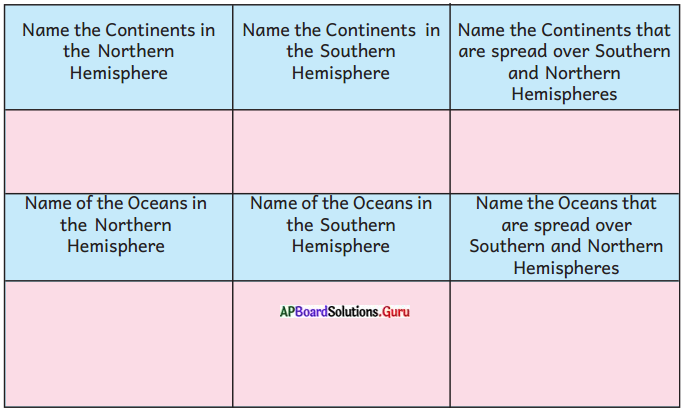
Answer:
| Name the Continents in the Northern Hemisphere | Name the Continents in the Southern Hemisphere | Name the Continents that are spread over Southern and Northern Hemispheres |
| Europe North America |
Australia Antarctica |
Africa Asia South America |
| Name the Continents in the Northern Hemisphere | Name the Continents in the Southern Hemisphere | Name the Continents that are spread over Southern and Northern Hemispheres |
| Arctic Ocean | Southern Ocean | Pacific Ocean Atlantic Ocean Indian Ocean |
Question 7.
Why do latitudes get smaller towards the pole? Which latitude is the biggest circle?
Answer:
The equator is the largest circle and divides the globe into two equal halves. So it is at the center of the Earth. Circles of latitude are all great circles with the center of Earth in the middle. The circles of latitude get smaller as the distance from the Equator increases. So the latitudes get smaller towards the poles. The Equator is the biggest latitude.
![]()
(Textbook Page No. 18)
Question 8.
Fill in the table with the help of a globe/map.
| Latitude | Value in degrees |
| North Pole | |
| Arctic Circle | |
| Tropic of Cancer | |
| Equator | 0° |
| Tropic of Capricorn | |
| Antarctic Circle | |
| South Pole |
Answer:
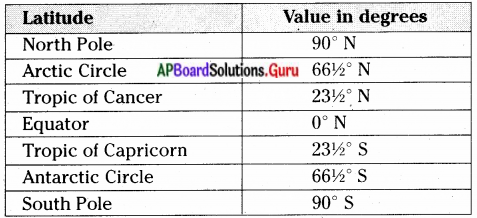
(Textbook Page No. 20)
Question 9.
Identify and write down the Latitude and Longitude between the extents of the given Andhra Pradesh map. You can take the help of Atlas.
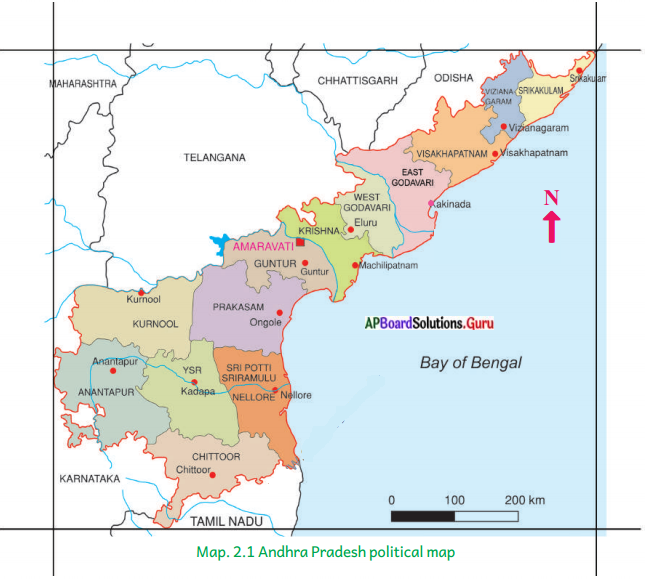
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh Latitude: 12°41’ N to – 19°07′ N
Longitude : 77° – 84°40′ E.