AP State Syllabus AP Board 6th Class Science Solutions Chapter 8 How Fabrics are Made Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 6th Class Science Solutions 8th Lesson How Fabrics are Made
6th Class Science 8th Lesson How Fabrics are Made Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Fill in the Blanks.
1. When we burn artificial fibres it gives a ——– smell.
Answer:
Pungent
2. Fibre → ——– → Fabric.
Answer:
Yarn
3. The process of removing seeds from cotton wool is called ——–.
Answer:
ginning
4. ——– fibre is called golden fibre.
Answer:
Jute
5. An example of a natural fibre ——–.
Answer:
cotton, wool, silk
![]()
Choose the correct answer.
1. Artificial fibre is
A) Cotton
B) Wool
C) Acrylic
D) Jute
Answer:
C) Acrylic
2. An instrument for spinning
A) Needle
B) Knife
C) Spindle
D) Scissor
Answer:
C) Spindle
3. Making fabric from cotton yarn is called
A) Spinning
B) Ginning
C) Weaving
D) Cutting
Answer:
C) Weaving
4. Jute fibre is obtained from this part of a jute plant
A) Root
B) Leaves
C) Flowers
D) Stem
Answer:
D) Stem
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Name the things you find in your home that are made of different fibres.
Answer:
Shirt – Cotton
Swetter – Wool
Carry bag – Polythene
Raincoat – Pvc
Saree – Silk
Doormat – Coir
Umbrella – Pvc
Gunny bag – Jute
Question 2.
Yarn is stronger than fibre. Why?
Answer:
- The tiny strands like structures are called fibres.
- A single fibre can easily break up.
- But the yarn is a strand made up of multiple fibres.
- The number of fibres increases the thickness or fitness of yarn will increases.
- So the yarn is stronger than fibre.
![]()
Question 3.
Write differences between natural fabrics and artificial fabrics.
Answer:
| Natural fibres | Artificial fibres |
| 1) Those are deriving from plants and animals. | 1) These are deriving from chemicals. |
| 2) Water absorbing capacity is good. | 2) Poor in water absorption. |
| 3) Produce ash when burn. | 3) Produces pungent smell. |
| 4) Takes much time to dry. | 4) Takes less time to dry. |
| 5) These fibres are coarse and rough in nature. | 5) These fibres are smooth in nature. |
Question 4.
How do you get jute yarn? Write the process.
Answer:
- Jute fibre is obtained from stem of jute plant.
- The stem of the harvested plant is cut and immersed in water for some days.
- When the stem is soaked in water it becomes rotten and easy to peel.
- Then the fibres are separated from the stem and twisted in to yarn.
- By weaving of these yarn, we can make gunny bags.
Question 5.
What will happen if a raincoat is made from cotton fabric?
Answer:
- The raincoat is fully waterproof.
(The raincoat should allow the flow of water on it without absorbing any drop of water. - But if the raincoat is made from cotton fabric it absorbs rainwater falling on it.
Question 6.
Make a flowchart showing the process of getting fabric from the cotton plant?
Answer:
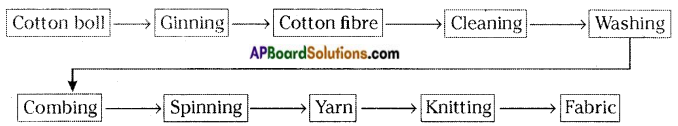
Question 7.
Siri donated cloth bags to her schoolmates on her birthday. Why should we appreciate her?
Answer:
- Siri donated cloth bags on her birthday. This can be practised by all in the world.
- Because the polythene covers take much time to decompose and pollute the soil.
- They also (polythene covers) prevent the percolation of rainwater into the ground.
- But the cloth bags decompose easily and mixes in the soil and do not cause any harm to the environment.
- So this is a good step to protect the environment.
Question 8.
Prepare some slogans to promote using natural fibre bags instead of polythene bags.
Answer:
- Stop using plastic bags
- No Plastic – Yes Fabric
- Say no to plastic bags
- Long live earth – Not Plastic
- Be a part of the solution – Not a part of pollution
- Save our planet – use reusable bags
![]()
Activities and Projects
6th Class Science Textbook Page No. 92
Question 1.
Prepare a bag using cloth. Collect pieces of fabric and make designs on your bag by using them. Display it in your school.
Answer:
The students can do this activity depending upon their skill. (Student Activity)
Question 2.
Make a scrapbook containing pictures of different types of fabric and name them.
Answer:
(Student Activity)
They can take the help of cloth shop people to identify the different fabric in naming them.
Question 3.
Discuss with your teacher or your parents and prepare a chart showing spinning mills in our state.
Answer:
The student has to collect information from internet. (Student Activity)
Question 4.
Collect news items about handloom workers and cotton growers. Analyze one news item in your own way.
Answer:
Student can do this activity depending on their skill. (Student Activity)
Question 5.
What did you do to know whether artificial fibres give a pungent smell while burning? Write the steps of your experiment.
Answer:
- Cloth pieces of different artificial fibres are taken and they are burnt one after another.
- Wool does not burn quickly.
- Fibres like Nylon. Polyester, Terylene, Rayon, when they are burnt they give out the pungent smell.
- These materials shrink while burning.
![]()
Question 6.
Observe these logos. What do they mean? Collect information about this from your school library.
Answer:
- ‘apco’ is the abbreviation of Andhra Pradesh State Handlooms Weavers Co-operative Society Limited.

- apco was registered in 1976.
- Co-optex is the abbreviation of the Tamilnadu Handloom Weavers Cooperative Society Limited.
- Co-optex is a pioneer marketing organization of handloom fabrics, through its network of 203 showrooms spread all over India with an annual turnover of around Rs.1000 crores established in 1935.
- The multi-hued butterfly logo is today synonymous with the quality, durability and fair trade practice of Co-Optex.
6th Class Science 8th Lesson How Fabrics are Made Activities
Activity – 1
I. List the fabric items in your house and state what type of fabric they are made of. Classify them into cotton, silk, wool, polyester, terylene, etc. (Page No. 85)
Try to enrich the list as much as you can. For identifying the fabrics, you can take the help of your elders and teachers.
| S.No. | Type of Fabric | Fabric Items |
| 1. | Cotton | |
| 2. | Silk | Kurta, Saree, … |
| 3. | Wool | |
| 4. | Polyester | |
| 5. | Linen | Trousers,… |
Answer:
| S.No. | Type of Fabric | Fabric Items |
| 1. | Cotton | Shirts, Sarees, Dresses, Dhotis, Doors curtains etc |
| 2. | Silk | Kurtha, Sari, Ropes |
| 3. | Wool | Sweaters, Socks |
| 4. | Polyester | Shirts, Sarees, Dhotis, Trousers |
| 5. | Linen | Trousers, Sarees |
i) Which kind of fabric is mostly used in your house?
Answer:
Cotton and silk fabrics used mostly in my house.
ii) How can you identify the type of fabric?
Answer:
By touch and look, generally, we identify the type of fabric.
![]()
Activity – 2
Fibre. (Page No. 85)
2. Take a piece of fabric. With the help of a magnifying lens, observe how the fabric is. Pull out threads one by one from the fabric. Observe these threads.

i) What did you observe?
Answer:
The thread has small fine like structures.
Take one thread. Scratch its end. Observe it through a magnifying lens.
ii) Are you able to see the fine structure of the thread?
Answer:
Yes, it has fine structures.
Take a needle and try to insert this thread into the eye of the needle. Can you? Isn’t it difficult?
iii) Have you ever seen what people do to overcome this problem?
Answer:
Generally when we are not able to put a thread into the eye of the needle, either we twist the end of the thread or we wet the end using saliva.
Activity – 3
Characteristics of Fabrics. (Page No. 86)
3. Collect some natural and artificial fabrics and observe the following chara- cterstics. Record your observations in table.
| S. No. | Character | Natural fabric | Artificial fabric |
| 1. | Water absorbing nature | ||
| 2. | Time taken to dry | ||
| 3. | Smell while burning | ||
| 4. ‘ | Result after burning | ||
| 5. | Stretching capacity of yarn | ||
| 6. | Smoothness |
Answer:
| S. No. | Character | Natural fabric | Artificial fabric |
| 1. | Water absorbing nature | good | poor |
| 2. | Time taken to dry | more time | Less time |
| 3. | Smell while burning | normal | pungent smell |
| 4. | Result after burning | turn into ash | shrink during burning |
| 5. | Stretching capacity of yarn | less | more |
| 6. | Smoothness | coarse | smooth |
i) Which type of fabrics are smooth in nature?
Answer:
Natural fabrics are smooth in nature.
ii) Which type of fabrics dry in a short time?
Answer:
Artificial fabrics dry in a short time.
iii) Do you find any relation between smoothness and time to dry?
Answer:
Yes, the smooth clothes take less time to dry.
iv) Which fabrics give ash when they are burnt?
Answer:
Natural fabrics give ash when they are burnt.
![]()
Activity – 4
Making Cotton Yarn. (Page No. 87)
4. Collect cotton bolls from nearby houses or cotton-growing fields.

Remove seeds from the cotton bolls and separate cotton. Take a small piece of cotton; observe it using a magnifying lens or under a microscope.
Answer:
i) What do you observe?
Answer:
I observe small hairy structures. These are the fibres of cotton.
Activity – 5
Spinning Yarn. (Page No. 87)
5. Take a cotton boll and remove the seeds from it. Take some cotton in one hand and gently start pulling out cotton by using the thumb and forefinger figure.

Continuous twisting of the fiber will make yarn. Is it strong or not?
Answer:
The yarn that we make from cotton wool is not strong enough to be used for weaving. To get strong yarn from fibre an instrument is used as wheel and spindle.
Activity – 6
How is jute yarn? (Page No. 89)
6. Collect gunny bags. Pull out the threads from the bag and observe under a magnifying lens. You will see strands of yarn. Observe how the fibre looks like? Compare these fibres with cotton fibres.
Answer:
Like cotton, jute yarn is also useful in making fabric. It is also called golden fibre. Jute fabric is not the same as cotton fabric. It is harder, stronger and rougher.
![]()
Activity – 7
Mat Making. (Page No. 90)
7. Write the produce of mat making.
Answer:
Take coconut leaves or two different colour paper strips. Cut and remove the middle vein of the leaf to get two halves. Now put these strips parallel to each other. Take one more strip and insert horizontally and alternately between the vertical strips. Finally, you will get a sheet-like structure. This is the way a mat is made. In the same manner, weave a paper sheet by using paper strips.