Practice the AP 6th Class Science Bits with Answers Chapter 7 కొలుద్దాం on a regular basis so that you can attempt exams with utmost confidence.
AP 6th Class Science Bits Chapter 7 కొలుద్దాం with Answers
I. బహుళైచ్ఛిక ప్రశ్నలు
కింది వాటికి సరియైన జవాబులు గుర్తించుము.
1. పొడవు యొక్క ప్రమాణం
A) సెంటీ మీటర్
B) మిల్లీ. మీటర్
C) కిలో మీటర్
D) ఒక మీటర్
జవాబు:
D) ఒక మీటర్
2. తూకములు మరియు కొలతల వైవిధ్యం గురించి తెలుపు శాస్త్రం
A) చరక సంహిత
B) రాజ తరంగిణి
C) అర్థశాస్త్రం
D) కాదంబరి
జవాబు:
C) అర్థశాస్త్రం
![]()
3. విమానం లేదా ఓడలు ప్రయాణించే దూరాన్ని దేనితో కొలుస్తారు?
A) నాటికల్ మైల్స్
B) కిలోమీటర్లు
C) అడుగులు
D) మైల్స్
జవాబు:
A) నాటికల్ మైల్స్
4. ద్రవాల ఘనపరిమాణంనకు ప్రమాణం
A) మి.లీ.
B) సెం.మీ.
C) మి.మీ.
D) కి.మీ.
జవాబు:
A) మి.లీ.
5. క్రింది వానిలో సరైనది
A) 1 సెం.మీ – 100 మిమీ
B) 1 మీ = 100 సెం.మీ
C) 1 కి.మీ = 100 మీ.
D) అన్నీ
జవాబు:
B) 1 మీ = 100 సెం.మీ
6. కోణమానిని (ప్రొట్రాక్టర్)లో కోణాలు
A) 90 – 180
B) 0 – 90
C) 0 – 180
D) 0 – 360
జవాబు:
C) 0 – 180
7. వక్ర మార్గం పొడవును దేనితో కొలుస్తారు?
A) టేప్
B) గ్రాఫ్ పేపర్
C) దారము
D) కొలపాత్ర
జవాబు:
C) దారము
8. ప్రమాణ స్కేల్ ఎక్కడ భద్రపరచబడింది?
A) యు.ఎస్.ఎ
B) రష్యా
C) యు.కె
D) ఫ్రాన్స్
జవాబు:
D) ఫ్రాన్స్
9. చదరపు మిల్లీమీటరు …. గా సూచిస్తాము.
A) మీ.
B) మి.మీ.
C) సెం. మీ
D) కి.మీ. 7
జవాబు:
B) మి.మీ.
![]()
10. పెద్ద దూరాలను దేనితో కొలవవచ్చు?
A) మి.మీ
B) కి.మీ.
C) సెం.మీ.
D) పైవన్నీ
జవాబు:
B) కి.మీ.
II. ఖాళీలను పూరించుట కింది ఖాళీలను పూరింపుము.
1. 1 సెం.మీ = ………….. మి.మీ.
2. నాణేల మందం …………. తో కొలుస్తారు.
3. చదరపు మిల్లీమీటర్ యొక్క సంకేతం …………
4. 1 కిమీ = ………….. మీటర్లు.
5. క్రమరహిత ఆకారపు వస్తువు ఘనపరిమాణాన్ని కొలవడానికి ………….. ఉపయోగించబడుతుంది.
6. అడుగు, జాన మరియు మూర వస్తువుల పొడవును కొలవడానికి ………….. పద్ధతులు.
7. …………… అనేది స్కేల్ లో అతి చిన్న ప్రమాణం .
8. …………. చదరపు మీటర్ యొక్క సంకేతం.
9. ………….. వస్తువు ఆక్రమించిన ఉపరితలం.
10. ద్రవాల ఘనపరిమాణాన్ని ………. లో కొలుస్తారు.
జవాబు:
- 10 మిమీ.
- స్కేల్
- చ.మి.మీ.
- 1000 మీ.
- కొలపాత్ర
- సాంప్రదాయక
- మిల్లీమీటర్/మి.మీ.
- మీ²
- ఘనపరిమాణం
- మిల్లీ లీటర్లు/మి. లీ.
III. జతపరుచుట
కింది వానిని జతపరుచుము.
1.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| ఎ) కొలపాత్ర | 1) ఓడ ప్రయాణించే దూరం |
| బి) మీటర్ టేప్ | 2) ద్రవాల ఘనపరిమాణం |
| సి) నాటికల్ మైళ్ళు | 3) టైలర్ |
| డి) బిఘా | 4) గ్రామ్ |
| ఇ) ద్రవ్యరాశి | 5) మొఘల్ కొలత పద్దతి |
జవాబు:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| ఎ) కొలపాత్ర | 2) ద్రవాల ఘనపరిమాణం |
| బి) మీటర్ టేప్ | 3) టైలర్ |
| సి) నాటికల్ మైళ్ళు | 1) ఓడ ప్రయాణించే దూరం |
| డి) బిఘా | 5) మొఘల్ కొలత పద్దతి |
| ఇ) ద్రవ్యరాశి | 4) గ్రామ్ |
2.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| ఎ) సెంటీమీటర్ | 1) వెడల్పు |
| బి) చదరపు మిల్లీమీటర్ | 2) 3 అడుగులు |
| సి) గజం | 3) సెం.మీ. |
| డి) మిల్లీమీటర్ | 4) మి.మీ² |
| ఇ) వైశాల్యం | 5) మి.లీ. |
జవాబు:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| ఎ) సెంటీమీటర్ | 3) సెం.మీ. |
| బి) చదరపు మిల్లీమీటర్ | 4) మి.మీ² |
| సి) గజం | 2) 3 అడుగులు |
| డి) మిల్లీమీటర్ | 5) మి.లీ. |
| ఇ) వైశాల్యం | 1) వెడల్పు |

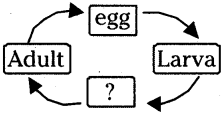
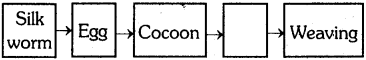
 The process in the picture is
The process in the picture is The equipment show in the figure is
The equipment show in the figure is