These AP 7th Class Science Important Questions 9th Lesson Heat, Temperature and Climate will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP Board 7th Class Science 9th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Heat, Temperature and Climate
Question 1.
What is heat?
Answer:
Heat is a form of energy which flows from hotter body (higher energy) to cooler body (lower energy).
Question 2.
How is heat measured?
Answer:
Heat is measured in Joules or calories with calorimeter.
Question 3.
What is temperature?
Answer:
The degree of hotness or coldness is called temperature.
Question 4.
How do we call the variations of hotness, coldness?
Answer:
The variations of hotness, coldness can be termed as degree of hotness and coldness.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the units of temperature?
Answer:
Temperature is measured in degrees of Celsius, degrees of Fahrenheit or Kelvin using a thermometer.
Question 6.
What is the SI unit of temperature?
Answer:
The SI unit of temperature is kelvin (K).
Question 7.
Write the different modes of transfer of heat?
Answer:
- Conduction of heat
- Convection of heat
- Radiation of heat.
Question 8.
What is conduction?
Answer:
The process of transfer of heat from hotter to colder end through the conductor is called conduction.
Question 9.
What is convection of heat?
Answer:
The process of transfer of heat from source of heat to surface by the motion of par¬ticles is called “convection of heat”.
Question 10.
What is radiation of heat?
Answer:
The process of transfer of heat in the form of waves is called radiation.
Question 11.
What is thermal contact?
Answer:
The contact which transfers heat by any mode is called Thermal contact.
![]()
Question 12.
What is the condition for conduction of heat?
(OR)
When does conduction take place?
Answer:
Conduction takes place, only when the conductor is in touch (contact) with the source of heat. The contact which transfers heat by any mode is called Thermal contact. Conduction doesn’t take place without thermal contact.
Question 13.
What are called convectional currents?
Answer:
Heat is transferred by means of currents called convectional currents.
Question 14.
How does heat transfer in liquids and gases?
Answer:
In liquids and gases heat is transmitted by mode of convection of heat.
Question 15.
What is a medium?
Answer:
The material which helps in transfer of heat from one place to another is called a medium. Solid, liquid and gaseous substances act as medium for transfer of heat.
Question 16.
How does heat transfer if there is no medium?
Answer:
Heat transfer, in the form of waves from one place to another. It does not require any medium.
Question 17.
Write one application of radiation of heat.
(OR)
How does a thermal scanner work?
Answer:
The thermal scanner receives the heat in the form of radiation to measure our body temperature.
Question 18.
What happens if we heat and cool a metal?
Answer:
The metal expands on heating and contracts on cooling.
![]()
Question 19.
Which device is used to measure the temperature?
Answer:
Thermometers are used to measure temperature. .
Question 20.
Based on which principle a Thermometer does work?
Answer:
Thermometer works on the expansion of liquids (mercury).
Question 21.
Where the thermometers are used?
Answer:
People use thermometers in homes, hospitals, automobiles, industries and restaurants etc., to measure temperatures of different objects and substances.
Question 22.
Which is essential for our healthy living? (OR) Why should we protect environment?
Answer:
A clean environment is essential for heaithy living. So, we want a concrete plan to protect environment.
Question 23.
Why does alcohol use in thermometer? (OR)How can a alcohol thermometer mea-sures very low temperatures?
Answer:
The freezing point of alcohol is less than -100°C. So, it can be used to measure very low temperatures.
Question 24.
Write the different types of thermometers?
Answer:
The different types of thermometers are Clinical Thermometer, Laboratory Thermometer, Digital Thermometer and Six’s makimum and minimum thermometer.
Question 25.
Which instrument is used to measure the maximum (highest) and minimum (lowest) temperatures of a place in a day?
Answer:
Six’s maximum and minimum thermometer is one of the Meteorological Instruments used to measure maximum (highest) and minimum (lowest) temperatures of a place in a day.
Question 26.
What is the normal temperature of the human body?
Answer:
The normal temperature,of the human body is 37°C or 98.4°F.
Question 27.
Why does smoke and hot air move up?
Answer:
Smoke and hot air moves up because it expands and becomes lighter. . .
Question 28.
What is the use of ventilators in our house?
Answer:
Smoke and hot air moves up because it expands and becomes lighter through ventila¬tors and exhaust fans on the upper parts of the wall.
Question 29.
What happens to the air on heating?
Answer:
On heating, the air expands, occupying more space and becomes lighter.
![]()
Question 30.
What happens when air is compressed?
Answer:
The air pressure becomes more when air is compressed.
7th Class Science 9th Lesson Heat, Temperature and Climate Short Questions and Answers
Question 1.
When do we feel hot and cool?
Answer:
- The heat when heat energy flows from hotter body to our body. We feel hot. Here we gain heat energy from the hotter body.
- We feel cool, when heat energy flows from our body to colder body. Here, we lose heat energy.
Question 2.
How does heat flow? How do we determine its direction?
Answer:
- Heat flows from a body of high temperature to a body of low temperature.
- This direction is determined by temperature. ‘
Question 3.
How do we written degree of Celsius, degree of Fahrenheit and Kelvin?
Answer:
- Degree Celsius: Celsius is written as °C and read as degree Celsius.
- Degree Fahrenheit: Fahrenheit is written as °F and read as degree fahrenheit.
- Kelvin is written as K and read as Kelvin.
Question 4.
What is Air pressure? How does it measure? What are the effects of the air pres-sure?
Answer:
Air pressure:
The force applied by air on any surface in contact is called “air pressure”.
Measuring of air pressure:
Air pressure is measured in height of mercury level in centimeters, and it is measured with a barometer. Now a days aneroid barometers are used to measure air pressure.
Effects of air pressure:
The air pressure becomes more when it is compressed. When air expands and rises up it creates low pressure, which drives the air high pressure from surrounding to move and occupy that place.
![]()
Question 5.
Why are cooking utensils made of metals while their handles are made of plastic or wood?
Answer:
- Some materials allow heat through them, this property is called conductivity.
- We use metals to make cooking vessels because they allow heat through them.
- We use material which does not allow heat to pass through as handles.
- So, cooking utensils made of metals while their handles are made of plastic or wood.
Question 6.
Write four applications of expansion of metals on heating.
Answer:
- The electric power lines (wires) are held loose on poles
- Rollers are kept under the beams of metal bridges
- Mercury is used in thermometers
- Small gaps are left between rails in railway tracks
Question 7.
Write the different modes of transfer of heat?
Answer:
Transfer of heat is in different types of materials. Heat gets transferred in three different modes, They are
- Conduction of heat
- Convection of heat
- Radiation of heat
1) Conduction of heat:
This process of transfer of heat from hotter to colder end through the conductor is called conduction. This mode of transfer of heat happens more in solid conductors.
2) Convection of heat:
This process of transfer of heat from source of heat to surface by the motion of particles is called “convection of heat”. In liquids and gases heat is transmitted by mode of convection of heat.
3) Radiation of heat:
This process of transfer of heat in the form of waves is called radiation. Radiation does not need any material medium. Sun’s heat transfers to earth in the form of radiation.
Question 8.
Write the differences between good conductors and poor conductors?
Answer:
| Good conductors | Poor conductors |
| 1) The materials which allow heat to pass through them are called conductors of heat. | 1) The materials which do not allow heat to pass through them easily are poor conductors of heat. |
| 2) Example: Aluminum, iron and copper etc. | 2) Example : Water, air, clothes, glass, cork, plastic, wood etc. |
| 3) Heat can pass. | 3) Heat cannot pass. |
| 4) These are used to prepare cooking cooking vessels. | 4) These are used to prepare handles of vessels. |
Question 9.
How does a thermos flask work?
(OR)
Describe working of a thermos flask.
Answer:
- Thermos flaSk has a two layered glass container and the air between these layers is removed to create vacuum.
- The inner silver coating protects the contents (tea, coffee, milk) poured in the flask from losing heat through radiation.
- As there is no medium between the walls of the flask. Neither conduction nor con-vection of heat takes place.
- As a result, heat is not transferred outside the flask so it is retained inside the flask for a few hours.
Question 10.
What is the reason for in the expansion of rails, mercury in thermometer, air inside the puri etc?
Answer:
- This is due to increase in the energy of particles present in these substances.
- Particles of substances occupy more space when they get heated.
- This is the reason for in the expansion of rails, mercury in thermometer, air inside the puri etc.
Question 11.
How does hot air balloon work?
Answer:
- Warm air is lighter than cold air.
- This property of air is used in flying of hot air balloons,
- It contains a bag which is called as envelope, and it is filled with heated air.
- There is a basket under the envelope which carries passengers and a source of heat.
![]()
Question 12.
Why mercury is used in thermometers?
Answer:
Mercury is used in thermometers, because it has the best properties to measure temperature.
Those are
- It’s expansion is uniform.
- It is bpaque and shining.
- It does not stick to the sides of glass tube.
- It is a good conductor of heat.
- It has a high boiling point (357°C) and a low freezing point (-39°C). Hence a wide range of temperatures can be measured using a mercury.
Question 13.
Why alcohol is used in thermometers?
Answer:
Alcohol is used in thermometers, because it has the best properties to measure temperature. Those are
- The freezing point of alcohol is less than -100°C.
- So, it can be used to measure very low temperatures.
- It’s expansion per degree Celsius rise in temperature is very large.
- It can be colored brightly and hence is easily visible.
Question 14.
What are the melting point of ice and boiling point of water in different scales?
Answer:
1) Celsius scale :
Melting point of ice is 0°C and boiling point of water is 100°C
2) Fahrenheit scale :
Melting point of ice is 32°F and boiling point of water is 212°F
3) Kelvin scale :
Melting point bf ice is 273K and boiling point of water is 373K
Question 15.
Write the Formulas for temperature conversion 1) Celsius to Fahrenheit 2) Celsius to Kelvin.
Answer:

Question 16.
Explain two applications of transfer of heat.
Answer:
Thermal scanning:
The thermal scanner receives the heat in the form of radiation to measure our body temperature.
Thermos flask:
It has a two layered glass container and the air between these layers is removed to create vacuum. The inner silver coating protects the contents (tea, coffee, milk) poured in the flask from losing heat through radiation. As there is no medium between the walls of the flask. Neither conduction nor convection of heat takes place. As a result, heat is not transferred outside the flask so it is retained inside the flask for a few hours.
Question 17.
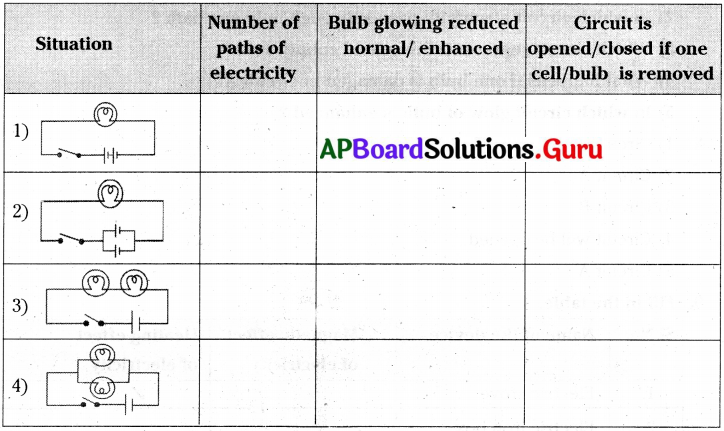
Fill in the table with suitable answers.
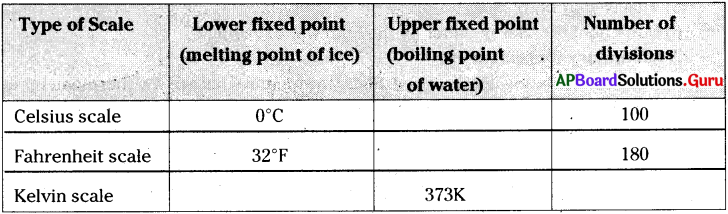
Answer:
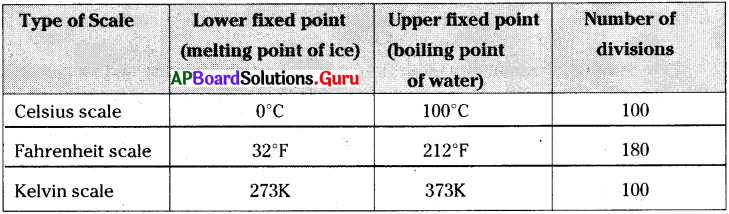
Question 18.
What is the use of a Clinical Thermometer? How it convenient to record the reading?
Answer:
- Clinical Thermometer is used in hospitals to measure the temperature of the human body.
- It has a kink that prevents the mercury from flowing back into the bulb when it was taken out of the patient’s mouth.
- This helps to record the temperature conveniently.
Question 19.
Where a Laboratory Thermometer is used? How it is better than the clinical ther-mometer?
(OR)
Describes laboratory Thermometer.
Answer:
- Laboratory Thermometer is used in school labs, industries etc. to measure temperature. It has no kink.
- It is made of a long stem and the bulb of mercury, so it can measure higher tempera-tures than clinical thermometer.
Question 20.
How does a Digital Thermometer work?
Answer:
- Digital Thermometer works without Mercury.
- It has a display which shows readings directly.
- It is very easy to use it, we can use it by just pressing on/off button present on it.
- Even children can also handle this one.
Question 21.
How do you use a clinical thermometer and a laboratory thermometer?
Answer:
Clinical thermometer
- Wash the clinical thermometer properly with an antiseptic solution.
- To lower the mercury level, hold the thermometer firmly and give some jerks.
- Ensure that it falls below 35°C. Now place the bulb of the thermometer under your tongue.
- After one or two minutes, take the thermometer out and note the reading.
- This is your body temperature.
- Don’t hold the thermometer by the bulb while reading it.
A Laboratory thermometer:
- Take cold or hot water in a bowl. Place the mercury bulb of the thermometer in the water so that the bulb immerses in it.
- Wait for some time till the mercury level shows a constant reading.
- Note down that reading.
![]()
Question 22.
How does sunstroke occur?
(OR)
What happens when humidity increases in the air?
Answer:
- Evaporation of sweat from our body makes us cool to maintain our body temperature.
- In summer, the humidity of air is high. Due to high humidity and temperature, it becomes difficult to evaporate the sweat from our body to cool It down.
- But still our body losses water.
- High temperatures, along with humidity sometimes may cause heat stroke or sun¬stroke.
Question 23.
What is the first aid for sunstroke?
Answer:
First Aid for sunstroke :
- Call 108 immediately. Move the victim to a cool ventilated place.
- Then loosen his dress and remove extra clothing. Put a cold wet towel on his head, back of the neck, on the grain and under the armpits.
- Fan air over the patient while wetting their skin with water from a sponge or wet cloth. Give plenty of cool, lightly salted water to drink often but in small sips.
- Help the person stay calm without any anxiety.
Question 24.
What is weather of a place? What are its measuring components?
Answer:
- The day-to-day variations in the components like temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed are called weather.
- Maximum and minimum temperature of a day, air pressure, rainfall, wind speed and humidity are called measuring components of weather.
Question 25.
How do Meteorologists decide the climate of the place?
Answer:
- Meteorologists (scientists who study and work on weather) record weather every day. .
- These records of the weather have been preserved for the past several decades.
- They help us to determine the weather pattern of a place.
- The average weather pattern taken over a long period, say 25 years or more, is called the climate of the place.
Question 26.
Why does climate affect pur life style? What are its measuring components?
Answer:
- Climate of a place remains unchanged for a long period of time. So, it affects our lifestyle.
- The measuring components of climate are maximum and minimum temperature of a day, air pressure, rainfall, wind speed and humidity.
Question 27.
What are the differences between weather and climate?
Answer:
| Weather | Climate |
| Weather keeps on changing rapidly. | Climate of a place remains unchanged for a long period of time. |
| It affects our daily life. | It affects our life style |
| Atmospheric conditions in a speciiic area and time. | Atmospheric conditions of a place for a long period of time. |
| It is not constant. | It remains constant for 25 years or more. |
Question 28.
How weather and climate is effected our life?
Answer:
- Daily weather and long-term climatic conditions influence the life style of humans and other living things directly and indirectly.
- Some of them are diet, clothing, housing, occupations etc.
Question 29.
Doctor put the thermometer in the mouth of Karthikeya’s sister, Neha. By seeing this Karthikeya got some doubts and asked doctor. What could be those doubts?
Answer:
- What is in the thermometer?
- How does it show the temperature?
- How can you say Neha got the fever?
- How much time shall it place in the mouth?
Question 30.
Guess what will happen if we use the clinical thermometer to measure the temperature of the ice cubes or boiling water?
Answer:
We cannot measure too low and too high temperatures by using a clinical thermometer. It is made for clinical use only, so by using this we can measure from 35°C to 42°C only. If we measure temperature of boiling water or ice cubes it will break or it does not work.
Question 31.
Guess what will happen if a low air pressure is formed in your area?
Answer:
If a low air pressure is formed in our area, air blow from high air pressure area to occupy the low air pressure area. Sometimes this wind causes damage to roofs, trees etc.
![]()
Question 32.
Kalyan said that the climate was changed by being seen the dark clouds in the sky. Is the word climate correct in his statement?
Answer:
No. climate is different from weather. The changes occur during the period of some hours is called changing in weather. Climate is average weather conditions of a long period. So he had to use weather instead of climate in his statement.
Question 33.
What will happen, if there is no kink in the clinical thermometer?
Answer:
The kink prevents the mercury from flowing back into the bulb when it was taken out of the patient’s mouth. This helps to record the temperature conveniently. If there is no kink the level of the mercury will fall down in the gap of taking out from the patient and seeing the reading. So, it may show incorrect reading.
Question 34.
What is your observation in the activity of metal spoon with fixed pins and a candle and write the reason.
Answer:
I will observe the dropping of pins one after another from the flame end of the spoon. This is due to the transfer of heat from the end kept in the flame (hotter end) towards your hand (colder end) through a spoon (metal).
Question 35.
What are your observations in the activity of expansion of metal on heating?
Answer:
I will observe movement in the straw. The needle rolls on the second block of wood because of the expansion of the cycle spoke. If we remove the candles the needle rolls back causing movement in the straw opposite to the previous motion.
Question 36.
Read the graph and answer the following questions.
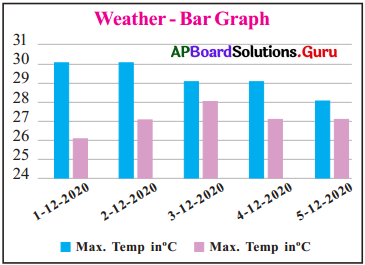
1. Which component was shown in the graph?
Answer:
Temperature
2. On which day the maximum temperatures recorded?
Answer:
On the dates, 1-12-2020 and 2-12-2020 the maximum temperature was recorded.
Question 37.
Take a glass and keep a postcard oh it. Wave your notebook above the post card to displace the air just above the postcard. What is your observation? What is the reason for it?
Answer:
The moving air creates low pressure. Hence the postcard lifts up due to the higher pressure on the card from air inside the glass.
Question 38.
Observe the figure and give answers to the following questions.
1. What mode of transfer of heat is observed in the spoon?
2. What is the source of heat?
3. What will happen after some time?
4. What is the medium here?

Answer:
1. Conduction of heat is observed in the spoon
2. Candle is the source of heat.
3. All the pins will fall down.
4. Metal in the spoon is the medium (solid)
Question 39.
Fill in the table with suitable answers.
| Component in the weather | Units | Device to measure |
| Temperature | Kelvin or °C or °F | |
| Air pressure | Mercury level in centimeters | |
| Millimeters | Rain gauge | |
| Humidity | Grams per cubic meter. |
Answer:
| Component in the weather | Units | Device to measure |
| Temperature | Kelvin or C or °F | Thermometer |
| Air pressure | Mercury level in centimeters | Barometer |
| Rain fall | Millimeters | Rain gauge. |
| Humidity | Grams per cubic meter. | Hygrometer |
Question 40.
Fill in the table with suitable answers.
| Phenomenon | Examples |
| Convection | 1) Milk 2)…………………. 3) ……………………. |
| Conduction | 1) Metal spoon 2)………. 3) ……………… |
| Radiation | 1) Sun to earth 2)………. 3) ………………. |
| Insulators | 1) Rubber 2)…………….. 3) ……………… |
| Conductors | 1) Iron spoke 2)…………. 3) ……………… |
Answer:
| Phenomenon | Examples |
| Convection | 1) Milk 2) Eater 3)oil |
| Conduction | 1) Metal spoon 2)copper vessel 3)nail |
| Radiation | 1) Sun to earth 2) flask inner to outer 3) sun to moon |
| Insulators | 1) Rubber 2) glass 3) water |
| Conductors | 1) Iron spoke 2) vessels 3) copper wire |
Question 41.
Draw the diagram of mercury laboratory thermometer.
Answer:
![]()
Question 42.
Draw the diagram of alcohol laboratory thermometer.
Answer:
![]()
Question 43.
Draw the diagram of a thermos flask and label its inner parts.
Answer:
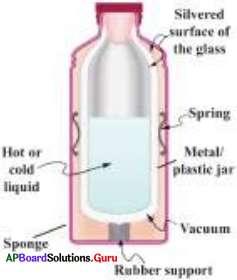
44. Draw the diagram showing the arrangement of apparatus to show the expansion of liquids on heating?
Answer:

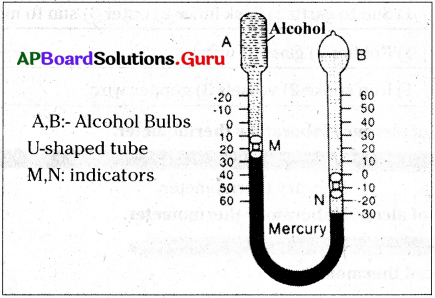
45. Draw the diagram of Six minimum and maximum temperatures and label the parts.
Answer:
7th Class Science 9th Lesson Heat, Temperature and Climate Long Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Compare different modes of transfer of heat.
Answer:
| Conduction | Convection | Radiation |
| 1) The process of transfer of heat from hotter to colder end through the conductor is called conduction of heat. | The process of transfer of heat from source of heat to surface by the motion of particles is called convection of heat. | The process of transfer of heat in the form of waves is called radiation. |
| 2) In solids heat is transmitted by mode of conduction of heat. | In liquids and gases heat is transmitted by mode of convection of heat. | Radiation does not need any material medium |
| 3) Ex: metals | Ex: water, milk | Ex : Sun’s heat to earth |
| 4) No movement in the particles. | Movement in the particles. | No movement in the particles |
| 5) It needs thermal contact. | It does not need thermal contact. | It does not need thermal contact. |
Question 2.
Write about different types of thermometers.
Answer:
Clinical thermometer:
- Wash the clinical thermometer properly with an antiseptic solution.
- To lower the mercury level, hold the thermometer firmly and give some jerks.
- Ensure that it falls below 35°C. Now place the bulb of the thermometer under your tongue.
- After one or two minutes, take the thermometer out and note the reading.
- This is your body temperature.
- Don’t hold the thermometer by the bulb while reading it.
Laboratory thermometer:
- Take cold or hot water in a bowl. Place the mercury bulb of the thermometer in the water so that the bulb immerses in it.
- Wait for some time till the mercury level shows a constant reading.
- Note down that reading.
Digital Thermometer:
- It works without mercury.
- It has a display which shows readings directly.
- It is very easy to use it.
- We can use it by just pressing on/off button present on it.
- Even children can also handle this one.
Six’s maximum and minimum thermometer:
- It is one of the Meteorological Instruments used to measure maximum (highest) and minimum (lowest) temperatures of a place in a day.
- It has a cylindrical ‘Bulb A’, and ‘Bulb B’ connected through a ‘U-shaped tube’ con¬taining mercury.
- Bulb A contains alcohol, and bulb B contains alcohol and its vapours.
- When the temperature increases, the alcohol in the bulb A expands and pushes the mercury in the U tube, this makes indicator(M) to move up.
- This indicates the maximum temperature of the day.
- When the temperature decreases, alcohol in the bulb A contracts and pulls the mercury back.
- This makes indicator (N) to move up.
- This indicates the minimum temperature of the day.
- After taking readings the indicators M and N are brought to their original places by using a magnet.
![]()
Question 3.
What is humidity? How does it measure? How does it affect or body? What is the first aid of sunstroke?
Answer:
HumidityAll the evaporated water from different water bodies go into air. This water vapour present in the air is called humidity.
Measurement of humidity:
Hygrometer is used to measure humidity in air and it is expressed in grams per cubic meter.
Effects of humidity:
Evaporation of sweat from our body makes us cool to maintain our body temperature. In summer, the humidity of air is high. Due to high humidity and temperature, it becomes difficult to evaporate the sweat from our body to cool it down. But, still our body losses water. High temperatures, along with humidity sometimes may cause heat stroke or sunstroke.
First Aid for sunstroke:
Call 108 immediately. Move the person out of the heat. Fan while spraying water to cool him. Let the person drink water to rehydrate.
Question 4.
Read the following table and answer the questions.
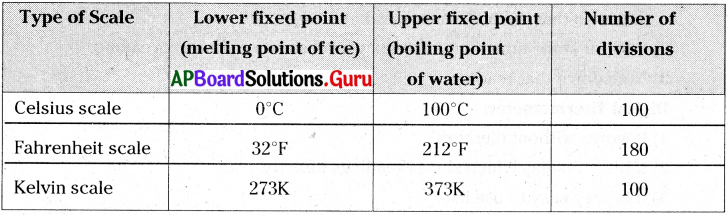
i) At what temperature, the ice melts? Express in Celsius.
ii) Which measurements are given in the table?
iii) Convert, 100°C into Fahrenheit and kelvin scale.
iv) What are the SI units of temperature?
Answer:
i) 0°C .
ii) Measurements of temperature are given.
iii) 100°C =212°F =373K
iv) Kelvin
Question 5.
How do you appreciate the weather reports?
Answer:
- The day-to-day variations in the components like temperature, humidity, rainfall, , wind speed are called weather.
- It keeps on changing and changes are very fast too.
- One day it may be dry and sunny and the next day it may rain.
- It gives the information about atmospheric conditions in a specific area and time.
- We can get details of weather from weather reports and you can see these symbols on television, newspapers and in weather forecasting.
- Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the atmosphere using components of weather for a given location and time.
- Weather reports are very useful to farmers, fishermen etc.
- So I appreciate the weather reports.
Question 6.
How do you appreciate the properties of the mercury and alcohol as they are used in the thermometers?
Answer:
Properties of mercury:
- Its expansion is uniform.
- It is opaque and shining.
- It does not stick to the sides of glass tube.
- It is a good conductor of heat.
- It has a high boiling point (357°C) and a low freezing point (-39°C).
Hence a wide range of temperatures can be measured using mercury.
Properties of alcohol:
- The freezing point of alcohol is less than -100°C. So, it can be used to measure very low temperatures.
- It’s expansion per degree Celsius rise in temperature is very large.
- It can be coloured brightly and hence is easily visible.
Hence a wide range of temperatures can be measured using alcohol. Clinical ther-mometers, laboratory thermometers, six minimum and maximum thermometers etc. are made with alcohol or mercury or both.
Hence I appreciate the properties of the mercury and alcohol as they are used in the thermometers
AP Board 7th Class Science 9th Lesson 1 Mark Bits Questions and Answers Heat, Temperature and Climate
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer and write its letters in the brackets.
1. It is a form of energy that flows from a hotter body to a cooler body.
A) Heat
B) Light
C) Sound
D) Electricity
Answer:
A) Heat
2. When heat energy flows from our body to Lassi. Here,
A) Lassi loss Heat energy
B) Body lose heat energy
C) Body gain heat energy
D) A and C
Answer:
B) Body lose heat energy
3. Joules are units of
A) Humidity
B) Climate
C) Heat
D) Air pressure
Answer:
C) Heat
![]()
4. The degree of hotness or coldness is called ………..
A) Humidity
B) Temperature
C) Heat
D) Air pressure
Answer:
D) Air pressure
5. Temperature is measured in…….
A) Degrees of Celsius
B) Degrees of Fahrenheit
C) Kelvin
D) All
Answer:
D) All
6. The SI unit of temperature is ………….
A) Degrees of Celsius
B) Degrees of Fahrenheit
C) Kelvin
D) All
Answer:
C) Kelvin
7. Kelvin is written as
A) °C
B) °F
C) °K
D) K
Answer:
D) K
8. Which is correct?
i) Heat is the degrees of hotness or coldness.
ii) Heat is measured in joules
A) i only
B) ii only
C) both i & ii
D) both are incorrect
Answer:
B) ii only
9. Cooking utensils are made of ………..
A) conductors
B) insulators
C) fuels
D) none of the above
Answer:
A) conductors
10. Handles of cooking vessels are made of …………….
A) conductors
B) insulators
C) fuels
D) none of the above
Answer:
B) insulators
11. A: Metals are used to make cooking vessels.
R: Metals allow heat through them.
Which is correct?
A) A & R are correct and R supports A
B) A & R are correct but R does not support A
C) A is correct but R is wrong
D) R is Correct but A is wrong
Answer:
A) A & R are correct and R supports A
12. The ability of a material to conduct heat is called …………..
A) Thermal conductivity
B) Thermal resistivity
C) Thermometer
D) None
Answer:
A) Thermal conductivity
13. It is not a good conductor.
A) Copper
B) Steel
C) Plastic
D) Cast iron
Answer:
C) Plastic
![]()
14. Insulator is….
A) Water
B) Glass
C) Plastic
D) All
Answer:
D) All
15. Heat cannot pass in the mode of
A) Conduction
B) Convection of heat
C) Radiation of heat
D) None
Answer:
D) None
16. In which heat is transferred from one end to another end by the mode of conduction.
A) Steel spoon
B) Water
C) A and B
D) Sun to earth
Answer:
A) Steel spoon
17. This mode of transfer of heat happens more in solid conductors
A) Conduction
B) Convection of heat
C) Radiation of heat
D) None
Answer:
A) Conduction
18. This process of transfer of heat from source of heat to surface by the motion of particles
A) Conduction
B) Convection of heat
C) Radiation of heat
D) all
Answer:
B) Convection of heat
19. This is not a medium of heat energy.
A) Solid
B) Liquid
C) Gas
D) None
Answer:
D) None
20. This mode of transfer of heat doesn’t require any media.
A) Conduction
B) Convection of heat
C) Radiation of heat
D) All
Answer:
C) Radiation of heat
21. The process of transfer of heat in the form of waves is called
A) Conduction
B) Convection of heat
C) Radiation of heat
D) All
Answer:
C) Radiation of heat
22. Which instrument can control the transfer of heat (loss of heat)?
A) Thermos flask
B) Thermometer
C) Thermal scanner
D) All
Answer:
A) Thermos flask
![]()
23. The flask retains hot inside the flask for
A) a few hours
B) ever
C) never
D) a few weeks.
Answer:
A) a few hours
24. Thermos flask was invented by
A) Sir James cook
B) Sir James Chadwick
C) Sir James Dewar
D) Sir James watts
Answer:
C) Sir James Dewar
25. Which of the following expands on heating and contracts on cooling?
A) Solid
B) Liquid
C) Gas
D) All
Answer:
D) All
26. Air on cooling
A) contracts
B) occupy less space.
C) expand
D) A and B
Answer:
D) A and B
27. Warm air is lighten than cold air. This property of air is used in
A) hot air balloons
B) kites
C) rockets
D) all
Answer:
A) hot air balloons
28. Thermometer contains bulb of
A) mercury
B) alcohol
C) A or B
D) silver
Answer:
C) A or B
29. Mercury is a in room temperature.
A) solid
B) liquid
C) gas
D) all
Answer:
A) solid
30. This is not a property of the mercury .
A) Its expansion is uniform.
B) It is a good conductor of heat.
C) It easily sticks to the sides of glass tube.
D) It has a high boiling point.
Answer:
C) It easily sticks to the sides of glass tube.
![]()
31. The boiling point and a freezing point of the mercury are
A) -39°C and 357°C
B) 357°C and-39°C
C)100°C and 0°C
D) none
Answer:
B) 357°C and-39°C
32. A: The freezing point of alcohol is more than -100°C.
R: Alcohol can be used to measure very low temperatures.
A) A & R are correct and R supports A
B) A & R are correct but R does not support A
C) A is correct but R is wrong
D) R is correct but A is wrong
Answer:
D) R is correct but A is wrong
33. Number of divisions in Fahrenheit scale is
A) 100
B) 212
C) 180
D) 32
Answer:
C) 180
34. Number of divisions in Kelvin scale is
A) 100
B) 212
C) 180
D) 32
Answer:
A) 100
35. Number of divisions in Celsius scale is
A) 100
B) 212
C) 180
D) 32
Answer:
A) 100
36. Which prevents the mercury from flowing back into the bulb in clinical thermometer.
A) Capillary
B) Kink
C) Bulb
D) Magnet
Answer:
B) Kink
37. Laboratory thermometer can measure higher temperatures than clinical thermometer because, it has
A) long bulb
B) long stem
C) short bulb
D) short stem
Answer:
B) long stem
38. This thermometer can work without Mercury.
A) Six max and min thermometer
B) Digital Thermometer
C) Clinical thermometer
D)All
Answer:
B) Digital Thermometer
39. Who invented Six’s maximum and minimum thermometer in 1780?
A) Sir James cook
B) James watt
C) Sir James Dewar
D) James Six
Answer:
D) James Six
![]()
40. The correct order is
i) After one or two minutes, take the thermometer out and note the reading,
ii) Place the bulb of the thermometer under your friend’s tongue.
iii) Wash the clinical thermometer properly with an antiseptic solution.
iv) To lower the mercury level, hold the thermometer firmly and give some jerks.
A) iv, ii, i, iii
B) iv, iii, ii, i
C) iii, iv, ii, i
D) ii, iii, iv, i
Answer:
C) iii, iv, ii, i
41. The normal temperature of the human body is
A) 37°C
B) 98.4°F
C) 310K
D) all
Answer:
D) all
42. Ventilators are working on
A) Air expands on heating
B) Air contracts on heating
C) Metal expands on heating
D) Air contracts on cooling
Answer:
A) Air expands on heating
43. Which is used to measure the air pressure?
A) Hygrometer
B) Thermometer
C) Barometer
D) Rain gauge
Answer:
C) Barometer
44. A: If roofs were weak, they could be lifted and blown away.
R: The moving air creates high pressure.
A) A & R are correct and R supports A
B) A & R are correct but R does not support A
C) A is correct but R is wrong
D) R is correct but A is wrong
Answer:
C) A is correct but R is wrong
45. Rain fall is measured with a
A) hygrometer
B) thermometer
C) barometer
D) rain gauge
Answer:
D) rain gauge
46. This is not a measuring component of weather
A) humidity
B) temperature
C) wind speed
D) none
Answer:
D) none
47. Humidity is measured in
A) g/cubic meter
B) mm/cubic meter
C) °C
D) m/°C
Answer:
A) g/cubic meter
48. In summer, the humidity of air is
A) low
B) high
C) no change
D) zero
Answer:
B) high
49. High temperatures, along with humidity sometimes may cause
A) kwashiorkor
B) beriberi
C) corona
D) sunstroke
Answer:
D) sunstroke
50. It gives the information about atmospheric conditions in a specific area and time.
A) Weather
B) Climate
C) A and B
D) None
Answer:
A) Weather
51. This deals with a long period.
A) Weather
B) Climate
C) A and B
D) None
Answer:
B) Climate
52. It affects our lifestyle
A) Weather
B) Climate
C) A and B
D) None
Answer:
B) Climate
![]()
53. Which phenomenon measures atmospheric conditions in a specific area and time?
A) Weather
B) Climate
C) A and B
D) None
Answer:
A) Weather
II. Fill in the blanks
1. Heat is a form of energy that flows from a ………………. body to a ………………. body.
2. Heat is measured in ………………. with calorimeter
3. Heat flows from a body of high temperature to a body of low temperature. This direction is determined by ………………. .
4. The degree of ………………. is called ‘temperature’.
5. Degree of Celsius is written as ………………. .
6. Degree of Fahrenheit is written as ………………. .
7. Some materials allow heat through them, this property is called ………………. .
8. Water, air, clothes, glass, cork, plastic, wood etc. are some examples of ………………. .
9. This process of transfer of heat from hotter to colder end through the conductor’ is called ………………. .
10. The contact which transfers heat by any mode is called ………………. .
11. Water is a ………………. of heat.
12. Heat is transferred by means of ………………. called convectional currents.
13. The materials which help in transfer of heat from one place to another are called ………………. .
14. Sun’s heat transfers to earth in the form of ………………. .
15. The thermal scanner receives the heat in the form of ………………. to measure our body temperature.
16. The inner ………………. in thermos flask protects the contents (tea, coffee, milk) poured in the flask from losing heat through radiation.
17. As there is ………………. between the walls of the flask; neither conduction nor convection of heat takes place.
18. Particles of substances occupies ………………. space when they get heated.
19. Small gaps left between rails in railway tracks, because metal ………………. on heat
20. ………………. are used to measure temperature.
21. The principle involved in working of a thermometer is ………………. .
22. The melting point of ice is ………………. °C
23. The melting point of ice and boiling point of water in Fahrenheit are ………………. .
24. The melting point of ice and boiling point of water in SI units are ………………. .
25. The formula to convert Celsius to Kelvin is ………………. .
26. The formula to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit is ………………. .
27. ………………. is used in hospitals to measure the temperature of the human body.
28. Clinical Thermometer has a ………………. that prevents the mercury from flowing back into the bulb when it was taken out of the patient’s mouth.
29. After taking readings in six max and min thermometer the indicators I<sub>2</sub> and I<sub>1</sub> are brought to their original places by using ………………. .
30. The normal temperature of the human body is ………………. .
31. Smoke and hot air moves up because it ………………. on heating and becomes lighter.
32. The force applied by air oh any surface in contact is called ………………. .
33. The air pressure becomes ………………. when it is compressed.
34. When air expands and raises up it creates ………………. .
35. ………………. drives the air high pressure from surrounding to move and occupy that place.
36. Air pressure is measured in height of ………………. level in centimeters
37. ………………. is measured in millimeters by using a rain gauge.
38. The water vapour present in the air is called ………………. .
39. ………………. is used to measure humidity in air and it is expressed in grams per cubic meter.
40. Evaporation of ………………. from our body makes us cool to maintain our body temperature.
41. The day-to-day variations in the components like temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed are called ………………. .
42. ………………. forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the conditions of the atmosphere using components of weather for a given location and time.
43. It is easier to know about weather with the help of ………………. than tables.
44. ………………. study and work on weather and record weather every day.
45. The average weather pattern taken over a long period, say 25 years or more, is called the ………………. of the place.
46. Expansion of IMD is ………………. .
47. The abnormal variation in the components of climate is called ………………. .
Answer:
- hotter, cooler
- Joules or calories
- temperature
- hotness or coldness
- °C
- °F
- conductivity
- insulators
- conduction
- Thermal contact
- poor conductor
- currents
- medium
- radiation
- radiation
- silver coating
- no medium or vacuum
- more
- expand
- Thermometers
- expansion of liquids on heating
- 0
- 32°F, 212°F
- 273K, 373K
- K °C + 273
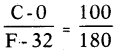
- Clinical Thermometer
- kink
- a magnet
- 37°C or 98.4°F
- expands
- air pressure
- more
- low pressure
- Low pressure
- mercury
- Rainfall
- Humidity
- Hygrometer
- Sweat
- weather
- Weather
- graphs
- Meteorologists
- Climate
- Indian Meteorological Department
- climate change
III. Match the following
1.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) heat | a) cm of mercury level |
| 2) temperature | b) Kelvin |
| 3) air pressure | c) mm |
| 4) rain fall | d) Joule |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) heat | d) Joule |
| 2) temperature | b) Kelvin |
| 3) air pressure | a) cm of mercury level |
| 4) rain fall | c) mm |
2.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) humidity | a) barometer |
| 2) temperature | b) hygrometer |
| 3) air pressure | c) rain gauge |
| 4) rainfall | d) thermometer |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) humidity | b) hygrometer |
| 2) temperature | d) thermometer |
| 3) air pressure | a) barometer |
| 4) rainfall | c) rain gauge |
3.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) water | a) radiation |
| 2) heat | b) convection |
| 3) metal | c) expansion |
| 4) vacuum | d) conduction |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) water | b) convection |
| 2) heat | c) expansion |
| 3) metal | d) conduction |
| 4) vacuum | a) radiation |
4.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) nail | a) clinical thermometer |
| 2) cloth | b) lab thermometer |
| 3) mercury | c) conductor |
| 4) alcohol | d) insulator |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) nail | c) conductor |
| 2) cloth | d) insulator |
| 3) mercury | a) clinical thermometer |
| 4) alcohol | b) lab thermometer |
5.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) weather | a) low pressure |
| 2) climate | b) long period |
| 3) wind | c) water vapour |
| 4) humidity | d) rapid change |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) weather | d) rapid change |
| 2) climate | b) long period |
| 3) wind | a) low pressure |
| 4) humidity | c) water vapour |
6.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) gas expansion | a) alcohol thermometer |
| 2) liquid expansion | b) parachute |
| 3) solid expansion | c) railway rails |
| 4) gas contraction | d) LPG cylinder |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) gas expansion | b) parachute |
| 2) liquid expansion | a) alcohol thermometer |
| 3) solid expansion | c) railway rails |
| 4) gas contraction | d) LPG cylinder |
7.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Kelvin | a) °F |
| 2) Fahrenheit | b) K |
| 3) Celsius | c) J |
| 4) Heat | d) °c |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Kelvin | b) K |
| 2) Fahrenheit | a) °F |
| 3) Celsius | d) °c |
| 4) Heat | c) J |
Do You Know?
→ Heat is measured In Joules or Calories with calorimeter.
→ Warm air is lighter than cold air. This property of air is used in flying of hot air balloons. It contains a bag which is called as envelope, and it is filled with heated air. There is a basket under the envelope which carries passengers and a source of heat.
→ Formulas for temperature conversion
1) Celsius to Fahrenheit 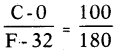
2) Celsius to Kelvin C=K – 273
→ Now a days cameras have been developed to detect heat. Those are called thermal- cameras.
![]()
→ The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) studies climate of our country. 23rd March is celebrated as World Meteorological Day.
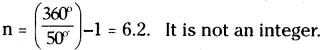
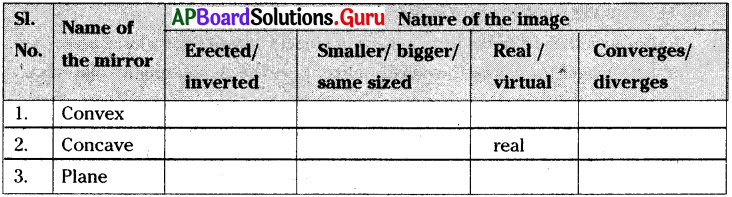
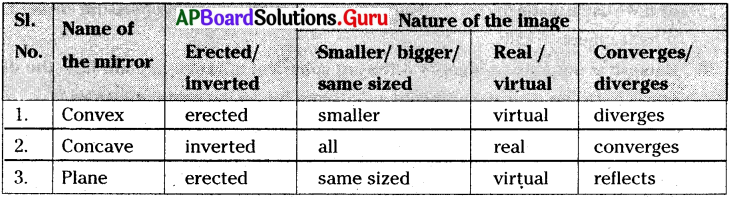






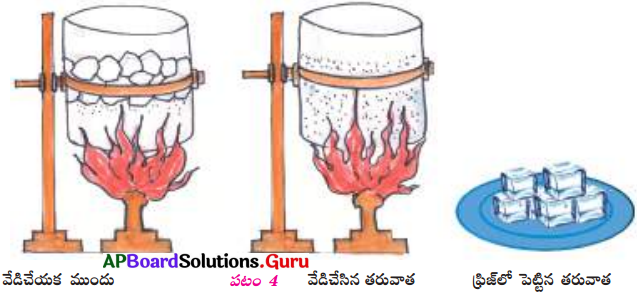
 This diagram indicates
This diagram indicates

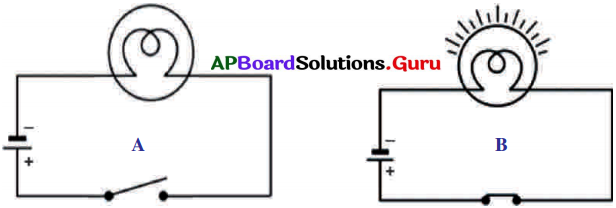
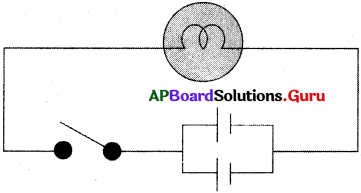

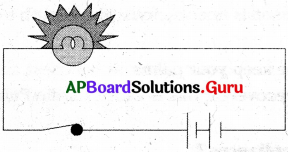

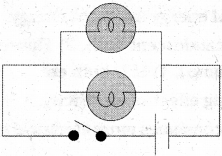
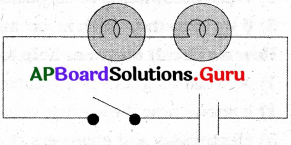

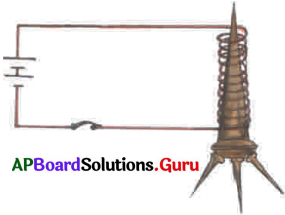




















 ఈ పటంలో చూపబడిన మార్పు
ఈ పటంలో చూపబడిన మార్పు