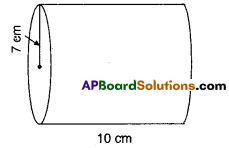
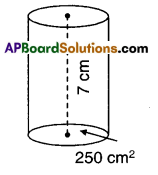
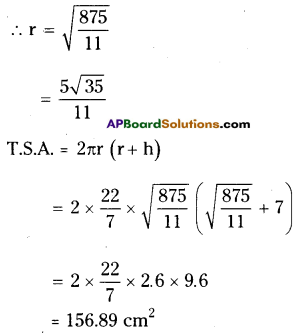
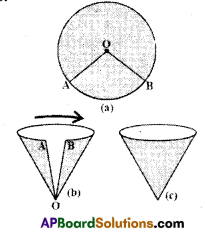
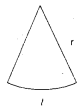
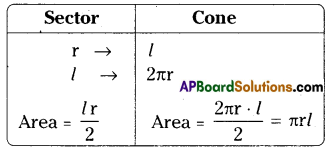
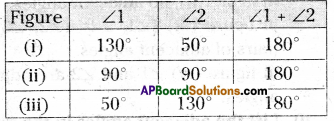
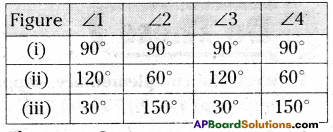
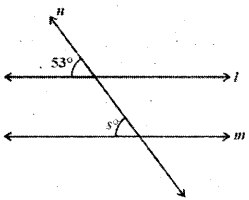
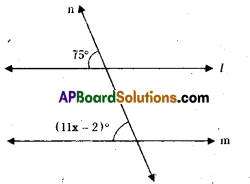
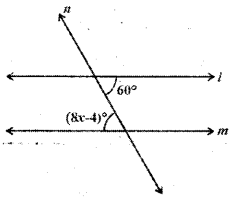
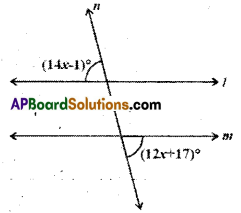
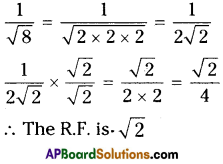
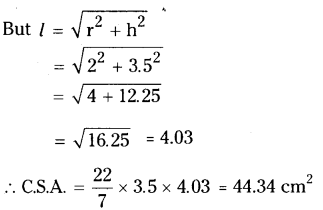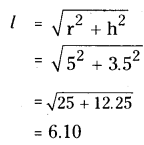AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 11 Areas InText Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Maths Solutions 11th Lesson Areas InText Questions
![]()
Activity
Question
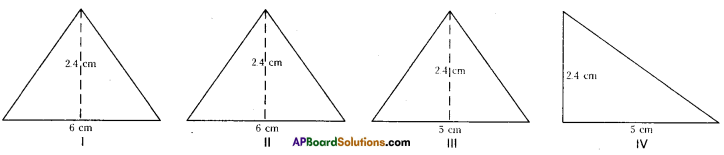
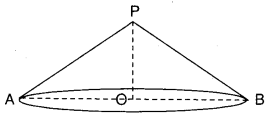
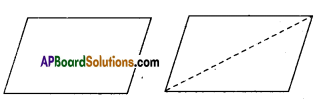
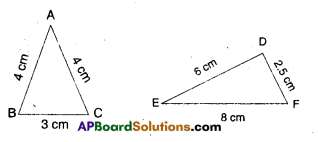
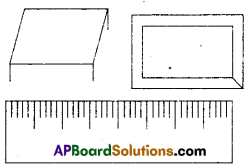
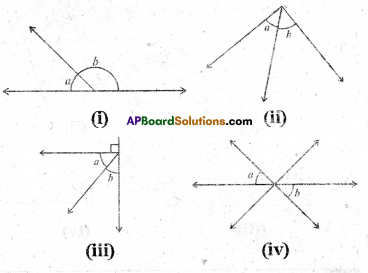
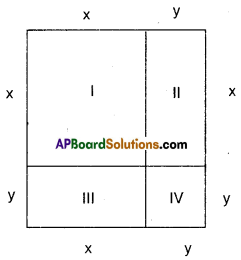
Observe Figure I and II. Find the area of both. Are the areas equal?
Trace these figures on a sheet of paper, cut them. Cover fig. 1 with fig. II. Do they cover each other completely? Are they congruent?
Observe fig. Ill and IV. Find the areas of both. What do you notice?
Are they congruent?
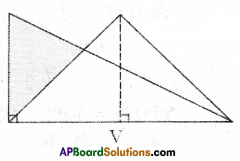
Now, trace these figures on sheet of paper. Cut them let us cover fig. Ill by fig. IV by coinciding their bases (length of same side).
As shown in figure V are they covered completely?
We conclude that Figures I and II are congruent and equal in area. But figures III and IV are equal in area but they are not congruent
Think, Discuss and Write
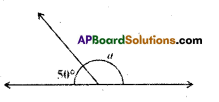
Question 1.
If 1 cm represents 5 in, what would be an area of 6 cm2 represents ?
[Page No. 247]
Solution:
1 cm2 = 5 m
1 cm2 = 1 cm × 1 cm = 5m × 5m = 25m2
∴ 6 cm2 = 6 × 25 m2 = 150 m2
Question 2.
Rajni says 1 sq. m = 1002 sq. cm. Do you agree ? Explain.
Solution:
No
1 sq. m = 100 cm2
![]()
Think, Discuss and Write
Question
Which of the following figures lie on the same base and between the same parallels? In such cases, write the common base and two parallels. [Page No. 249]
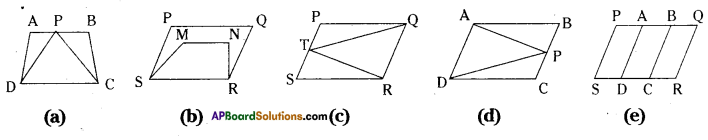
Solution:
a) In figure (a) ΔPCD and □ ABCD lie on same base CD and between the same parallels AB//CD.
b) No,
c) ΔTRQ and □ PQRS lie on the same base QR and between the same par-allels PS//QR.
d) ΔAPD and □ ABCD lie on the same base AD and between the same par-allels AD//BC.
e) No.
Activity
Question
Take a graph sheet and draw two par-allelograms ABCD and PQCD on it as show in the Figure, [Page No. 250]
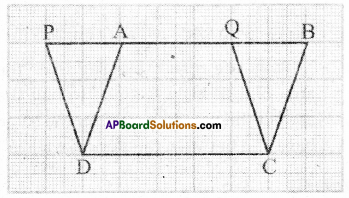
The parallelograms are on the same base DC and between the same parallels PB and DC. Clearly the part DCQA is common between the two parallelo-grams. So if we can show that ΔDAP and ΔCBQ have the same area then we can say ar(PQCD) = ar(ABCD)
![]()
Activity
Draw pairs of triangles one the same base or ( equal bases) and between the same parallels on the graph sheet as shown in the Figure.
Let AABC and ADBC be the two triangles lying on the same base BC and between parallels BC and FE.
Draw CE II AB and BF II CD. Parallelograms AECB and FDCB are on the same base BC and are between the same parallels BC and EF.
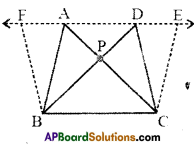
Thus ar (AECB) = ar (FDCB).
We can see ar (ΔABC) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ar (parallelogram AECB) …………….(i)
and ar (ΔDBC) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ar (parallelogram FDCB) ……………..(ii)
From (i) and (ii), we get ar (ΔABC) = ar (ΔDBC)
You can also find the areas of ΔABC and ΔDBC by the method of counting the squares in graph sheet as we have done in the earlier activity and check the areas are whether same.[Page No. 254]
![]()
Think, Discus and Write
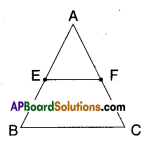
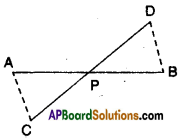
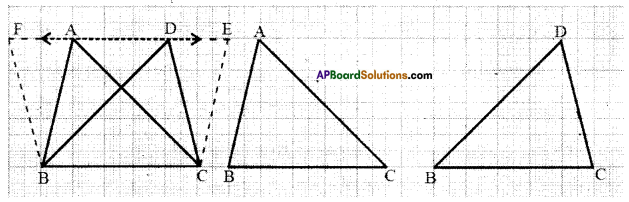
Draw two triangles ABC and DBC on the same base and between the same parallels as shown in the figure with P as the point of intersection of AC and BD. Draw CE//BA and BF//CD such that E and F lie on line AD.
Can you show ar(ΔPAB) = ar(ΔPDQ) ?[Page No. 254]
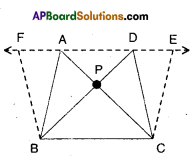
[Hint: These triangles are not congruent but have equal areas.
Solution:
□ ABCE = 2 × ΔABC
[∵ ΔABC; □ABCE lie on the same base BC and between the same parallels BC // AE]
ΔABC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × □ ABCE ……………(1)
Also □ BCDF = 2 × ΔBCD…………..
[∵ΔBCD and □ BCDE lie on the same base BC and between , the same parallels BC//DE]
ΔBCD = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × □ BCDF ……………… (2)
But □ABCE = □BCDF
[ ∵ □ABCE and □BCDF lie on the same base BC and between the same parallels BC//FE]
From (1) & (2); ΔABC = ΔBCD
ΔPAB + ΔPBC = ΔPBC + ΔPDC
⇒ ΔPAB = ΔPDC
Hence proved.