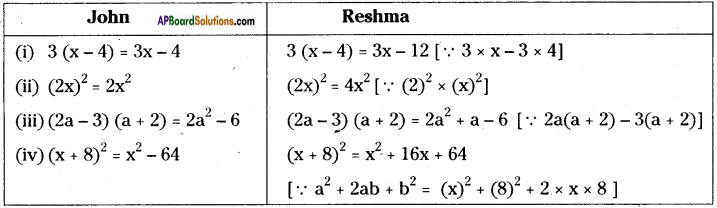
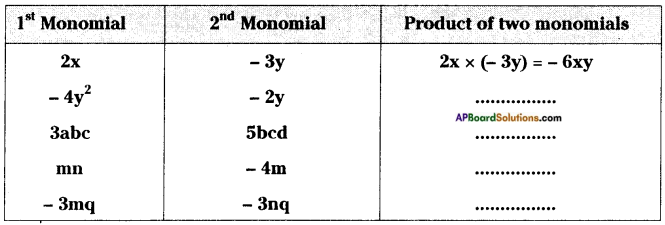
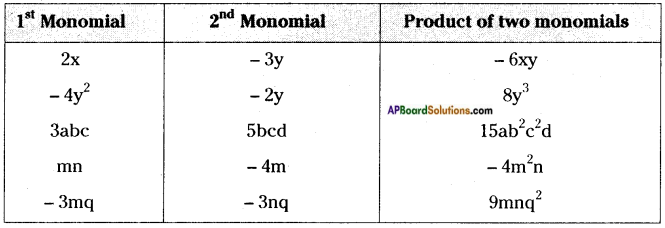
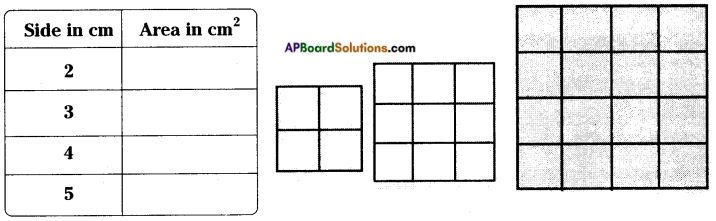
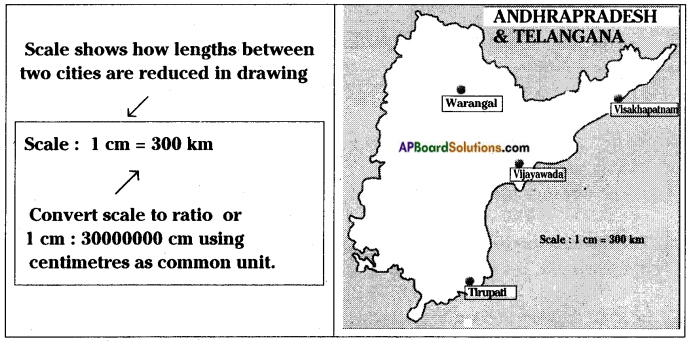
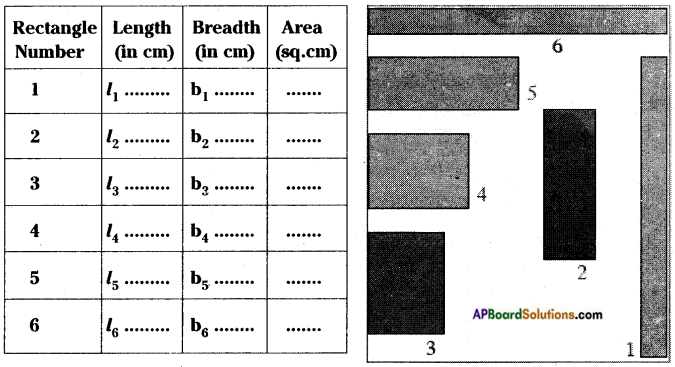
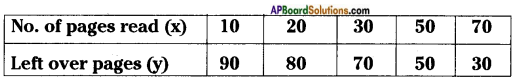
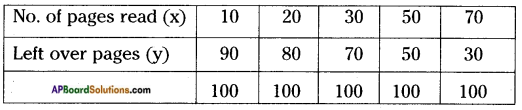
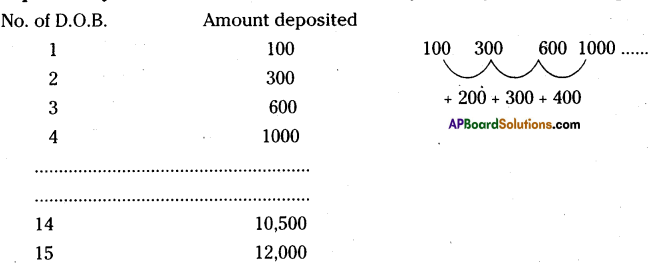
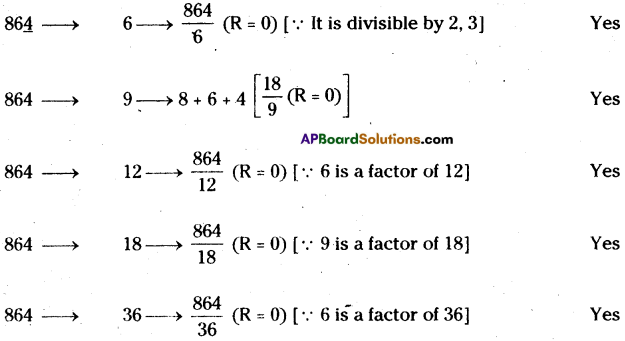
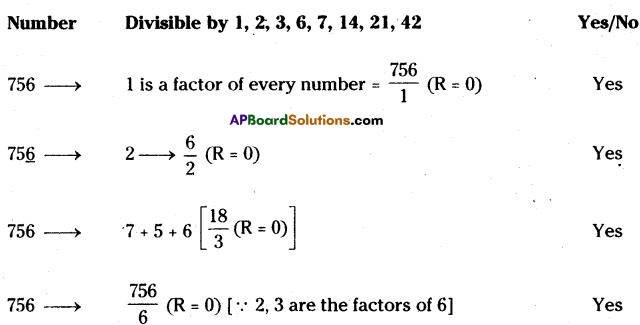
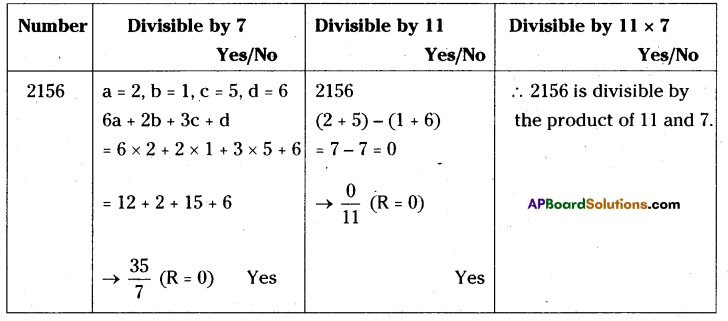
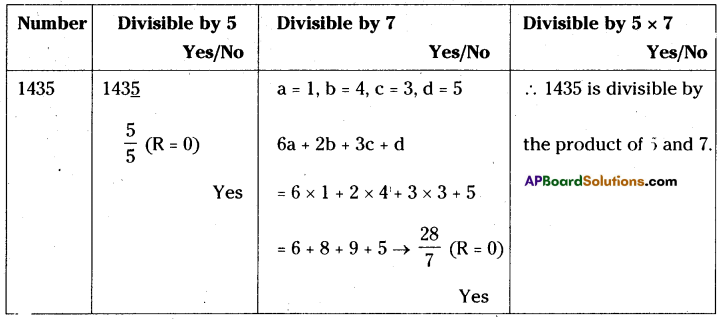
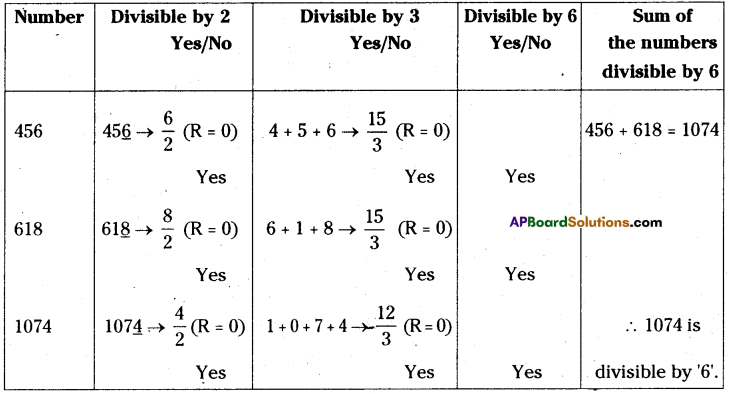
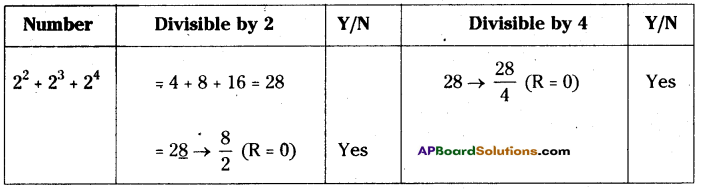
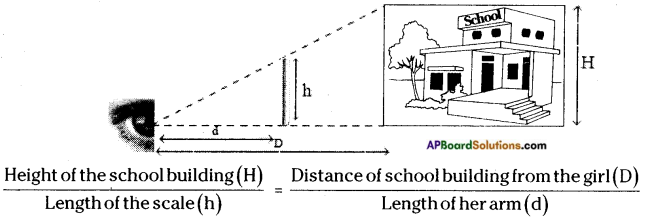
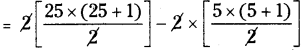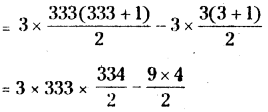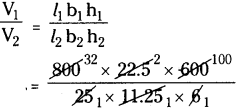AP State Syllabus 8th Class Maths Solutions 13th Lesson Visualizing 3-D in 2-D InText Questions
AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 13 Visualizing 3-D in 2-D InText Questions and Answers.
8th Class Maths 13th Lesson Visualizing 3-D in 2-D InText Questions and Answers
Do This
Question 1.
Name some 3 – Dimensional objects. [Page No. 282]
Answer:
- Cube
- Cylinder
- Sphere
- Cuboid
- Cone
![]()
Question 2.
Give some examples of 2 – Dimensional objects. [Page No. 282]
Answer:
- Square
- Rectangle
- Line segment
- Circle
- Triangle
Question 3.
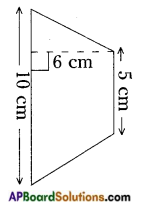
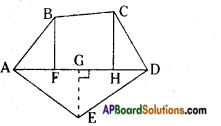
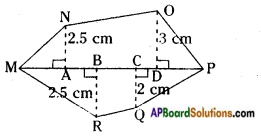
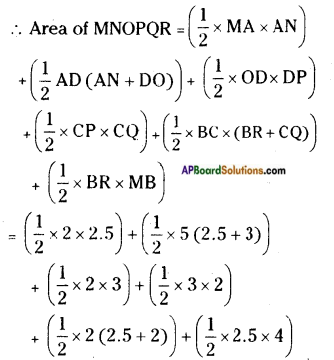
Draw a kite in your notebook. Is it 2 – D or 3 – D object? [Page No. 282]
Answer:
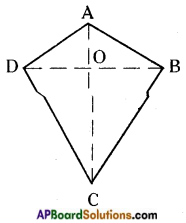
Kite is a 2 – D object.
Question 4.
Identify some objects which are in cube or cuboid shape. [Page No. 282]
Answer:
Shapes of Cube Shapes of Cuboid
a) Chalk piece box a) Duster
b) Dice b) Cell phone (Cuboidal in shape)
c) Cube shaped cake c) Plasma T.V.
Question 5.
How many dimensions that a circle and sphere have? [Page No. 282]
Answer:
Circle has 2 dimensions.
Sphere has 3 dimensions.
![]()
Question 6.
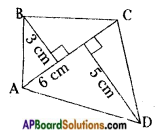
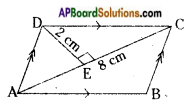
Identify the faces, edges and vertices of given figures. [Page No. 288]
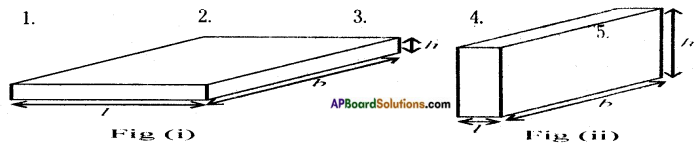
Answer:
Question 7.
Write the names of the prisms given below: [Page No. 290]
Answer:
(i) Cube
(ii) Triangular prism
(iii) Pentagonal prism
(iv) Hexagonal prism
(v) Rectangular prism
Question 8.
Write the names of the pyramids given below: [Page No. 290]
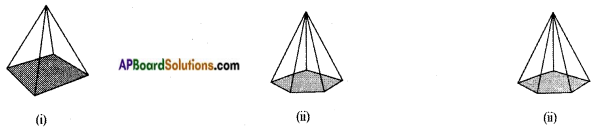
Answer:
(i) Square pyramid
(ii) Pentagonal pyramid
(iii) Hexagonal pyramid
![]()
Question 9.
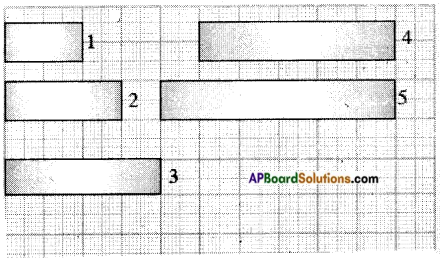
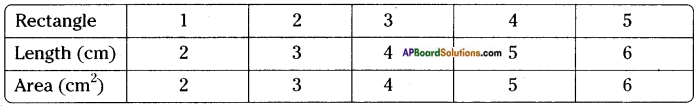
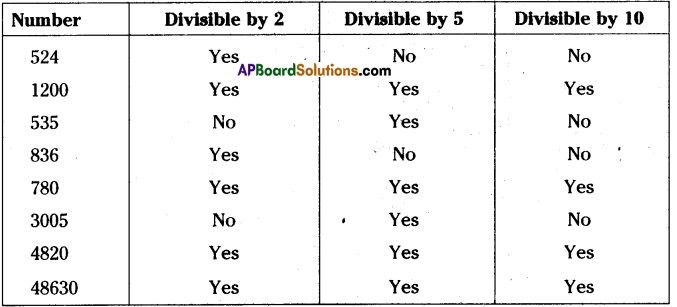
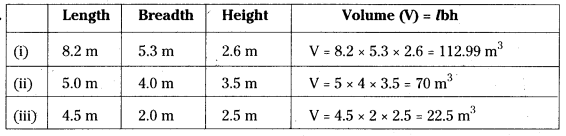
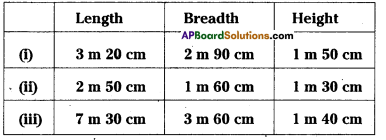
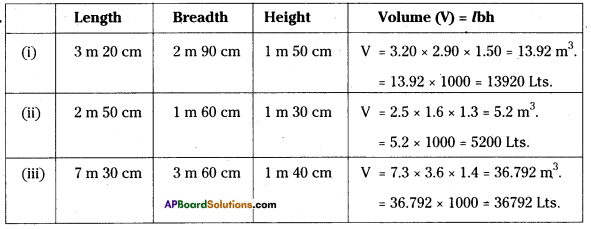
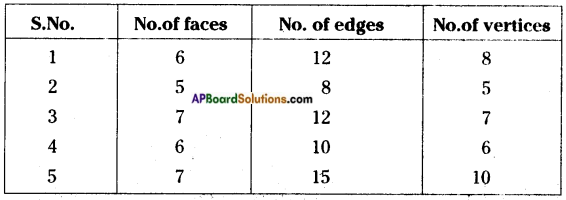
Fill the table: [Page No. 290]
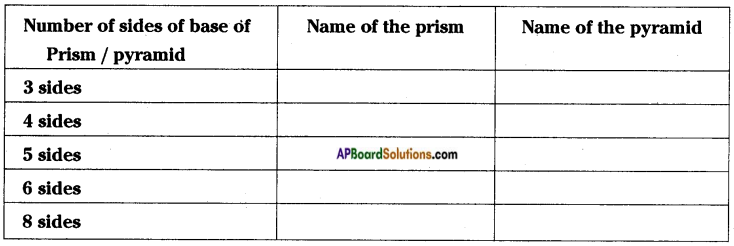
Answer:
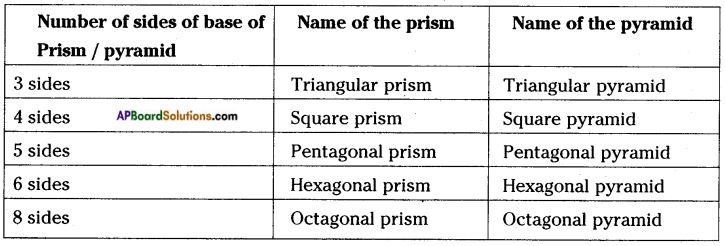
Question 10.
Explain the difference between prism and pyramid. [Page No. 290]
Answer:
Upper and lower sides of a prism are equal in number. But, in a pyramid the base is a plane and all the edges are coincide in a single point on the top.
Try These
Question 1.
Name three things which are the examples of polyhedron. [Page No. 287]
Answer:
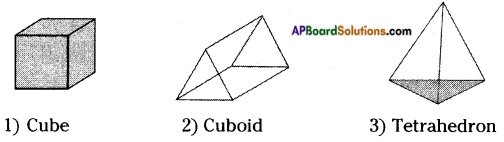
![]()
Question 2.
Name three things which are the examples of non-polyhedron. [Page No. 287]
Answer:
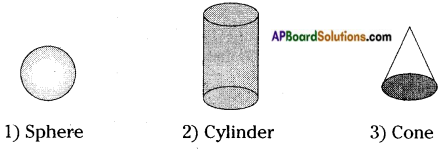
Think, Discuss and Write
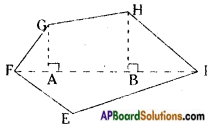
Question 1.
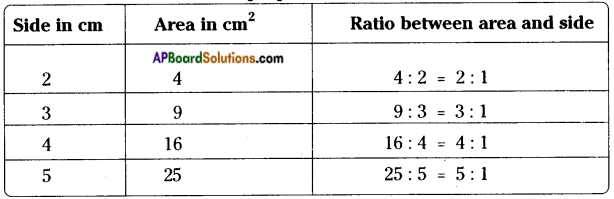
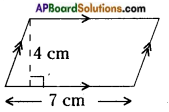
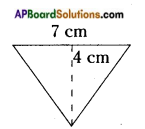
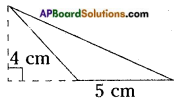
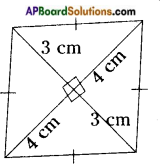
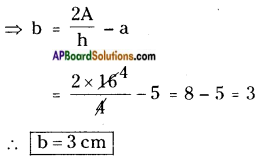
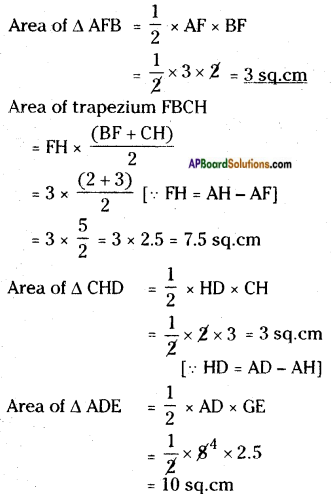
How to find area and perimeter of top view and bottom view of the given figure. [Page No. 283]
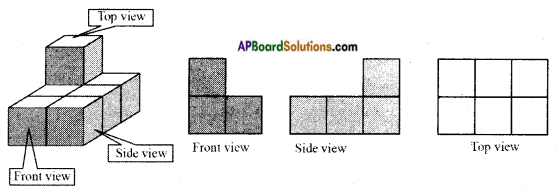
Answer:
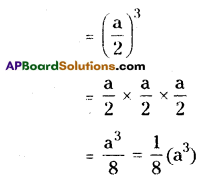
Let the side of each face be ‘1’ unit say.
Shapes of different positions (I) Their areas (II)
1. Front view A = (1 × 1) + (1 × 1) + (1 × 1) = 3 Sq. Units
2. Top view A = (1 + 1 + 1) × (1 + 1) = 3 × 2 = 6 Sq. Units
3. Bottom view A = (1 + 1 + 1) × (1 + 1) = 3 × 2 = 6 Sq. Units
Perimeters (III)
1. —————> 1 + 1 + 1 = 3 Units
2. —————> 2(l + b) = 2 (3 + 2) = 2 × 5 = 10 Units
3. —————> 2(l + b) = 2 (3 + 2) = 2 × 5 = 10 Units