AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 6 Sense Organs.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Biology Important Questions 6th Lesson Sense Organs
9th Class Biology 6th Lesson Sense Organs 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How many sense organs are present in human beings? What are they?
Answer:
We have five sense organs.
They are :
1. Eye
2. Ear
3. Nose
4. Tongue
5. Skin.
Question 2.
What are the main parts of an eye?
Answer:
Our eye contains eyelids, eye lashes, eyebrows and lachrymal glands.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the three layers that covers an eye?
Answer:
Eye has three main layers. They are sclerotic layer or sclera, choroid layer and retina.
Question 4.
How eye is different from other sense organs?
Answer:
The unique characteristic of the eye that makes it different from other sense organs, lies in its ability to take the information from light waves then transforms the characteristics of light into neutral signals that the brain can process.
Question 5.
What are the recent findings regarding the structure of eye?
Answer:
Presence of some other receptor cells sensitive to edges and boundaries of objects and those that respond to light and shadow and motion in the retina have been reported recently.
Question 6.
How iris patterns are useful to issue ‘AADHAR’?
Answer:
Iris patterns are individual specific and can be used for identification as our finger prints.
Question 7.
Write about the diseases and defects of the eye.
Answer:
The main diseases and defects of the eye are night blindness, Xeropthalmia, myopia (Near sightedness, hypermetropia (far sightedness), glaucoma, cataract and colour blindness.
Question 8.
What are the functions of ear?
Answer:
- To collect and transform vibrations produced by sound to nerve impulses to be carried to the brain.
- To maintain balance or equilibrium.
Question 9.
What are the uses of hairs and mucous in the nasal cavity?
Answer:
The hairs and mucous in the nasal cavity kept dust, germs and other unwanted materials away from gaining entry into our bodies through the nose.
![]()
Question 10.
How do we see movies?
Answer:
The impression of an image stay in the retina for about 1/16th of a second. If the still images of an object are flashed at the rate faster than 16 per second, the eye receive it as moving. In this way we see movies.
Question 11.
How do we take care of our skin?
Answer:
- Taking bath regularly
- Use soap to clean the body
- In any redness, itching, discoloration and rashes appear we consult the dermatologist,
Question 12.
Write two diseases of skin.
Answer:
Leprosy, chicken pox, measles, leucoderma, pellagra etc.
Question 13.
You entered into a darkroom from outside which is very bright. What happens?
Answer:
We can not see anything in the dark room for sometime because Iris size is very small.
Question 14.
Why coffee tastes less sweet if it is taken after eating sweet?
Answer:
Because a higher level of the same stimulus masks that of the lower level.
Question 15.
What changes the focal length of the eye lens?
Answer:
Ciliary muscles and suspensor ligaments adjust the focal length of the eye lens.
Question 16.
What is the main function of the cornea?
Answer:
Cornea protects the eye from direct exposure to light.
Question 17.
What are the main function of melanin?
Answer:
- The colour of the skin is due to the presence of ’Melanin”.
- Due to this, the skin is sensitive to touch, temperature and pressure.
![]()
Question 18.
What are the important functions of our ear?
Answer:
a) Hearing
b) Maintaining equilibrium of the body.
Question 19.
What is MSG?
Answer:
Monosodium Glutamate (Huching) often used in Asian cuisine
9th Class Biology 6th Lesson Sense Organs 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is stimulus? How the information from surroundings reaches the brain?
Answer:
- Something external that influences an activity is called stimulus.
- Information carried by these stimuli are picked up by the certain organs called as receptors.
- The receptors present in sense organs convert the information into nerve signals.
- Nerve signals are carried by sensory nerves to the brain and processed to create a sensation.
Question 2.
What are photoreceptors? How they sense light?
Answer:
- The real work in the retina is performed by light sensitive cells known as photore-ceptors.
- These receptors consists of two different types of specialised cells the rods and cones that absorb light energy and respond by creating nerve impulse.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a short note on rods of retina.
Answer:
- Nearly 125 million tiny rods are present in the retina.
- Rods contain the pigment rhodopsin. which defect low intensities of light at night.
- Rods cannot make the fine distinctions that give rise to our sensations.
Question 4.
Write briefly about cones of retina.
Answer:
- Cones contain a pigment called idopsin which helps in identifying colours in bright light.
- Cones are about 7 million in number and concentrate most in the very centre of the retina in a small region called fovea, which gives us sharp vision.
Question 5.
How eyes are protected?
Answer:
- Eye is protected by eyelids, eye lashes, eyebrows and lachrymal or tear glands.
- The protective cover conjunctiva covers the front part of the eye.
- Lachrymal glands wash the unwanted substances out of the eye.
- The fluids present in the eyeball protect the lens and other part of the eye from mechanical shocks.
- Cornea protects eye from direct exposure to light.
![]()
Question 6.
Write briefly about middle ear.
Answer:
- Middle ear plays an important role in amplifying the vibrations received on the tympanum membrane.
- The chain of three bones malleus, incus and stapes helps to the same.
- Oval window is a membrane, covered ending of the middle ear, it opens into the inner ear through round window.
Question 7.
What is the sensory nature of skin?
Answer:
- Skin is sensitive to touch, temperature and pressure.
- It contains the separate receptors such as tactile receptors for touch, pacinian corpuscles for pressure, nocireceptors for temperature etc.
Question 8.
What is melanin? What is its function?
Answer:
- Melanin is the pigment present in skin.
- This pigment gets stimulation, when exposed to sunlight.
- The skin becomes dark to protect other layers of the skin from harmful effects of light.
Question 9.
What illusions tells us about sensation?
Answer:
- When our mind deceives us by interpreting a stimulus pattern incorrectly, we are experiencing an illusion.
- Such illusions can help us to understand some fundamental properties of sensation and particularly the descripancy between what we see and external reality.
Question 10.
Identify the iabelled parts of the tongue.
Answer:
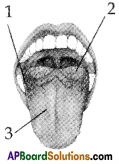
1) Foliate papillae
2) Vallate papillae
3) Fungi form papillae
Question 11.
What are the different receptors present in the skin?
Answer:
a) Tactile receptors for skin
b) Pacinian corpuscles for pressure
c) Nociceptors for temperature etc.
Question 12.
What happens when light is thrown on the face of your friend?
Answer:
My friend immediately closes his/her eyes because of the light. This is because the eye gets damaged if more light enters inside at a time.
9th Class Biology 6th Lesson Sense Organs 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is the centre for ail the sensitive activities? How it interpret the information? Give example.
Answer:
- Brain is the centre for all the sensitive activities.
- It receive information in the form of nerve signals through sensory nerves.
- It interpret the information sends off signals through another type of nerves called as motor nerves.
- Motor nerves take the signals to parts that show response.
- For example, when a mosquito bits you on your leg the sensation is carried to the spinal cord through sensory nerves.
- The spinal cord sense the message to the hand to kill the mosquito through motor nerves. Then we kill it.
Question 2.
Describe the structure of an eye with a neat diagram.
Answer:
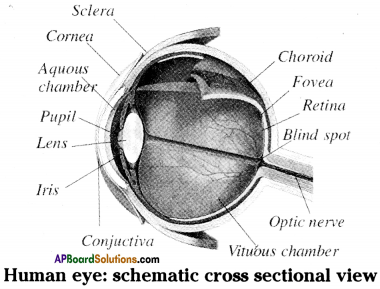
- Our eye contains eyelids, eye lashes, eyebrows and lachrymal glands.
- A thin layer called conjunctiva covers the front portion of the eye.
- The eyeball is located in the eye socket only 1/6 portion of the eyeball is invisible to us.
- Eye has three main layers. They are sclerotic layer or sclera, choroid layer and retina.
- The sclera bulges to form cornea.
- The end of sclera connects to the optic nerve.
- The choroid layer is black in colour and contains lot of blood vessels.
- Choroid layer encloses the eye except the part pupil.
- The part formed by the choroid layer around the pupil is iris.
- Biconvex lens is present behind the pupil.
- The lens divides the inner eyeball as aqueous chamber and vitreous chamber.
- Retina contains the cells called rods and cones.
- The area of no vision called blind spot and the area of the best vision called yellow spot are present in the retina.
- The yellow spot is also called macula or fovea.
![]()
Question 3.
Write about the functioning of an eye.
Answer:
- The eye gathers light through convex lens, focusses it and forms an image in the retina at the back of the eye.
- The lens turns the image left to right and upside down.
- Brain tends to maintain this reversal in its sensory processing regions.
- Most information from the sense organs crosses over to the opposite side of the brain.
- In the brain’s sensory areas are typically reversed and inverted.
- The eye forms an image that gets extensive further processing in the brain.
Question 4.
Write a short note on external ear.
Answer:
- External ear is a flap like structure, called the pinna.
- Pinna has wax producing ceruminous glands and oil producing sebaceous glands.
- These help to keep the ear canal lubricated prevent the dust and other particles from entering into the ear canal.
- The ear canal is also called auditory meatus.
- A thin layer called tympanum or ear drum is present at the end of the auditory meatus.
- Ear drum is present in between external and middle ear. It is in the shape of a cone.
- Its narrow area connects to the first bone malleus of the middle ear.
Question 5.
Write briefly about inner ear.
Answer:
- Internal or inner ear consists of bony labyrinth enclosing the membranous labyrinth.
- The membranous labyrinth consists of vestibule, three semicircular canals and cochlea.
- The anterior part of the vestibule is sacculus and the posterior part is utriculus.
- Nerve fibres from them form vestibular nerve.
- Vestibule and semicircular or semilunar circles together form vestibular apparatus.
- Vestibular apparatus maintains the equilibrium of the body, pertaining to the posture and balance of the body.
- Cochlea is a spiral shaped structure. It has three parallel tubes called scala vestibuli, scala media and scala tympani.
- Cochlear nerve fibres form cochlear nerve.
- The vestibular and cochlear nerves join together to form auditory nerve.
Question 6.
How the hearing or auditory sensation occurs?
Answer:
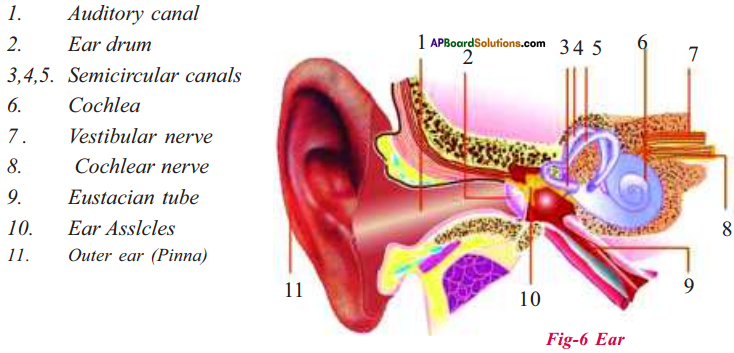
- External ear collect the sound waves. They enter into the auditory meatus.
- Then they strike tympanum. The vibrations from tympanum reach the malleus, incus and stapes.
- They magnify the intensity of the sound vibrations.
- The stapes transmits the vibrations to the membrane of oval window.
- Then they transmit to the cochlea.
- The basillar membrane is moved then the vibrations reach to the organ of corti.
- The impulses are sent to the brain through auditory nerve.
- The hearing can be done according to the responses given by the brain.
Question 7.
Write a short note on the structure of nose.
Answer:
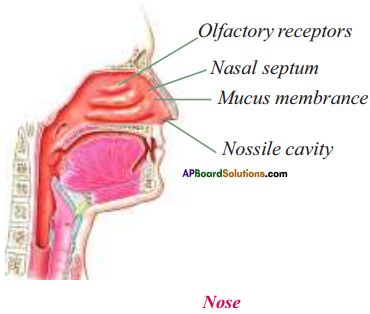
- Our external nose has two nostrils. They lead to nasal cavity.
- Nasal septum divides the nasal cavity into two halves.
- The nasal cavity is lined with mucous membrane and small hairs.
- Olfactory receptors are present in the mucous membrane.
Question 8.
What are the different kinds of structures that are seen on our tongue?
Answer:
- We can clearly see flake like structures called the filiform papillae.
- The roundish structures on the tongue are fungiform papillae.
- There are large roundish ones at the back of the tongue are circumvallate papillae.
- On the sides of the tongue are the bump like structures are foliate papillae.
- Taste buds are present on all of these except the fili form papillae that are not the sites of taste sensation.
Question 9.
Write a short note on skin.
Answer:
- Skin is the outermost covering of our body.
- It regulates the body temperature and eliminates certain waste material through sweat.
- It is the sense organ of touch.
- The sense of touch is done by the cutaneous receptors.
- It is the largest organ of all.
- It provides the first level of protection to the body.
![]()
Question 10.
What are the diseases effecting the skin?
Answer:
Some of the diseases effecting the skin are
- Viral diseases such as measles, chicken pox etc.
- Bacterial diseases such as leprosy.
- Leucoderma, the disease due to the deficiency of melanin.
- Pellagra the disease due to deficiency of vitamins.
- Fungal diseases such as ringworm.
Question 11.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram showing the structure of the skin.
Answer:
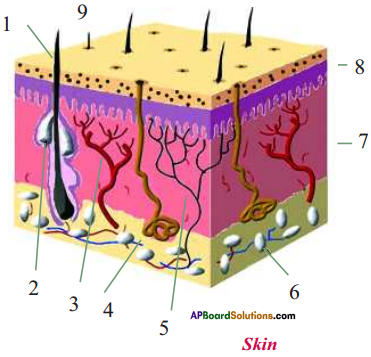
- hair
- oil gland
- blood vessel
- sweat gland
- nerve
- fat lobules
- endodermis
- epidermis
- pore
Question 12.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram showing the structure of nose.
Answer:

Question 13.
Draw a neat and labelled diagrams showing Rods and Cones of the eye.
Answer:
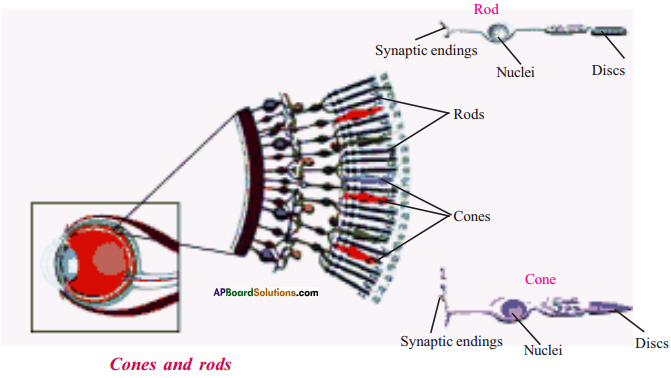
9th Class Biology 6th Lesson Sense Organs Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Look at the following picture. Label the parts 1, 2, 3, 4 and answer the following questions.
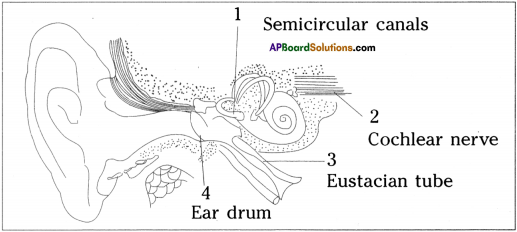
1) Ear is broadly divided into how many parts?
2) Name the bones of middle ear in correct order.
3) Which part of ear vibrates on receiving sound waves?
4) Name the part of ear that is associated with balancing.
Answer:
- 3 parts. They are
a) External ear
b) Middle ear and
c) Internal ear - Malleus, incus, stapes
- Ear drum
- Vestibular apparatus.
Question 2.
What happens if our tympanum ruptured?
Answer:
- If tympanum (or) ear drum is damaged, the sound vibration will not reach the auditory nerve. Hence, it will not carry the hearing impulses to the brain.
- Deafness will occur.
Question 3.
Draw a labelled diagram of eye. What happens if there are no cones in eye?
Answer:

- Cones are very useful in identifying different colours. They are responsible for bright light vision.
- If cones are absent, we can’t identify the array of colours and see in bright light.
Question 4.
Explain how skin works as a sense organ.
Answer:
- Skin is the largest sense organ in our body.
- It gives us the sense of touch which has supreme importance in the sphere of senses.
- It provides the first level of protection to the body.
- Skin is sensitive to touch, temperature and pressure. It contains the separate receptors such as tactile receptors for touch, pacinian corpuscles for pressure nociceptors for temperature, etc.
- By the above reasons, we can say that skin is a sense organ.
![]()
Question 5.
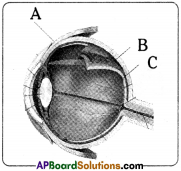
1. Label A, B and C.
2. What is the function of lens?
3. Name the cells present in Retina.
4. Give examples of two defects of eye.
Answer:
- A) Sclera
B) Choroid
C) Retina - The eye gathers light through a convex lens, focuses it and forms an image in the retina at the back of the eye.
- Rods and cones are the specialised cells present in Retina.
- Night blindness, glaucoma, cataract, dry eye, etc.
Question 6.
Observe the figure and answer the following questions.
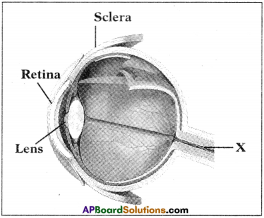
a) Correct the wrongly labelled ones.
b) What is the function of X?
c) There are two types of photo receptors in the Retina of human eye. What are they?
Answer:
a) Retina
b) The denoted part x’ is optic nerve. Optic nerve carries the information of the object seen to brain.
c) Rods and cones are the two types of photo receptors present in human eye.