AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Biology Solutions Chapter 4 Movement of Materials Across the Cell Membrane Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Biology Solutions 4th Lesson Movement of Materials Across the Cell Membrane
9th Class Biology 4th Lesson Movement of Materials Across the Cell Membrane Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
The structure which controls the entry and exit of the materials through the cell is
A) Cell wall
B) Cell membrane
C) Both
D) None of them
Answer:
Cell membrane.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks.
a) The smell of flowers reaches us through the process of …………………..
Answer:
Diffusion
b) The MIC gas of Bhopal tragedy was spread throughout the city through the process of …………………
Answer:
Diffusion
c) Water enters the potato osmometer due to a process called ………………
Answer:
Osmosis
d) The fresh grape wrinkles, if kept in salt water because of …………………
Answer:
Osmosis
![]()
Question 3.
What do you mean by permeability of membrane? Explain with suitable example.
Answer:
Allowing only certain materials to pass through the membrane is called permeability.
Example :
- The cell membrane is very much permeable to gases such as carbondioxide, oxygen, nitrogen and fat solvent compounds such as alcohol, ether and chloroform.
- It is impermeable to polysaccharides, phospholipids and proteins.
Question 4.
If the dried vegetables are kept in water they become fresh. What is the reason?
Answer:
- The dried vegetables have less water content and high salt concentration in cells.
- When they are kept in water they absorb water and become fresh.
- The water enter into the vegetables by a process known as osmosis.
Question 5.
Name the process by which we can get fresh water from sea water.
Answer:
Reverse Osmosis.
![]()
Question 6.
What will happen to a marine fish if kept in fresh water aquarium? Support your answer with reasons.
Answer:
The marine fish dies.
Reasons:
- Usually marine fishes have high concentration of salts in their body.
- When they are kept in fresh water, the water from the fresh water aquarium enters the body of fishes due to osmosis.
- More amount of fresh water enters the cells of fish. This results in bursting of cells and fish dies.
Question 7.
Why do the doctors administer saline (salt solution) only, but not the distilled water?
Answer:
- Distilled water causes cells to lyse, so injecting distilled water into a vein will cause some degree of haemolysis.
- Haemolysis is the rupture of red blood cells.
- Large amount of distilled water would cause much more damage not just limited to haemolysis and also cause brain damage or cardiac arrest and death.
- That is why fluids are administered to patients as saline (which include appropriate amount of salt)
![]()
Question 8.
What will happen if 50% glucose solution (dextrose) is injected intravenously (into vein)?
Answer:
- 50% glucose solution (dextrose) is used for reduction of increased cerebrospinal pressure and cerebral edema.
- If 50% glucose solution is injected intravenously it may produce allergic reactions in sensitive persons.
- The allergic reactions include nervous excitement infection at the joint site, tissues necrosis, venous thrombosis extending from the site of injection etc.
- Hence concentrated dextrose (glucose) should be administered via central vein only after suitable dilution.
Question 9.
What will happen if cells do not have ability of permeability?
Answer:
- If the cells do not have ability of permeability they would not be able to carryout any of their fundamental life functions.
- Oxygen, glucose, fats, proteins and vitamins are needed by cells to perform life process.
- Mature cells become impermeable to any molecules or atoms it would die of toxicity and it would not be able to remove its wastes.
Question 10.
Draw the flow chart showing different stages in doing the experiment with egg.
Answer:

Question 11.
You have purchased a coconut in the market. By shaking it you found there is less water in coconut. Can you fill the coconut with water without making a hole to the coconut?
Answer:
- No, it is not possible to fill the coconut with water without making a hole.
- The husk of coconut is mostly made up of sclerenchymatous cells which are dead.
- Osmosis do not takes place in dead cells.
- It is not possible to fill the coconut with water without making a hole.
![]()
Question 12.
What are your observations in experiments to know about diffusion?
Answer:
Observations in experiments to know about diffusion are :
- Materials kept in medium (water/air) get dissolves in the medium.
- These dissolved molecules gradually move randomly in all directions. (from center to periphery)
- They move from higher concentration to lower concentration.
- This movement occures till these molecules spread equally throughout the medium.
Question 13.
Discuss with your friends and write the list of incidences where diffusion occurs.
Answer:
- A sugar cube in a glass of milk/water diffuses throughout it and make it sweet.
- The smell of cookies diffuses through the house as they bake.
- Tea leaf pigments diffuse through the tea bag into the water to give it colour and taste.
- Air freshner/deodorent molecules diffuse into the air when put on so we can smell it.
- If the cooking gas is leaked it spreads all over the house through diffusion.
- CO2 bubbles in soft drink diffuses out of soda leaving the soda flat.
- Robbin Blue drops diffuses in water, making the water blue.
- Agarbatti, mosquito repellents work on the principle of diffusion.
Question 14.
How diffusion is useful in everyday life?
Answer:
- A wilted carrot made firm again by soaking in water.
- Cigarette smoke. It diffuses into air and spreads through the room.
- A sugar cube in a glass of water that is not stirred will dissolve slowly and the sugar molecules will distribute over the water by diffusion.
- The smell of cookies diffuses through the house as they bake.
- Tea leaf pigments diffuse through the tea bag to give the water its colour and taste of tea.
- Air freshner / deodorant molecules diffuse into the air when put on. So we can smell it.
- If the cooking gas is leaked, it spreads all over the house through diffusion.
- CO2 bubbles in soft drink diffuses out of our soda leaving our soda flat.
- Air freshners, agarbatti, mosquito repellents work on the principle of diffusion.
![]()
Question 15.
Give examples of three daily life activities in which osmosis is involved?
Answer:
- Water enters into the roots through osmosis.
- In our body waste materials are filtered from the blood.
- Osmosis helps in the opening and closing of stomata.
9th Class Biology 4th Lesson Movement of Materials Across the Cell Membrane Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
Look at the substances in the table identify the (✓) substances that should go into the cell and should go out of the cell?
Answer:
| Substance | Should go into the cell | Should go out of the cell |
| Oxygen | ✓ | |
| Glucose | ✓ | |
| Proteins | ✓ | |
| Fats | ✓ | |
| Vitamins | ✓ | |
| Minerals | ✓ | |
| Carbondioxide | ✓ | |
| Wastes | ✓ |
Procedure :
- Keep the raw eggs in dil HCl / toilet cleaning acid for 4 to 5 hours.
- Take out the egg with the help of table spoon.
- Wash the eggs under tap water.
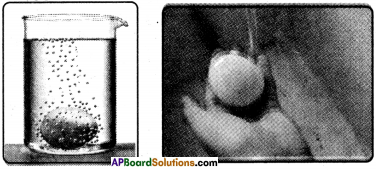
- Measure the circumference of each egg with long strip of paper, as its widest place, and mark on the paper with pen or pencil.
- Prepare a concentrated salt solution in a beaker.
- Place one egg in the beaker with tap water and place the other in the salt water.
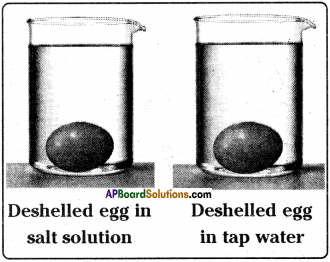
- Leave the beakers for 2 to 4 hours.
- Take the eggs out, wipe them and measure the circumference with the same strip of paper. Mark on the paper with pen or pencil.
Observation :
The egg placed in salt water shrinks, the egg placed in the tap water swells.
Result:
- Shrinking of egg placed in the salt water is due to exosmosis in which water molecules leave the cell.
- Swelling of egg placed in the tap water is due to endosmosis in which water molecules enter the cell.
Lab Activity – 3
Question 2.
Prepare semi-permeable membranes and conduct an experiment to prove osmosis with it.
Answer:
Preparing semi-permeable membranes.
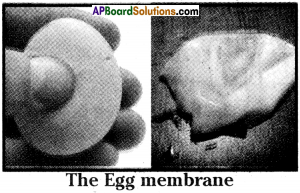
- Take two raw eggs.
- Keep the two eggs in dil. HCl for 4 to 5 hours.
- The shells which are made of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) are dissolved.
- Wash the eggs under tap water.
- Carefully pierce a pencil sized hole in the egg membrane and drain the contents.
- Wash the membrane with fresh water. Now the semi-permeable membrane is ready for use.
Experiment of osmosis with egg membranes :
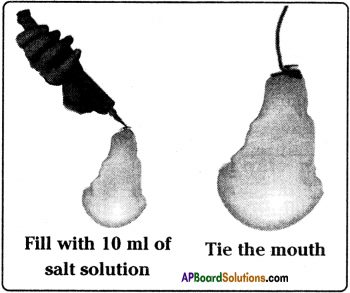
Aim :
To prove osmosis through semi- permeable membrane of an egg.
Materials required :
Two egg membranes, three beakers, sugar, water, thread, measuring jar, disposable syringe.
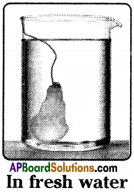
Procedure :
- Take one egg membrane and fill it with 10 ml of saturated sugar solution with a syringe.
- Tie its mouth with a thread.
- Measure 100 ml of tap water in a beaker.
- Keep the egg membrane in fresh water beaker.
- Leave it for overnight.
- Take the second egg membrane and fill it with 10 ml of tap water with the syringe.
- Prepare 100 ml of saturated sugar solution and keep the egg membrane in it.
- Leave it for overnight.
- Measure the contents of the egg membranes and beakers.
Observations:
- Water entered into the egg membrane in which sugar solution is filled. So size of the membrane increased.
- Water left from the egg membrane in which water is filled. The size of the membrane decreased.
Result: Water move across membranes from solutions of one concentration to the other through a process called osmosis.
Activity – 4
Question 3.
How do you observe the diffusion of coffee powder in water? Write your findings.
Answer:
- Take half bowl water.
- Prepare a small ball of coffee powder.
- Slowly put in water and observe.
Observations:
- The ball of coffee powder starts dissolving in water.
- The water around the coffee powder will appear dark in colour.
- As time progresses, all the water in the beaker becomes coloured.
- Initially pale in colour and slowly all the water in the beaker becomes uniformly coloured. Coffee powder molecules diffuse into the water forming uniform colour.
Activity – 5
Question 4.
Observe the diffusion of potassium permanganate in water. Write your findings.
Answer:
- Keep a crystal of KMNO4 (Potassium permanganate) in the centre of the petridish with the help of a forceps.
- Carefully fill the petridish with water.
- Observe the movement of pink colour in the petridish every minute.
- Also observe the spreading of colour from centre to periphery.
Observations:
- Potassium permanganate crystal starts dissolving in water.
- The water around the crystal will appear in pink colour.
- As time progresses all the water in the beaker becomes coloured.
- Initially pale in colour and slowly all the water in the beaker become uniformly pink coloured.
Diffusion :
The permanganate molecules moves from higher concentration to lower concentration in water through diffusion.
Activity – 6
Question 5.
How do you observe the diffusion of copper sulphate in water? Write your findings.
Answer:
- Keep a small crystal of copper sulphate in the center of the petridish with the help of a forceps.
- Carefully fill the petridish with water.
- Observe the movement of blue colour in the petridish every minute.
- Also observe the spreading of colour from centre to periphery.
Observations :
- Copper sulphate crystal starts dissolving in water.
- The water around the crystal will appear in blue color.
- As time progresses, all the water in the beaker becomes coloured.
- Initially pale blue in colour and slowly all the water in the beaker becomes uniformly blue in color.
Diffusion :
The copper sulphate molecules move from higher concentration to lower concentration in water through diffusion.