AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Physical Science Solutions Chapter 10 Reflection of Light at Plane Surfaces Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Physical Science Solutions 10th Lesson Reflection of Light at Plane Surfaces
8th Class Physical Science 10th Lesson Reflection of Light at Plane Surfaces Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
State the laws of reflection of light (OR)
Name the laws of reflection of light
Answer:
Laws of reflection:
- When light gets reflected from a surface, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence, i.e., ∠i = ∠r.
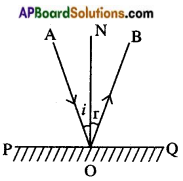
- The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray lie in the same plane, i.e., AO, ON, OB are in same plane.
![]()
Question 2.
How do you verify the 1st law of reflection of light with an experiment?
(OR)
Raghu found that for a plane mirror angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Write the experiment to prove this fact. (OR)
Prove: ∠i = ∠r (LAB ACTIVITY – 1)
Answer:
Aim: Verification of first law of reflection.
Required materials: Mirror strip, drawing board, white paper, pins, clamps, scale and pencil.
Procedure:
- Take a drawing board and fix a white paper on it with the help of clamps.
- Draw a straight line AB at the centre of the paper and also a normal (ON) to AB at the point ‘O’.
- Draw a straight line PQ making certain angle (angle i) with ON.
- Fix two pins at P and Q on the paper vertically.
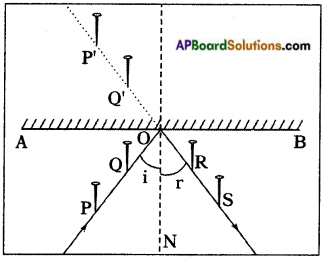
- Observe the images of pins – P’ of the pin P and Q’ of the pin Q, in the mirror kept along the line segment AB.
- Fix two more pins R and S such that they are in the same line as that of P’ and Q’.
- Join R, S and 0 as shown in figure.
- Measure the angle between RS and ON (angle of reflection).
- We will find that ∠i = ∠r. (angle of incidence = angle of reflection)
- Repeat the experiment with different angles of incidence and measure the corresponding angles of reflection.
- We can find angle of incidence = angle of reflection in all these cases.
Thus first law of reflection is proved.
Question 3.
How do you verify the 2nd law of reflection of light with an experiment?
(OR)
John found that incident ray, reflected ray and normal drawn to surface lie on the
same plane. What are the apparatus required for this experiment? How are you able to prove this fact experimentally?
Answer:
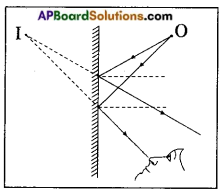
2nd Law of reflection: The incident ray, the reflected ray and normal all lie in the same plane.
- As shown in the figure, a light ray incident on a plane mirror and touches at a point ‘O’. Here AO is called incident ray.
- When a ray of light falls on a mirror, the mirror sends it back in another direction OB. Here OB is called reflected ray.
- Normal is a line which is perpendicular to the mirror at the point of incidence. So the line ON’ is the normal to the mirror surface at point ‘O’.
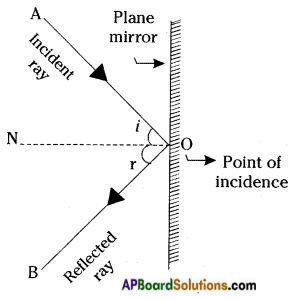
- Here the incident ray (AO), the reflected ray (OB) and the normal (ON) all lie in the same plane of the paper.
Hence 2nd law of reflection is proved.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the image formation by pin hole camera with the help of the diagram.
(ACTIVITY – 1)
Answer:
- Draw a ray diagram of the formation of an image in a pinhole camera.
- Observe the flame of a candle with a pinhole camera making a big hole to it.
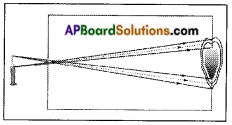
- We can understand that the light rays coming from the top of the candle flame fall at different points on the screen.
- Similarly, the rays coming from bottom of the candle points on the screen.
- Thus, we get blurred image on the screen due to the big hole of the camera.
Question 5.
Find the plane of the reflection experimentally for the incident ray which passes through the heads of the pins pierced in front of the mirror.
(OR)
Sudheer wants to verify the laws of reflection. What apparatus he requires to prove them? State the laws of reflection and write the experimentation process he follows.
Answer:
Aim: Verification of laws of reflection.
Required material: Mirror strip, drawing board, white paper, pins, clamps, scale and pencil.
Procedure:
- Take a drawing board and fix a white paper on it with the help of clamps.
- Draw a straight line AB at the centre of the paper and also a normal (ON) to AB at the point ‘O’.
- Draw a straight line PQ making certain angle (∠i) with ON.
- Fix two pins at P and Q on the paper vertically.
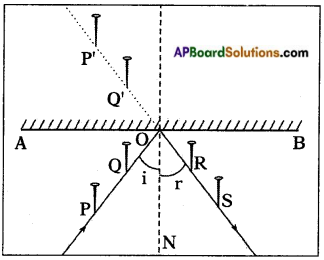
- Observe the image P’ of the pin P and Q’ of the pin Q, in the mirror kept along line segment AB.
- Fix two more pins R and S such that they are in the same line as that of P’ and Q’.
- Join R, S and O.
- Measure the angle between RS and ON (∠r) .We will find ∠i = ∠r.
- Repeat the experiment with different angles of incidence and measure the corresponding angles of reflection.
- We find that each case angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. That is first law.
- We can find that the incident ray is the ray which is passing through points P and Q touching the paper.
- The reflected ray is the ray which is passing through the points R and S touching the same paper and ON is the normal to the mirror at O. All lie in same plane. That is second law which states incident ray, reflected ray and normal drawn to plane lie in the same plane.
![]()
Question 6.
Have you ever observed the image of the sky in rain water pools on earth? Explain the reflection of light in this context.
Answer:
Surface of the rain water pool acts as a plane mirror, because of its smooth surface. The light rays from the sky and clouds incident at this surface and reflect. Hence, the images of the sky and clouds appear in the rain water pools.
Question 7.
Discuss the merits and demerits of using mirrors in building elevation.
(OR)
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using mirrors in building elevation?
Answer:
Merits:
- The mirrors used in elevating building are tough, reinforced and laminated glasses so they provide safety to the building.
- They make the building attractive.
- They absorb heat energy, so they cool inside the building.
- If we use plane mirrors in building elevation it is easy to wash with water and no need of regular painting.
Demerits:
- Elevation of buildings with mirrors is not suggestable.
- These mirrors reflect sun rays at day time and reflects lighting from near by electrical bulbs at night time, which causes confusion and disturbance for the vehicles and people who are running on the nearby roads lead to accidents.
- Birds like sparrows, crows will get confusion while flying on roads.
- They are also not safe enough to the buildings, which causes easy access to thieves.
- This glass elevation is not environmental friendly, because natural air does not enter into the building.
- They are easy to break and cause cuts and wounds.
Question 8.
If a ray incidence normally on a plane mirror, what will be the angle of reflection.
Answer:
If a ray incidence normally on a plane mirror, the angle of reflection will be zero.
![]()
Question 9.
Why does the image in plane mirror suffers lateral inversion?
Answer:
The light rays which come from our right side get reflected from the plane mirror reach our eye. Our brain feels that the rays is coming from the inside of the mirror. That is why our right side looks like left side in the image. This is called right-left inversion or lateral inversion.
Question 10.
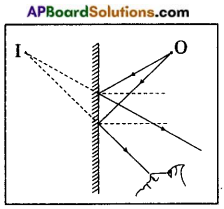
Draw a ray diagram to understand the formation of image for a pointed object by a plane mirror explain it.
Answer:
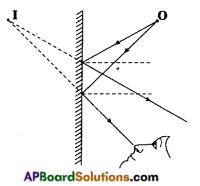
Observe the figure. ‘O’ is a point object.
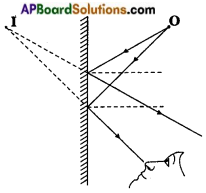
Some rays from ‘O’ reach the mirror and get reflected. When we look into the mirror, the reflected rays seem to be coming from the point T. So, point I is the image of point object ‘O’.
Question 11.
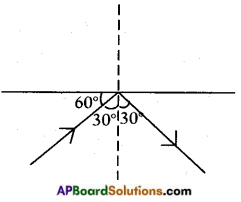
In the adjacent figure, AO and OB are incident and reflected rays respectively angle ∠AOB = 90°. Find the values of angle of incidence and angle of reflection.

Answer:
We know that angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
i = r …….. (1)
From the figure, ∠AOB indicates i + r = 90°
From (1)
⇒ i + i = 90°
2i = 90°
⇒ i = 90/2 = 45°
⇒ i = r = 45°
Angle of incidence i = 45°; Angle of reflection r = 45°.
![]()
Question 12.
Hinduja stands in front of a plane mirror at a distance of 5 m. from the mirror and observes her image in the mirror. If she moves 2 m. towards the plane mirror, then what will be the distance between Hinduja and his image?
Answer:
The distance between plane mirror and Hinduja = 5 m
The distance between plane mirror and Hinduja after moving 2 m towards mirror
= 5 – 2 = 3 m …….. (1)
The distance between plane mirror and Hinduja’s image after moving = 3 m …….. (2)
The distance between Hinduja and her image after moving = (1) + (2) = 3m + 3m = 6m.
Question 13.
Explain diagramatically the Image of letter ‘B’ in a plane mirror.
Answer:
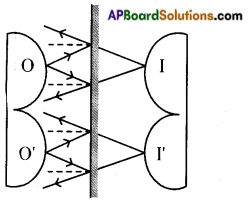
Question 14.
Why can’t we see our image in a white sheet of paper though it reflects light?
Answer:
By microscopic observation, we can find up and downs over surface of a paper. Hence paper is not a smooth fine surface. Even though sheet of white paper reflects the light rays, they do not form an image of an object.
Question 15.
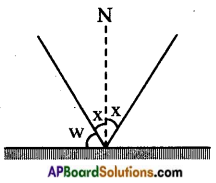
Observe the below figure. AB and BC are two plane mirrors arranged at 120°. A ray incidents at and angle 55° on AB. Find the value of ‘x’
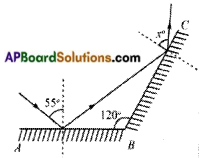
Answer:
Let us say, angles a, b, c, d as shown in the figure. From the figure, a = 55° [∵ i = r]
a + b = 90° [. Normal to the plane]
55° + b = 90°
⇒ b = 90° – 55° = 35°
120° + b + c = 180° [∵ Total of angles in a triangle]
120° + 35° + c = 180°
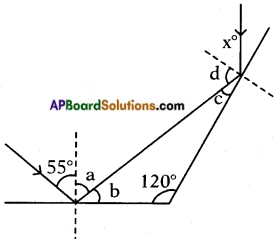
⇒ c = 180° – 155° = 25° c + d = 90° [∵ Normal to the plane]
25° + d = 90°
⇒ d = 90° – 25° = 65°
d = x [∵ i = r]
∴ x = 65°
![]()
Question 16.
The size of the image in the mirror seem to be decreased when you move the object towards your eye from the mirror. Draw the diagram showing angles depicting the situation.
Answer:
Question 17.
Collect the information about “Situations using the plane mirrors and prepare the report.
Answer:
Plane mirrors have many uses.
- Periscopes: They are used in periscopes to see bends and corners. It is used for observing enemy movements from trenches without any danger of being seen. Sailors on submarines use periscopes to see things above the water level.
- Kaleidoscopes: Kaleidoscope is a toy that uses light and mirrors to reflect objects and create beautiful, fascinating repeating patterns.
- Security: Mirrors are used while looking for explosives underneath a vehicle. Even these mirrors are used in shops to keep an eye on the customers. Mirrors are also used in blind turns of busy roads to see the vehicles coming from the other side.
- Telescopes and Microscopes: Plane mirrors are used in many scientific applications like telescopes and microscopes.
- Dressing mirrors: Plane mirrors are used in dressing tables to see ourselves, while dressing, shaving, etc.
- Ophthalmic doctors: They use plane mirrors to increase the distance of the eye test chart while examine the eye of a patient.
- Docorating mirrors: Plane mirrors are used to decorate the building for elivations. Some shops also used plane mirrors to get multiple images of the items in their shops.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
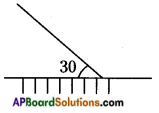
1. Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection. This rule is explained by …………… principle ( )
A) Fermat
B) Newton
C) Archemedes
D) Pascal
Answer: A
2. Which of the following letters doesn’t suffer lateral inversion? ( )
A) C
B) O
C) B
D) N
Answer: B
3. A ray of light incidents on a plane mirror at an angle of 90° to its surface. What will be the angle of relfection? ( )
A) 0°
B) 90°
C) 450°
D) 180°
Answer: A
![]()
4. If we move an object away from the plane mirror the size of images seems to be ( )
A) increases
B) decreases
C) of the same size
D) image can’t be seen
Answer: B
5. Which of the following is incorrect with respect to the image in a plane mirror? ( )
A) Image is erect
B) size of the image is same as the size of object
C) laterally inverted
D) image is real.
Answer: D
6. An object is placed 7cm distance from the plane mirror then distance of image is ( )
A) 3.5 cm
B) 14 cm
C) 7 cm
D) 21 cm
Answer: C
8th Class Physical Science 10th Lesson Reflection of Light at Plane Surfaces InText Questions and Answers
8th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 134
Question 1.
How can we get the image of a big building in a small mirror?
Answer:
Light rays travel in all directions from one object. Light rays coming from a building incident on the small area of a plane mirror and reflect. These reflected rays reach our eye. We see the image of the building in the mirror.
Question 2.
Can we get the image formed by a plane mirror on a screen?
Answer:
Cannot.
Question 3.
Why is there lateral inversion, when we look into a mirror?
Answer:
Our brain feels that the rays is coming from the inside of the mirror.
Question 4.
Why is the angle of reflection equal to the angle of incidence when a light ray gets reflected from a surface?
Answer:
Light always choose the path of least time to travel.
![]()
8th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 138
Question 5.
Is the angle of reflection equal to the angle of incidence in all cases?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 6.
Do the two rays and the normal lie in the same plane? If yes, which is that plane?
Answer:
Yes, plane of paper.
Question 7.
In which plane will the incident ray, reflected ray and the normal lie?
Answer:
Plane touching the heads of pins and parallel to the plane of paper.
Question 8.
How will the incident ray be?
Answer:
Incident ray touching heads of the pins (P and Q) and make some angle with plane of the paper.
Question 9.
How will the reflected ray be?
Answer:
Reflected ray will make some angle with plane of the paper.
Question 10.
How will the normal be?
Answer:
The normal will also make same angle as incident and reflected rays.
Question 11.
How will the plane of reflection be?
Answer:
Plane of reflection make some angle (which is equal to plane of the paper and incident ray) with plane of the paper.
Question 12.
How does a mirror form the image of a pin or any object? Let us discuss.
Answer:
The rays coming from the pin get reflected from the mirror and seem to be coming from the image in the mirror.
8th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 139
Question 13.
What is the size of the image compared to the size of the object?
Answer:
Size of the image is equal to size of the object.
Question 14.
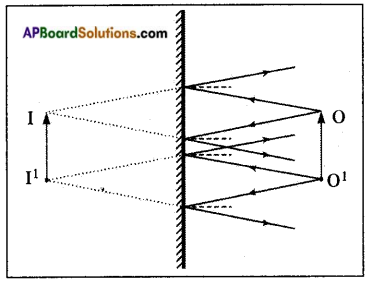
What do you say about the size of the image compared to the size of the object? Move the object towards your eye. What do you observe?
Answer:
Size of the image is same as size of the object. If we move the object towards our eye, size of the image of the object seems to be decreased.
Question 15.
Is the size of the image decreasing or increasing?
Answer:
Decreasing.
![]()
8th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 140
Question 16.
Why does an image suffer lateral (right-left) inversion? See the figure.

Answer:
Our brain feels that the rays are coming from the inside of the mirror and image is opposite to us. In this way image suffer lateral inversion.
Question 17.
What do you understand from the figure?
Answer:
The light rays which come from our right ear get reflected from the plane mirror and reach our eye. Our brain feels that the ray is coming from the inside of the mirror. That is why our right ear looks like left ear in the image.
Think, Discuss and Write
8th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 135
Question 1.
Does the explanation on pinhole match with your observation?
Answer:
Yes, it matches with my observation.
Question 2.
What happens if the hole Is much bigger, i.e., equal to the size of the flame?
Answer:
The image is extremely blurred.
Question 3.
If so, can we get the image of flame on the screen of pinhole camera? Why?
Answer:
No. Because the light rays coming from the top of the flame and bottom of the flame fall at different points on the screen. So it is blurred and is not formed on screen.
Question 4.
What happens if we observe the same flame with the same pinhole camera from a long distance?
Answer:
We may observe not only the flame, but the blurred image of entire candle.
Question 5.
What happens if we made two holes to pin hole camera?
Answer:
Two images will be formed.
![]()
8th Class Physical Science 10th Lesson Reflection of Light at Plane Surfaces Activities
Activity – 2
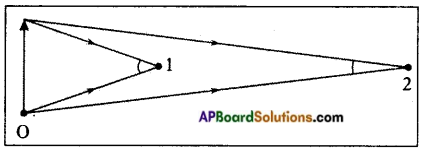
Question 1.
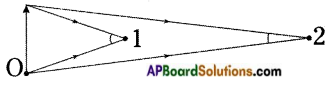
Which grain on the ground that a smart crow on tree A pick to reach B in short time (Shortest path)? Explain. (OR)
How do you support your answer to “When light gets reflected from a surface, it selects the path that takes the least time”? (OR)
Explain Fermat’s principle by using an activity.
Answer:
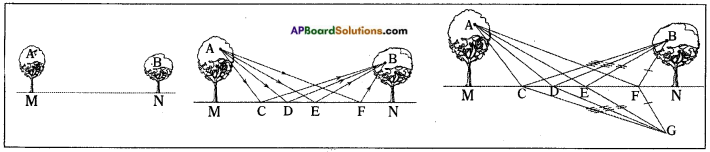
- The crow can pick the grain from any point on the ground, but the condition is selecting the shortest path.
- Let the speed of the crow is constants –
- Observe some of the paths in figure.
- To compare the lengths of these paths ACB, ADB, AEB and AFB, make the duplicates of them at point G as shown in figure.
- In the figure CB = CG,
∴ The length of path ACB = AC + CB = AC + CG = ACG - Similarly length of the path ADB = length of the path ADG Similarlylength of the path AEB = length of the path AEG Similarly length of the path AFB = length of the path AFG
- By observing the above paths, we will notice that AEG is the shortest path among all the paths, because it is the straight line distance between points A and G.
- So the smart crow will pick the grain from point E.
![]()
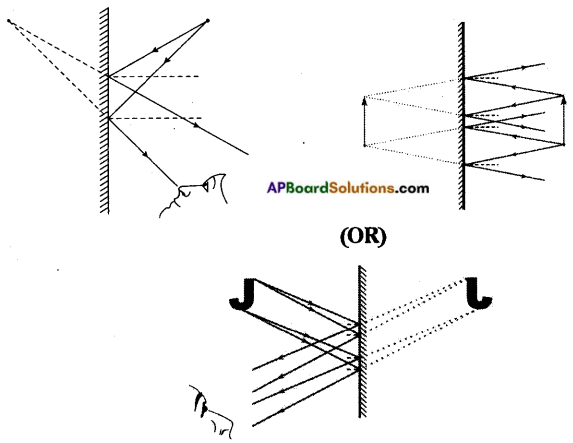
Activity – 3
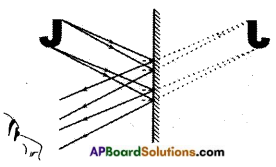
Question 2.
Look at the following figure.
Suppose if you have been given a plane mirror strip, what will you do to obtain figures as shown below figure (b) using mirror strip and the above figure (a)?

Answer:
The place of mirror that should be place on the figure vertically has been shown here under by a line.
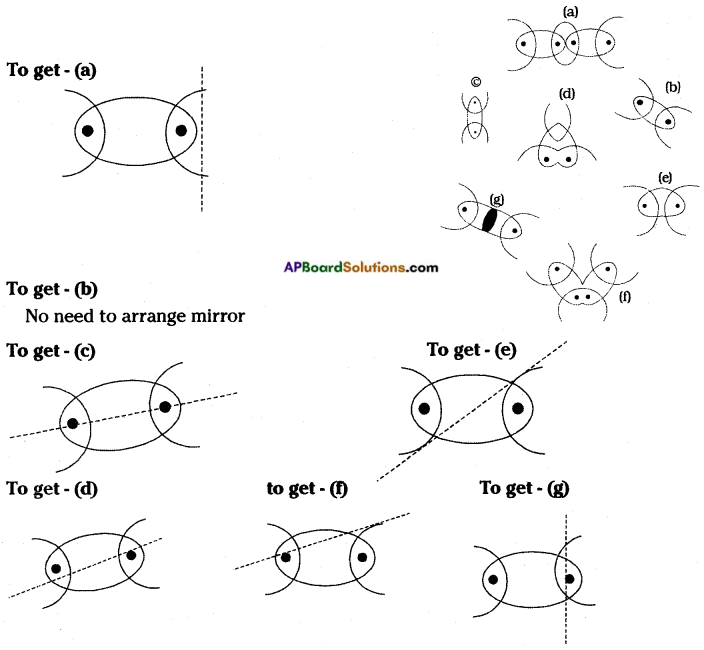
In the above diagrams, line indicates the position of mirror to be kept to get the required shapes.