AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 5 Coordination.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions 5th Lesson Coordination
10th Class Biology 5th Lesson Coordination 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
“Plants respond to stimuli.” During a project work on it, from which plants do you collect information and record it?
Answer:
a) Mimosa Pudica (Touch me not plant) b) Sunflower c) Cucumber d) Bittergourd
Question 2.
Write two points about insulin from the information you collected from internet. (OR)
Write two sentences about insulin hormone using the data collected from your school library.
Answer:
- Insulin is secreted by islets of longerhans of pancreas gland.
- Deficiency of insulin results in diabetis mellitus.
![]()
Question 3.
You have performed the activity of Seed Germination in a glass jar in your school lab. You might have observed the growth of shoot and root. What information did you record regarding the shoot growth after a week if the glass jar is tilted and plant kept horizontally.
Answer:
- More auxins collects on light falling side of the stem.
- Cells on that side grow faster and make the stem bends towards light due to phototropism.
Question 4.
Write the functions of Spinal-cord from the information collected from your school library and from internet.
Answer:
- Carries the information to the brain from the lower parts of the body.
- It carries the information from brain to body parts.
- It plays a key role in the reflex actions.
- It acts as relay centre.
Question 5.
Where do we find Cerebro-spinal fluid? Mention one of its functions.
Answer:
The space between the inner layers of brain is filled with fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It serves as a shock-absorbing medium and protects the brain against shocks, jerks along with the meninges and cranium.
Question 6.
Mention at least one activity done at school to show involuntary reflexes.
Answer:
Knee-jerk.
Question 7.
Write the name of the nerve given in the following diagram and write its function.
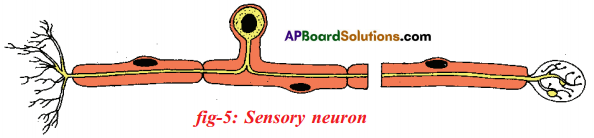 Answer:
Answer:
The given diagram is the sensory Neuron. They are also called Afferent nerves.
Function: They carry messages towards central nervous system (Brain or spinal cord) from nerve endings on the muscles of different sense organs, that sense the change in surroundings.
![]()
Question 8.
Identify the given part in the diagram and write its use.
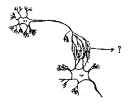 Answer:
Answer:
i) Synapse.
ii) It is a functional region of contact between two neurons where infromation from one neuron is transmitted to another neuron.
Question 9.
Name the part of the brain that maintains the equilibrium.
Answer:
The part of the brain that maintains the equilibrium is cerebellum.
Question 10.
Who discovered the first plant hormone auxin?
Answer:
The first plant hormone auxin was discovered by F.W. Went.
Question 11.
What was the belief of Greeks?
Answer:
The Greeks believed that all functions of the body were controlled by the brain, since damage to that organ produced remarkable changes in behaviour.
Question 12.
How many types of nerves are present in human body? What are they?
Answer:
Nerves are classified mainly into three types.
- Afferent neurons
- Efferent neurons
- Association neurons.
Question 13.
What are Afferent neurons?
Answer:
Afferent neurons: Nerves which carry messages towards the central nervous system (Spinal cord or brain) from sense organs are called afferent neurons. These are also called sensory nerves.
![]()
Question 14.
What are efferent neurons or nerves?
Answer:
Efferent neurons: Nerves which carry messages from the central nervous system to parts that shall carry out the response are called efferent neurons. They are also called as motor nerves.
Question 15.
What are association nerves?
Answer:
The nerves, which link together the afferent and efferent nerves are called association nerves.
Question 16.
What is stimulus?
Answer:
Stimulus is a thing or event that causes a specific functional reaction in an organ or tissue.
Question 17.
What is response?
Answer:
Response is a effect of a change in the environment of the organism or signals of change or stimuli.
Question 18.
What does rapidity of response indicate?
Answer:
Rapidity of response indicates an efficient communication system linking those parts that pick up stimuli to those that trigger a response.
Question 19.
How are responses bring about?
Answer:
Responses are brought about by rapid changes in some muscle.
Question 20.
According to Galen a Greek physiologist how many kinds of nerves are present in body?
Answer:
According to Galen, nerves are of two kinds. They are 1) for sensation and 2) for action.
Question 21.
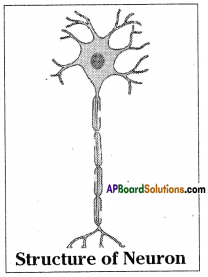
What are the major parts of neuron?
Answer:
The major parts of neuron are cell body or cyton, dendrites and axon.
![]()
Question 22.
What are the two types of projections that extend from cell body?
Answer:
The two types of projections that extend from cell body are dendrites and axon.
Question 23.
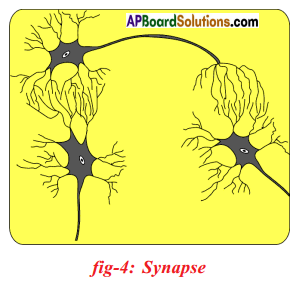
What is synapse?
Answer:
Synapse is the functional region of contact between two neurons.
Question 24.
Synapses are mainly found in?
Answer:
Synapses are mainly found in the brain, spinal cord and around the spinal cord.
Question 25.
What are reflexes?
Answer:
The responses to a stimulus on which we do not have control are called reflexes or reflex action.
Question 26.
What is the importance of reflex action?
Answer:
Reflex action save us from painful or dangerous stimuli.
Question 27.
How many types does the nervous system is divided?
Answer:
Nervous system is divided into two types. They are central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
Question 28.
What are the parts of central nervous system?
Answer:
The parts of the central nervous system are brain and spinal cord.
![]()
Question 29.
What are the three major divisions in brain?
Answer:
- Forebrain
- Mid brain and
- Hind brain.
Question 30.
What are the parts present in fore brain?
Answer:
The parts present in fore brain are cerebrum and diencephalon.
Question 31.
What are cranial nerves? How many cranial nerves are present?
Answer:
Nerves originate from brain are called cranial nerves. 12 pairs of cranial nerves arise from brain.
Question 32.
How many pairs of spinal nerves are present?
Answer:
31 pairs of spinal nerves are present.
Question 33.
Which is called peripheral nervous system?
Answer:
Peripheral nervous system consists of nerves arising from the brain and spinal cord. 12 pairs of cranial nerves from brain and 31 pairs of spiral nerves from spinal card together called peripheral nervous system.
Question 34.
What is autonomous nervous system?
Answer:
The peripheral nervous system that controls the involuntary actions of the body is called autonomous nervous system.
![]()
Question 35.
What are the systems involved in control and coordination in animals?
Answer:
The systems involved in control and coordination in animals are nervous system and endocrine system.
Question 36.
The hormone insulin is secreted by?
Answer:
The hormone insulin is secreted by Islets of Langerhans of pancreas gland.
Question 37.
Give examples for endocrine glands.
Answer:
The examples for endocrine glands are pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid, adrenal, hypothalamus, pancreas, thymus, testes and ovaries.
Question 38.
The nervous system that regulates heart beat, breathing, etc., is?
Answer:
The nervous system that regulates heart beat, breathing etc., is autonomous nervous system.
Question 39.
What is thigmotropism?
Answer:
The directional growth movement of a plant part in response to the touch of an object is called thigmotropism.
Question 40.
Name the receptors of taste and smell.
Answer:
The receptor of taste is gustatory receptor and that of smell is olfactory receptor.
Question 41.
What is reflex action? Give examples.
Answer:
Reflex action is a quick involuntary response to a stimulus by an effector.
e.g: Withdrawing our hand from hot object, blinking of eyelids when a moving object approaches eye.
![]()
Question 42.
What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Answer:
Reflex action is an involuntary action whereas walking is a voluntary action.
Question 43.
Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer:
The part of the brain that maintains posture and equilibrium of the body is cerebellum.
Question 44.
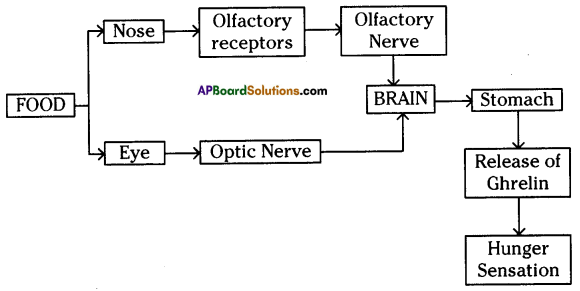
How do we detect the smell of agarbathi or incense stick?
Answer:
We detect the smell of agarbathi or incense stick when the olfactory receptors in the nose detect smell by sending nerve impulses to the olfactory centre of the brain.
Question 45.
What is target tissue?
Answer:
Tissues or organs on which hormones act are called target tissues or organs.
Question 46.
What are the main cells of the nervous system?
Answer:
The main cells of the nervous system are the neurons. Besides the neurons the nervous system also consists of glial cells.
Question 47.
What is phototropism?
Answer:
The movement of a plant part in response to light is called phototropism.
Question 48.
What is geotropism?
Answer:
The movement of a plant part in response to gravity is called geotropism.
Question 49.
What is chemotropism?
Answer:
The movement of a plant part in response to chemical stimulus is called chemotropism.
Question 50.
What is hydrotropism?
Answer:
The movement of a plant part in response to water is called hydrotropism.
![]()
Question 51.
How many nerve cells does human nervous system consist of?
Answer:
Human nervous system consists of about 100 billion cells.
Question 52.
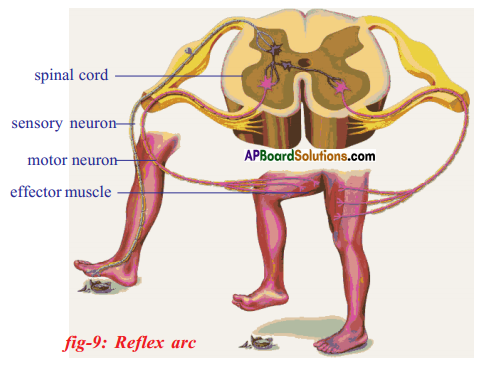
What is reflex arc?
Answer:
The structural and functional unit that carries reflex action is called reflex arc.
Question 53.
The three layers covering the brain are called?
Answer:
The three layers covering the brain are meninges.
Question 54.
What are the functions carried out by cerebrum?
Answer:
Cerebrum is a seat of mental abilities, controls thinking, memory, reasoning, perception, emotions and speech.
Question 55.
What are the functions of cerebellum?
Answer:
Cerebellum maintains posture, equilibrium and muscle tone.
Question 56.
Which parts are present in hind brain?
Answer:
Cerebellum and medulla oblongata are the parts present in hind brain.
Question 57.
What is the function of feedback mechanism?
Answer:
The function of feed back mechanism is to regulate the production and release of hormones in the body.
Question 58.
Thyroxine hormone controls the body’s function like?
Answer:
Thyroxine hormone controls body’s function like general growth rate and a metabolic activity.
Question 59.
What are voluntary actions? Give examples.
Answer:
The movements under the control of the conscious mind are called voluntary actions. Example : Kicking foot ball, lifting bucket of water, reading book, running, walking, playing, eating, etc.
![]()
Question 60.
What are involuntary actions? Give examples.
Answer:
The movements which are not under the control of the conscious mind are called involuntary actions. Example : Respiration, circulation, digestion.
Question 61.
What is nerve impulse?
Answer:
The information passing through a neuron in the form of electrical and chemical signals is called nerve impulse.
Question 62.
What are phytohormones?
Answer:
The hormones present in the plants are called phytohormones.
Question 63.
The phytohormone Abscisic acid is responsible for?
Answer:
Closing of stomata and seed dormancy are caused by the phytohormone Abscisicacid.
Question 64.
What are the functions of auxins?
Answer:
Auxins are responsible for cell elongation and differentiation of shoots and roots.
Question 65.
What is the speed of nerve transmission?
Answer:
Nerve transmission from stimulus to a response can occur at a maximum speed of about 100 meters per second.
Question 66.
What is vasomotor?
Answer:
Vasomotor refers to actions upon a blood vessel which alter its diameter.
Question 67.
What are dorsal and ventral root ganglion?
Answer:
The dorsal root and ventral root ganglions are the regions very close to the spinal cord in which the nerve cell bodies lie. Dorsal root ganglion is present on the dorsal side of spinal cord and ventral root ganglion is present on the ventral side of the spinalcord.
Question 68.
What is the function of dorsal root ganglion?
Answer:
The dorsal root ganglion carries messages of sensation toward brain or spinal cord.
![]()
Question 69.
What is the function of ventral root ganglion?
Answer:
The ventral root ganglion carry the instructions from the brain or spinal card to muscles.
10th Class Biology 5th Lesson Coordination 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What questions will you ask a doctor to know about endocrine glands?
Answer:
- Which glands are known as endocrine glands?
- Where can we find endocrine glands in our body?
- What do you call chemical substances secreted by Endocrine glands?
- Which endocrine gland is attached to the brain?
- What are the functions of endrocrine glands?
- What will happen if endocrine glands are absent?
Question 2.
How do you feel when you realize that plants respond to the stimuli of their surroundings?
Answer:
- It is very interesting and amazing to observe trophic and nastic movements of plants in our surroundings.
- For example, the bending of shoots of creepers towards light kept near the window.
- The plant roots always grow downwards.
- The creepers like cucumber and bittergourds develops tendrils in response to contact or touch.
- Butterflies fluttering around the flowers for nectar.
Question 3.
What will happen if a plant is placed near the window of your classroom? What is this process called?
Answer:
- The plant bends towards the sun light and grow.
- This process is called phototropism.
![]()
Question 4.
How do you appreciate the role of Spinal-cord in reflex actions?
Answer:
- Spinal cord responds very fast and immediate.
- The nerve impulses are transmitted very fast at the speed of 100 m/min.
- So that we are protected from many dangerous situations.
- So I really appreciate and amazing reflex actions of the spinal cord.
Question 5.
Read the following table:
| Name of the Gland | Location | Hormone secreted | Function |
| Thyroid | Neck | Thyroxine | General growth rate and Metabolic activity |
| Ovary | Abdomen | Estrogen | Growth of uterus and Control of menstrual cycle |
| Testis | Scrotal sac | Testosterone | Growth of beard, mustache and development of male sex organs. |
| Adrenal | Kidney | Adrenalin | Increase in heart beat, rise in blood sugar. |
Answer the following questions:
i) Which hormone is released at the time of emotions?
Answer:
Adrenaline
ii) Name the hormone responsible for the development of Secondary sexual characters.
Answer:
Estrogen, Testosteron.
Question 6.
Ram met with an accident. After that he lost the capacity to walk in straight manner and cannot smell anything. Which part of the brain got damaged in the above cases?
Answer:
- The forebrain and hind brain of Ram might have been damaged.
- The olfactory lobes of the forebrain are concerned with sense of smell. Here, Ram lost the sense of smell anything. Hence the olfactory lobes of forebrain got damaged.
- The cerebellum of hind brain maintains posture, equilibrium and muscle tone.
- After accident, Ram lost the capacity to walk in a straight manner and hence, I predict that cerebellum of Ram also got damaged.
Question 7.
What questions will you ask a doctor to know about pancreatic gland?
Answer:
- Where is pancreas located?
- Why is it called a mixed gland?
- What is the role of pancreas as an endocrine gland?
- Name the disorders occur to pancreas.
![]()
Question 8.
What is the role of Adrenalin in controlling emotions?
Answer:
Adrenalin increases rate of heart beat, causes rise in blood sugar, dilation of coronary artery and dilation of pupil of the eye.
Question 9.
What is the significance of the adrenal gland in the human body?
Answer:
Adrenal gland secrets adrenaline. It helps in
- Increase heart beat rate
- Rise in blood sugar
- Dilation of the coronary artery
- Dilation of pupil of the eye.
Question 10.
Write the difference between hormone and enzyme.
Answer:
| Hormone | Enzyme |
| 1. These are secreted by ductless glands. | 1. These are secreted by duct glands. |
| 2. These are travel through blood. | 2. These are travel through the ducts. |
| 3. Less in quantity. | 3. More in quantity. |
| 4. Reaction is slow. | 4. Reaction is fast. |
| 5. Involved in metabolic activities | 5. Involve in digestion. |
| 6. Ex: Insulin | 6. Ex: Lipase |
Question 11.
Observe the following table and answer the questions.
| Hormones | Uses |
| Thyroxine | Normal growth rate, effect on metabolism |
| Auxins | Cell elongation and differentiation of shoots and roots |
i) Name the phytohormone in the table.
ii) Name the hormone which influences growth rate in humans.
Answer:
i) Auxin
ii) Thyroxine.
![]()
Question 12.
What questions you will ask a neurologist on function of brain?
Answer:
- How does alcohol cosumption affect the brain?
- Which part of brain is responsible for creativity?
- How do we get fits ? 4) How do we get paralysis?
- What kind of food should we take to increase?
Question 13.
Label a, b, c, d in the diagram given below and write their functions.
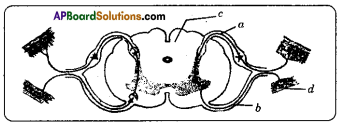 Answer:
Answer:
a) Sensory Neuron/-Afferent Neuron: These carry messages towards the central nervous system.
b) Motor Neuron /- Efferent Neuron: These carry messages from central nervous system to body parts
c) White Matter
d) Effector Muscles: Respond to stimuli.
Question 14.
Prepare a table showing tropic movements in plants in response to stimuli.
Answer:
| SI. No. | Tropic movement | Response to stimuli |
| 1. | Phototropism | Movement towards light. |
| 2. | Geotropism | Respond positively for gravitational force. |
| 3. | Hydrotropism | Roots grow towards presence of water in the soil. |
| 4. | Thigmotropism | Tendrils and climbing plants grow towards support. |
Question 15.
Explain two tropic movements with suitable examples.
Answer:
- Phototropism: Response of plant to light cite example is called phototropism.
Ex: sunflower - Geotropism: Response of a plant to gravitational force Ex: root growth of plant
- Hydrotropism: Response of root to water availability in the soil.
Ex : Plants which are growing very close to rocks and walls. - Thigmotropism: Response to make contact or touch is called Thigmotropism.
- Chemotropism: Response to chemical is called chemotropism (Stigma secretes sugary substances)
Question 16.
Write two voluntary functions and two involuntary functions you have observed in your body.
Answer:
a) Examples for voluntary functions:
- Cleaning the table
- Playing on the keyboard.
b) Examples for involuntary functions :
- Salivating when food is kept in the mouth
- Closing of eyes when bright light is focussed.
Question 17.
Plants show tropic movements in different situations. Give examples.
Answer:
- Movement of individual parts of plants is possible when they are subjected to external stimuli. This type of response is called tropism or tropic movement.
- The response of a plant to light is called phototropism. Respond of plants for gravity is called geotropism. Movement of plant towards water is called hydrotropism. The type of response by plants to make contact or touch is called thigmotropism. The response of plants to chemicals is called chemotropism.
- Pollen grains respond to this stimulus as pollen tubes grow to reach the ovule for fertilization.
Question 18.
Divide the following into groups. Walking, blinking of eye lids, heart beat, laughing, digestion of food and reading. How do you divide them into groups?
Answer:
These can be divided into voluntary actions, involuntary actions and reflex actions.
Voluntary actions: Walking, laughing, reading
Involuntary actions: Digestion of food, heart beat
Reflex actions: Blinking of eye lids
![]()
Question 19.
What are ganglia?
Answer:
- Ganglia or neural ganglia are the structures located in the peripheral nervous system (for example beside the spinal column or near viscera) made of concentration of neuron bodies.
- Examples of neural ganglia are the ganglia that concentrate cell bodies of sensory neurons in the dorsal roots of the spinal cord and the ganglia of the myenteric plexus responsible for the peristaltic movements of the digestive tube.
Question 20.
Write a brief note on the functioning of sympathetic nervous system.
Answer:
- This part of the autonomous nervous system increase the activity of an organ as per the need.
- For example, during running there is an increased demand for oxygen by the body.
- This is fulfilled by an increased breathing rate and increased heart rate.
- The sympathetic nervous system works to increase the breathing rate and the heart rate.
Question 21.
Explain briefly about the action of parasympathetic nervous system.
Answer:
- This part of the autonomous nervous system decrease the activity of an organ and it has calming effect.
- During sleep, the breathing rate and also the heart rate slows down.
- This is facilitated by the parasympathetic nervous system.
- It can be said that the parasympathetic nervous system helps in conservation of energy.
Question 22.
Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer:
- Insulin is produced by Islets of Langerhans of pancreas.
- Insulin regulates the level of glucose in the blood.
- Deficiency of insulin results in disease called ‘diabetes’.
- Such diabetic patients are given injections of insulin so that the sugar or glucose level in the blood can be controlled.
- Insulin is now produced in large quantities for the treatment of human sufferers from ‘sugar diabetes’.
Question 23.
What is chemotropism? Explain it with suitable example.
Answer:
- Response of a plant towards chemicals is known as chemotropism.
- If we taste the carpel of a flower, it is sweet.
- Butterflies flutter on flowers for nectar.
- Ripen stigma secretes sugary substance.
- This chemical substance stimulates the pollen grain which falls on the stigma.
- Pollen grains respond to this stimulus as pollen tubes grow to reach the ovule for fertilization.
![]()
Question 24.
What are plant growth substances? Give examples.
Answer:
- Plant growth substances are the chemical (organic) substances which are produced in plants and act at minute concentration on growth and other phisiological functions of plants.
- There are five major types of plant growth substances. They are auxins, Gibberellins, cytokinins, Ethylene and Abscisic Acid.
Question 25.
What is ethylene? Explain its action.
Answer:
- Ethylene is a gaseous growth inhibiting substance.
- Ethylene causes ripening of the fruits.
- It modifies the growth of the plant by inhibiting stem elongation.
- It accelerates abscission of leaves, flowers and fruits.
Question 26.
What is Apical dominance?
Answer:
- In some plants main stem grows by the activity of terminal bud without giving any branches.
- It means the activity of lateral buds is suppressed and this phenomenon of suppression of the growth of lateral buds by terminal bud is called Apical dominance.
![]()
Question 27.
What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer:
At synapse, in between the end of one axon and end of another dendrite electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals (neurotransmitter). These chemicals cross the gap or synapse and reach to dendrites of the next neuron and start electrical impulse there.
10th Class Biology 5th Lesson Coordination 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
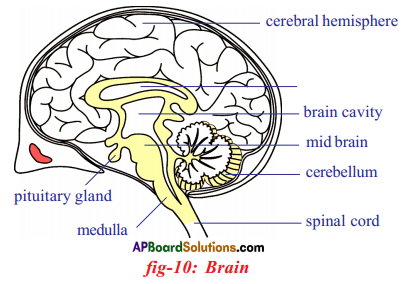
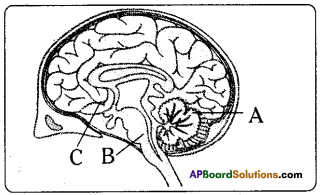 i) This diagram belongs to which system of the body?
i) This diagram belongs to which system of the body?
Answer:
Human nervous system
ii) Name the parts A and B.
Answer:
A. Cerebellum
B. Medulla oblongata
iii) The part ‘C is endocrinal gland. This is called master gland. What is the name of this gland?
Answer:
Pituitary gland
iv) Which part in this diagram is useful to solve problems and puzzles?
Answer:
Cerebrum
![]()
Question 2.
Name the important parts of the brain and write the functions of fore-brain.
(OR)
Write in a tabular form the different parts of human brain and their functions.
Answer:
- Brain has the following divisions.
1. Fore brain – Cerebrum, diencephalon
2. Mid brain – Optic lobes.
3. Hind brain – Cerebellum, medulla. - Functions of the various parts of the brain.
Parts of the brain Functions Cerebrum i) Seat of mental abilities, controls thinking memory, reasoning, perception, emotions and speech.
ii) Interprets sensations and responds to cold, heat, pain and pressure.Diencephalon i) Relay centre for sensory impulses, such as pain, temperature and light.
ii) Reflex centre for muscular activities.
iii) Centre for certain emotions such as anger.
iv) Centre for water balance, blood pressure, body temperature, sleep and hunger.
v) The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland, which functions as the master gland.Mid brain i) It relays motor impulses from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord and relays sensory impulses from the spinal cord to thalamus, reflexes for light and hearing. Cerebellum i) Maintains posture, equilibrium and muscle tone.
ii) Coordinates voluntary movements initiated by cerebrum.Medulla oblongata i) Contains centre for cardiac, respiratory and vasomotor activities.
ii) Coordinate reflexes like swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomiting.
Question 3.
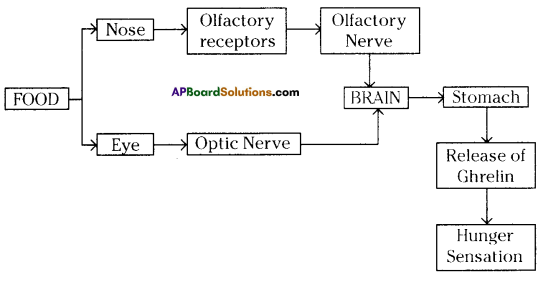
Observe the following diagram. What does it represent? Explain the process in a flow-chart.
 Answer:
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
Read the following table:
| Part of the Brain | Functions |
| a) Olfactory lobes | Sense of smell |
| b) Cerebrum | Mental abilities, memory, reasoning, perception, emotion and speech, respond to cold, heat, pain and pressure |
| c) Diencephalon | Controlling emotions, center for water balance, blood pressure, sensory impulses such as pain, temperature and light, sleep and hunger. |
| d) Cerebellum | Maintains posture, equilibrium and muscle tone, coordinates voluntary movements initiated by cerebrum. |
Now, identify the part of the brain which participate in the below situations.
a) Ravi is an intelligent boy. He can remember the things for a long time.
Answer:
Cerebrum
b) The drunken man does not walk properly.
Answer:
Cerebellum
c) Identifies the food items without seeing which are being prepared in the kitchen
Answer:
Olfactory Lobes
d) Naveen lost his money purse while coming to the school. But he is not crying.
Answer:
Diencephalon
e) It is time for lunch.
Answer:
Cerebrum
f) I cannot tolerate this type of heat in the summer.
Answer:
Cerebrum
g) Catching the ball perfectly.
Answer:
Cerebellum
h) There may be a drainage behind the house.
Answer:
Olfactory Lobes
![]()
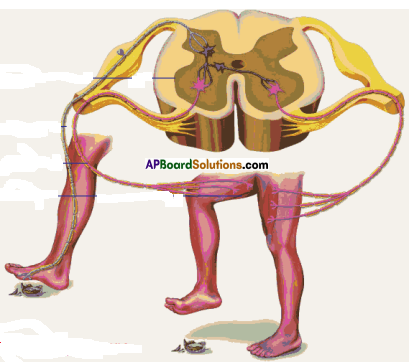
Question 5.
Look at the picture and answer the questions:
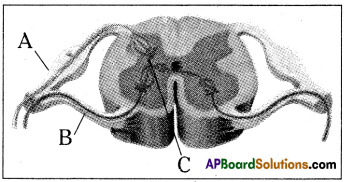 a) To which system does the diagram belong ?
a) To which system does the diagram belong ?
Answer:
The diagram belongs to T.S. of Spinal cord (peripheral).
b) What is the name of A, B parts ?
Answer:
A – Dorsal Root,
B – Ventral Root
c) What is ‘C’ ? What is its function ?
Answer:
C – Association neuron
It analyse the information – and send the order (function) through motor neuron to muscle.
d) Through which horn the sensory nerve enters ?
Answer:
Sensory nerve enters through dorsal horn.
Question 6.
Fill the following table related to Endocrine glands.
| 1. | Name of the endocrine gland | Location | Hormone secreted | Response of body to that hormone |
| 2. | ||||
| 3. | ||||
| 4. |
Answer:
| S.No. | Name of endocrine the gland | Location | Hormone secreted | Response of body to that hormone |
| 1. | Pituitary | Floor of brain | Somatotropin | Growth of bone. |
| Gonadotropin | Activity of ovary and testis. | |||
| 2. | Thyroid | Neck | Thyroxine | General growth rate and metabolic activity. |
| 3. | Ovary | Lower abdomen | Estrogen | Growth of the uterus and skeleton of the pelvis. |
| 4. | Testis | Scrotal sac | Testosterone | Growth of male secondary sexual characters. |
![]()
Question 7.
Observe the following table and answer the questions.
| Division -1 | Division – II |
| Auxins | Adrenalin |
| Gibberellins | Testosterone |
| Ethylene | Estrogen |
| Abscisic Acid | Thyroxin |
| Cytokinins | Growth Hormone |
a) On what basis the above classification done?
Answer:
Hormones in animals and hormones in plants.
b) From which gland is Adrenalin released?
Answer:
Adrenal gland.
c) Which hormone is responsible for closing of stomata?
Answer:
Abscisic Acid (ABA)
d) What are the functions of Auxins?
Answer:
Cell elongation and differentiation of shoots and roots.
Question 8.

A) What does the given picture represent?
B) Name the parts A, B and C.
C) What carries the nerve impulse to the spinal cord?
D) Wrhat is the function of association neuron?
Answer:
A) The given picture represents
T.S. of Spinal cord (peripheral).
B) A – Dorsal root B – Ventral root C – Association neuron
C) Through dorsal root the nerve impulse reaches the spinal cord.
D) Association neuron analyses the information and sends the order through motor neuron to muscle.
Question 9.
The following table is about parts of brain and their functions. Read it and fill the blanks.
| Part of the brain | Functions |
| Cerebrum | |
| Centre for certain emotions such as anger | |
| Midbrain | It relays motor impulses from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord and relays sensory impulses from the spinal cord to the thalamus, reflexes for sight and hearing. |
| Maintains posture, equilibrium and muscle tone. | |
| Medulla oblongata |
Answer:
| Cerebrum | i) Site of mental abilities, controls thinking, memory, reasoning, perception, emotions and speech.
ii) Interprets sensations and responds to cold, heat, pain and pressure. |
| Diencephalon | Centre for certain emotions such as anger. |
| Midbrain | It relays motor impulses from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord and relays sensory impulses from the spinal cord to the thalamus, reflexes for sight and hearing. |
| Cerebellum | Maintains posture, equilibrium and muscle tone. |
| Medulla oblongata | i) Contains centre for cardiac, respiratory and vasomotor activities. ii) Coordinates reflexes like swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomiting. |
![]()
Question 10.
Ramya ran away shouting loudly after seeing a snake on the way to school. Arrange the events involved in this situation in the correct order and rewrite it.
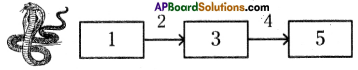 i) Brain receives the information, analyses and produces the reponse.
i) Brain receives the information, analyses and produces the reponse.
ii) Sensory nerves carry the information from sense organs to brain,
iii) Effector muscles exhibit the response.
iv) Sense organs receive the information from the environment.
v) Motor nerves carry the response from the brain to effector muscles.
Answer:
1-d, 2-b, 3 -a, 4-e, 5-c
d) Sense organs receive the information from the environment.
b) Sensory nerves carry the information from sense organs to brain,
a) brain receives the information analyse and produces the response.
e) Motor nerves carry the response from the brain to effector muscles.
c) Effector muscles exhibit the response.
Question 11.
Observe the following information and answer the following questions.
| S.No. | Hormones | Uses |
| 1. | Auxins | Cell elongation and differentiation of shoots and roots. |
| 2. | Abscisic acid | Closing of stomata, seed dormancy |
| 3. | Ethylene | Ripening of fruit |
| 4. | Cytokinins | Promote cell division, promote sprouting of lateral buds, delay ageing of fruits. |
i) What do we call the hormones that are present in plants?
Answer:
We call phyto hormones which are present in plants.
ii) Name the hormones which are helpful in the growth of the plants.
Answer:
Auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins are helpful in the growth of the plants.
iii) Farmers keep carbide powder in between raw mangoes. What might be the reason? What will be the end result after 3 to 4 days?
Answer:
Carbide release Ethylene, which promotes the fruit ripening. After 3 or 4 days fruits will ripen.
iv) Plants also respond like animals. Do you agree with this statement? Support your answer.
Answer:
Yes, plants also respond like animals. They shut off leaves in summer, germinate in rainy season, blooms according to seasons.
Question 12.
Read the following table and answer the questions given below.
| S.No. | Name of the gland | Location | Hormone secreted | Response of the body to hormone |
| 1. | Pituitary | Floor of brain | Somatotropin | Growth of bone. |
| Gonadotropin | Activity of ovary and testis. | |||
| 2. | Thyroid | Neck | Thyroxine | General growth rate and metabolic activity. |
| 3. | Ovary | Lower abdomen | Estrogen | Growth of the uterus and skeleton of the pelvis. |
| 4. | Testis | Scrotal sac | Testosterone | Growth of male secondary sexual characters. |
i) Write the importance of glands and hormones.
Answer:
Glands and hormones controls and coordinates various functions of the body with nervous system.
ii) Which hormone is responsible for growth of bone?
Somatotropin is responsible for growth of bone.
iii) What happens if testosterone is not secreted?
Secondary sexual characters in male are not developed if testosterone is absent.
iv) Where does the gland that secretes thyroxine is located?
Thyroid gland which secretes thyroxine is located near the neck.
v) Which glands are common in male and female?
Pituitary, thyroid, adrenal glands, parathyroid and pancreas are common in male and female.
![]()
Question 13.
Explain the different types of adaptations in plants with suitable examples.
Answer:
- Most plants can aerate their roots bj’ taking in the oxygen through the lenticels or through the surface of their root hairs.
- But plants which have their roots in very wet places, such as ponds or marshes, are unable to obtain oxygen.
- They are adapted to these water-logged conditions by having much larger air spaces which connect the stems with the roots, making diffusion from the upper parts much more efficient.
- The most usual adaptation is to have a hollow stem.
- The problem of air transport is more difficult for trees.
- An exception is the mangrove tree of the tropics which have aerial roots above the soil surface and takes in oxygen through these roots.
Question 14.
Karthik is suffering from excess sugar in urine and Varun is suffering from repeated dilute urination. What are the reasons for these diseases ? Explain.
Answer:
- Excess sugar in urine condition is known as diabetes milletus. (sugar diabetes)
- Repeated dilute urination is known as diabetes insipidus, (diuretic condition)
- Deficiency of insulin causes high level sugar in the blood and urine. It leads to diabetes milletus (Sugar diabetes).
- Vasopressin maintains osmotic concentration of body fluids. Deficiency of vasopressin causes excessive repeated dilute urination it is called as diabetes insipidus.
Question 15.
Analyse the following information and answer the questions.
| S.No | Organ | List-1 Effect of Nervous system |
List-2 Effect of Nervous system |
| 1. | Eye | Dialates pupil | Constricts pupil. |
| 2. | Mouth | Inhibits salivation | Stimulates salivation |
| 3. | Lungs | Relaxes bronchi | Constrict bronchi. |
| 4. | Heart | Accelerates heart beat | Heart beat to normally. |
| 5. | Blood vessels | Increase blood pressure | Decrease blood pressure. |
| 6. | Pancreas | Inhibits Pancreas activity | Stimulates Pancreas activity. |
i) Write two functions of Sympathetic Nervous System.
ii) Name two organs that are influenced by Parasympathetic Nervous System.
iii) Name the Nervous system mentioned in the table that increases the blood pressure.
iv) What systems constitute Autonomous Nervous System?
Answer:
i) Dilates pupil, inhibits salivation, relaxes branchi, accelerates heart beat, etc.
ii) Eye, heart, pancreas, etc.
iii) Sympathetic nervous system
iv) Sympathetic and para sympathetic nervous system.
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the Phytohormones which control growth in plants.
Answer:
Major plant hormones and their action:
| Hormones | Uses |
| Auxins | Cell elongation and differentiation of shoots and roots. |
| Cytokinins | Promote cell division, promotion of sprouting of lateral buds, delaying the ageing in leaves, opening of stomata. |
| Gibberellins | Germination of seeds and sprouting of buds; elongation of stems; stimulation of flowering; development of seedless fruits, breaking the dormancy in seeds and buds. |
| Abscisic acid | Closing of stomata; seed dormancy, promoting aging of leaves. |
| Ethylene | Ripening of fruit. |
Question 17.
Analyse the table and answer the following questions.
| Sl.No. | Part of Brain | Functions |
| 1. | Cerebrum | Mental abilities, memory, speech. |
| 2. | Diencephalon | Sensory impulses, emotional impulses, muscular activities. |
| 3. | Midbrain | Reflexes of sight and hearing. |
| 4. | Cerebellum | Equilibrium. |
| 5. | Medulla oblongata | Respiratory, cardiac centres, blood pressure. |
i) Which part of the brain recollects the childhood incidents?
Answer:
Cerebrum.
ii) Write two parts of hind brain.
Answer:
Cerebellum, medulla oblongata.
iii) Name the part of the brain that will not function in drunken person.
Answer:
Cerebellum.
iv) Name the part of the brain that controls involuntary actions.
Answer:
Medulla oblongata.
Question 18.
Write contrasts and comparisons of the style of response in plants and animals to the stimuli.
Answer:
- Both plants and animals react to various stimuli around them. But the method of responding to stimuli is not similar in plants and animals. .
- Higher animals respond to stimuli because they have a nervous system and an endocrine system.
- Plant do not have a well defined nervous or endocrine system. They do have some mechanism of control by means of some chemicals or hormones.
- Plants can sense the presence of stimuli like light, heat, water, touch, pressure, chemicals, gravity, etc.
- The hormones present in the plants called phytohormones control response towards the stimuli. Phytohormones coordinate the activities of the plant usually by controlling one or the other aspect of the growth of the plant.
Question 19.
Read the below paragraph and write answers.
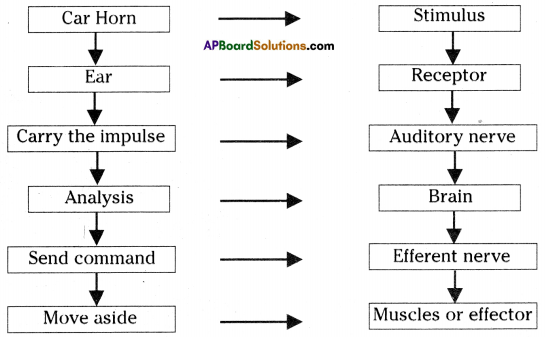
There is systematic method in showing response to stimuli. There is different stages in it. First stage starts with the response recognising the changes in outside or inside of the body atmosphere with recognising the stimuli. Transmitting the received information is second stage, analysing that information is third stage and showing correct response to that stimuli is the last stage.
a) What does this information shows?
b) Convert the above information into flow chart.
c) Write about the mechanism that conducts this action.
Answer:
a) It shows the systematic method in showing response to stimuli.
b)
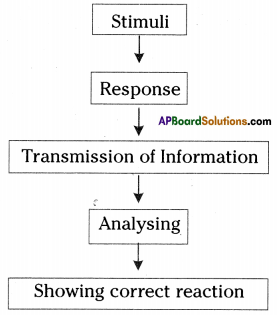
c) Nervous system can sense the changes inside and outside the body through specialised cells called Receptors. This information in the form of small electrical currents is sent to brain and analysed and responses are generated in the nervous system. These responses once again in the form of small electrical currents are conveyed to the appropriate organs such as muscles and glands at a greater speed. Nervous system may store this information for future use.
![]()
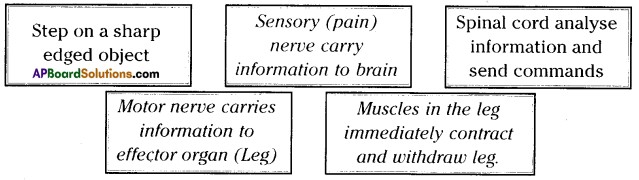
Question 20.
See the below action. What does it indicate? Explain with an example.
 Answer:
Answer:
- It indicates the stimulus – response action. This stimulus response can be explained with an example.
- Suppose a mosquito is biting you on your arm. Mosquito bite is stimulus.
- The receptor in the skin responds and send the information in the form of electrical impulses through sensory nerve to spinal cord or brain.
- Brain or spinal cord analyses the information that the mosquito bite is causing pains.
- The brain or spinal cord sends the message through motor nerve to the effector organ i.e., hand to kill the mosquito.
- As per the message our hand immediately hits the mosquito and kills it.
Question 21.
Rangaiah is not feeling well. The following table is the results of tests. Analyse the table.
| Tests | Present Status | Normal Range |
| Blood Test | ||
| 1. Blood Pressure | 160/90 | 120/80 |
| 2. Glucose (Fasting) | 120 | 60-100 |
| 3. Glucose (Post Lunch) | 220 | 160-180 |
| 4. Bilirubin | 1.0 | 0.1 – 0.8 |
| Urine Test | ||
| 1. 24 hours protein | 150 mg | 100 mg |
| 2. Sodium | 140 | 125-250 |
Write answers for the following questions.
i) How can you state that Rangaiah is diabetic?
Answer:
After blood test it was found that level of glucose (Fasting) is 120 whereas the normal range is 60 -100. After lunch the level of glucose in blood of Rangaiah further raised to 220, the normal being between 160 – 180. This shows that Rangaiah is diabetic.
ii) What are the tests to know about Bilirubin?
Answer:
We can know about bilirubin by blood test.
iii) What do you understand from the above report?
Answer:
It shows that Rangaiah is diabetic and his systolic pressure is slightly high. The levels of bilirubin in blood also slightly high, almost normal range. Urine test shows sodium levels are at normal range but 24 hours protein is much higher than normal levels.
iv) What questions do you ask the doctor on the above report?
Answer:
- What are symptoms shown by Rangaiah as diabetic patient?
- What are the ways to control sugar in the blood?
- Which hormone is responsible for raise of glucose in the blood?
- How sodium maintains blood pressure at normal levels?
- What is the role of bilirubin in digestion?
Question 22.
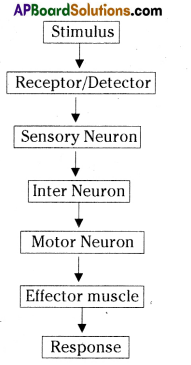
What is reflex arc? Write the components of reflex arc and their functions.
Answer:
- The structural and functional unit that carries out reflex action is called a reflex arc.
- It consists of five components.
- They are receptor, a sensory nerve, a association neuron, a motor nerve and an effector organ.
SI. No. Component of reflex arc Functions 1. Receptor Receives information and generates impulses. 2. Sensory neuron (Afferent) Carries information from the receptor to the interneurons in the spinal cord. 3. Interneuron (Association neuron) Processes the information and generates responses 4. Motor neuron (Efferent) Carries the information from the spinal cord to the effector organ. 5. Effector organ Receives the information from the efferent neuron and shows the appropriate responses.
Question 23.
What are endocrine glands ? What are their functions?
Answer:
Endocrine glands:
- Endocrine glands are the ductless glands.
- They secret complex organic substances called hormones directly into the blood.
- Hormones are transported through blood to different tissues.
- Their secretions act as biochemical messengers in the body.
Functions:
- The hormones secreted by these glands play an important role in co-ordinating various organ systems.
- Hormones can increase or decrease the metabolism and synthesis of substances like proteins, carbohydrates and lipids.
- Irregular functioning of these glands may lead to serious diseases.
- The quantity of hormone required is very minimum (1/10,00,000 gram).
- A slight increase or decrease may brings out large changes in the target tissue.
Question 24.
How does a nerve impulse travel through the body?
Answer:
- The information acquired at the dendritic tip of a nerve cell sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse.
- This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body and then along the axon to its end.
- At the end of the axon the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals.
- These chemicals cross the gap or synapse and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron.
- A similar synapse finally allows the delivery of such impulse from neurons to other cells such as muscles or glands.
![]()
Question 25.
How is the brain anatomically divided?
Answer:
- The cerebrum is divided into two cerebral hemispheres, the right and left.
- Each hemisphere is made of four cerebral lobes. Frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe and occipetal lobe.
- Each cerebral lobe contains the gray matter and the white matter.
- The gray matter is the outer portion and is made of neuron bodies, the gray matter is also known as the cerebral cortex.
- The white matter is the inner portion and it is white because it is in the region where axons of the cortical neuron pass.
Question 26.
What are the divisions of the autonomous nervous system?
Answer:
- Ganglia near the vertebral column are connected to the spinal cord by nerves.
- The two divisions of autonomic nervous system are sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system.
- The sympathetic nervous system is formed by the chain of ganglia on either sides of the vertebral column and the associated nerves.
- The parasympathetic nervous system is formed by the nerves arising from the ganglia of the brain and the posterior part of the spinal cord.
- These together constitute the autonomous nervous system which is the part of the peripheral nervous system consisting of twelve pairs of cranial nerves and thirty one pairs of spinal nerves.
Question 27.
What is autonomous nervous system? Explain how it controls voluntary functions with an example.
Answer:
- The peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary functions of the body is known as Autonomous nervous system.
- It has voluntary control of muscles of some areas of skin and the skeletal muscle.
- For example when we enter a dark room we can not see anything immediately. Slowly we are able to see the things around us in the room.
- This is because of increase in diameter of pupil, which allows more light in.
- When we come out of the dark room into broad day light the diameter of the pupil decreases allowing less light to enter into the eyes.
- Both these functions occur under the influence of the autonomous nervous system.
Question 28.
What is the master gland in the human body? What are the functions of the hormones it secretes? (OR)
Why is pituitary gland known as master gland? How does it control all the other glands in the body?
Answer:
- Pituitary gland is known as the master gland of the body as it controls the functions of all the other endocrine glands.
- It serves as a link between nervous system and endocrine system.
- The hormones secreted by pituitary gland and their functions are as follows.
| Hormone | Response of the body to hormone |
| a) Somatotrophin | Growth of bones |
| b) Thyrotrophin | Activity of thyroid gland |
| c) Gonadotrophin | Activity of ovary and testis |
| d) Andrenocortico trophic | Stimulates secretion from adrenal cortex |
| e) Luteinising hormone | In males – secretion of testosterone; In females – Ovulation, development of Corpus Luteum and secretion of progesterone. |
![]()
Question 29.
What are the differences between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement of our legs?
Answer:
- The stimulus of touch causes the response in a sensitive plant Mimosa pudica.
- Droping of the leaves takes place due to change in osmotic pressure at the base of the leaf.
- When the stimulus is over, the osmotic pressure increases causing the leaf to become normal.
- This is not a growth related movement.
- It is not connected with the direction of the stimulus.
- Nerve messages in the form of electrical impulse reaches the leg muscles from the brain.
- On reaching the leg muscles, the muscles contract causing the movement of the leg.
Question 30.
What is the need for a system of control and coordination of organisms? (OR)
How is control and coordination brought in organisms?
Answer:
- The various physiological processes in an organism are closely linked and depen¬dent on each other.
- The linking together of body activities in time and space is called coordination.
- Without coordination, the activities of the body would be disturbed a lot.
- For example when eating food at meal, the position of food is recorded by the eyes and as a result of this information the arms are moved to the right place to pick it up with precision and accuracy.
- As the food is raised to the mouth, the latter opens to receive it. Chewing movements commence and saliva is secreted.
- At the moment of swallowing, epiglottis closes trachea.
Question 31.
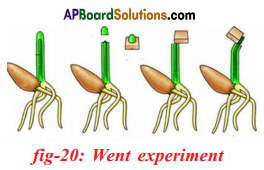
What is the experiment conducted by Charles Darwin and Francis Darwin? What is their conclusion?
Answer:
- Charles Darwin and his son Francis Darwin performed some experiments on phototropism.
- They covered the terminal portion of the tip of stem (coleoptile) with a cylinder of metal foil.
- Exposed the plant to light coming from the side.
- The characteristic bending of the seedling did not occur.
- If light was permitted to penetrate the cylinder, bending occurred normally.
- They concluded that when seedlings are freely exposed to a lateral light some influence is transmitted from upper to the lower part causing the material to bend.
![]()
Question 32.
What are the different types of tropisms found in plants?
Answer:
- The different types of tropisms found in plants are phototropism, geotropism, chemotropism, hydrotropism and thigmotropism.
- Different stimulus and type of tropism.
Stimulus Type of tropism
Light – Phototropism
Gravity – Geotropism
Chemical substance – Chemotropism
Water – Hydrotropism
Touch – Thigmotropism
Question 33.
Describe the story of invention of insulin. (OR)
Collect the information about insulin from internet and other sources and report on it.
Answer:
- In Latin “insula” means an Island.
- In 1868 Paul Langerhans of Germany working on the structure of Pancreas found Islets of Langerhans specialised cells richly supplied with blood vessel.
- But the function of pancreas remained unknown.
- Many others interested in the function of pancreas found that its removal from the body of an experimental animal would lead to the development of disease called ‘sugar diabetes’ (or) diabetes mellitus.
- Diabetes is a condition in which the amount of free sugar in the blood and in the urine is abnormally high.
- Later scientists found that when they tied the pancreatic duct that emerge from the duodenum caused the degeneration of pancreas but not Islets of Langerhans.
- Moreover the animal would not develop diabetes. This was really a strong evidence that the level of blood sugar is linked with the Islet cells.
- By 1912 workers were convinced that the Islets produced a secretion which directly liberated into the blood.
- Ten years later in Toronto, Banting, Best and Macleod finally succeeded in extracting insulin from degenerate animal pancreas whose ducts to the intestine had been tied.
- Insulin is now produced in large quantities for the treatment of human sufferers diabetes, to whom it is administered by injection into the skin.
![]()
Question 34.
Compare and contrast the nervous and hormonal mechanism for control and coor-dination in animals.
Answer:
| Nervous system | Hormonal system |
| 1) Nervous system has a network of nerves. | 1) Hormone system does not have such a network in the body. |
| 2) Nervous impulses pass from the receptors to the central nervous system and then to the effectors, through nerve fibers. | 2) Hormone system does not have such a network in the body. Hormones pass from the endocrine glands through blood. |
| 3) Nerve impulses reach only the cells required to respond. | 3) Hormones reach all the cells but special cells on the target organs using special molecules on their surfaces recognize the information and act. |
| 4) There is no feedback mechanism in generating electrical impulses. | 4) The timing and amount of hormones released are dependent on feedback mechanism. |
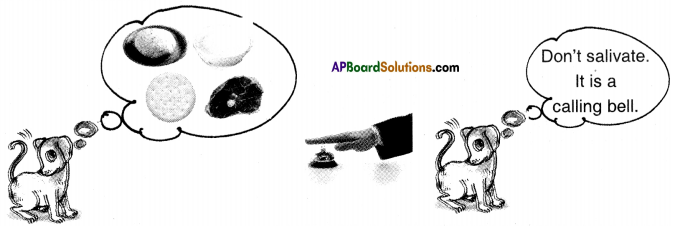
Question 35.
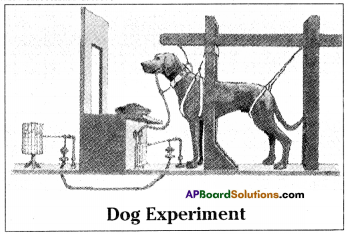
Write brief notes on Ivan Pavlov’s experiment on dog to demonstrate conditioned reflexes.
Answer:
- Conditioned reflexes are not inherited.
- Ivan Pavlov, a Russian scientist did experiments on conditioned reflexes. His experiments on dogs have become very famous.
- When the dog sees food, it secretes salvia. He rang a bell whenever the dog was given food.
- After doing this for few days he noticed that the dog secretes salvia when it hears the bell even if the food is not given.
- In otherwords dog associated the sound of the bell with the food and assumes that whenever the bell rings food is given.
- In expectation of food, saliva start flowing from its mouth. Human beings are no exception to this.
- For example, standing in attention when you hear National Anthem.
Question 36.
Collect information about the major plant hormones from library or internet?
Answer:
Some major plant hormones and their action are given in the following table.
Major plant hormones and their action.
| Hormones | Uses |
| Abscisic acid | Closing of stomata; seed dormancy. |
| Auxins | Cell elongation and differentiation of shoots and roots. |
| Cytokinins | Promote cell division, promotion of sprouting of lateral buds, delaying the ageing in leaves, opening of stomata. |
| Ethylene | Ripening of fruit. |
| Gibberellins | Germination of seeds and sprouting of buds; elongation of stems; stimulation of flowering; development of fruit, breaking the dormancy in seeds and buds. |
![]()
Question 37.
What are auxins? How do they affect plant growth?
Answer:
- Auxins are phytohormones which promote longitudinal growth in plants.
- The term auxin usually refers to a chemical compound called Jndole Acetic Acid (IAA) which is the principal nature auxine.
- IAA promotes growth and elongation of stems, roots and enlargement of many fruits.
- Auxins are known to loosen the cellulose frame work of cell wall which helps in cell enlargement.
- Auxins promotes cell division in vascular cambium and also root initiation.
- Auxins are also responsible for bending of plants in response to light (phototropism) and also to the gravity stimulus (Geotropism).
- Auxin is responsible for Apical dominance.
- A large number of auxins are synthesized by artificial methods in chemical laboratories.
- Substances like Naphthalene Acetic Acid (NAA) and Indole Butyric Acid (IBA) are used for inducing roots in cuttings.
- Auxin spray can prevent premature fruit drop .
- Auxin is also known to inhibit the abscission of leaves and fruits.
Question 38.
What is the role of Gibberellins in plant growth and development?
Answer:
- Gibberellins has a significant effect on stem elongation.
- It also increases the leaf lamina area. This is due to stimulation of cell division and cell elongation to both leaves and stem.
- It leads to the formation of seedless fruits.
- Gibberellins along with auxins promote cell elongation and leaf expansion.
- Parthenocarpy is induced in fruits like apple and pear with spray of Gibberellins.
- These substances are also known to induce enzymes like amylase, protease, lipase, etc. at the on set of seed germination and break the seed dormancy.
- These substances are used for fruit setting and also for growing seed less fruits.
- In beverages industry gibberellin is used to stimulate amylase activity in barley seeds. This is known to enhance the malting of barley grains.
Question 39.
What are the functions of cytokinins?
Answer:
- Cytokinins are capable of stimulating cell division along with auxins.
- They promote cell elongation.
- They have ability to delay the pocess of ageing in leaves.
- Cytokinins can prolong the life of fresh leaf crops like cabbage, spinach.
- They are also used for keeping the flowers fresh.
- Cytokinins are most effective in breaking dormancy of buds and seeds.
- The levels of cytokinins decrease in senescing leaves.
Question 40.
What is ABA? Explain its function in the plant.
Answer:
- ABA means Abscisic acid. It is the plant growth inhibiting substance.
- It induces dormancy in buds, tubers and many seeds.
- ABA is responsible for the formation of separation layer or abscission layer between main plant and the leaf or between plant and flower or fruit. It results in the falling of leaves, fruits and flowers.
- It prevents the water loss during drought conditions by closing the stomata.
Question 41.
Draw a diagram of Reflex area and describe the functions of different parts of Reflex arc.
Answer:
![]()
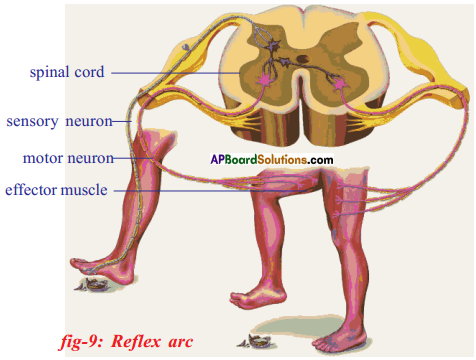 Functions of different parts of Reflex arc : Reflex arc consists of a receptor, a sensory nerve (afferent) an association neuron or inter neuron, motor nerve (effferent) and a effector organ.
Functions of different parts of Reflex arc : Reflex arc consists of a receptor, a sensory nerve (afferent) an association neuron or inter neuron, motor nerve (effferent) and a effector organ.
| S.No. | Component of the Reflex arc | Function |
| 1. | Receptor | Receives information and generates impulses. |
| 2. | Sensory (Afferent) nerve | Carries information from the receptor to the inter neurons in the spinal cord. |
| 3. | Inter neurons | Processes the information and generates responses |
| 4. | Motor (efferent) nerve | Carries the information from the spinal cord to the effector organ. |
| 5. | Effector organ | Receives the information from the efferent neuron and shows the appropriate response. |
Question 42.
Write a brief account on peripheral nervous system.
Answer:
- The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves that arise from the brain and
spinal cord; and a vast system of dorsat and ventral root nerve cell heads. - The peripheral nervous system has 43 pairs of nerves.
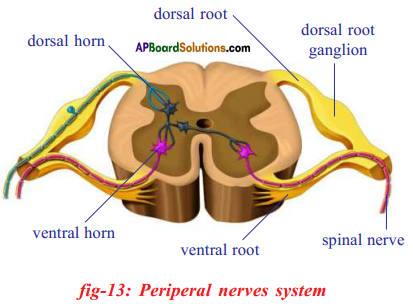
- Of these 12 pairs are called cranial nerves and the rest of 31 pairs are called spinal nerves.
- Nerves attached to the spinal cord have two types of connections or roots – One to the back or the dorsal side and other to front or the ventral side of cord.
- The peripheral nervous system can either involuntarily control several functions of regions like our internal organs, blood vessels, smooth and cardiac muscles. So it is called autonomous nervous system.
![]()
Question 43.
Write briefly about the spinal cord. (OR)
Describe the transverse section of spinal cord with the help of a diagram.
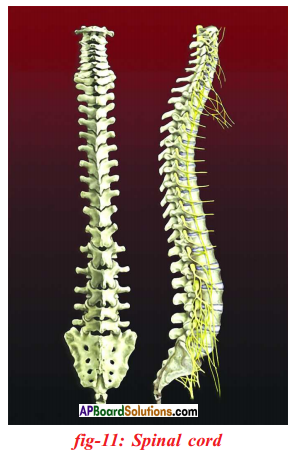
Answer:
- Spinal cord is a long and cylindrical structure.
- It passess through vertebral column extending all along the dorsal surface of trunk.
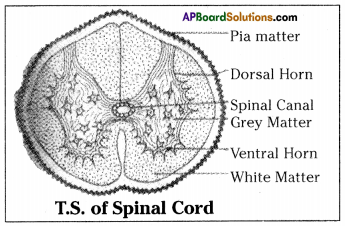
- In other words, vertebrae of the vertebral column protect the spinal cord from injuries.
- In a cross section of the spinal cord, the grey matter appears like butterfly or in the shape of letter ‘H’.
- Each segment of the ‘H’ shaped grey matter is called a horn.
- The upper horns are called dorsal horns, and the lower horns are called ventral horns.
- In the middle of the grey matter is a canal called spinal canal.
- It runs all along the length of spinal cord and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
- From the sides of spinal cord, 31 pairs of nerves take their origin and supply branches to various parts of the body.
Question 44.
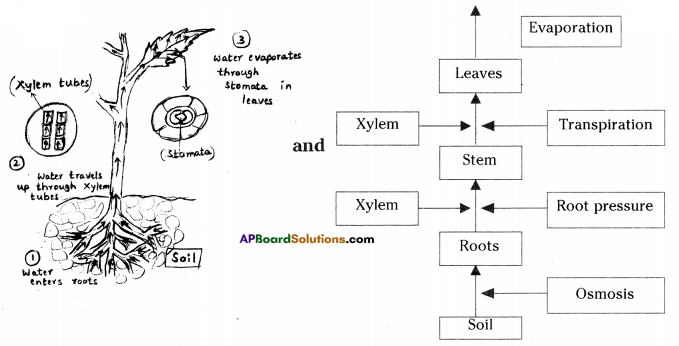
Describe an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism. (OR)
The roots of a plant move or grow towards water in the soil. How do you prove this with the help of an experiment ?
Answer:
Aim: To prove that roots grow towards water.
Apparatus or materials: Two glass troughs, soil, two similar plants, clay pot, water.
Procedure:
- Take two glass troughs A and B,
- Fill each one of them with two thirds of soil,
- Plant a tiny seedling in trough A.
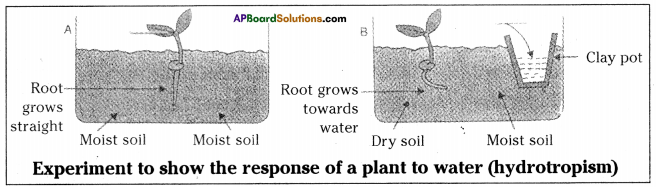
- In trough B, plant a similar seedling and place a small clay pot inside the soil.
- Water the soil in the trough A daily and uniformly.
- Do not water the soil in trough B, but put some water in the clay placed in the soil.
- Leave both the troughs for a few days.
Observation: On examining the roots later, it will be found that the root in the trough B has bent towards the source of water. Roots in trough A grew normally straight. Result: The growth of roots towards water is known as hydrotropism. In this experiment roots bent towards water. By this experiment it was proved that roots always grow towards water.
![]()
Question 45.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.
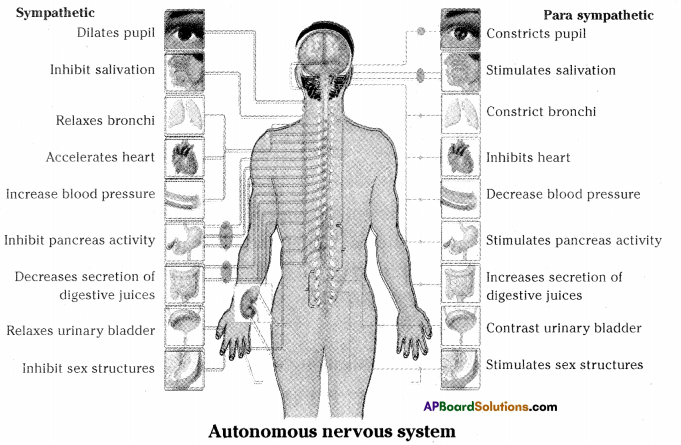 i) To which organs of the body do the nerves go from the ganglions near the vertebral column ?
i) To which organs of the body do the nerves go from the ganglions near the vertebral column ?
Answer:
Eyes, salivary glands, heart, lungs, liver, stomach, gall bladder, intestine, adrenal gland, sex organs are the body parts, the nerves go from the ganglions near the vertebral column.
ii) Which are the organs that receives nerves starting from the brain ?
Answer:
Nose, eye, tongue, ear, head, neck and shoulder receive nerves from the brain.
iii) Which are the organs whose activities are influenced by the sympathetic nervous system?
Answer:
Eyes, lungs, kidneys, gastro intestinal tract, heart, stomach, sweat glands, sex organs, adrenal gland, salivary glands.
iv) Which tire the organs whose activities are influenced by the parasympathetic nervous system ?
Answer:
Eye, lungs, kidneys, gastro intestinal tract, heart, stomach, sweat glands, sex organs, adrenal gland, salivary glands.
v) What do you understand about the functions of parasympathetic nervous system ?
Answer:
- The major functions of parasympathetic nervous system is to keep the body in its normal state and it is called as rest and digestive system or feed or breed system.
- The function of parasympathetic nervous system is to restore the body to its nor¬mal functioning after all the stress is gone.
- The parasympathetic nervous system helps the body to do simple things such as breathing regularly, excreting hormones, eating and digesting food.
- It also keeps a person alive when sleeping.
vi) What do you understand about the functions of sympathetic nervous system ?
Answer:
- The major functions of the sympathetic nervous system is to activate the response of the body during stressful situation including the fight or flight mechanism of the body.
- Sympathetic nervous system is essentially responsible for helping the body to get ready for action or feeling.
- It dilates the pupil so one can see better especially in the dark, it increases heart rate so that to increase supply of oxygen to the muscles, decreases digestion so that the energy be better utilized for fighting and so on.
![]()
Question 46.
Describe the structure of brain with the help of a neat diagram.
Answer:
- Proportionate to the body size, the human brain is the largest of all animals.
- The brain is present in the hard bony box like structure called cranium.
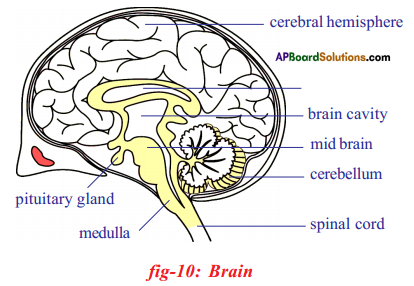
- It is covered by three layers called the meninges. The meninges are continued and cover the spinal cord as well.
- The space between the inner layers is filled with fluid called cerebro – spinal fluid.
- It serves as a shock – absorbing medium and protects the brain against shocks / jerks along with meninges and cranium.
- The nerve cell bodies together with capillaries form a mass called grey matter while the myelinated axons form white matter.
- The grey matter is in the outer layers while the white matter is present towards inner layers.
Question 47.
Describe the structure of cerebrum.
Answer:
- Fore brain is the largest part of the brain. It is also called CEREBRUM.
- A deep groove in the middle of the cerebrum divides into two equal halves.
- Each calf is called as a cerebral hemisphere.
- Right and left cerebral hemispheres are connected each other by a bundle of axon.
- The outer portion of the cerebral hemisphere is gray in colour and is called CEREBRAL CORTEX.
- There are several ridges called GYRI and the grooves are called SULCI.
- They increase the surface area of the cortex in order to accumulate more number of neurons.
- In the cerebral cortex, there are centres to receive and analyse various informations like visual (sight), auditory (hearing), olfactory (smell), etc.
- Three very deep grooves present across each cerebral hemisphere divides it into four lobes. FRONTAL, PARIETAL, TEMPORAL, and OCCIPITAL LOBES.
![]()
Question 48.
Write a brief account of Adrenal glands.
Answer:
There are two adrenal glands one on the top of each kidney. Adrenal gland has 2 parts.
- Cortex – outer part
- Medulla – Inner part
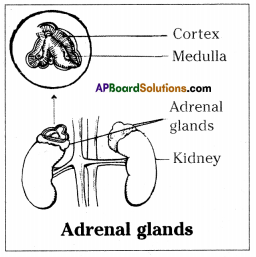
i) Adrenal cortex: Adrenal cortex secretes two hormones i) cortisol and ii) Aldosterone
a) Cortisol regulates the protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism.
b) Aldosterone increases the re-absorption of water and sodium in the kidney. It regulates the sodium levels in the body.
ii) Adrenal medulla: It secretes a hormone called Adrenaline at times of physical and mental stress. It is secreted in conditions like:
- fall in blood sugar levels
- When the person is injured.
- When exposed to cold conditions
- Suffering from pain
The hormone helps in facing such as situation. Therefore it is called the hormone of FIGHT or FLIGHT.
Question 49.
What is feedback mechanism? Illustrate with an example.
Answer:
- It is necessary that the hormones are secreted by the endocrine glands in our body in precise quantities which are required for the normal functioning of the body.

- This means there should be some mechanism to regulate the production and release of hormones in the body.
- For example, anger is always short lived factor and adrenalin is the hormone responsible for anger.
- When the levels of adrenalin in the blood came down slowly, we come to normal state.
- When we are afraid the rate of heart-beat increases, the breathe rate will be faster, blood pressure increases.
- After sometime we come to normal state only when we reach a safe spot.
- The timings and amount of hormones released by endocrine gland is controlled by the feed back mechanism, which is in build in our body.
![]()
Question 50.
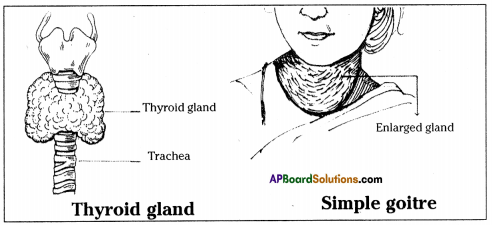
Write short note on simple goitre. (OR)
What happens if we do not take sufficient amounts of iodine in food? (OR)
Why are people advised to take iodised salt in the food they eat?
Answer:
- Iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroxine in the body.
- If there is a reduced intake of iodine in food, it hinders the formation of thyroxine and results in increase the size of the thyroid gland.
- This results in the enlargement of neck. This condition is called simple goitre.
![]()
 Answer:
Answer: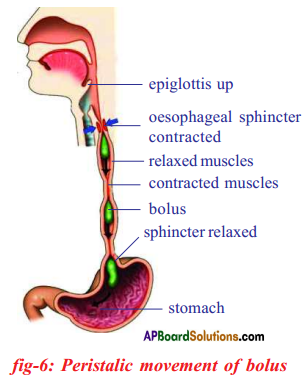 b) Circular muscles and longitudinal muscles of oesophagus help in the movement of food ‘bolus’.
b) Circular muscles and longitudinal muscles of oesophagus help in the movement of food ‘bolus’.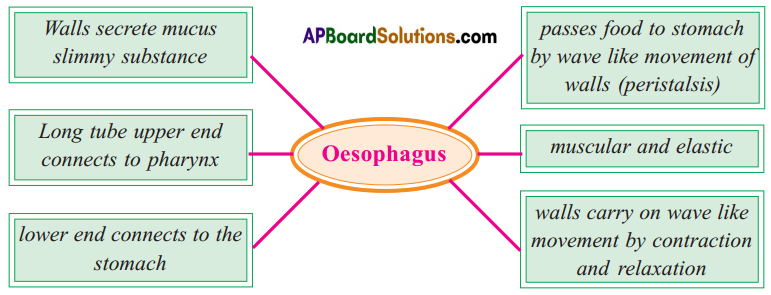
 Procedure:
Procedure:
 i) No, the production of oil doesn’t meet the consumption in India.
i) No, the production of oil doesn’t meet the consumption in India.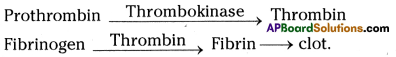

 Answer:
Answer:
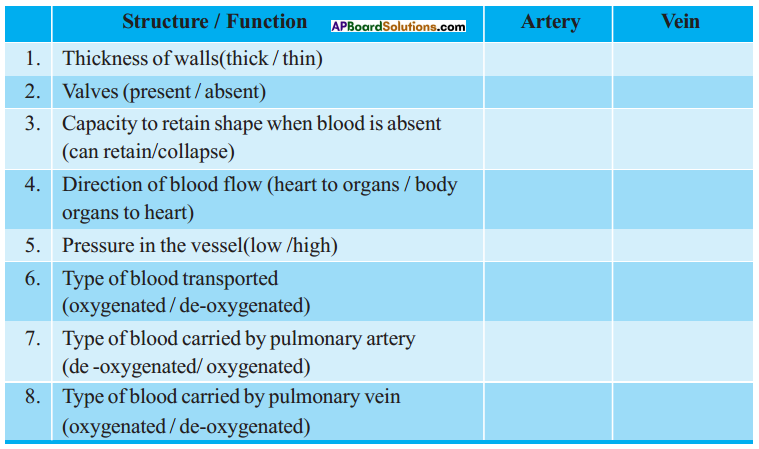
 2) You feel something pushing your fingers rhythmically up and down.
2) You feel something pushing your fingers rhythmically up and down.

 a) What will you prove by this experiment?
a) What will you prove by this experiment? a) What will you prove by this experiment?
a) What will you prove by this experiment?
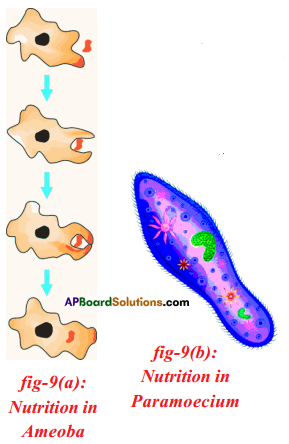
 Palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma consist of chloroplast.
Palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma consist of chloroplast. i) What is the aim of this experiment?
i) What is the aim of this experiment? Parasitic Nutrition in Cuscuta :
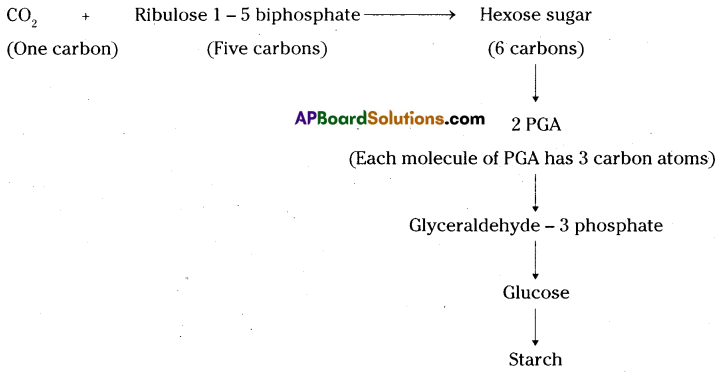
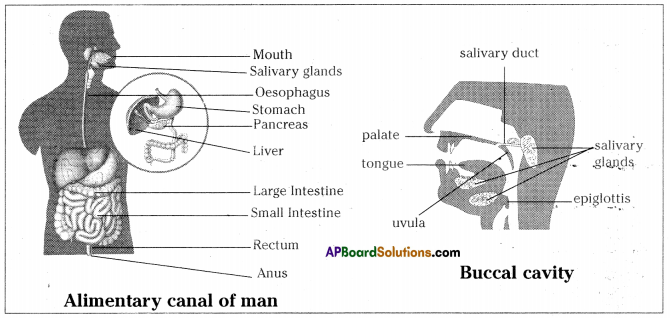
Parasitic Nutrition in Cuscuta :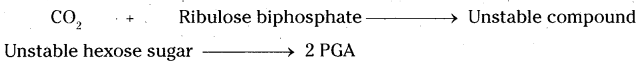
 a) What apparatus do you use during the conduction of the experiment?
a) What apparatus do you use during the conduction of the experiment?


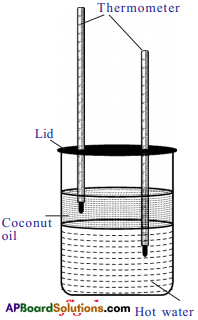
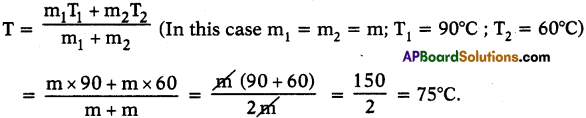
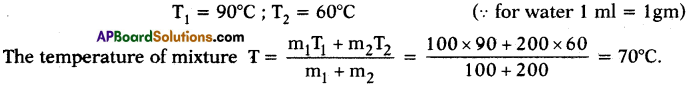
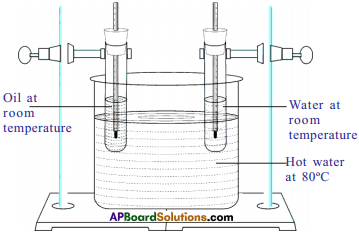



 Required materials: A chart, twine thread, fevicol, sticker.
Required materials: A chart, twine thread, fevicol, sticker.


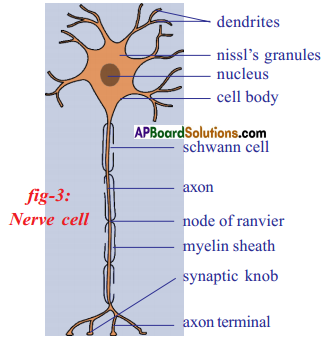 Structural unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell or neuron. Neuron is highly specialised cell. Neurons carry impulses or messages. New nerve cells are not produced to replace the damaged or destroyed nerve cell. A neuron has three parts. They are
Structural unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell or neuron. Neuron is highly specialised cell. Neurons carry impulses or messages. New nerve cells are not produced to replace the damaged or destroyed nerve cell. A neuron has three parts. They are


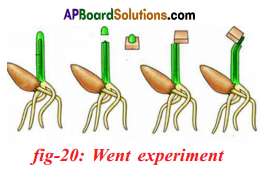 Went interpreted these experiments as showing that the coleoptile tip exerted it’s effect by means of chemical stimulus rather than a physical stimulus such as an electrical impulse.
Went interpreted these experiments as showing that the coleoptile tip exerted it’s effect by means of chemical stimulus rather than a physical stimulus such as an electrical impulse.


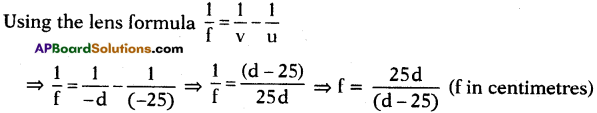

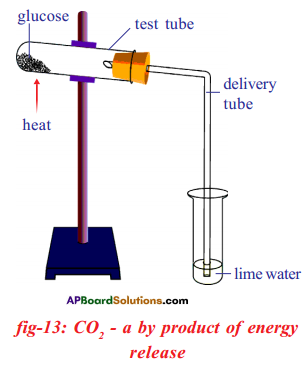

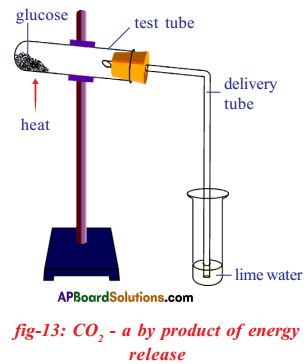
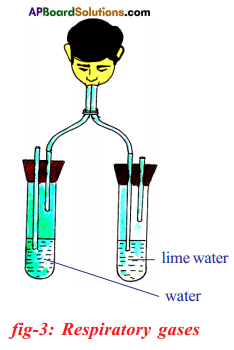 (a) Which gas turns lime water milky in this experiment?
(a) Which gas turns lime water milky in this experiment?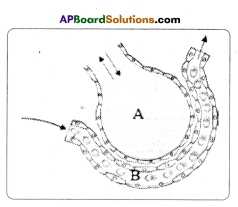 A) To which biosystem is this picture related?
A) To which biosystem is this picture related?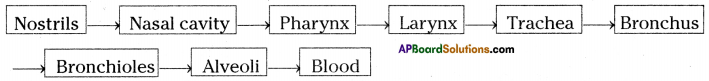
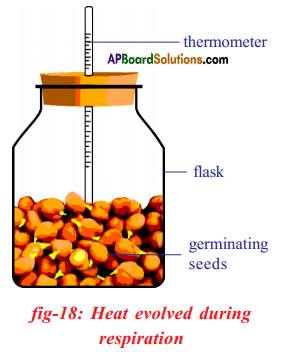 a) What is the aim of this experiment?
a) What is the aim of this experiment?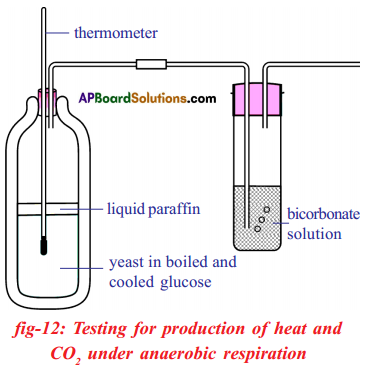 a) What do you prove by conducting this experiment?
a) What do you prove by conducting this experiment?
 i) Which process do we know with the help of this experiment?
i) Which process do we know with the help of this experiment?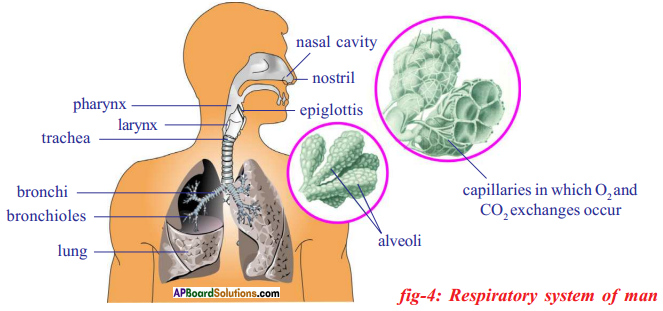

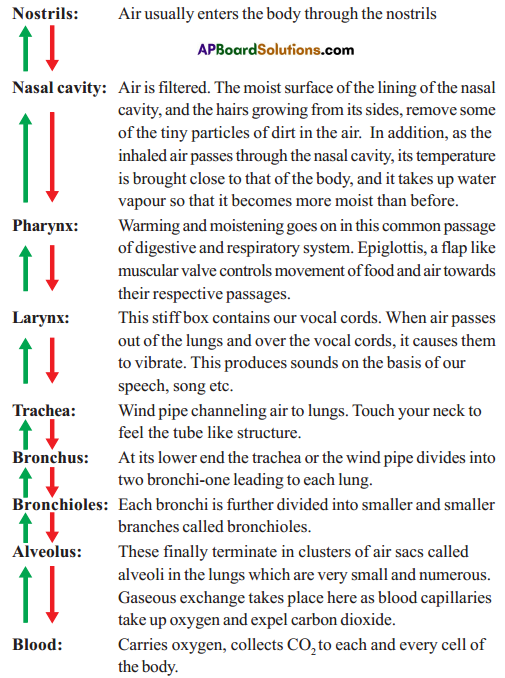
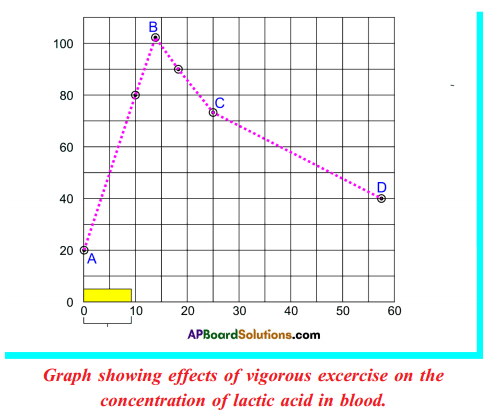
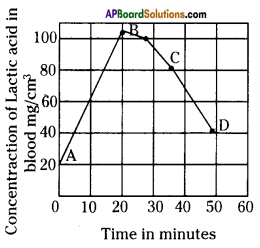 Graph showing effects of vigorous excercise on the concentration of lactic acid in blood.
Graph showing effects of vigorous excercise on the concentration of lactic acid in blood.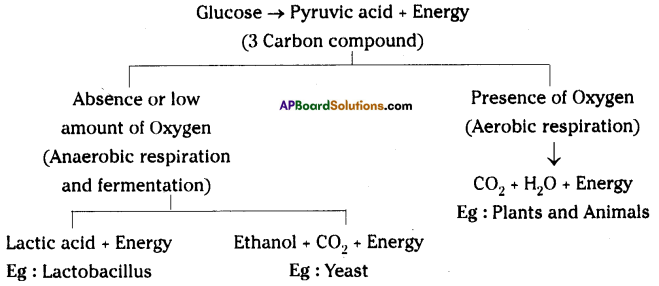

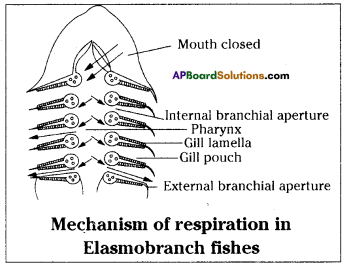
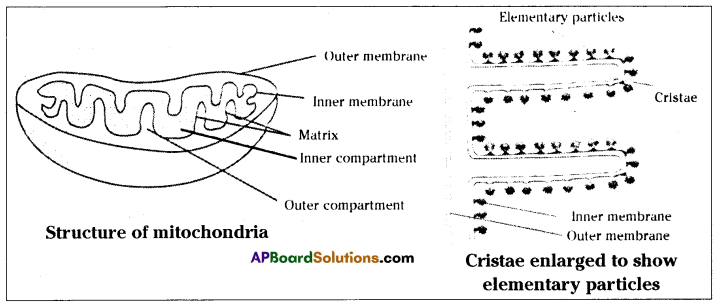
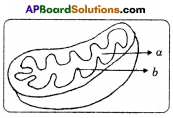
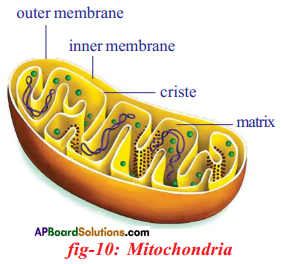 Oxidation of glucose molecule occurs in the mitochondria, ot cell. This is known as cellular respiration. The energy produced during cellular respiration stored in the form of ATP molecule. Energy producing cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria hence we call it cell of power or power house of the ceil.
Oxidation of glucose molecule occurs in the mitochondria, ot cell. This is known as cellular respiration. The energy produced during cellular respiration stored in the form of ATP molecule. Energy producing cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria hence we call it cell of power or power house of the ceil.

 Role of different sets of teeth in mastication:
Role of different sets of teeth in mastication:
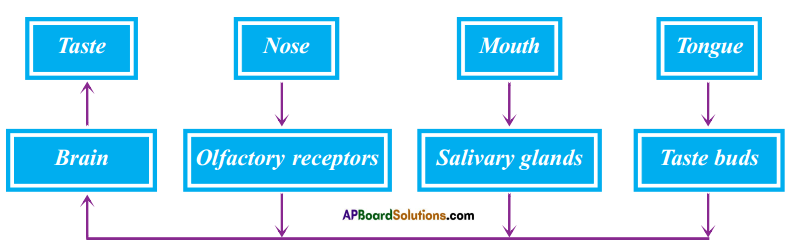
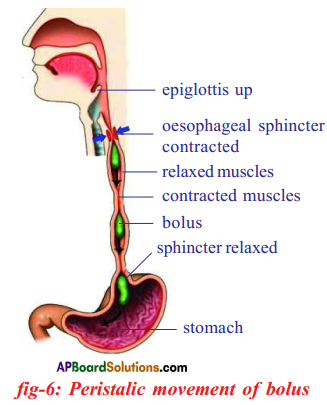 Importance of mucus on the walls of food pipe :
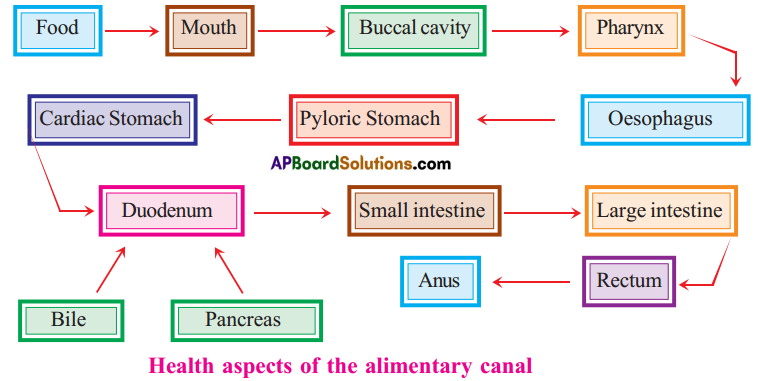
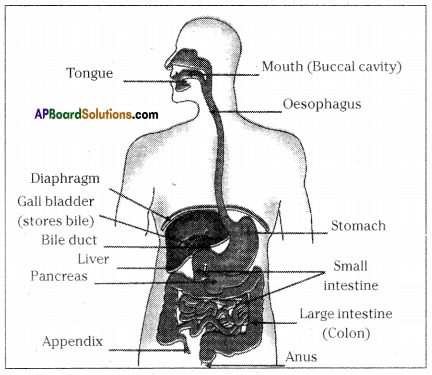
Importance of mucus on the walls of food pipe :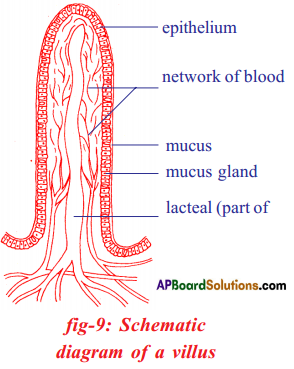 Coordination of digestive system with circulatory system :
Coordination of digestive system with circulatory system :