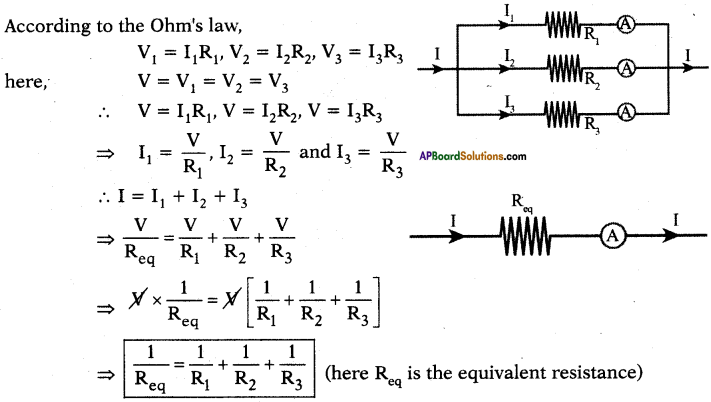
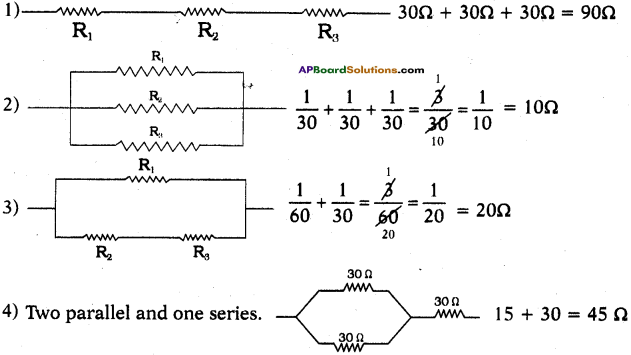
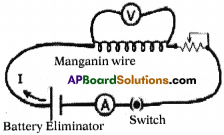
AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Maths Textbook Solutions Chapter 12 Applications of Trigonometry Ex 12.2 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Maths Solutions 12th Lesson Applications of Trigonometry Exercise 12.2
10th Class Maths 12th Lesson Applications of Trigonometry Ex 12.2 Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
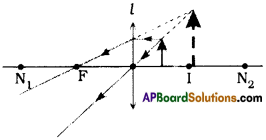
A TV tower stands vertically on the side of a road. From a point on the other side directly opposite to the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of tower is 60°. From another point 10 m away from this point, on the line joining this point to the foot of the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 30°. Find the height of the tower and the width of the road.
Answer:
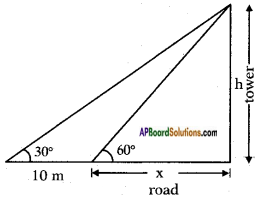
Let the height of the tower = h mts say
Width of the road be = x m.
Distance between two points of observation = 10 cm.
Angles of elevation from the two points = 60° and 30°.
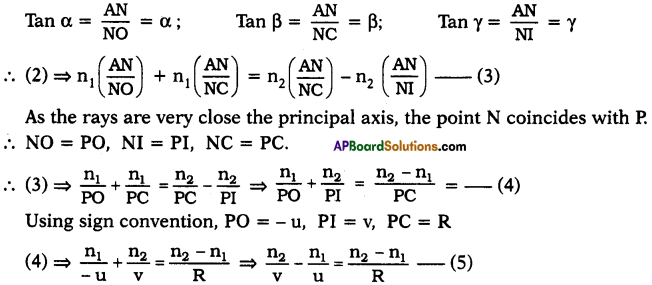
From the figure
tan 60° = [latex]\frac{h}{x}[/latex]
√3 = [latex]\frac{h}{x}[/latex]
⇒ h = √3x …….(1)
Also tan 30° = [latex]\frac{h}{10+x}[/latex]
⇒ [latex]\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{h}{10+x}[/latex]
⇒ h = [latex]\frac{10+x}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] ………(2)
From equations (1) and (2) h
h = √3x = [latex]\frac{10+x}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
∴ √3x = [latex]\frac{10+x}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
√3 × √3x = 10 + x
⇒ 3x – x = 10
⇒ 2x = 10
⇒ x = [latex]\frac{10}{2}[/latex] = 5m
∴ Width of the road = 5 m
Now Height of the tower = √3x = 5√3 m.
![]()
Question 2.
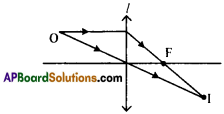
A 1.5 m tall boy is looking at the top of a temple which is 30 metre in height from a point at certain distance. The angle of elevation from his eye to the top of the crown of the temple increases from 30° to 60° as he walks towards the temple. Find the distance he walked towards the temple.
Answer:
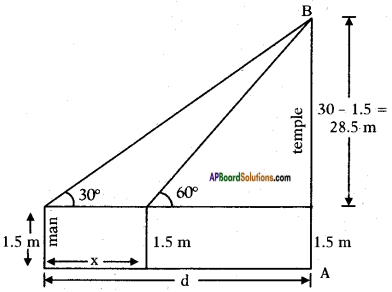
Height of the temple = 30 m
Height of the man = 1.5 m
Initial distance between the man and temple = d m. say
Let the distance walked = x m.
From the figure
tan 30° = [latex]\frac{30-1.5}{d}[/latex]
⇒ [latex]\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{28.5}{d}[/latex]
∴ d = 28.5 × √3m ………(1)
Also tan 60° = [latex]\frac{28.5}{d-x}[/latex]
⇒ √3 = [latex]\frac{28.5}{d-x}[/latex]
⇒ √3(d-x) = 28.5
⇒ √3(28.5 × √3-x) = 28.5
⇒ 28.5 × 3 – √3x = 28.5
⇒ √3x = 3 × 28.5-28.5
⇒ √3x = 2 × 28.5 = 57
∴ x = [latex]\frac{57}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{19 \times 3}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] = 19√3
= 19 × 1.732
= 32.908 m.
∴ Distance walked = 32.908 m.
Question 3.
A statue stands on the top of a 2 m tall pedestal. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of the statue is 60° and from the same point, the angle of elevation of the top of the pedestal is 45°. Find the height of the statue.
Answer:
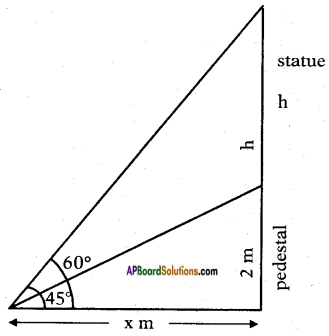
Height of the pedestal = 2 m.
Let the height of the statue = h m. Angle of elevation of top of the statue = 60°.
Angle of elevation of top of the pedestal = 45°.
Let the distance between the point of observation and foot of the pedestal = x m.
From the figure
tan 45° = [latex]\frac{2}{x}[/latex]
1 = [latex]\frac{2}{x}[/latex]
∴ x = 2 m.
Also tan 60° = [latex]\frac{2+h}{x}[/latex]
⇒ √3 = [latex]\frac{2+h}{x}[/latex]
⇒ 2√3 = 2 + h
⇒ h = 2√3 – 2
= 2(√3-1)
= 2(1.732 – 1)
= 2 × 0.732
= 1.464 m.
![]()
Question 4.
From the top of a building, the angle of elevation of the top of a cell tower is 60° and the angle of depression to its foot is 45°. If distance of the building from the tower is 7 m, then find the height of the tower.
Answer:
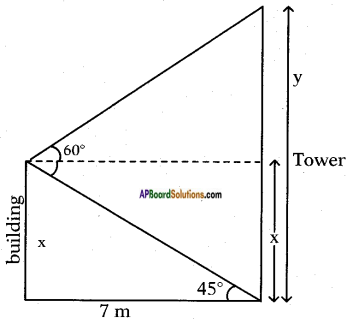
Angle of elevation of the top of the tower = 60°.
Angle of depression to the foot of the tower = 45°.
Distance between tower and building = 7 m.
Let the height of the building = x m and tower = y m.
From the figure
tan 45° = [latex]\frac{x}{7}[/latex]
1 = [latex]\frac{x}{7}[/latex]
∴ x = 7 m.
Also tan 60° = [latex]\frac{y-x}{7}[/latex]
⇒ √3 = [latex]\frac{y-x}{7}[/latex]
⇒ 7√3 = y – 7
∴ y = 7 + 7√3
= 7 (√3 + 1)
= 7(1.732 + 1)
= 2.732 × 7
= 19.124 m.
Question 5.
A wire of length 18 m had been tied with electric pole at an angle of eleva¬tion 30° with the ground. As it is covering a long distance, it was cut and tied at an angle of elevation 60° with the ground. How much length of the wire was cut ?
Answer:
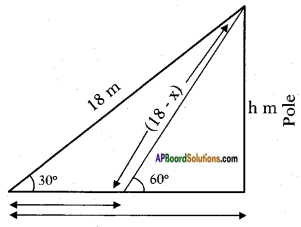
Length of the wire = 18 m
Let the length of the wire removed = x
Height of the pole be = h
From the figure
sin 30° = [latex]\frac{h}{18}[/latex]
⇒ [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{h}{18}[/latex]
⇒ h = [latex]\frac{18}{2}[/latex] = 9 m
Also sin 60° = [latex]\frac{h}{18-x}[/latex]
[latex]\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{9}{18-x}[/latex]
√3(18-x) = 9 × 2
18√3 – √3x = 18
√3x = 18√3 – 18
√3x = 18(√3-1)
x = [latex]\frac{18(\sqrt{3}-1)}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
= [latex]\frac{6 \times 3(\sqrt{3}-1)}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
= 6√3(√3-1)
= 6(3-√3)
= 18 – 6√3
= 18 – 10.392
= 7.608 m.
![]()
Question 6.
The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of the tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 30 m high, find the height of the building.
Answer:
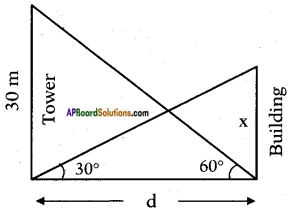
Height of the tower = 30 m
Angle of elevation of the top of the tower = 60°.
Angle of elevation of the top of the building = 30°.
Let the distance between the foot of the tower and foot of the building be d m and height of the building be x m.
From the figure
tan 60° = [latex]\frac{30}{d}[/latex]
√3 = [latex]\frac{30}{d}[/latex]
⇒ d = [latex]\frac{30}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{10 \times 3}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] = 10√3m
Also tan 30° = [latex]\frac{x}{d}[/latex]
⇒ [latex]\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{x}{10 \sqrt{3}}[/latex]
⇒ x = [latex]\frac{10 \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] = 10 m
∴ Height of the building = 10 m
Question 7.
Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite to each other on either side of the road, which is 120 feet wide. From a point between them on the road, the angles of elevation of the top of the poles are 60° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the poles and the distances of the point from the poles.
Answer:
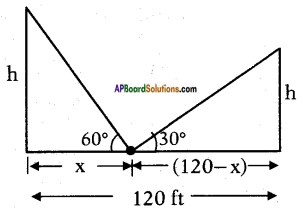
Width of the road = 120 f.
Angle of elevation of the top of the 1st tower = 60°.
Angle of elevation of the top of the 2 tower = 30°.
Let the distance of the point from the 1st pole = x.
Then the distance of the point from
the 2nd pole = 120 – x.
and height of each pole = h say.
From the figure
tan 60° = [latex]\frac{h}{x}[/latex]
⇒ √3 = [latex]\frac{h}{x}[/latex]
⇒ h = √3x ……..(1)
Also tan 30° = [latex]\frac{\mathrm{h}}{120-\mathrm{x}}[/latex]
⇒ [latex]\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{120-\mathrm{x}}[/latex]
⇒ h = [latex]\frac{120-x}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
From (1) and (2)
√3x = [latex]\frac{120-x}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
⇒ √3.√3x = 120-x
⇒ 3x = 120 – x
⇒ 3x + x = 120
⇒ 4x = 120
⇒ x = [latex]\frac{120}{4}[/latex] = 30 ft
Now h = √3x = √3 × 30 = 1.732 x 30 = 51.960 feet
∴ Distances of the poles = 30 ft. and 120 – 30 fts = 90 ft.
Height of each pole = 51.96 ft.
![]()
Question 8.
The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points at a distance of 4 m and 9 m, find the height of the tower from the base of the tower and in the same straight line with it are complementary.
Answer:
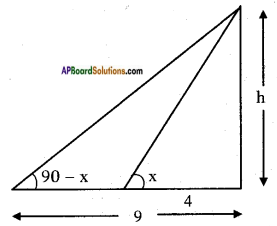
Let the height of the tower = h m.
Angles of elevation of the top of the tower from two points = x° and (90° – x)
From the figure
tan x = [latex]\frac{h}{4}[/latex] ……. (1)
Also tan (90° – x) = [latex]\frac{h}{9}[/latex]
⇒ cot x = [latex]\frac{h}{9}[/latex]
⇒ [latex]\frac{1}{\tan x}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{h}{9}[/latex]
∴ tan x = [latex]\frac{9}{h}[/latex] …….. (2)
From (1) and (2)
tan x = [latex]\frac{h}{4}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{9}{h}[/latex]
∴ [latex]\frac{h}{4}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{9}{h}[/latex]
h × h = 9 × 4
⇒ h2 = 36
⇒ h = 6 m
Question 9.
The angle of elevation of a jet plane from a point A on the ground is 60°. After 4 flight of 15 seconds, the angle of elevation changes to 30°. If the jet plane is flying at a constant height of 1500√3 meter, find the speed of the jet plane. (√3 = 1.732)
Answer:
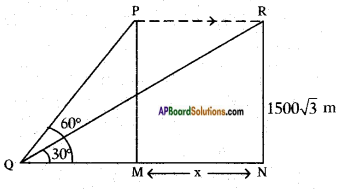
Height of the plane from the ground PM = RN = 1500√3 m.
Angle of elevation are 30° and 60°.
From the figure
tan 60° = [latex]\frac{PM}{QM}[/latex]
√3 = [latex]\frac{1500 \sqrt{3}}{\mathrm{QM}}[/latex]
QM = [latex]\frac{1500 \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] = 1500 m
Also tan 30° = [latex]\frac{RN}{QN}[/latex]
[latex]\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{1500 \sqrt{3}}{\mathrm{QM}+\mathrm{MN}}[/latex]
QM + MN = 1500√3 × √3
1500 + MN = 1500 × 3
MN = 4500 – 1500
MN = 3000 mts.
∴ Distance travelled in 15 seconds = 3000 mts.
∴ Speed of the jet plane = [latex]\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { time }}=\frac{3000}{15}[/latex] = 200 m/s
= 200 × [latex]\frac{18}{5}[/latex] kmph
= 720 kmph
Speed = 200 m/sec. or 720 kmph.








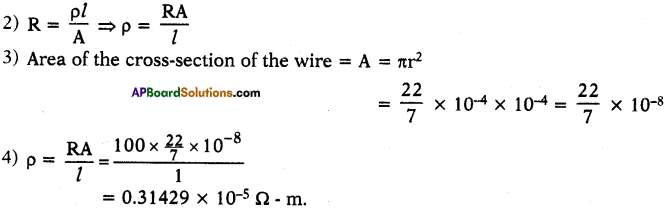


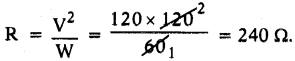
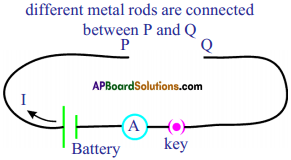
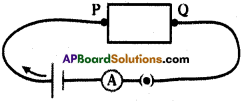
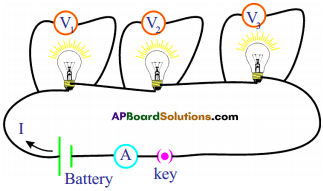
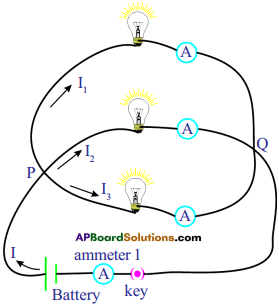

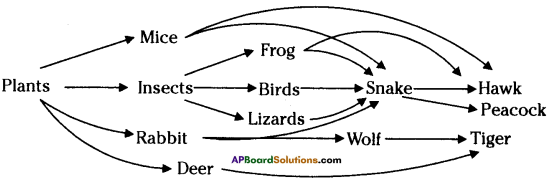
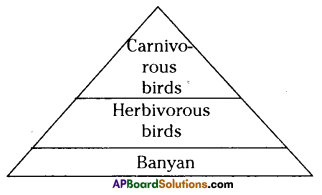
 i) Write any two food chains from the diagram.
i) Write any two food chains from the diagram.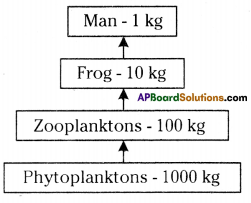 Answer:
Answer: i) As per the number of organisms in the tropic level, which group of organisms
i) As per the number of organisms in the tropic level, which group of organisms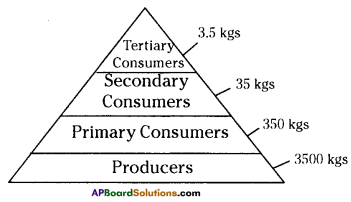
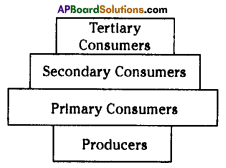

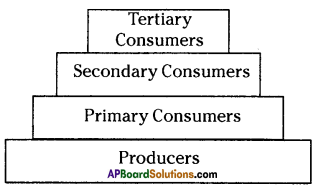

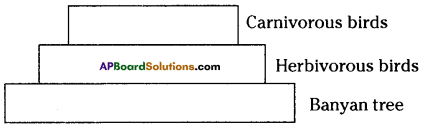

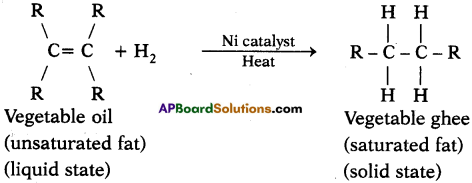
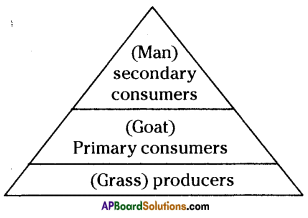
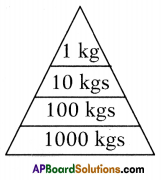 The pyramid of biomass for the given food chain, at each step 90% of the food is lost. That means 1000 kg of phytoplankton to produce 100 kg of Zooplankton to form 10 kg of fish to produce 1kg of human tissues. The fewer the steps in the food chain the more energy will be for the species at the top.
The pyramid of biomass for the given food chain, at each step 90% of the food is lost. That means 1000 kg of phytoplankton to produce 100 kg of Zooplankton to form 10 kg of fish to produce 1kg of human tissues. The fewer the steps in the food chain the more energy will be for the species at the top.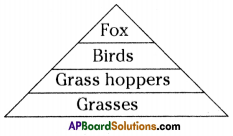
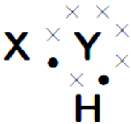
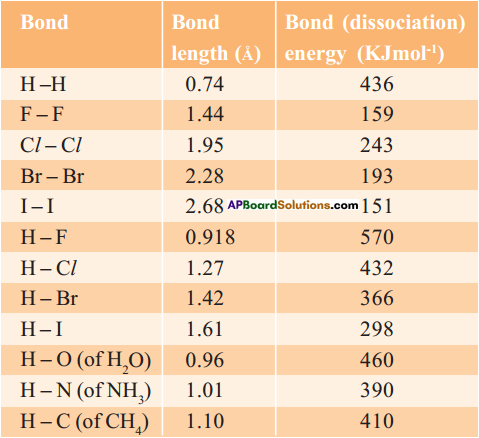






 symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.
symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.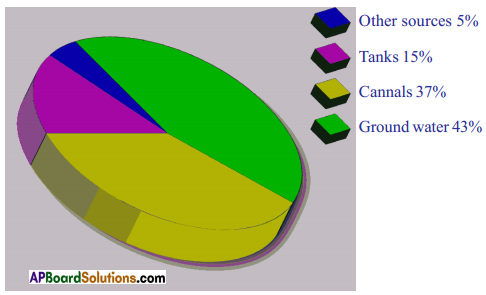 A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?
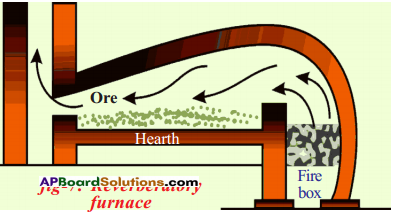
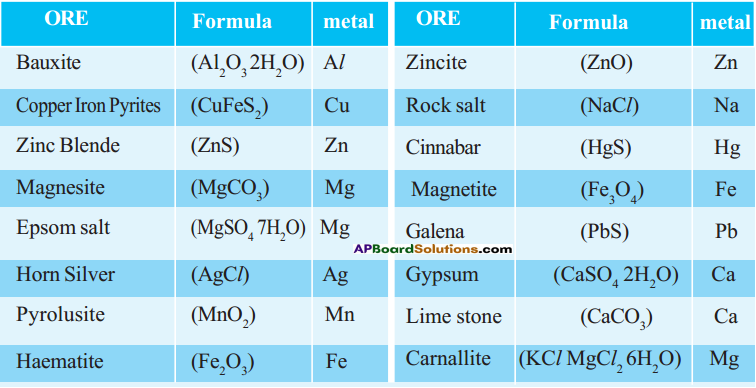
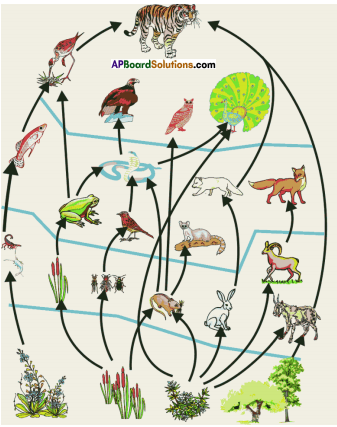
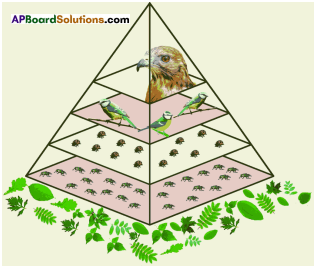
A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?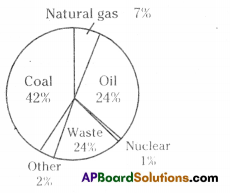 i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.
i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.
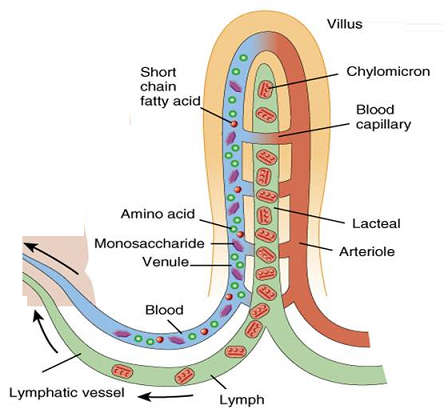
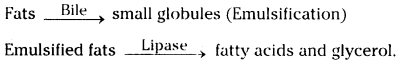

 Answer:
Answer: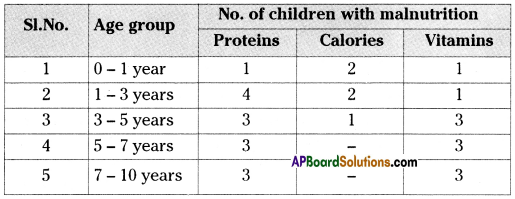
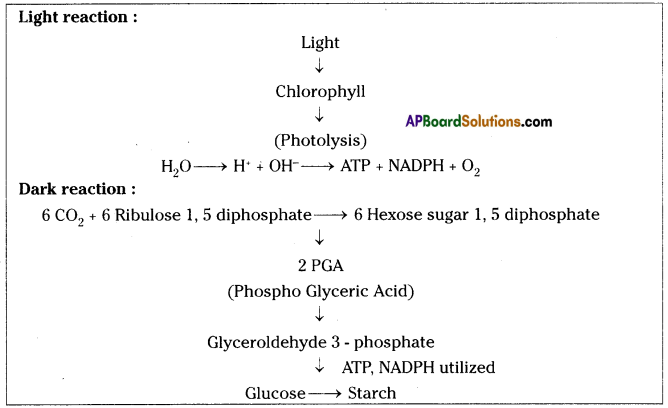
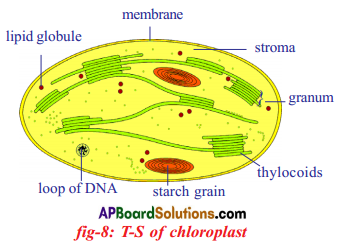
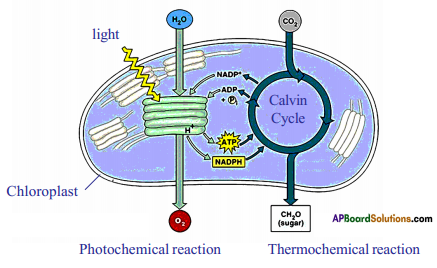
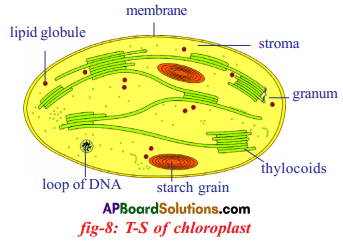 Role of Chloroplast in photosynthesis:
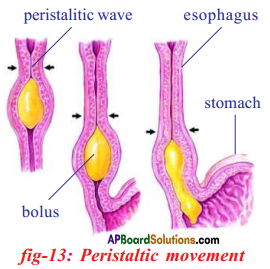
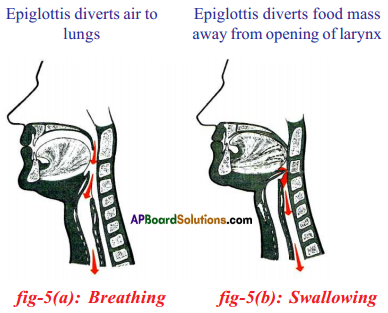
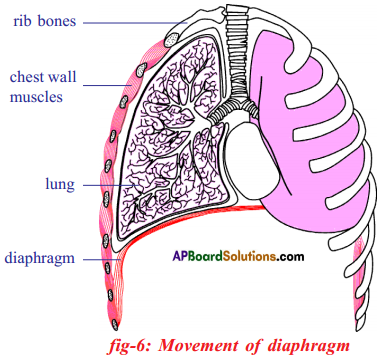
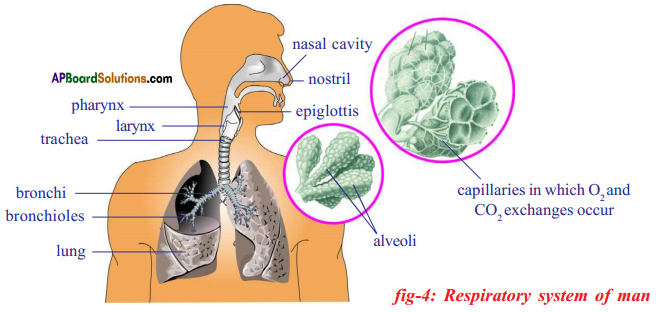
Role of Chloroplast in photosynthesis: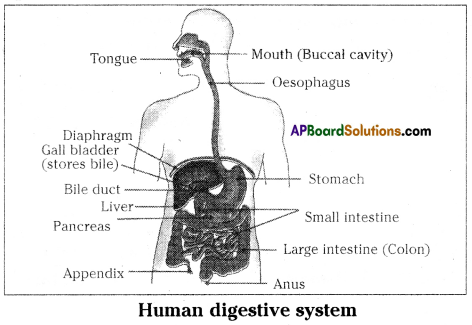 Parts where peristalsis takes place: Oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Parts where peristalsis takes place: Oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.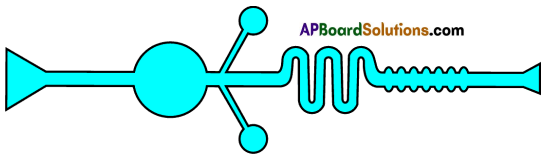 Answer:
Answer: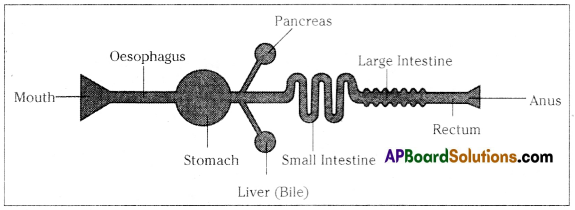
 Answer:
Answer: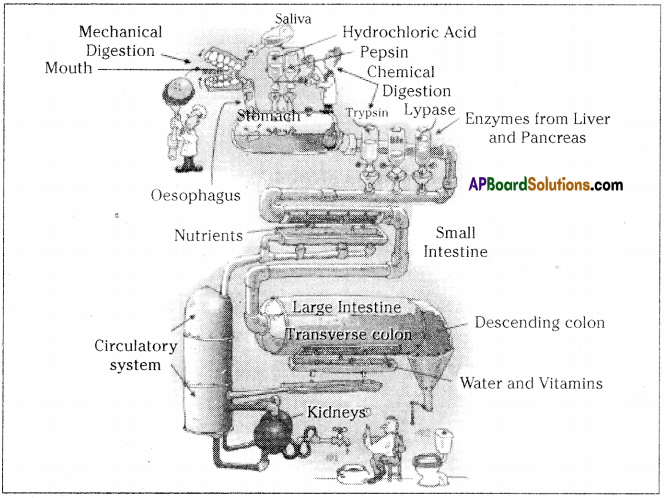
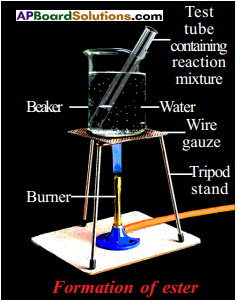
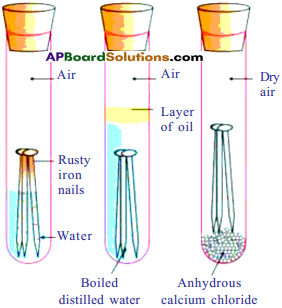
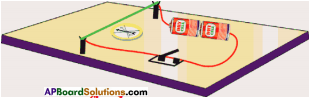
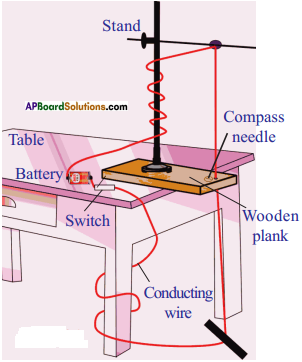
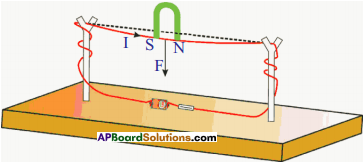
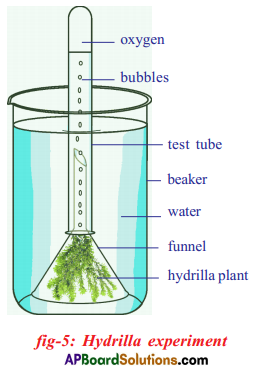
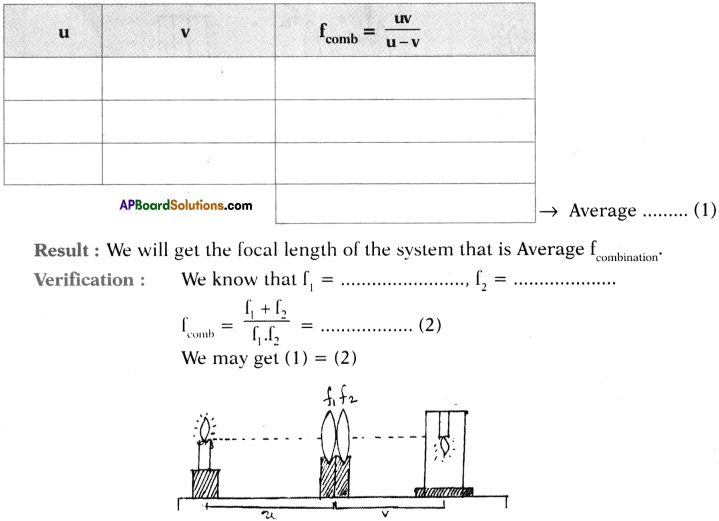
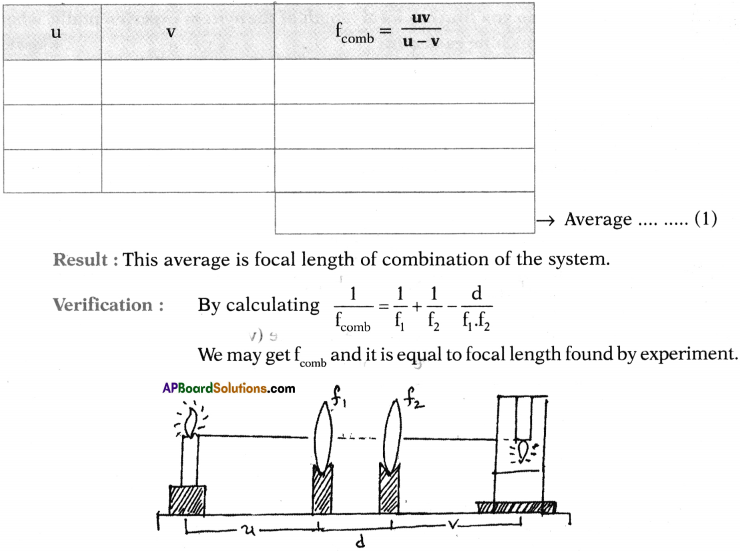
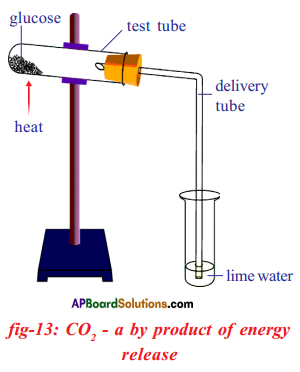
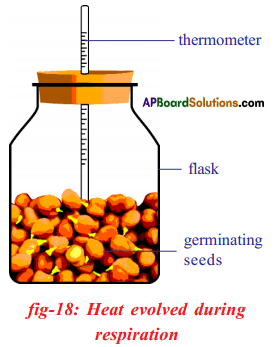
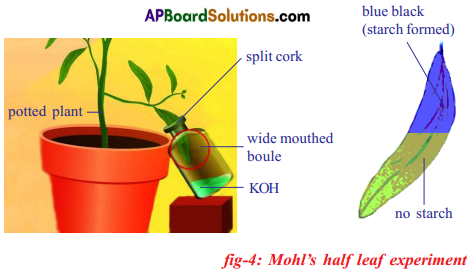 Apparatus:
Apparatus:
 Priestly should have tilted the bell jar to one side and introduced the mint plant without disturbing the experimental set up.
Priestly should have tilted the bell jar to one side and introduced the mint plant without disturbing the experimental set up.






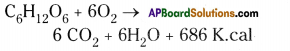
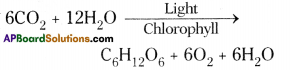




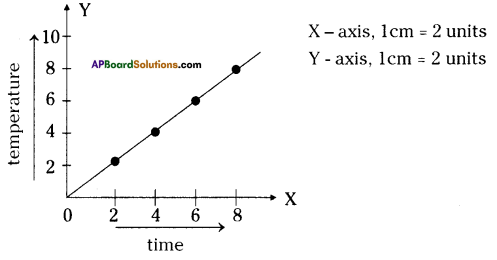
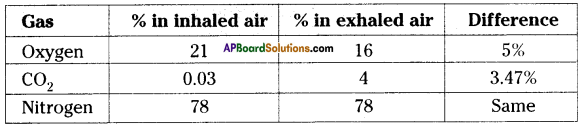
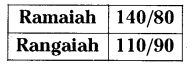
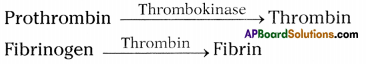
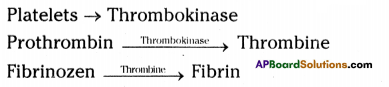
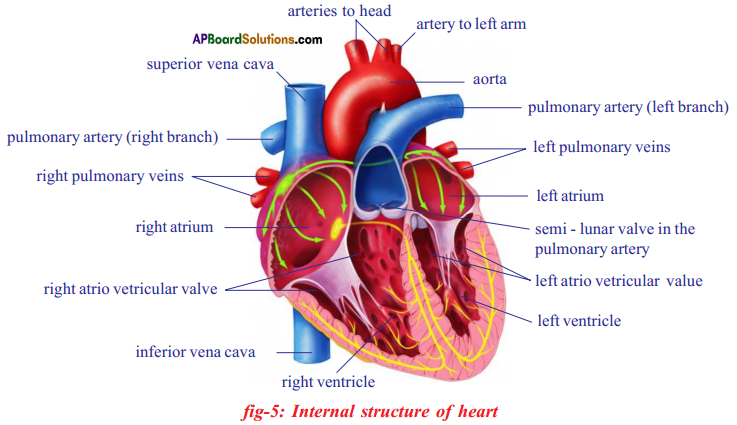
 Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer:

 Required material: A healthy potted plant, a polythene cover, water.
Required material: A healthy potted plant, a polythene cover, water.