AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 3 Transportation.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions 3rd Lesson Transportation
10th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Transportation 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What happens if blood platelets are absent in blood?
Answer:
- Blood clotting do not be takes place.
- So bleeding from the injuries occurs continuously leads to death of the person.
![]()
Question 2.
When do you think that our pulse rate goes up?
Answer:
Running, Exercise, Fear, Tension, Climbing up stairs.
Question 3.
List out the apparatus required to conduct root pressure experiments in plant.
Answer:
Clamp, glass tube, strong rubber tube, potted plant.
Question 4.
What happens if there are no valves in the Heart?
Answer:
- The valves between each atrium and its ventricles are one way valves. They allow the blood to flow from atrium to the ventricles without any hindrance, back flow of blood is stopped.
- If there are no valves in the heart, blood flow will not be proper, heart can not pump the blood properly into the blood vessels.
Question 5.
What is meant by pulse?
Answer:
- When we keep our finger at the wrist where the artery is passing into the hand, we feel the pressure of blood moving in it. This is the pulse,
- The rate of pulse will be equal to the number of heart beats.
Question 6.
Two person’s Blood Pressure is like this:
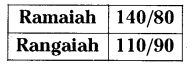
Whose Blood Pressure is high? What does it indicate?
Answer:
The normal blood pressure is 120/80
The numerator 120 indicates systolic pressure.
The denominator 80 indicates diastolic pressure.
Ramaiah B.P. is 140/80. So he has high blood pressure.
Question 7.
How does lymph differ from blood?
Answer:
- RBC are present in blood, RBC are absent in lymph.
- Blood is Red in colour, lymph is colourless.
![]()
Question 8.
Name the largest artery in the body.
Answer:
Aorta is the largest artery in the body.
Question 9.
Name the apparatus, shown in the figure below.
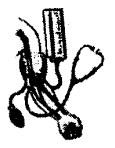
Answer:
Sphygmomanometer.
Question 10.
List out the materials you have used to observe the goat heart in your laboratory.
Answer:
- Freshly collected specimen of goat’s heart
- Soda straws
- Used pen refils
- The sharp and long blade
- Tray
- A jug of water
- Dissection scissors
- Forceps
- Gloves
Question 11.
Name any two valves present in human heart.
Answer:
- The valve that is present between left atrium and left ventricle is mitral valve or bicuspid valve.
- The valve that is present between right atrium and right ventricle is the tricuspid valve.
Question 12.
Siri injured while playing, and the blood is flowing continuously from the wound, what may be the reason for this?
Answer:
a) Vitamin – K is helpful for clotting of blood. Perhaps Siri might be suffering from a deficiency of Vitamin – K. So, blood is flowing continuously from the wound,
b) He may be suffering from thalassemia.
![]()
Question 13.
Prepare two questions, which you ask the doctor to know more details about high blood pressure.
Answer:
a) How can we know that we have high blood pressure?
b) What are the adverse affects of high blood pressure?
c) How can we prevent high blood pressure?
d) What diet should you prescribe for high BP patients?
Question 14.
What is the number of heart beats in new born babies.
Answer:
Number of heart beats in new born babies are 100-150 times.
Question 15.
What is the number of heart beats in well trained adult athletes.
Answer:
Number of heart beats in well trained adult athletes are 40 – 60 times.
Question 16.
Where is heart located in our body? How is it protected?
Answer:
Heart is located in between the lungs and protected by rib cage.
Question 17.
What is the size of our heart?
Answer:
The size of our heart is approximately size of our fist.
Question 18.
What is the shape and structure of heart?
Answer:
The heart is a pear shaped structure, triangle in the outline, wider at the anterior end and narrower at the posterior end.
Question 19.
What protects the heart from shocks?
Answer:
The space between the two layers of pericardial membrane (Pericardium) is filled with pericardial fluid which protects the heart from shocks.
Question 20.
What divides the heart into four parts?
Answer:
The heart is divided into four parts by grooves.
Question 21.
What are the blood vessels that supply blood to muscles of the heart?
Answer:
The blood vessels that supply blood to muscles of the heart are coronary vessels.
Question 22.
Which is the largest artery in the body?
Answer:
Aorta is the largest artery in the body.
![]()
Question 23.
Which artery supplies deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs?
Answer:
Pulmonary artery supplies deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs.
Question 24.
What are the two veins that collect blood from anterior parts and posterior parts of the body?
Answer:
Superior venacava (pre-caval vein) collects blood from anterior parts of the body and inferior venacava (Post-caval vein) collects blood from posterior parts of the body.
Question 25.
Who studied the veins in the leg and what did he notice?
Answer:
In 1574, an Italian doctor, Girolamo Fabrici, studied the veins in the leg and noticed the presence of valves in them.
Question 26.
What are the very fine blood vessels that connect smallest arteries and veins called?
Answer:
The very fine blood vessels that connect smallest arteries and veins are called capillaries.
Question 27.
Who discovered the capillaries in the wings of bats ?
Answer:
Marcello Malpighi discovered the capillaries (1661) in the wings of bats.
Question 28.
On which day the human heart starts beating during the embryonic development?
Answer:
The human heart starts beating around 21st day during the embryonic development.
Question 29.
What is cardiac cycle ?
Answer:
One contraction and one relaxation of atria and ventricles is called one cardiac cycle.
Question 30.
One cardiac cycle completes in approximately?
Answer:
The whole process of one cardiac cycle completes in approximately in 0.8 seconds.
Question 31.
The cardiac cycle includes?
Answer:
The cardiac cycle includes an active phase systole and a resting phase the diastole of atria and ventricles.
![]()
Question 32.
The number of heart beats in Blue Whale?
Answer:
The number of heart beats in Blue Whale are 7 times.
Question 33.
The number of heart beats in the bird Coaltit?
Answer:
The number of heart beats in the bird coaltit are 1200 times.
Question 34.
What is Edema?
Answer:
Edema is the condition in which the lower part of the legs will be swollen due to overnight journey in sitting position without moving legs.
Question 35.
What is single circulation of blood?
Answer:
If blood flows through heart only once in one circulation is called single circulation, e.g: Fish.
Question 36.
What is double circulation of blood?
Answer:
If the blood flows through the heart twice in one circulation is called double circulation, e.g : Frog and man.
Question 37.
What is lymph?
Answer:
Lymph is the substance that contains blood without solid particles.
Question 38.
What is tissue fluid?
Answer:
To supply nutrients to the cells the liquid portion of the blood with nutrients flows out of the capillaries. This is called tissue fluid.
Question 39.
What is serum?
Answer:
The light yellow coloured liquid portion after formation of the blood clot is called serum.
Question 40.
In which organism does protoplasm show Brownian movements?
Answer:
Protoplasm shows Brownian movements in Amoeba.
Question 41.
Which organisms use sea water for transportation?
Answer:
The poriferans/parazoans like sponges use sea water for transportation.
![]()
Question 42.
Which takes up the function of digestion and transportation of nutrients to each and every cell of the body in cnidarians?
Answer:
Gastrovascular cavity takes up the function of digestion and transportation of nutrients to each and every cell of the body in cnidarians. e.g: Hydra and Jelly fish.
Question 43.
In which animals is the digestive system highly branched and digested food to all the cells is supplied?
Answer:
The digestive system is highly branched and supplies digested food to all the cells in platyhelminthes.
Question 44.
Which takes up the function of collection and distribution of materials in Nematyhelminthes?
Answer:
The Pseudocoelom takes up the function of collection and distribution of materials in Nematyhelminthes.
Question 45.
What are the first Eucoelomate animals?
Answer:
The Annelids are the first eucoelomate animals.
Question 46.
Which have developed the heart, a pulsative organ to pump the blood?
Answer:
The Arthropods have developed the heart, a pulsative organ to pump the blood.
Question 47.
What is lymphatic system?
Answer:
Lymphatic system is a parallel system to venous system which collects tissue fluid from tissues and transports it to the venous system.
Question 48.
What is open type of circulatory system?
Answer:
The transportation system which supplies nutrients to the tissues directly is called open type of circulatory system, e.g: Arthropods, many molluscs and lower chordates.
Question 49.
What is closed type of circulatory system?
Answer:
The transportation system where the blood takes the responsibility of delivering the materials, which flows in the blood vessels is called closed type of circulatory system, e.g : Annelids, echinoderms, cephalopod molluscs and all the higher animals.
![]()
Question 50.
Where do doctors measure blood pressure in human beings?
Answer:
Doctors measure blood pressure in the upper arm artery.
Question 51.
What is the instrument used to measure blood pressure?
Answer:
The instrument used to measure blood pressure is a sphygmomanometer.
Question 52.
What is the normal blood pressure of a human being?
Answer:
The normal blood pressure of a human being is 120/80.
Question 53.
What is Hypertension? (OR)
What is high blood pressure?
Answer:
In some people high blood pressure more than the normal blood pressure of 120/80 is present during rest period. Such a condition is called Hypertension usually called high B.P.
Question 54.
Which vitamin plays an important role in coagulation of blood?
Answer:
Vitamin – K plays an important role in the coagulation of blood.
Question 55.
What is Haemophilia?
Answer:
Due to genetic defect, the blood may not coagulate or clot. This type of defect is called haemophilia.
Question 56.
What is Thalassemia?
Answer:
Thalassemia is a group of inherited blood disorders characterized by mild to severe anaemia caused by haemoglobin deficiency in the red blood cells.
Question 57.
Why is the blood pressure more in arteries than veins?
Answer:
The arteries receives blood directly from the heart hence the pressure is more in arteries than veins.
![]()
Question 58.
Why is the wall of left ventricle thicker than that of the right ventricle?
Answer:
The left ventricle pumps blood to more distant parts of the body such as from heart to fingers and toes. Hence the wall of left ventricle is thicker than that of the right ventricle.
Question 59.
How is xylem situated in the root and the stem?
Answer:
In the root the xylem tissue is situated towards the exterior while in the stem it is arranged in bundles towards the center.
Question 60.
Which process plays an important role in the absorption of water by root hairs?
Answer:
Osmosis plays an important role in the absorption of water by root hairs.
Question 61.
What is transpiration?
Answer:
Evaporation of water in the form of water vapour through stomata of leaves is called transpiration.
Question 62.
What are the different types of nutrients required for plant growth?
Answer:
Micronutrients and macronutrients are the different types of nutrients required for plant growth.
Question 63.
Which tissue transports water to all the other parts of the plant?
Answer:
Xylem tissue transports water to all the other parts of the plant.
Question 64.
Which tissue transports food to all the other parts of the plant?
Answer:
Phloem tissue transports food to all the other parts of the plant.
![]()
Question 65.
What is the amount of water that an oak tree can transpire per day?
Answer:
The amount of water that oak tree can transpire per day is 900 liters.
Question 66.
How many liters of water does a fully grown maize plant transpire in a week?
Answer:
Fully grown maize plant transpires 15 liters per week.
Question 67.
How does the opening and closing of stomata take place?
Answer:
When guard cells are filled with water, the walls of the cells are pulled away and the pores open up. When the water content is low the walls of guard cells collapse and close the stomata.
Question 68.
The rate of transpiration depends upon?
Answer:
The rate of transpiration depends on temperature, humidity, wind velocity, soil, water content, etc.
Question 69.
How does the transpiration help the leaf of a plant?
Answer:
Transpiration helps to keep the leaf surface at a lower temperature than the surrounding air.
Question 70.
What is translocation?
Answer:
The transport of soluble product of photosynthesis through phloem is known as translocation.
Question 71.
Why are the artery walls very strong and elastic?
Answer:
Because they are carrying blood away from the heart to every cell of the body tissue and are doing with a lot of pressure. So the walls are thick to enable it to do its job and are elastic.
Question 72.
The lumen size is bigger in vein when compared with artery. Why?
Answer:
Veins are generally large in diameter, carry more blood volume and have thinner wall in proportion to their lumen.
![]()
Question 73.
What is the function of the Gastrovascular cavity?
Answer:
Digestion and transportation of nutrients to each cell of the body in cnidarians is the function of Gastrovascular cavity.
Question 74.
What is the meaning of the word lymph in Latin?
Answer:
In Latin, lymph means water.
Question 75.
It is advisable to take limited food in journey? Why?
Answer:
The body movements will be less in the journey. So taking little food is good for easy digestion.
Question 76.
It is advised to take low amounts of salt in food? Why?
Answer:
Salt (sodium) levels will be more in accumulated water at the time of edema. If salt is not reduced in food the salt levels increase in blood and cause other problems in the body. Hence it is advised to take low amounts of salt in food.
Question 77.
When do you think that our pulse rate goes up?
Answer:
Our pulse rate goes up after jogging, running, strenuous exercise, during fear, anxiety, etc.
Question 78.
Sometimes barks of the tree damaged more than a half, even though tree is alive. How is this possible?
Answer:
In the root the xylem tissue is situated towards the exterior while in the stem it is arranged in bundles towards the center. Hence if the barks of the tree are damaged more than a half there is no obstruction to flow of water, the tree is alive.
Question 79.
Which animals do great damage particularly to beech and sycamore?
Answer:
Grey squirrels do great damage particularly to beech and sycamore.
![]()
Question 80.
Which predators are encouraged by foresters to keep down the population of voles and rabbits that damage plants?
Answer:
Foxes, Badgers, Hawks, Owls are encouraged by foresters to keep down the population of voles and Rabbits that damage plants.
Question 81.
What is Rhesus factor?
Answer:
- It is an antigen occuring on the red blood cells of many humans (85%) and same other primates known as the rhesus factor.
- It also plays major role in transfusion.
- Rhesus factor was first discovered in rhesus monkeys.
10th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Transportation 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Using the data collected by you, from internet and other sources, make a report on coagulation of blood.
Answer:
The process of clotting of blood from the blood vessels when a person injured is known as blood coagulation. Blood platelets starts the process of blood coagulation. When the blood flows out, the platelets release an enzyme called “Thrombokinase”. Thrombokinase acts on prothrombin converting it into thrombin.
Thrombin acts on another substance called fibrin that is present in dissolved state converting it into insoluble fibrin. The blood cells entangle in the fibrin fibres forming the clot.
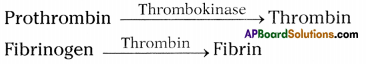
Question 2.
By the information provided by scientist William Harvey, complete the following table.
| SI. No. | Vessel Structure / function | Artery | Vein |
| 1. | Thickness of walls (Thick / Thin) | ||
| 2. | Valves (Present / Absent) | ||
| 3. | Pressure in the vessels (low / high) | ||
| 4. | Direction of blood flow (heart to organs / body organs to heart) |
Answer:
| SI. No. | Vessel Structure / function | Artery | Vein |
| 1. | Thickness of walls (Thick / Thin) | Thick | thin |
| 2. | Valves (Present / Absent) | Absent | Present |
| 3. | Pressure in the vessels (low / high) | high | low |
| 4. | Direction of blood flow (heart to organs body organs to heart) | heart to organs | body organs to heart |
Question 3.
How did you prepare a match-stick Stethoscope in your school?
Answer:
- Take a shirt button.
- Insert a matchstick into the button.
- Place it on wrist.
- We have to observe the movements of the matchstick.
![]()
Question 4.
After reading the functions of lymphatic system, what precautions you would suggest to your elders about Edema ?
Answer:
- Should not sit in the same position for long time.
- Should move legs frequently.
- Should sit in a up right position.
- Take low salt diet.
- Do exercise regularly.
- Protect themselves from extreme temperature changes.
Question 5.
What will happen if pulmonary veins are tied with a thread?
Answer:
The pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from the lungs and open into left auricle. If the pulmonary veins are tied with a thread the oxygenated blood will not supply to the heart and body parts from the lungs. Hence the person will die because of lack of oxygen.
Question 6.
Suggest some precautions to avoid cardiac problems.
(OR)
What changes would you like to bring in your life style to avoid cardiac problems?
Answer:
I will bring following changes in my lifestyle.
- Avoid heavy fat food and junk food.
- Try to spend stress free life as stress leads to cardiac problems.
- I will do regular physical exercise or work to keep myself fit.
- Keep away from bad habits like smoking and alcohol consumption.
- After 40 years, yearly twice I will consult cardiologist.
Question 7.
Read the Para:
Platelets play major role in the coagulation of blood. Whenever the blood flows from the wound, platelets releases the enzyme called Thrombokinase. Thrombokinase acts on another substance present in the blood called prothrombin converting it into thrombin. Thrombin acts on another substance called fibrin that present in the dissolved state converting it into insoluble Fibrin fibers. The blood cells entangle in the Fibrin fibers forming the clot.
Now, answer the following questions:
a) What happens if blood is not coagulated?
Answer:
If blood is not coagulated, it bleeds continuously from the wound, some times it leads to death of a person.
b) Which enzyme helps in the coagulation process?
Answer:
The enzyme thrombokinase helps in coagulation process.
c) How is Thrombin formed?
Answer:
Thrombokinase acts on another substance present in blood called prothrombin converting it into thrombin.
d) What do we call the yellow coloured fluid appear after the formation of the clot?
Answer:
The yellow coloured fluid appear after the formation of the clot is SERUM.
![]()
Question 8.
Observe the following table and answer the questions.
| Name of the animal | Weight of the body | Weight of the heart | No. of beats / min. |
| Blue whale | 1,50,000 kgs | 750 kgs | 7 |
| Elephant | 3,000 kgs | 12-21 kgs | 46 |
| Man | 60-70 kgs | 300 grams | 76 |
| Coal Tit Bird | 8 grams | 0.15 grams | 1200 |
i) What is meant by Cardiac cycle?
Answer:
One contraction and one relaxation of atria and ventricles is called one Cardiac Cycle.
ii) Write relation between the weight of the heart and heart beat.
Answer:
If the heart weight increases the rate of heart beat decreases and if the heart weight is less and the rate of heart beat is more.
Question 9
Look at the following table and answer the questions.
| Name of the Student | Systolic Pressure | Diastolic Pressure |
| Kiran | 120 | 80 |
| Rajesh | 160 | 100 |
a) Who is healthy person? Why?
b) Who is suffering from hypertension? What are the reasons?
Answer:
a) Kiran is a healthy Person as he has normal blood pressure of 120/80 mm/Hg.
b) Rajesh is suffering from hypertension. Reasons for hypertension are eating foods with high salt, obesity, smoking habits, alcohol consumption, lack of physical exercises and hereditary reasons.
Question 10.
What would happen if transpiration doesn’t occur in plants?
Answer:
i) Transpiration is a process by which plants lose excess of water in the form of water vapour, which in turn returns to environment and comes down as rain. Forests have the highest rainfall due to transpiration.
ii) If plants do not transpire, it affects rainfall.
![]()
Question 11.
Neelima conducted an activity on her friends and got the following results.
| S.No. | Name | Heart beat at rest/min | Heart beat after jogging / min | Pulse rate at rest / min |
| 1. | Jeevan | 72 | 109 | 72 |
| 2. | Raju | 75 | 110 | 74 |
| 3. | Reshma | 73 | 111 | 73 |
i) What is the relation between heart beat and pulse rate?
Answer:
Heart beat rate is equal to pulse rate.
ii) Why is the heart beat rate more after jogging?
Answer:
In the jogging muscles need more oxygen to produce high energy. To supply this oxygen heart beat is increased after jogging.
Question 12.
A person is injured while playing on the ground. Blood is flowing continuously. What might be the reasons?
Answer:
In this case blood is not clotting. Because
- He may be suffering from ‘Haemophilia’.
- Blood platelets are less in number.
- He may suffer from vitamin-K deficiency.
- Enzyme ‘Thrombokinase’ may not release.
Question 13.
What questions do you pose to your teacher to understand ‘blood clotting’?
Answer:
- What is coagulation?
- How does blood coagulate?
- What are the factors responsible for coagulation?
- What happens if coagulation occurs in blood vessels?
- Which substance prevents coagulation of blood in blood vessels?
- Which vitamin is required for coagulation of blood?
- What happens if coagulation of blood does not occur when we meet with accidents?
- Which cells present in blood help in coagulation of blood?
![]()
Question 14.
Where are the valves located in human heart? Write their names.
Answer:
Valves present in human heart.
| Name of the valve | Location | Allows blood to flow from |
| 1. Tricuspid Valve | Right auriculoventricular septum | Right atrium to right ventricle. |
| 2. Bicuspid Valve (Mitral Valve) | Left auriculoventricular septum. | Left atrium to left ventricle. |
| 3. Pulmonary Valve | At the origin of pulmonary aorta in the right ventricle. | Allows blood to flow from right ventricle into pulmonary aorta. |
| 4. Systemic Valves (Aortic Valves) | At the origin of systemic- aorta in the left ventricle. | Allows blood to flow from left ventricle into the systemic aorta. |
Question 15.
What happens if there are no valves in veins?
Answer:
- If the valves are absent in veins blood will not flow in unidirection and flows backward too.
- Blood will not be supplied to heart properly.
- Bulging of veins may takes place.
Question 16.
Which items do you take into consideration to explain the differences of arteries and veins?
Answer:
I would like to consider the following items to explain the difference between arteries and veins. They are thickness of walls, valves, capacity to retain shape when blood is absent, direction of blood flow, pressure in the vessels, type of blood transported, type of blood carried by pulmonary artery and type of blood carried by pulmonary vein.
Question 17.
When you know the heart pumping method is circulatory system, which issue do you remember particularly? What’s the reason for that?
Answer:
The heart beats faster during and after an exercise remembered by me. Because at that time our body needs more energy under these conditions. The faster breathing of heart pumps blood more rapidly to the body organs which supplies more oxygen to the body cells for rapid respiration to produce more energy. That is a great job for heart muscle.
Question 18.
Classify different types of blood vessels in humans. On what bases do you classify blood vessels?
Answer:
- There are three types of blood vessels called arteries, veins and capillaries present in humans.
- These blood vessels are classified on the basis of thickness of walls, valves, capacity to retain shape when blood is absent, direction of blood flow, pressure in the vessel, type of blood transported, type of blood carried by pulmonary artery or vein.
Question 19.
Anil fell down while going to school, got knee injury, started bleeding. After sometime he wondered on seeing blood clot? Why did blood clot?
Answer:
Blood clotting normally occurs when there is damage to blood vessel. Platelets immediately begin to combine to the cut edges of the vessel and release chemicals to attract even more platelets. A platelet clot is formed and the external bleeding stops.
![]()
Question 20.
How is the human heart protected from shocks or injuries?
Answer:
Protection of human heart:
- Heart in human beings is protected in different ways.
- It is enclosed in a double layered, transparent thin membrane called pericardium.
- The space between the inner and outer layers is called pericardial space.
- This space is filled with a fluid called pericardial fluid.
- Pericardium and pericardial fluid protect the heart from physical shocks.
- It is also protected by ribcage or chest cavity.
Question 21.
Describe the blood vessels that carry away blood from human heart.
Answer:
- The rigid vessels called arteries which originate from the heart supply blood to various organs in the body.
- From the upper part of the left ventricle a thick blood vessel called Systemic Aorta arises. It supplies oxygenated blood to the body parts.
- From the upper part of the right ventricle pulmonary artery arises. It supplies deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
- A pair of coronary arteries (vessels) carry oxygenated blood to the muscles of heart.
Question 22.
What is a mitral valve? What is its function?
Answer:
- Mitral valve: The valve present between left atrium and vertricle is known as mitral valve.
- Function: It allows blood to flow from left atrium to left ventricle. It also known as bicuspid valve.
Question 23.
Describe the external features of heart.
Answer:
- Heart is a hollow organ. It is situated slightly towards left side in the middle of the chest cavity.
- It is made up of cardiac muscle.
- It is pear shaped wider at the anterior and narrower at the posterior end.
- It is protected by ribcage and vertebral column.
- Generally it is the size of the one’s fist.
Question 24.
What are the differences between right ventricle and left ventricle?
Answer:
| Right ventricle | Left ventricle |
| 1. Smaller in size. | 1. Larger in size. |
| 2. Pulmonary artery takes its origin. | 2. Aorta takes its origin. |
| 3. Receives deoxygenated blood from right auricle. | 3. Receives oxygenated blood from left auricle. |
| 4. Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs. | 4. Pumps oxygenated blood to all parts of the body except lungs. |
| 5. Tricuspid valve guards the auriculo – ventricular aperture. | 5. Bicuspid valve (mitral) guards the left auriculo – ventricular aperture. |
Question 25.
How can Thalassemia major be treated?
Answer:
- Thalassemia major should be diagnosed as early as possible in order to prevent growth restriction, thin bones and infections in the first year of life.
- If Hb is less than 70% or the child shows signs of poor growth and development.
- Regular transfusion is the treatment of choice.
- This can usually be achieved by carrying out transfusions of concentrated red blood cells at intervals of every three to four weeks.
- Today Thalassemia major can be cured by stem cell transplantation.
![]()
Question 26.
Why is double circulation necessary in human beings? Or Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
Answer:
- In humans the right side and left side of the human heart is useful to keep deoxygenated and oxygenated blood from mixing.
- The separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood ensures a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body.
- It is useful in case of humans which constantly require energy to maintain their body temperature constant.
27. In some people blood does not coagulate. Give the reasons for it.
(OR)
What is Haemophilia? What are the causes for it?
Answer:
- Normally the blood that comes out from a wound clots in 3 – 6 minutes. But in some people due to vitamin K deficiency it takes more time to clot.
- Due to genetic defect blood may not coagulate. This type of defect is called Haemophilia.
- Haemophilia is a common disorder in the children who have born from the marriages between very close relatives.
10th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Transportation 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is coagulation of blood ? Explain the process of coagulation in brief.
(OR)
Collect information from internet and other sources about blood clotting and prepare a note on it.
Answer:
When the blood vessel is injured, the platelets collect at the site of the injury and form a clot and prevents further loss of blood. This is known as coagulation of blood. Process of Coagulation:
- When the blood flows out from injuries, the platelets release an enzyme called thrombokinase.
- Thrombokinase acts on another substance present in the blood called prothrombin converting it into thrombin.
- Thrombin acts on another substance called fibrin, that is present in dissolved state converting it into insoluble fibrin.
- The blood cells entangle in the fibrin fibers forming the clot.
- The fibrin fibers are attached to the edges of the wound and pull them together.
![]()
Question 2.
B1, B2, B3, A, C, D, E, K are the symbols of vitamins. Classify these vitamins based on solubility and diseases due to vitamins deficiency.
| S.No. | Water soluble | Disease due to deficiency | Fat solube | Disease due to deficiency |
Answer:
| S.No. | Water soluble | Disease due to deficiency | Fat solube | Disease due to deficiency |
| I | B1 | Beri – Beri | A | Eye, Skin disease |
| 2 | B2 | Glossitis | D | Rickets |
| 3 | B3 | Pellagra | E | Fertility disorders |
| 4 | Vit C | Scurvy | K | Delay in Blood clotting |
Question 3.
Ramu got injured while playing Kabaddi. His blood clotted within 6 minutes. Write the procedure involved in it.
Answer:
When the blood flows out from injuries, the platelets release an enzyme called thrombokinase.
2) Thrombokinase acts on inactive prothrombin and converts into thrombin.
3) Thrombin converts the soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrine fibers.
4) The blood cells entangle in the fibrin fibers forming the clot.
(or)
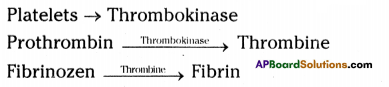
![]()
Question 4.
Read the para:
In the heart, superior vena cava and inferior vena cava opened into right atrium. The pulmonary veins bring blood from the lungs and open into left atrium. The valve present between the right atrium and right ventricle is referred as ‘Tricuspid valve ’. The valve present between the left atrium and left ventricle is refferred as Bicuspid valve. A major blood vessel that originate from right ventricle is Pulmonary Aorta. The valves present at the region of Pulmonary Aorta are called pulmonary valves. A major blood vessel originates from left ventricle is Systemic Aorta. The valves present at the region of Systemic Aorta are called systemic valves.
Now, fill the table with the above information.
| Name of the valve | Location | Way of blood flow | Nature of the blood oxygenated / deoxygenated |
| a. Tricuspid Valve | |||
| b. Bicuspid Valve | |||
| c. Pulmonary Valves | |||
| d. Systemic Valves |
Answer:
| Name of the valve | Location | Way of blood flow | Nature of the blood oxygenated / deoxygenated |
| a. Tricuspid Valve | Right auriculo ventricular septum | Right atrium to right ventricle | Deoxygenated blood |
| b. Bicuspid Valve | Left auriculo ventricular septum | Left atrium to left ventricle | Oxygenated blood |
| c. Pulmonary Valve | At the origin of pulmonary aorta in the right ventricle. | From right ventricle into pulmonary aorta | Deoxygenated
blood |
| d. Systemic Valves | At the origin of systemic aorta | From left ventricle into the systemic aorta | Oxygenated blood |
Question 5.
Study the given paragraph and answer the questions.
When you cut yourself the blood flows out of the wound for only a short time. Then the cut is filled with a reddish solid material. This solid is called a blood clot. When blood flows,out, the plate lets release an enzyme called thrombokinase. Thrombokinase acts on another substance present in the blood called pro – thrombin converting it in to thrombin. Thrombin acts on another substance called fibrinogen that is present in dissolved state converting it in to insoluble fibrin. The blood cells entangle in the fibrin fibers forming the clot.
A) Which blood cells are helpful in blood coagulation?
B) Which enzyme is responsible for blood coagulation? When is it released?
C) How does soluble fibrinogen in blood convert into insoluble fibrin fibers?
D) What will happen, if blood doesn’t coagulate when wound occurs?
Answer:
A) Blood platelets
B) Thrombokinase is responsible for blood coagulation. When the blood flows out the platelets release this enzyme thrombokinase.
C) Thrombin converts fibrinogen in blood into insoluble fibrin.
D) Blood bleeding from the injuries occurs continuously leads to death.
![]()
Question 6.
i) Label the parts of heart in the diagram below:
ii) Which blood vessel brings deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body?
iii) Which chamber(s) of the heart have more thick walls? Why?
Answer:
i)
- Artery to left arm
- Pulmonary artery
- Left atriu
- Left artrioventricular valve
- Inferior vena cava
- Right atrio – ventricular valve
- Right atrium
- Superior vena cava
ii) Superior vena cava / Inferior vena cava
iii) Ventricles; to pump blood.
Question 7.
Describe the internal structure of heart with a neat labelled diagram.
(OR)
What is called pumping station in human body? Explain its structure with suitable diagram.
Answer:
- Heart is called pumping station in human body.
- Internally heart is divided into four parts by grooves.
- Two upper parts are called atria, and two lower parts are called ventricles.
- The two atria are separated from each by inter-atriolar septum and the right and left ventricles are separated from each other by inter-ventricular septum.
- The inter-atriolar septum and inter-ventricular septum prevent mixing of deoxygenated blood in the right side of the heart with oxygenated blood in the left side of the heart.
- The walls of the ventricles are relatively thicker than atrial walls.
- The largest artery is the aorta which arises from the left ventricle supplies blood to all the body parts except lungs.
- Pulmonary artery that arises from the right ventricle carries deoxygenated blood to lungs.
- The right atrium and right ventricle are connected to each other by right atrioventricular aperture.
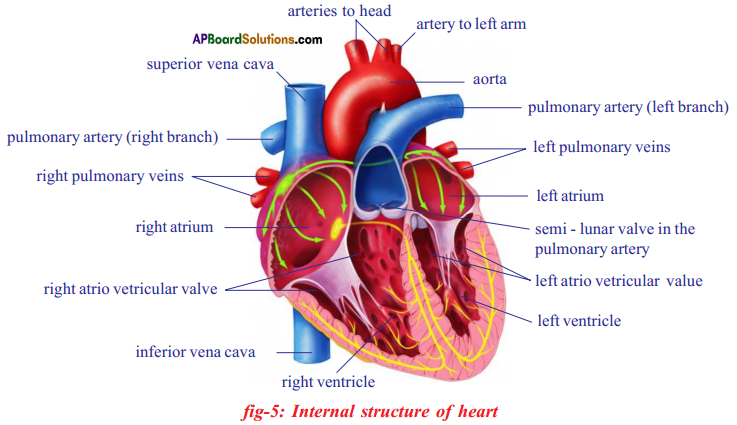
- The left atrium and left ventricle are connected to each other by left atrioventricular aperture.
- Tricuspid valve guards the right auriculoventricular aperture and mitral valve or bicuspid valve guards the left atrioventricular aperture.
- Blood from the anterior parts of the body is collected by superior venacava which opens into right atrium.
- Blood from the posterior parts of the body is collected by inferior venacava or post caval vein which also opens into right atrium.
- Coronary arteries supply blood to the muscles of the heart whereas coronary veins collect blood from the heart. It also opens into right atrium.
![]()
Question 8.
Write about the valves, their positions, their functions in human heart. How many blood vessels are attached to heart? Write about their positions and functions.
Answer:
Valves and their positions in Human Heart:
- The valve present in between right atrium and right ventricle is Tricuspid valve.
- The valve present in between left atrium and left ventricle is Bicuspid valve.
- The valve present at the region of pulmonary arota is called Pulmonary valves.
- The valves present at the region of systemic arota is called systemic valves.
Blood vessels attached to the heart, their positions and functions:
- The blood vessels found in the walls of the heart are coronary vessels which supply blood to muscles of the heart.
- From the upper part of the left ventricle aorta arises it supplies oxygenated blood to the body parts.
- From the upper part of the right ventricle pulmonary artery arises which supplies deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
- The vein which is right side of the heart is superior venacava.
- The vein which is coming from the posterior part of the heart is inferior venacava which collects blood from posterior part of the body.
Question 9.
Read the table and answer the following questions.
| S.No. | Name of the Phylum | Type of transport system |
| 1. | Cnidarians | Gastro vascular cavity |
| 2. | Platyhelminthes | Digestive system |
| 3. | Nematyhelminthes | Pseudocoelom |
| 4. | Annelida | Blood vessels |
| 5. | Arthropoda | Open circulatory system |
i) In which phylum, blood vessels are first formed?
Answer:
Blood vessels first formed in phylum annelida.
ii) In which phylum, organisms have haemoglobin in their blood?
Answer:
Organisms in phylum annelida have haemoglobin in plasma of blood,
iii) In which phylum, digestive system helps in transportation?
Answer:
The digestive system in the phylum cnidarian helps in transportation,
iv) Why do arthropods have open circulatory system?
Answer:
In arthropods blood vessels are absent, sinuses are present. So they have open circulatory system.
![]()
Question 10.
Write a short note on Human Lymphatic System and its functions.
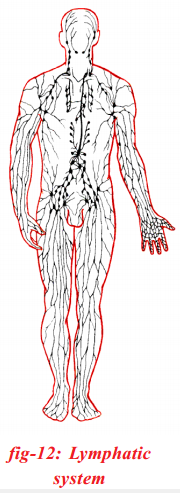 Answer:
Answer:
- Lymphatic system consists of lymph capillaries, lymph vessels, lymph nodes and lymph glands.
- To supply nutrients to the cells (tissues), the liquid portion of the blood with nutrients flows out of the capillaries. This is called tissue fluid.
- To transport the tissue fluid into the main blood stream, a separate system called lymphatic system is present.
- Lymph is the vital link between blood and tissues by which essential substances pass from blood to cells and excretory products from cells to blood.
- Lymph is the substance that contains blood without solid particles.
- From intercellular spaces, lymph goes into lymphatic capillaries.
- Lymphatic capillaries join to form large lymph vessels which finally open into larger veins.
- Lymph flows only in one direction, that is from tissues to heart through veins.
Functions of Lymph:
a) Lymph carries digested and absorbed fats from small intestine to different tissues of the body.
b) It helps in removing waste materials from the cells in the body to drain into blood.
c) Lymph protects cells in the tissues from infection.
Question 11.
Explain the process of coagulation of blood.
Answer:
- When the blood flows out from injuries, the platelets release an enzyme called thrombokinase.
- Thrombokinase acts on another substance present in the blood called prothrombin converting it into thrombin.
- Thrombin acts on another substance called fibrin, that is present in dissolved state converting it into insoluble fibrin.
- The blood cells entangle in the fibrin fibers forming the clot.
- The fibrin fibers are attached to the edges of the wound and pull them together.
![]()
Question 12.
Observe the given diagram. Which type of cardiac cycle does it indicate? Explain the process that happens here.
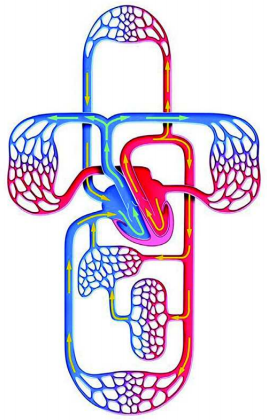 Answer:
Answer:
- It indicates double circuit circulation. It includes pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation.
- Here blood flows through the heart twice for completing one circulation. Hence it is called double circulation.
- In this circuit deoxygenated blood from organs of body is collected into the right auricle and then sent into right ventricle. From right ventricle blood is pumped to the lungs. In the lungs blood is oxygenated and is returned to the left auricle by pulmonary vein. This circulation is known as pulmonary circulation.
- In systemic circulation the oxygenated blood from the left auricle is pumped into the left ventricle. From the left ventricle blood is pumped into the systemic aorta. This aorta supplies blood to various organs of the body.
Question 13.
In human body “A” is a pumping organ. From lungs blood vessel “B” with oxygen¬ated blood enters upper “C” part of left chamber of the organ. When “C” chamber contracts blood flows into “D” lower left chamber. “D” chamber contracts blood is pumped to all parts of the body except lungs through blood vessel E. Deoxygen¬ated blood from body parts is collected by blood vessel “F’ and opens upper “G” right chamber. This chamber contracts blood flows “H” lower chamber. Lastly “H” contracts De-oxygenated blood sent to lungs by blood vessel “I”.
a) “A” represents what organ?
b) (i) B (ii) E (iii) F and (iv) I are what blood vessels? Write their names.
c) (i) C (ii) D are what chambers?
d) (i) G (ii) H are what chambers? Write their names.
Answer:
a) Heart
b) i) B – Pulmonary vein
ii) E – Systemic aorta
iii) F – Superior or Inferior venacava
iv) I – Pulmonary artery
c) i) C – Left atrium
ii) D – Left ventricle
d) i) G – Right atrium
ii) H – Right ventricle
![]()
Question 14.
Which blood vessels bring blood to human heart and from where?
Answer:
- There are three large veins that bring blood to heart from all the body parts.
- From upper parts of the body (from head and neck) blood is collected by superior venacava.
- The inferior venacava brings deoxygenated blood from lower parts of the body like abdomen, hands and legs. These caval veins open into right auricle.
- The third vein called pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from lungs and open into left ventricle.
- In addition to these, veins called coronary veins bring deoxygenated blood from the walls of the heart. They also open into right auricle.
Question 15.
Give an account of valves in the human heart. (OR)
Write about different valves present in human heart and their uses.
Answer:
- Heart has valves which allow the flow of blood only in one direction and prevents its flow in backward direction. Valves are held in position by tough connective tissue called chordaetendinae.
- Right auriculo – ventricular aperture is controlled by a tricuspid valve which allows the blood flow from right auricle to right ventricle.
- Left auriculo – ventricular aperture is provided with bicuspid valve which controls the blood flow from left auricle to left ventricle.
- At the origin of pulmonary aorta in the right ventricle three half moon shaped or semilunar valves present which allow the blood to flow from right ventricle into pulmonary aorta.
- At the origin of systemic aorta in the left ventricle there are three semilunar aortic valves which allow the blood flow from left ventricle into the aorta.
Question 16.
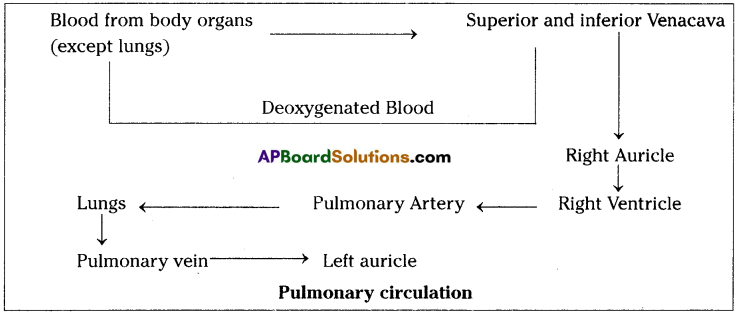
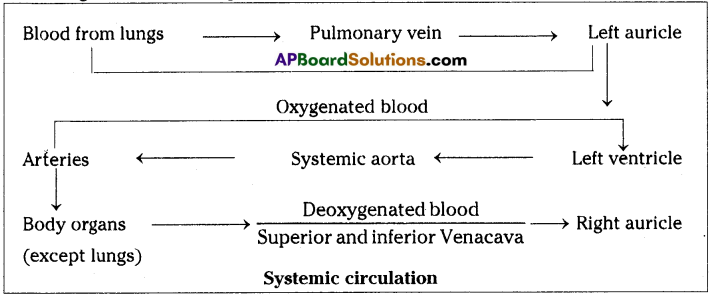
What is pulmonary circuit ? Explain it with the help of a block diagram.
Answer:
- In pulmonary circulation the deoxygenated blood collected by superior and inferior venacava enters right auricle.
- From right auricle the deoxygenated blood enters right ventricle from there it send to the lungs by pulmonary artery.
- From lungs pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood into left auricle. From here blood enters into left ventricle.
![]()
Question 17.
What is systemic circuit? Explain it with the help of a block diagram.
Answer:
- In systemic circulation oxygenated blood from left atrium is pumped into left ventricle.
- From left ventricle the blood is carried to different parts of the body through systemic Aorta.
- The deoxygenated blood from all the body parts is collected into right auricle through inferior and Superior Venacava.
Question 18.
Complete the following table with the details of arteries and veins.
| Blood vessels | Draw figure | Thickness of the wall | Layers of the wall | Lumen size | Capacity to retain the shape |
Answer:

Question 19.
How did multicellular animals solve their problem of transport of substances?
(OR)
Write about the evolution we see in the transport system of multicellular animals.
Answer:
- Early in the evolution, multicellular animals have solved their problem of transport by dissolving majority of the required substances in water and then transporting to various body parts. Ex: Sponges to Heimenthes.
- Later on the evolution, special fluids like blood and lymph have been developed for the transport of substances within the body. Ex: Insects.
- In primitive animals, necessary force for transport of these fluids was given by contraction and relaxation of body muscles. These fluids were circulated with in the body cavity. Ex: Earthworm.
- Later on evolution, for circulation of fluids a closed circulatory system was developed. This consists of heart, blood vessels and blood. Ex: Amphibians, reptiles, aves and mammals.
![]()
Question 20.
What is blood pressure? How is it measured?
Answer:
- The pressure with which the blood flows in the blood vessels is known as blood pressure.
- Blood pressure is measured in the upper artery.
- There are two pressure readings.
- One measures the strongest pressure during the time blood is forced out of the ventricles. This is called systolic pressure.
- For a healthy young adult it will be 120 mm of Hg.
- The second reading is taken during the rest period, as the ventricles refills with blood. This is called diastolic pressure.
- The diastolic pressure will be 80 mm of Hg.
- Doctors measure the blood pressure with a device called sphygmomanometer.
Question 21.
How do you prove that transpiration is done through stomata of a leaf? (OR) Describe an experiment to show that water is lost from the stomata of leaf.
Answer:
Aim: To prove that transpiration is done through stomata present in the leaves.
 Required material: A healthy potted plant, a polythene cover, water.
Required material: A healthy potted plant, a polythene cover, water.
Procedure: Take a well watered plant. Tie a polythene cover to one of its small branch and keep it in the sunlight. After sometime observe the inner sides of the polythene cover.
Observation: It is observed that the inner sides of polythene cover is moist with water drops.
Inference: The excess of water from the plant evaporates through stomata of leaves into the atmosphere. This process is called Transpiration.
![]()
Question 22.
Explain the process of absorption of water by the root hair and movement of water in xylem.
Answer:
- The soil water is an extremely dilute solution of salts, more dilute than that of the cell sap in the root hair.
- Therefore water will pass into the vacuole of the root hair by osmosis.
- The entry of water dilutes the contents of the root hair vacuole so that it becomes weaker than its neighbour.
- Therefore water passes into the neighbouring cell which in turn becomes diluted, finally water enters the xylem vessels.
- As there are vast numbers of root hairs and root cells involved, a pressure in the xylem vessels develops which forces the water upwards.
- This total pressure is known as root pressure which is responsible for movement of water in xylem.
- The water which passed into the xylem vessels forms a continuous system of tubes through root and stem into the leaves.
- The evaporation of water creates the main pull from above root pressure gives a variable and minor push from below.
Question 23.
Explain the process of transport of mineral salts and water in plants.
(OR)
Explain how root pressure and transpiration pull help in the transport of mineral salts and water in plants.
Answer:
- Xylem tissue transports water and mineral salts in plants.
- Xylem vessels and tracheids of root, stem and leaves are interconnected to form a continuous system of water and minerals conducting channels to each part of the plant.
- The cells of root hair present in the soil absorb water from the soil by osmosis.
- The entry of water dilutes the contents of the root hair vacuole so that it becomes weaker than its neighbour.
- Therefore water passes into the neighbouring cell which in turn becomes diluted, finally water enters the xylem vessel.
- This creates a column of water that is steadily pushed upward, called root pressure.
- Root pressure is not enough to push water and dissolved minerals to leaves in the tall trees.
- There is a continuous loss of water through stomata of the leaves in the form of water vapour. This process is called transpiration.
- The water lost due to transpiration is taken up from the xylem vessels and tracheids in the leaves.
- This loss of water during transpiration creates a suction pressure which pulls water from the xylem cells of roots.
- This results in enhanced absorption and upward movement of water and dissolved minerals from roots to the leaves due to transpiration.
- At night when stomata are closed root pressure has an effect on transportation of water.
- Transpiration pull is the major force in the movement of water and dissolved minerals in the xylem during daytime.
![]()
Question 24.
Write an experiment to illustrate the conduction of sugars by phloem.
(OR)
How are sugars conducted by phloem in plants?
Answer:
- Experiments to illustrate the conduction of sugars by the phloem have been done by removing a ring of bark from a shoot to expose the wood.
- Remove all tissues from the cambium outwards including the phloem.
- After a few days, when the tissues above and below the ring were analyzed.
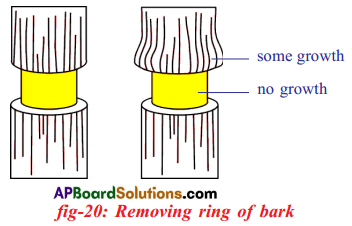
- It was shown that food had accumulated above the ring but was not present below it.
- If it is left for sometime, the stem increases in thickness immediately above the ring, but no growth occurred below it.
- So, any damage to the phloem all around the stem will prevent food from passing down to the roots and the tree will eventually die.
Question 25.
Write about the changes in the evolution of transport system in animals.
Answer:
- In Amoeba due to Brownian movements nutrients and oxygen are distributed throughout the protoplasm equally.
- The parazones like sponges use sea water for transportation. Sponges create their own currents by beating of flagella that are present in their body.
- Cnidarians developed blind sac like gastro vascular cavity, which has taken up the function of digestion and transportation of nutrients, e.g.: Hydra and jelly fish.
- In platyhelmenthes, the digestive system supplies digested food to all the cells directly, excretory system collects wastes from each cell individually.
- In animals belonging to Nematyhelmenthes the pseudocoelom has taken up the function of collection and distribution of materials.
- In Annelids, animals have developed a pulsative vessel to move the fluid and the transporting medium is blood.
- In Arthropods have developed a pulsative organ to pump the blood. The blood flows in the tissues, directly supplying the nutrients to the tissues.
- Transportation system which supplies nutrients to the tissues directly is called open type of circulatory system, e.g. : Arthropods, many molluscs and lower chordates.
- The other type of transportation system where the blood takes the responsibility of delivering the materials, which flows in the blood vessels.
- Such type of closed circulatory system is present in annelids, echinoderms, cephalopod molluscs and all the higher animals.
![]()
Question 26.
Briefly explain about Thalassemia disease.
(OR)
What is thalassemia disease ? What is the main cause for it?
Answer:
- Thalassemia is a group of inherited blood disorders characterized by mild to severe anaemia caused by haemoglobin deficiency in the red blood cells.
- In individuals with thalassemia, the production of the oxygen carrying blood pigment haemoglobin is abnormally low.
- There are two main types of thalassemia: alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia.
- In each variant a different part of the haemoglobin is defective.
- Individuals with mild thalassemia may have symptoms such as anaemia, enlarged liver and spleen; increased susceptibility, slow growth, thin and brittle bones and heart failure.
Question 27.
What are the facts known about Thalassemia?
Answer:
- Thalassemia is a serious inherited Blood disorder.
- 4.5% of world population (250 million) suffering with Thalassemia minor.
- There are over 35 million Indians are carriers of the abnormal Gene for Thalassemia.
- It is estimated that about 1,00,000 infants are born with major Haemoglobinopathies every year in the world.
- 10,000 – 12,000 Thalassemic children are born every year in our country.
- Survival depends upon repeated blood transfusion and costly medicines.
- Thalassemia can be prevented by awareness, pre marital or pre conceptual screening followed by ante-natal diagnosis is required.
Question 28.
What is the effect of Rhesus factor in childrens if Rh+ person marries Rh– woman?
Answer:
- If a Rh+ man marries a Rh– woman, some of the children are likely to be RlT.
- If a child is Rh+ some of its blood will leak into its mother’s circulation and cause antibodies to form in her blood.
- If the mother has more children the amount of antibodies in her blood often increases with each pregnancy, and in some instances the antibodies in her blood may pass into the baby’s blood in sufficient quantities to produce very serious anaemia and even death.
- When such cases occur, the baby is given a complete transfusion soon after birth sp that the baby’s blood is replaced by blood containing no antibodies to the rhesus factor.
![]()
Question 29.
What are the components of the circulatory system in human beings? What are their functions?
Answer:
- The circulatory system or transport system in human beings consists of heart, blood and blood vessels.
- Heart is a pumping organ to push blood around the body. It receives deoxygenated blood from body organs and pump it to lungs for oxygenation.
- Heart receives oxygenated blood from lungs and sends it to different body parts.
- Blood is a fluid connective tissue consists of a fluid medium known as plasma in which white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets are suspended.
- Blood transports food, carbondioxide and nitrogenous wastes in dissolved form.
- Red blood cells transports oxygen.
- Platelets present in blood help in coagulation of blood.
- Blood pushed by the heart flows in blood vessels called arteries and also comes back to the heart in the blood vessels called veins.
Question 30.
Draw T.S. of flow of blood in arteries and veins. Write flow of blood in between them.
(OR)
Write the differences between T.S. of artery, T.S. of vein and T.S. of blood capillary.
Answer:
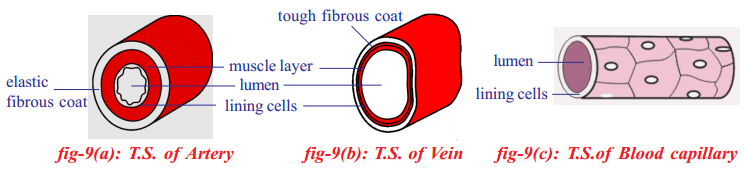
- In arteries, oxygenated blood flows. Arteries supply oxygenated blood to all body parts except lungs. Pulmonary artery supplies deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs.
- Veins collects deoxygenated blood from all body parts into the right atrium. Pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from lungs into left atrium.
- Blood capillaries are the microscopic vessels that connect smallest arteries and veins.
![]()
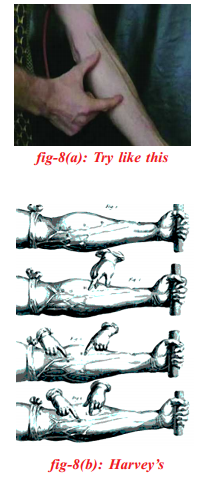
Question 31.
What was the classical experiment conducted by William Harvey to demonstrate movement of blood in veins ?
(OR)
How do you repeat the classical experiment to demonstrate the movement of blood in veins?
Answer:
- In early 17th century William Harvey conducted an experiment to demonstrate the movement of blood in veins.
- Tie a tornquit just above the elbow of a person, whose blood vessels are prominent in the hand.
- Ask that person to hold the fist with a piece of cloth rolled in the hand. Now the blood vessels can be seen more prominently.
- Find undivided blood vessel, where we have to work for the next few minutes.
- At the end of the vessel farthest from the elbow apply steady pressure, so as to close its cavity.
- Now apply pressure from elbow towards the palm slowly and observe the changes in the blood vessels.
Question 32.
What are the structural and functional differences of arteries, veins and capillaries?
Answer:
- The walls of arteries are made up of muscle fibers and are elastic. When the blood enters with a pressure into the arteries then walls will stretch and this enables the arteries to withstand the increase in the pressure without bursting.
- Veins are closer to the skin and contain valves. They are made of connective tissue called Tunica adventitia or Tunica externa. Middle layer has bands of smooth muscle called Tunica media. Generally veins are thin, lined internally with endothelial cells Tunica intina.
- Blood capillaries are microscopic vessels made of single layer of cells. They allow diffusion of various substances. They establish continuity between arterioles and venules. Capillaries is the Latin word which means “hair” because they were as thin as the finest of hairs.

![]()
Question 33.
What is the cardiac cycle? Explain it with the help of a diagram.
(OR)
Draw a diagram of different stages of systole and diastole. Explain.
Answer:
One contraction and one relaxation of atria and ventricles is called one cardiac cycle.
- We start with imagination that all the four chambers of the heart are in relaxed state.
- Blood from venecava and pulmonary veins enters the right and left atria respectively.
- Now the atria contract and forcing the blood to enter into the ventricles.
- On ventricular contraction due to pressure the blood moves into the aorta and pulmonary artery.
- When the valves between the atria and ventricles are closed we can hear the sharp sound of the heart lub.
- When the ventricles start relaxing, the pressure in the ventricles is reduced. The blood which has entered the arteries tries to come back into the ventricles. The valves which are present in the blood vessels are closed to prevent backward flow of blood into the ventricles.
- Now we can listen to a dull sound of the heart dub. The atria filled up with blood and are ready to pump them into the ventricles.
- The sequential events in the heart which are cyclically repeated are called cardiac cycle. It includes an active phase systole and a resting phase the diastole of atria and ventricles.
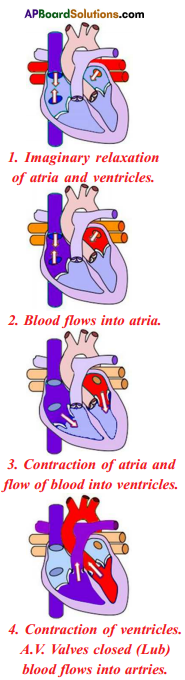
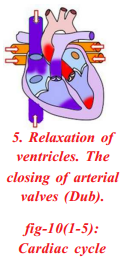
Question 34.
What is hypertension? How is it caused? Mention the preventive steps to be taken.
Answer:
- Blood flows in the blood vessels with a specific pressure called Blood Pressure (B.P.) In healthy individuals, the normal B.P. is 120/80.
- The numerator (120) represents Systolic pressure and the denominator (80) represents Diastolic pressure.
- Blood pressure is measured by the doctors by an instrument called SPHYGMOMANOMETER.

- However in some people blood pressure is very high more than normal B.P. This condition is called Hypertension.
- One of the reasons for hypertension is the blocking of arteries by cholesterol. Constant stress and strain for a long time, improper functioning of kidneys, smoking and alcohol consumption are the reasons for high B.P.
- Hypertension can be prevented by diet control moderate exercise, avoiding stress and strain, avoiding
alcohol consumption and smoking.
![]()