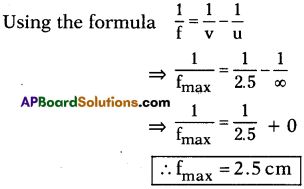
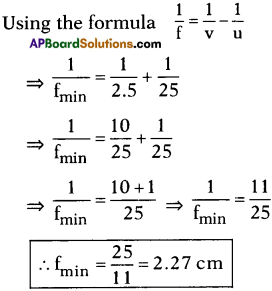
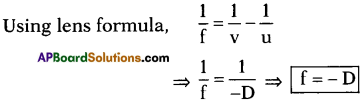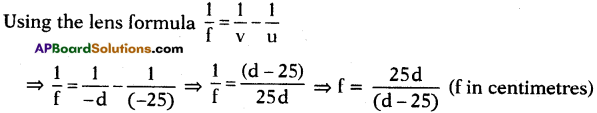AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Physics Solutions Chapter 12 Electromagnetism Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Physics Solutions 12th Lesson Electromagnetism
10th Class Physics 12th Lesson Electromagnetism Textbook Questions and Answers
Review of Your Previous Knowledge
Question 1.
How do electric appliances work?
Answer:
Electrical appliances work due to the electric force. Electrical force works in displacing the charges. Electric force is independent of the state of rest or the motion of the charged particle. Electric motor, washing machine are some of the examples of electric appliances.
Question 2.
How do electromagnets work?
Answer:
An electromagnet acquires the magnetic properties only when electric current is passed through the solenoid. Once the current is switched off, it almost loses its magnetic properties as retentivity of soft iron is very low. The strength of the electromagnet depends upon number of turns per unit length of the solenoid and the current through the solenoid.
![]()
Question 3.
Is there any relation between electricity and magnetism?
Answer:
The first evidence that there exists such a relationship between electricity and magnetism was observed by Oersted. When current carrying conductor was parallel to the axis of the needle, and the needle was deflected. This was much against his expectations. On reversing the direction of the current the needle moved in opposite direction.
Question 4.
Can we produce magnetism from electricity?
Answer:
We can produce magnetism from electronic current. Ampere with his Ampere’s swimming rule explained the direction of electric current and the deflection of magnetic needle.
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Are the magnetic field lines closed? Explain. (AS1)
Answer:
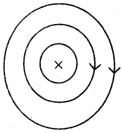
- Magnetic field lines are closed.
- If we observe the field lines formed by a current carrying straight wire, circular field lines are formed. They are closed circles.
- If we observe the field lines by a current carrying solenoid the field lines out side the solenoid are continuous with those inside.
- Thus the magnetic field lines are closed loops.
Question 2.
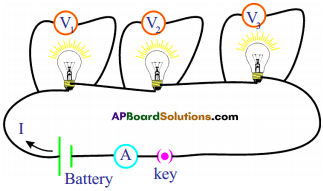
See figure, magnetic lines are shown. What is the direction of the current flowing through the wire? (AS1)
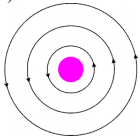
Answer:
If field lines are in anti-clockwise direction as shown in the diagram, the direction of current is vertically upwards. This can be demonstrated with right hand thumb rule.
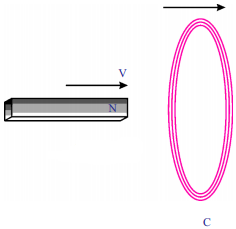
Question 3.
A bar magnet with north pole facing towards a coil moves as shown in figure. What happens to the magnetic flux passing through the coil? (AS1)
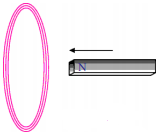
(OR)
Why would induced current be generated in the coil when a north pole of a bar magnet pushed into it ?
Answer:
If north pole of the magnet moves towards the coil, there is a continuous change of magnetic flux linked with closed coil, then current is generated in the coil.
![]()
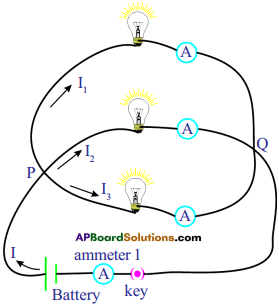
Question 4.
A coil is kept perpendicular to page. At P, current flows into the page and at Q it comes out of the page as shown in figure. What is the direction of magnetic field due to the coil? (AS1)
![]()
Answer:
At the top, anti-clockwise direction.
At the bottom, clockwise direction.
Try This:

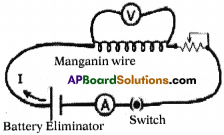
Take a test tube and wound minimum 50 turns of 24 guage insulated copper wire with 2cms length at the centre of test tube as shown in figure, ‘l Now solenoid is ready. Take 3cms length of iron nail and make it floats on water with appropriate foam (thermocol) on the water. Now connect the j two ends of solenoid two 3-6 volts battery eliminator and switch on the eliminator. You can observe the motion of the nail towards the solenoid. (If not move decrease the water level or increase the potential).
Try to explain motion of the nail into the water using solenoid concept.
Question 5.
The direction of current flowing in a coil is shown in the figure. What type of magnetic pole is formed at the face that has flow of current as shown in the figure? (AS1)
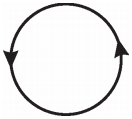
Answer:
North. Since the current in the coil flows in anti-clockwise direction, north pole is formed at the face we are watching. 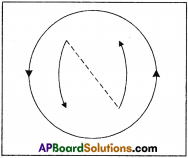
Question 6.
Why does the picture appear distorted when a bar magnet is brought close to the screen of a television? Explain. (AS1)
(OR)
Explain magnetic force on moving charge and current carrying wire.
(OR)
What happens when you bring a bar magnet near a picture of TV screen ? What inference do you conclude from this activity?
Answer:
This is due to the fact that magnetic field exerts a force on the moving charge.
TV screen Activity :
- Take a bar magnet and bring it near the TV screen.
- Then the picture on the screen is distorted.
- Here the distortion is due to the motion of the electrons reaching the screen are affected by the magnetic field.
- Now move the bar magnet away from the screen.
- Then the picture on the screen stabilizes.
- This must be due to the fact that the magnetic field exerts a force on the moving charges. This force is called magnetic force.
- The magnitude of the force is F = Bqv where B is magnetic induction, ‘q’ is the charge and v is the velocity of the charged particle.
![]()
Question 7.
Symbol ‘X’ indicates the direction of a magnetic held into the page. A straight long wire carrying current along its length is kept perpendicular to the magnetic field. What is the magnitude of force experienced by the wire? In what direction does it act? (AS1)
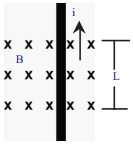
Answer:
1) Magnetic force (F) experienced by the wire with the magnitude of ILB :
Here I = Current, L = Length of the wire B = Magnetic field
2) Direction of the magnetic force (F) :
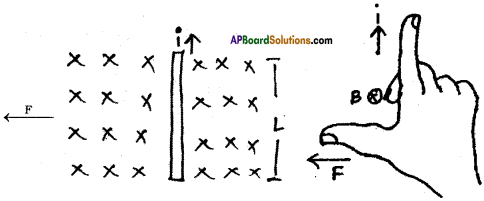
1) The direction of force can be find by using Right hand rule.
2) Fore finger → i (North)
Middle finger → B (into the page)
Thumb → F (Towards west parallel to the paper)
Question 8.
Explain the working of electric motor with a neat diagram. (AS1)
(OR)
Which device converts electrical energy into mechanical energy? Explain the working of that device with a neat diagram.
Answer:
Electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Electric motor:
It is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Principle :
It is based on the principle that a current carrying conductor placed perpendicular to the magnetic field experiences a force.
Construction :
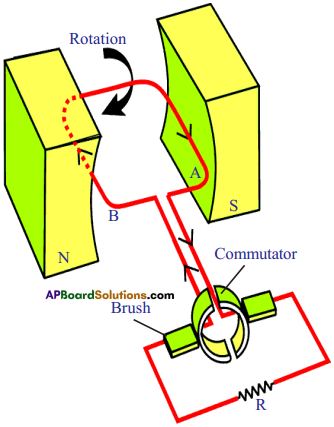
a) Armature coil:
It contains a single loop of an insulated copper wire in the form of a rectangle.
b) Strong magnetic field :
Armature coil is placed between two permanent poles (N & S) of a strong magnet.
c) Slip-ring Commutator:
It consists of two halves (C1 and C2) of a metallic ring. The two ends of the armature coil are connected to these two halves of the ring. Commutator reverses the direction of current in the armature coil.
d) Brushes:
Two carbon brushes B1 and B2 press against the commutator. These brushes act as the contact between the commutator and terminals of the battery.
e) Battery :
A battery is connected across the carbon brushes. The battery supplies the current to the armature coil.
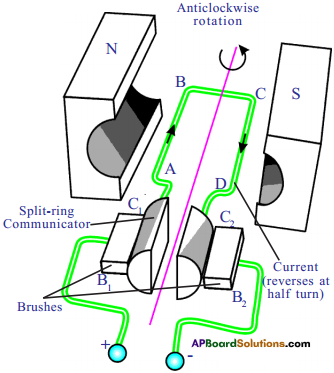
Working and Theory :
- When current flows through the coil, AB and CD experience magnetic force.
- In the arm, AB of the coil experiences a force in one direction, similarly, in CD it experiences in opposite direction.
- These two equal and opposite forces constitute a couple; which rotates the coil.
- At this position, the supply of current to the coil is cut off because contacts of commutator and brushes break.
- Hence no force acts on the arms of the coil.
- The coil will not come to rest because of rotational inertia of motion, till the commutator again comes in contact with the brushes B1 and B2.
- Now the direction of the current in the arms AB and CD is reversed.
- Then the couple again rotates in opposite direction.
- The coil of DC motor continues to rotate in the same direction. Hence electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy.
- The speed of rotation of the motor depends on
a) current through the armature
b) number of turns of the coil
c) area of the coil
d) magnetic induction.
![]()
Question 9.
Derive Faraday’slaw of induction from law of conservation of energy. (AS1)
Answer:
Faraday’s law :
Whenever there is a continuous change in magnetic flux linked with coil closed the current is generated in the coil.
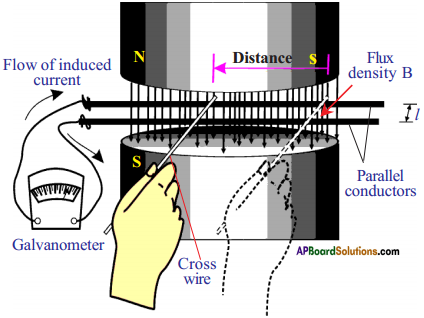
- Consider a pair of parallel bare conductors which are separated by 7′ meters.
- They are placed in uniform magnetic field of induction ‘B’ supplied by ‘N’ and ‘S’ poles of the magnet.
- A galvanometer is connected to the ends of the parallel conductors.
- We can close the circuit by touching the parallel conductor with another bare conductor which is taken in our hand.
- If we move our hand to the left, the galvanometer needle will deflect in one direction.
- If we move our hand to the right, the needle in the galvanometer moves in opposite direction.
- A current will be set up in the circuit only when there is an EMF in the circuit. Let EMF be ‘ε’.
- The principle of conservation energy tells us that this electric energy must come from the work that we have done in moving the cross wire.
Question 10.
The value of magnetic field induction which is uniform is 2T. What is the flux passing through a surface of area 1.5 m2 perpendicular to the field? (AS1)
Answer:
B = 2T ; Φ == ? ; A = 1.5 m²
We know B = \(\frac{\phi}{\mathrm{A}}\)
or Φ = BA = 2 × 1.5 =3 Webers
Question 11.
An 8N force acts on a rectangular conductor 20 cm long placed perpendicular to a magnetic field. Determine the magnetic field induction if the current in the conductor is 40 A. (AS1)
Answer:
F = 8N ; l = 20 cm or 20 × 10-2 m ; B = ? ; i = 40 Amp
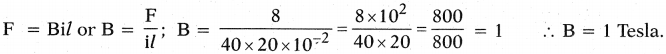
Question 12.
Explain with the help of two activities that current carrying wire produces magne tic field. (AS1)
(OR)
How can you verify that a current carrying wire produces a magnetic field with the help of experiment?
Answer:
Activity – 1
- Take a thermocole sheet and fix two thin sticks ol height 1cm.
- Join the two sticks with the help of copper wire.
- Take a battery, tap key and connect them in series with the copper wire which is thin.
- Keep a marine compass needle beneath the wire.
- If you press the tap key, current flows in the copper wire.
- Immediately the magnetic needle gets deflected.
- This indicates that the magnetic field is increased when current flows through the conductor.
Activity – 2
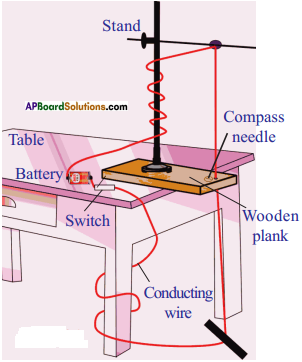
- Take a wooden plank and make a hole.
- Place the plank on the table.
- Place the retort stand on it.
- Pass copper wire through the hole.
- Connect the two ends of the wire with battery through switch.
- Place some compass needle around the hole.
- When the current flows the magnetic needle deflects.
- We can verify this by changing the direction of current.
- So we can conclude the magnetic field surrounds a current carrying conductor.
Question 13.
How do you verify experimentally that the current carrying conductor experiences a force when it is kept in magnetic field? (AS1)
Answer:
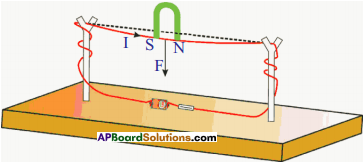
- A copper wire is passed through splits of wooden sticks.
- Connect the wire to 3 volts battery.
- Close the switch of the battery and pass the current.
- Bring the horse-shoe magnet near the wire.
- Then a force is experienced on the wire.
- Reverse the polarities of the magnet, then the direction of the force is also reversed.
- The right hand rule helps the direction of flow of current and the direction of current.
Question 14.
Explain Faraday’s law of induction with the help of an activity. (AS1)
(OR)
Write an activity which proves changing magnetic flux produces induced current in the circuit.
Answer:
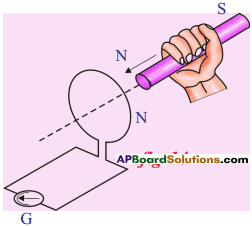
- Connect the terminals of a coil to a sensitive ammeter.
- Push a bar magnet towards the coil, with its north pole facing the coil, the needle in the galvanometer deflects.
- It shows that a current is set up in the coil.
- The galvanometer does not deflect if the magnet is at rest.
- If the magnet is moved away from the coil, the needle in the galvanometer again deflects in opposite direction.
- Further this experiment enables us to understand that the relative motion of the magnet and coil set up a current in the coil. It makes no difference whether the magnet is moved towards the coil. This is one form of Faraday’s law.
![]()
Question 15.
Explain the working of AC electric generator with a neat diagram. (AS1)
(OR)
Which device converts mechanical energy into electrical energy? Explain the working of that device with a neat diagram.
Answer:
Generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
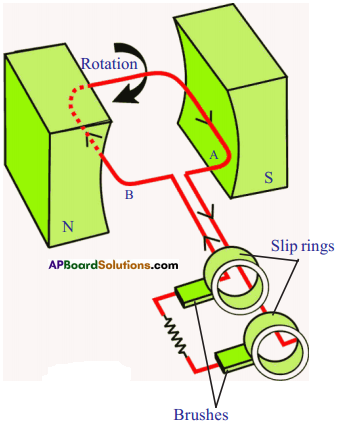
- As armature is rotated about an axis, the magnetic flux linked with armature changes. Therefore, an induced current is produced in the armature.
- If the armature rotates in anti-clockwise direction, from Flemming’s right hand rule the direction of current and deflection of the coil are noted.
- Alter armature has turned through 180°, it occupies another position.
- By applying Flemming’s right hand rule we can find the direction of current and deflection of the needle.
- Hence we can conclude the induced current is alternating in nature.
Question 16.
Explain the working of DC generator with a neat diagram. (AS1)
Answer:
- The principle and working of D.C generator is same as that of AC generator except that in place of slip – rings as sliding contacts, we have a slip-ring or a commutator.
- In a slip ring, there are two half rings.
- The ends of armature coil are connected to these rings and these rings rotate the armature.
- By using slip-ring, the direction of induced current does not change in the external circuit throughout the complete rotation of the armature. In other words, the current in the external circuit always flows in the same direction. Hence the induced current is unidirectional.
Question 17.
Rajkumar said to you that the magnetic field lines are open and they start at north pole of bar magnet and end at south pole. What questions do you ask Rajkumar to correct him by saying “field lines are closed”? (AS2)
Answer:
- If the magnetic field lines start at north pole and end at south pole, where do the lines go from south pole?
- What is happening within the bar magnet?
- Are the magnetic field lines passing through bar magnet?
- What is the direction of magnetic field lines inside the bar magnet? (Recall the solenoid activity).
- Can you say now, that the magnetic field lines are open?
![]()
Question 18.
As shown in figure, both coil and bar magnet move in the same direction. Your friend is arguing that there is no change in flux. Do you agree with his statement? If not, what doubts do you have? Frame questions about the doubts you have regarding change in flux. (AS2)
Answer:
- What happens if both magnet and coil move in same direction?
- What happens if both magnet and coil move in opposite direction?
- What is the direction of the current in the coil?
- If both move in same direction, is there any linkage of flux with the coil?
- When ‘N’ pole is moved towards the coil what is the direction of current?
- If magnet is reversed, what is the direction of current in the coil?
Question 19.
What experiment do you suggest to understand Faraday’s law? What items are required? What suggestions do you give to get good results of the experiment? Give precautions also. (AS3)
Answer:
Aim :
To understand Faraday’s law of induction.
Materials required :
A coil of copper wire, a bar magnet, Galvanometer, etc.

Procedure :
- Connect the terminal of a coil to a sensitive galvanometer as shown in the figure.
- Normally, we would not expect any deflections of needle in the galvanometer because there is to be no electromotive force in this circuit.
- Now if we push a bar magnet towards the coil, with its north pole facing the coil, we observe the needle in the galvanometer deflects, showing that a current is set up in the coil.
- The galvanometer does not deflect if the magnet is at rest.
- If the magnet is moved away from the coil, the needle in the galvanometer again deflects, but in the opposite direction, which means that a current is set up in the coil in the opposite direction.
- If we use the end of south pole of a magnet instead of north pole in the above activity, the deflections are exactly reversed.
- This experiment proves “whenever there is a continuous change of magnetic flux linked with a closed coil, a current is generated in the coil”.
Precautions :
- The coil should be kept on an insulating surface.
- Bar magnet should be of good magnetic moment.
- The centre of the galvanometer scale must be zero.
- The deflections in the galvanometer must be observed while introducing the bar magnet into the coil and also while withdrawing it.
![]()
Question 20.
How can you verify that a current carrying wire produces a magnetic field with the help of an experiment? (AS3)
Answer:
Experiment:
- Take a thermocole sheet and fix two thin wooden sticks of height 1cm.
- These sticks are joined with the help of a copper wire.
- Connect battery and tap key to this copper wire.
- Place a magnetic compass beneath the wire.
- Now press the tap key and allow the current through the wire. It is observed that magnetic needle deflects.
- If you change the direction of the current, the direction of deflection of needle also changes.
- So we can say current carrying conductor produces magnetic field.
Question 21.
Collect information about generation of current by using Faraday’s law. (AS4)
Answer:
Faraday’s law is useful in generation of current.
- According to this law, the change in magnetic flux induces EMF in the coil.
- Fie also proposed electromagnetic induction.
- Electromagnetic induction is a base for generator, which produces electric current.
- Transformer also works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which is helpful in transmission of electricity.
- Hence Faraday’s law is used in the generation and transmission of current.
Question 22.
Collect information about material required and procedure of making a simple electric motor from internet and make a simple ntotor on your own. (AS4)
Answer:
Aim :
Preparation of a simple electric motor.
Material requried :
A wire of nearly 15 cm, 1.5v Battery, Iron nail, strong magnet, paper clip.
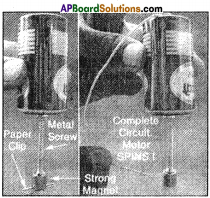
Procedure:
- Attach the magnet to the head of the iron nail.
- Attach a paper clip to the open end of the magnet.
- Now attach the other end of the nail (Free end) to the cap (positive terminal) of the battery.
- Now connect the negative terminal of the battery and the head of the iron nail through a wire.
- We observe that the paper clip rotates.
Another model:
Materials required :
1.5 m enamelled copper wire (about 25 gauge), 2 safety pins,
1.5 v battery, magnets, rubber bands or bands cut from cycle tube.
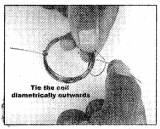

Procedure :
- Wind copper wire on the battery nearly 10 – 15 turns to make a coil.
- Remove the coil and fix the ends as shown in the figure.
- Scrape the insulation com¬pletely on one end of the coil.
- Scrape the insulation on top, left and right of the other end. The bottom should be insulated.
- Now complete the electric mo¬tor as shown in the figure. “5
Question 23.
Collect information of experiments done by Faraday. (AS4)
Answer:
Experiment – 1

- Connect the terminals of a coil to a sensitive galvanometer as shown in the figure.
- Normally, we would not expect any deflection of needle in the galvanometer because there is no EMF in the circuit.
- Now, if we push a bar magnet towards the coil, with its north pole facing the coil, the needle in the galvanometer deflects, showing that a current has been set up in the coil, the galvanometer does not deflect if the magnet is at rest.
- If the magnet is moved away from the coil, the needle in the galvanometer again deflects, but in the opposite direction, which means that a current is set up in the coil in the opposite direction.
- If we use the end of south pole of a magnet instead of north pole, the results i.e., the deflections in galvanometer are exactly opposite to the previous one.
- This activity proves that the change in magnetic flux linked with a closed coil, produces current.
- From this Faraday’s law of induction can be stated as “whenever there is a continuous change of magnetic flux linked with a closed coil, a current is generated in the coil”. This induced EMF is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux passing through it.
Experiment – 2
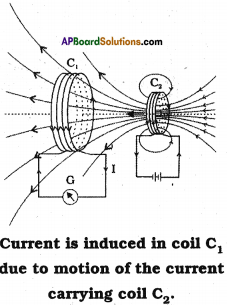
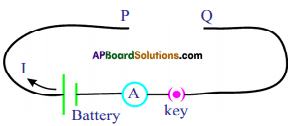
- Prepare a coil of copper wire C1 and connect the two ends of the coil to a galvanometer.
- Prepare another coil of copper wire similar to C2 and connect the two ends of the coil to a battery via switch.
- Now arrange the two coils C1 and C2 nearby as shown in the figure.
- Now switch on the coil C2. We observe a deflection in the galvanometer connected to the coil C1.
- The steady current in C2 produces steady magnetic field. As coil C2 is moved towards the coil C1 the galvanometer shows a deflection.
- This indicates that electric current is induced in coil C1.
- When C2 is moved away, the galvanometer shows a deflection again, but this time in the opposite direction.
- The deflection lasts as long as coil C2 is in motion.
- When C2 is fixed and C1 is moved, the same effects are observed.
- This shows the induced EMF due to relative motion between two coils.
![]()
Question 24.
Draw a neat diagram of electric motor. Name the parts. (AS5)
Answer:

Question 25.
Draw a neat diagram of an AC generator. (AS5)
(OR)
Draw the diagram of electric generator and label its parts. A.
Answer:

Question 26.
How do you appreciate the Faraday’s law, which is the consequence of conservation of energy? (AS6)
Answer:
- Law of conservation of energy says energy neither be created nor be destroyed, but can be converted from one form to another.
- Faraday’s law says whenever there is a continuous change of magnetic flux linked with a closed coil, a current is generated in the coil. This induced EMF is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux passing through it.
- We have to do some work to move the magnet through a coil. This work produces energy.
- This energy is converted into electrical energy in the coil.
- In this way conservation of energy takes place in electromagnetic induction.
![]()
Question 27.
How do you appreciate the relation between magnetic field and electricity that changed the lifestyle of mankind? (AS6)
Answer:
- Changing life style of mankind is a result of many inventions, utilising a lot of scientific principles.
- Scientists all ways going on searching for new principles and new applications to make our life more comfortable.
- If you consider electricity, right from amber stone to nuclear power, so many changes have been incorporated.
- The idea of Oersted and Faraday that current carrying wire produces electricity and electromagnetic induction, enable us to use electric motors, generators, fans, mixers, grinders, induction stoves, etc.
- All these appliances makes our life more comfortable. Hence Faraday and Oersted rendered a lot of servies in this field.
- Hence, I appreciate the relation between magnetic field and electricity that changed the life style of mankind.
So if current is more, induction is also more.
Question 28.
Give a few applications of Faraday’s law of induction in daily life. (AS7)
Answer:
Applications:
The daily life applications of Faraday’s law of induction are
- Generation of electricity
- Transmission of electricity
- Metal detectors in security checking
- The tape recorder
- Use of ATM cards
- Induction stoves
- Transformers
- Induction coils (spark plugs in automobiles)
- Break system in railway wheels
- AC and DC generators
- Windmills, etc.
![]()
Question 29.
Which of the various methods of current generation protects the nature well? Give examples to support your answer. (AS7)
Answer:
Windmill :
- Electricity is produced when an armature of a generator rotates between two poles of a strong magnet.
- Whereas when wind falls on the wheel of a windmill, it rotates. So the armature of the generator rotates between two poles of a magnet along with the rotation of the wheel of the windmill.
- Thus electric current is produced.
- This is how, KE of the wind is converted into electric energy.
Advantages :
Wind energy produces no smoke and no harmful gases. So this form of energy is pollution free or environment-friendly.
Fill in The Blanks
1. The SI unit of magnetic field induction is ………………….
2. Magnetic flux is the product of magnetic field induction and …………………
3. The charge is moving along the direction of magnetic field. Then force acting on it is ………………..
4. A current carrying wire of length L is placed perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B. Then the force acting on the wire with current I is ……………..
5. Faraday’s law of induction is the consequence of …………………
Answer:
- weber/m² (or) Tesla
- area
- zero
- ILB
- Law of conservation of energy
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy?
A) motor
B) battery
C) generator
D) switch
Answer:
A) motor
2. Waich converts mechanical energy into electrical energy?
(OR)
The device used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy among the following is
A) motor
B) battery
C) generator
D) switch
Answer:
C) generator
![]()
3. The magnetic force on a current carrying wire placed in uniform magnetic field if the wire is oriented perpendicular to magnetic field, is
A) 0
B) ILB
C) 2ILB
D) ILB/2
Answer:
B) ILB
10th Class Physics 12th Lesson Electromagnetism InText Questions and Answers
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 221
Question 1.
Why does the needle get deflected by the magnet?
Answer:
Because of strength of the magnetic field of the magnet, the needle gets deflected since it is in the field.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 213
Question 2.
How can we find the strength of the field and direction of the field?
Answer:
We can find the strength of the field with magnetic flux and the direction of the field from the tangent drawn to the line of force.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 214
Question 3.
Can we give certain values to magnitude of the field at every point in the magnetic field?
Answer:
In uniform magnetic field it is same whereas in non-uniform magnetic field it is different.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 215
Question 4.
What is the flux through unit area perpendicular to the field?
Answer:
Flux density or magnetic induction.
Question 5.
Can we generalize the formula of flux for any orientation of the plane taken in the field?
Answer:
Yes, Φ = BA cos θ
![]()
Question 6.
What is the flux through the plane taken parallel to the field?
Answer:
Magnetic flux (or) Magnetic field.
Question 7.
What is the use of introducing the ideas of magnetic flux and magnetic flux density?
Answer:
Magnetic flux and flux density help in understanding the concept of electromagnetic induction and relation between electricity and magnetism.
![]()
Question 8.
Are there any sources of magnetic field other than magnets?
Answer:
Current carrying straight wires and loops act as sources of magnetic filed.
Question 9.
Do you know how old electric calling bells work?
Answer:
Yes. They work on the principle of magnetic effect of electric currents.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 218
Question 10.
What happens when a current carrying wire is kept in a magnetic field?
Answer:
- Magnetic field applies force on current carrying wire.
- So it gets deflected and the direction of deflection is given by right hand rule.
- Or there will be no force acting on the wire when wire is in the direction of the field.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 219
Question 11.
Do you feel any sensation on your skin?
Answer:
Yes. The hair on my skin rises up when I stand near TV screen.
Question 12.
What could be the reason for that?
Answer:
It is due to the magnetic field produced by electric charges in motion.
![]()
Question 13.
Why does the picture get distorted?
Answer:
Due to motion of electrons that form the picture is affected by the magnetic field of bar magnet.
Question 14.
Is the motion of electrons reaching the screen affected by the magnetic field of the bar magnet?
Answer:
Yes. The motion of electrons reaching the screen is affected by the magnetic field of the bar magnet.
Question 15.
Can we calculate the force experienced by a charge moving in a magnetic field?
Answer:
Yes, If the force is F, it is given by the expression F = qvB.
Question 16.
Can we generalize the equation for magnetic force on charge when there is an angle ‘0’ between the directions of field “B” and velocity “v”?
Answer:
No, Then force F is given by the formula F = qvB sin θ.
![]()
Question 17.
What is the magnetic force on the charge moving parallel to a magnetic field?
Answer:
When the charge moves parallel to the magnetic field the value of “θ” becomes zero. In the equation F = qvB sin θ, since θ = θ, the value of force F also becomes zero.
Question 18.
What is the direction of magnetic force acting on a moving charge?
Answer:
By applying right hand rule we can guess the direction of magnetic force acting on a moving charge is the “thumb” direction.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 221
Question 19.
Can you determine the magnetic force on a current carrying wire which is placed along a magnetic field?
Answer:
F = BIl sin θ. If the current carrying wire is placed along direction field θ = 0.
∴ F = 0
Question 20.
What is the force on the wire if its length makes an angle ‘θ’ with the magnetic field?
Answer:
F = Bqv sin θ or F = Bil sin θ, where ‘i’ is current. WorhA
Here B = magnetic induction, q = charge, v = velocity of the charge and ‘θ’ is the angle between direction of field and velocity.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 222
Question 21.
How could you find its (current carrying wire) direction?
Answer:
We can find by using right hand rule.
Question 22.
Is the direction of deflection observed experimentally same as that of the theoretically expected one?
Answer:
Yes. But it depends on polarities of the horse shoe magnet.
![]()
Question 23.
Does the right hand rule give the explanation for the direction of magnetic force exerted by magnetic field on the wire?
Answer:
The right hand rule does not help us to explain the reason for deflection of wire.
Question 24.
Can you give a reason for it (deflection of wire)?
Answer:
There exists only magnetic field due to external source. When there is a current in the wire, it also produces a magnetic field. These fields overlap and give non-uniform field. This is the reason for it.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 223
Question 25.
Does this deflection fit with the direction of magnetic force found by right hand rule?
Answer:
Yes. This deflection fits with the direction of magnetic force found by right hand rule.
Question 26.
What happens when a current carrying coil is placed in a uniform magnetic field?
Answer:
It gets deflected since magnetic lines of force are perpendicular to the length of the coil.
![]()
Question 27.
Can we use this knowledge to construct an electric motor?
Answer:
Yes. This is the principle of electric motor.
Question 28.
What is the angle made by AB and CD with magnetic field?
Answer:
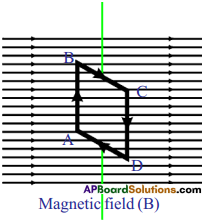
AB and CD are at right angles to the magnetic field.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 224
Question 29.
Can you draw the direction of magnetic force on sides AB and CD?
Answer:
Yes. The direction of magnetic force on sides AB and CD can be determined by applying right hand rule.
Question 30.
What are the directions of forces on BC and DA?
Answer:
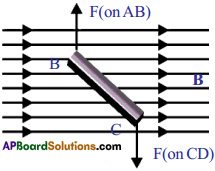
ADBC, magnetic force pulls the coil up and at DA magnetic force pulls it down.
Question 31.
What is the net force on the rectangular coil?
Answer:
Net force on the rectangular coil is zero.
Question 32.
Why does the coil rotate?
Answer:
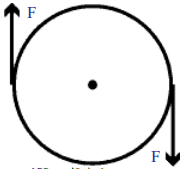
The rectangular coil rotates in clockwise direction because of equal and opposite pan’ of forces acting on the two sides of the coil.
Question 33.
What happens to the rotation of the coil if the direction of current in the coil remains unchanged?
Answer:
The coil comes to halt and rotates in anti-clockwise direction.
Question 34.
How could you make the coil rotate continuously?
Answer:
If the direction of current in coil, after the first half rotation, is reversed, the coil will continue to rotate in the same direction.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 225
Question 35.
How can we achieve this (convertion of electrical energy to mechanical energy)?
Answer:
Brushes B1 and B2 are used to achieve this.
![]()
Question 36.
What happens when a coil without current is made to rotate in magnetic field?
Answer:
When the coil rotated due to the change in magnetic flux electricity is generated.
Question 37.
How is current produced?
Answer:
The current is produced from the battery to the coil.
Question 38.
Why is there a difference in behaviour in these two cases?
Answer:
The A.C. supply changes its direction a number of times in a second. But D.C. is unidirectional current. So there is a difference in the behaviour of the metal ring in these two cases.
Question 39.
What force supports the ring against gravity when it is being levitated?
Answer:
The magnetic force developed in the coil of copper wire supports the ring against gravity when it is being levitated.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 226
Question 40.
Could the ring be levitated if DC is used?
Answer:
The metal ring is levitated because the net force on it should be zero according to Newton’s second law.
Question 41.
What is this unknown force acting on the metal ring?
Answer:
The change in polarities at certain intervals at the ends of the solenoid causes the unknown force acting on the metal ring.
![]()
Question 42.
What is responsible for the current in the metal ring?
Answer:
The field through the metal ring changes so that flux linked with the metal ring changes and this is responsible for the current in metal ring.
Question 43.
If DC is used, the metal ring lifts up and falls down immediately. Why?
Answer:
The flux linked with metal ring is zero. When the switch is on, at that instant there should be a change in the flux linked with ring. So the ring rises up and falls down. If the switch is off, the metal ring again raises up and falls down. There is no change in flux linked with ring when the switch is off.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 227
Question 44.
What could you conclude from the above analysis (metal ring lifts up and falls down)?
Answer:
The relative motion of the magnet and coil sets up a current in the coil.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 228
Question 45.
What is the direction of induced current?
Answer:
The direction of the induced current is such that it opposes the charge that produced it.
![]()
Question 46.
Can you apply conservation of energy for electromagnetic induction?
Answer:
Yes, we can apply. The mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 229
Question 47.
Can you guess what could be the direction of induced current in the coil in such case?
Answer:
The direction of the induced current in the coil must be in anti-clockwise direction.
Question 48.
Could we get Faraday’s law of induction from conservation of energy?
Answer:
Yes, we can get. Here we have to ignore the friction everywhere.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 230
Question 49.
Can you derive an expression for the force applied on crosswire by the field “B”?
Answer:
Yes. The force applied F = BIl.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 232
Question 50.
How could we use the principle of electromagnetic induction in the case of using ATM card when its magnetic strip is swiped through a scanner? Discuss with your friend or teacher.
Answer:
If the card is moved through a card reader, then a change in magnetic flux is produced in one direction, which induced potential or EMF. The current received by the pickup coil goes through signal amplification and translated into binary code, so that it can be read by computer.
![]()
Question 51.
What happens when a coil is continuously rotated in a uniform magnetic field?
Answer:
An induced current is generated in the coil.
Question 52.
Does it (continuous rotation of coil) help us to generate electric current?
Answer:
Yes. Continuous rotation of coil helps us to generate electric current.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 233
Question 53.
Is the direction of current induced in the coil constant? Does it change?
Answer:
Yes, it changes. When the coil is at rest in vertical position, with side (A) of coil at top position side (B) at bottom position, no current will be induced in it.
Question 54.
Can you guess the reason for variation of current from zero to maximum and vice-versa during the rotation of coil?
Answer:
The reason for variation of current from zero to maximum and vice-versa during the rotation of coil current generated follows the same pattern so that in first half except that the direction of current is reversed.
![]()
Question 55.
Can we make use of this current? If so, how?
Answer:
Two carbon brushes are arranged in such a way that they press the slip rings to obtain current from the coil. When these brushes are connected to external devices like TV, Radio we can make them work with current supplied from ends of carbon brushes.
10th Class Physics Textbook Page No. 234
Question 56.
How can we get DC current using a generator?
Answer:
By connecting two half-slip rings instead of a slip ring commutator on either side to the ends of the coil we can get D.C. current.
![]()
Question 57.
What changes do we need to make in an AC generator to be converted into a DC generator?
Answer:
Instead of two slip rings, we have to use a slip ring commutator to change A.C. generator into a D.C. generator.
10th Class Physics 12th Lesson Electromagnetism Activities
Activity – 2
Question 1.
Show that the magnetic field around a bar magnet is three dimensional and its strength and direction varies from place to place.
Answer:
- Take a sheet of white paper and place it on the horizontal table.
- Place a bar magnet in the middle of the sheet.
- Place a magnetic compass near the magnet it settles to a certain direction.
- Use a pencil and put dots on the sheet on either side of the needle. Remove the compass. Draw a small line segment connecting the two dots. Draw an arrow on it from south pole of the needle to north pole of the needle.
- Repeat the same by placing the compass needle at various positions on the paper. The compass needle settles in different directions at different positions.
- This shows that the direction of magnetic field due to a bar magnet varies from place to place.
- Now take the compass needle to places far away from magnet, on the sheet and observe the orientation of the compass needle in each case.
- The compass needle shows almost the same direction along north and soiath at places far from the magnet.
- This shows that the strength of the field varies with distance from the bar magnet.
- Now hold the compass a little above the table and at the top of the bar magnet.
- We observe the deflection in compass needle. Hence we can say that the mag¬netic field is three dimensional i.e., magnetic field surrounds its source.
- From the above activities we can generalize that a magnetic field exists in the region surrounding a bar magnet and is characterized by strength and direction.
Activity – 3
Question 2.
Explain how you draw magnetic lines of force in the magnetic field.
(OR)
What is the name given to the imaginary lines joining from north pole to south pole of a bar magnet called? Explain how you can draw those lines around a bar magnet.
Answer;
These lines are called magnetic lines of forces.
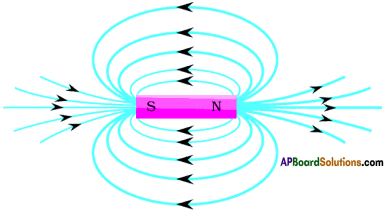
Procedure:
- Take a white drawing sheet.
- Place a marine compass at the centre of the sheet.
- Draw a line which shows north and south of the earth on the drawing sheet.
- Now remove the compass needle and place a bar magnet at the centre of the sheet showing north of the bar magnet pointing north of the earth.
- Place the magnetic compass near the bar magnet without contact. The needle comes to rest after oscillations.
- Locate the end of the pointer with pencil. Now place the compass needle at this point and once again notice the end of the pointer.
- We can repeat the same around the magnet, and draw all the points with the help of the pencil.
- We can draw the lines taking the needle too far to the magnet and we can observe the orientation of needle of compass.
- So we can conclude that the strength of field varies with distance from the bar magnet.
- These lines of force are from north of the bar magnet to south of the bar magnet.
Activity – 4
Question 3.
Explain the direction of magnetic field around the straight conductor carrying current.
(OR)
What field would be formed around straight conductor carrying current? How do you find the direction of that field experimentally?
Answer:
Magnetic field would be formed around current carrying conductor.

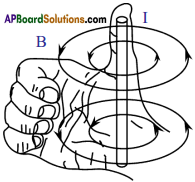
Procedure:
- Take a wooden plank and make a hole and place il on the table.
- Place a stand on the plants, and suspend a c opper wire from the stand and see that it passes through the hole made to the plank.
- Connect a battery and switch to this wire in series. Place some magnetic needle at the hole.
- If the current is passed through the wire, the magnetic needle deflects and it is directed as the tangent to the circle
- If the current flows in downward direction, the field lines are in anti-clockwise direction and if the current flows in upward direction, the field lines are in clockwise direction.
- The direction ol the current and magnetic fines of force can be easily explained with the help of right hand thu mb rule. If you hold the current carrying conductor with your right hand grip stretching the thumb, the direction of the I humb shows the direction of the current, the direction of the other four fingers shows direction of magnetic lines of force.
Activity 5
Question 4.
Explain the direction of magnetic field due to circular coil.
Answer:
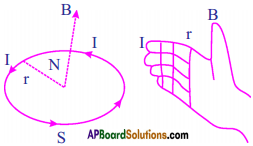
Procedure :
- Take a thin wooden plank and cover it with whitepaper.
- Make two holes to the plank and pass insulated copper wire through the holes and wind the wire 4 to 5 times through the holes such that it looks like a coil.
- The ends of the wire are connected to the battery terminals.
- Now place a compass needle at the centre of the coil.
- Put dots on either side of the compass. Repeat this by keeping at the dots. We can observe that field lines are circular.
- Here the direction of the field is perpendicular to the plane of the coil.
- The direction of the magnetic field due to coil points towards you when the current in the coil is in anti-clockwise direction.
- When you curl your right hand fingers in the direction of current, thumb gives the direction of magnetic field.
Activity – 6
Question 5.
Explain the magnetic field due to solenoid.
(OR)
What is the name given to the device which is a long wire wound in a close pack helix? Find the direction of magnetic field around that device.
Answer:
It is called solenoid.
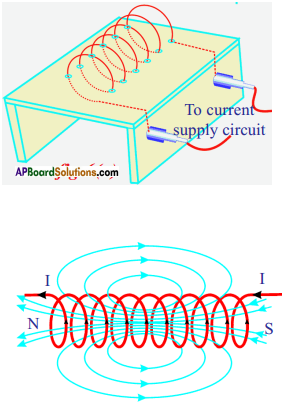
Procedure :
- Take a wooden plank covered with white paper.
- Make holes on its surface.
- Pass copper wire through the holes.
- Join the ends of the coil to a battery through a switch.
- Current passes through the coil, when we switch on the circuit.
- Now sprinkle iron filings on the surface of the plank, around the coil. Then orderly pattern of iron filings is seen on the paper.
- The iron filings arrange themselves in orderly way and look like lines of force.
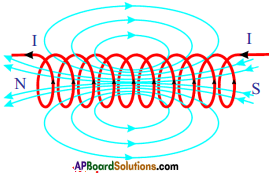
- The long coil is known as solenoid. The direction of the field due to solenoid is determined by using right hand rule.
- One end of the solenoid behaves like a north pole and the other behaves like south pole.
- Outside the solenoid the direction of the field lines of force is from north to south while inside the direction is from south to north. Thus the magnetic field lines are closed loops.
- Hence electric charges in motion produce magnetic field.
Activity – 8
Question 6.
Explain the field lines due to horse-shoe magnet between its poles.
(OR)
Which field is set up between poles of a horse-shoe magnet? Explain the field lines due to horse magnet between its poles.
Answer:
Non-uniform magnet is set up between poles of a horse shoe magnet.

Procedure :
- The field in between north and south pole of horse-shoe magnet are straight and parallel.
- If the wire is passing perpendicular to the paper, the magnetic lines of force are concentric circles, when the current is passed.
- The direction of field lines due to the wire in upper part coincides with the direction of field lines of horse-shoe magnet.
- The direction of field lines by the wire in lower part is opposite to the direction of field lines of horse-shoe magnet.
- Hence the net field in upper part is strong and in the lower part is weak.
- Hence a non-uniform field is created around the wire.
Activity – 9
Question 7.
Explain electromagnetic induction.
(OR)
Which current will levitate the ring in the following figure? Explain the experimental activity.
Answer:
AC will levitate the ring.
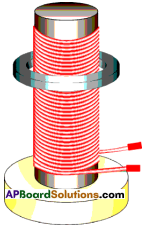
Procedure :
- Fix a soft iron cylinder on the wooden base vertically.
- Wind copper wme around the soft iron.
- Take a metal ring which is slightly greater in radius than the radius of soft iron cylinder and insert it through the soft iron cylinder.
- Connect the ends of the coil to an AC source and switch on the current.
- Here metal ring levitates on the coil (appears to rise and floats in the air).
- In this experiment we can conclude that if AC current is used, the magnetic induction changes in both magnitude and direction in the solenoid and in the ring. The field through the metal ring changes, so that flux linked with the metal ring changes.
- If DC current is used, the metal ring lifts up and falls down immediately.










 symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.
symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.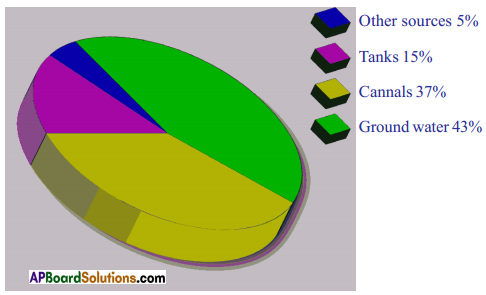 A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?
A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?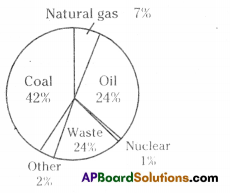 i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.
i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.
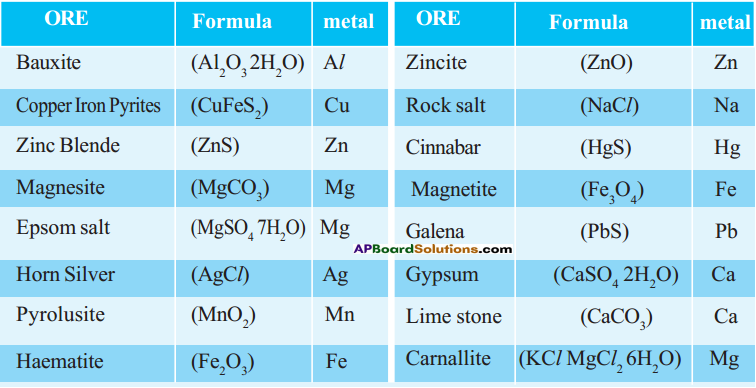
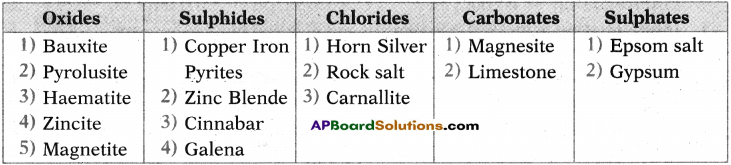

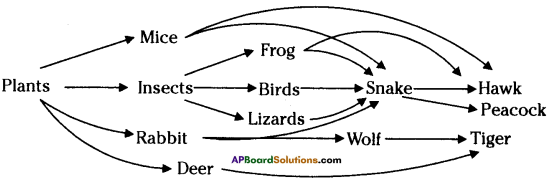
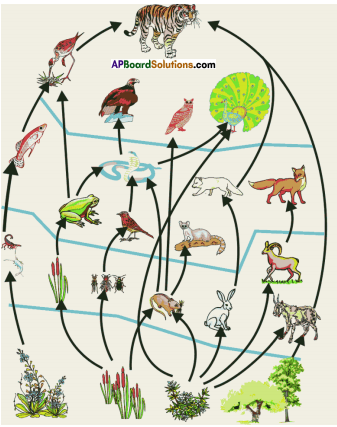 i) Write any two food chains from the diagram.
i) Write any two food chains from the diagram.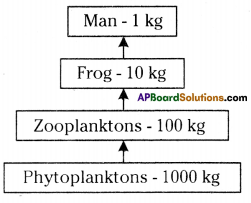 Answer:
Answer: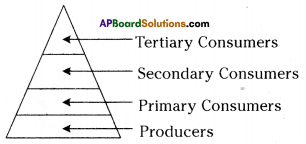 i) As per the number of organisms in the tropic level, which group of organisms
i) As per the number of organisms in the tropic level, which group of organisms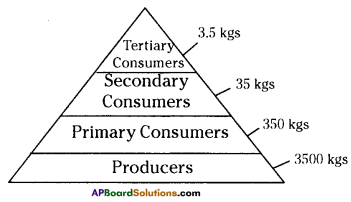
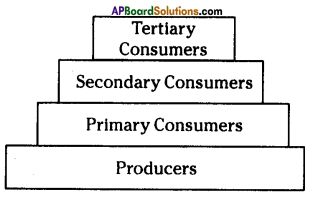
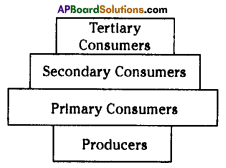

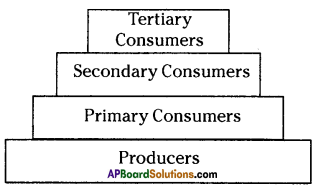

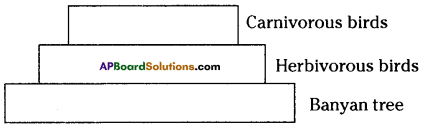
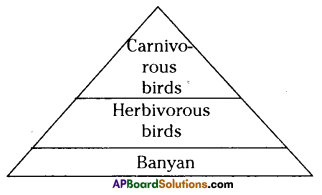

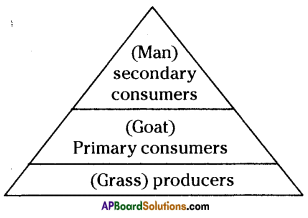
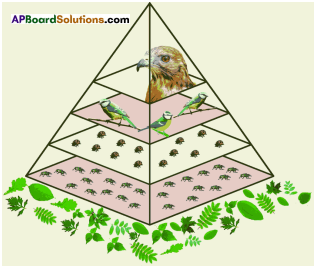
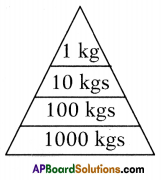 The pyramid of biomass for the given food chain, at each step 90% of the food is lost. That means 1000 kg of phytoplankton to produce 100 kg of Zooplankton to form 10 kg of fish to produce 1kg of human tissues. The fewer the steps in the food chain the more energy will be for the species at the top.
The pyramid of biomass for the given food chain, at each step 90% of the food is lost. That means 1000 kg of phytoplankton to produce 100 kg of Zooplankton to form 10 kg of fish to produce 1kg of human tissues. The fewer the steps in the food chain the more energy will be for the species at the top.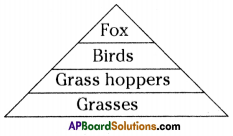
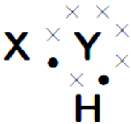




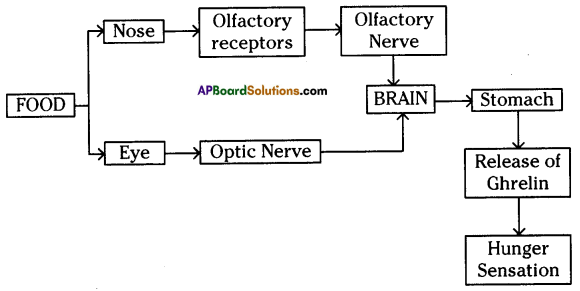
 Answer:
Answer: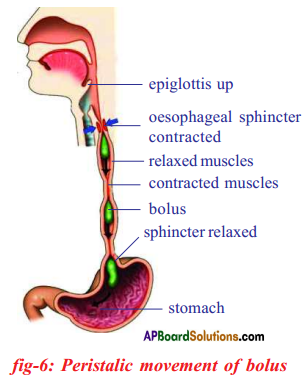 b) Circular muscles and longitudinal muscles of oesophagus help in the movement of food ‘bolus’.
b) Circular muscles and longitudinal muscles of oesophagus help in the movement of food ‘bolus’.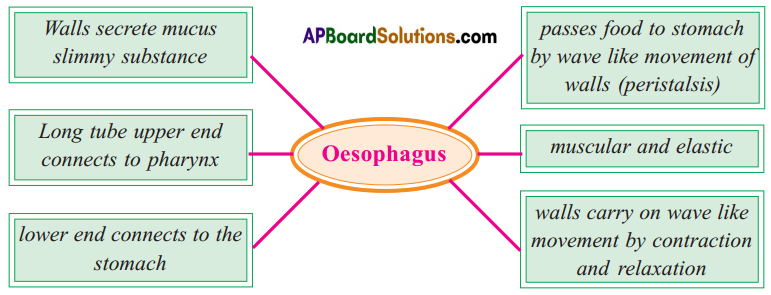
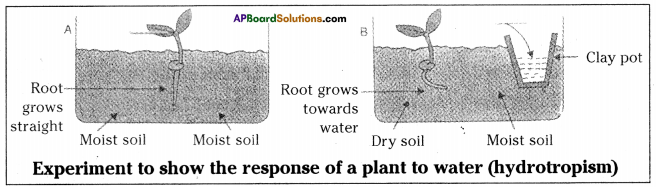
 Procedure:
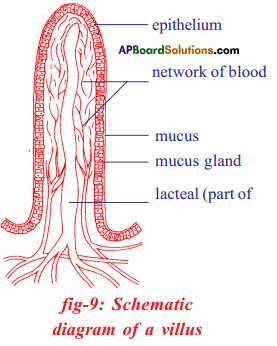
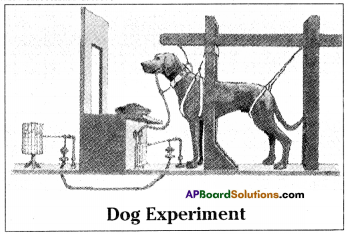
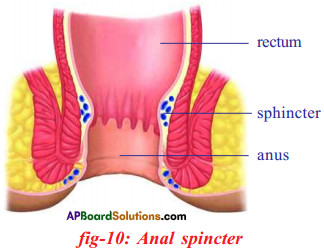
Procedure: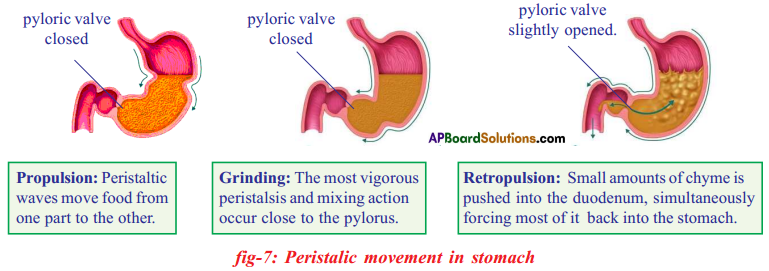

 Answer:
Answer: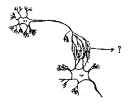 Answer:
Answer: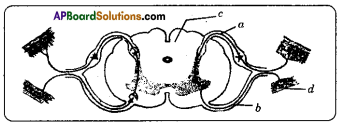 Answer:
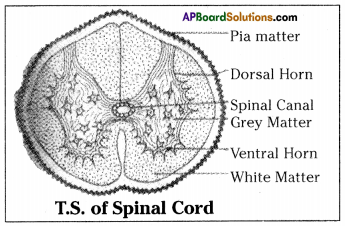
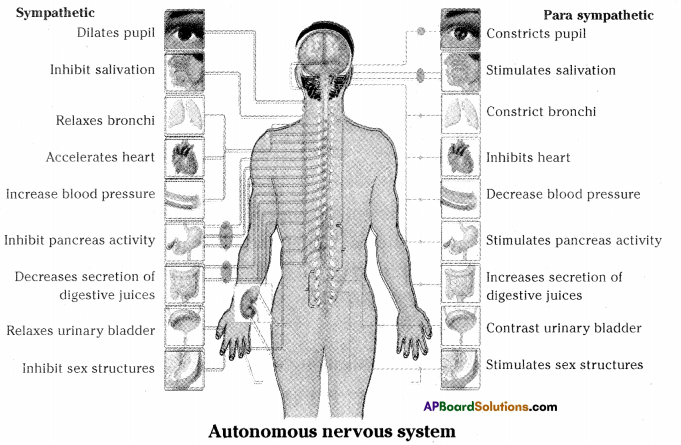
Answer: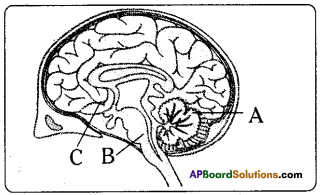 i) This diagram belongs to which system of the body?
i) This diagram belongs to which system of the body?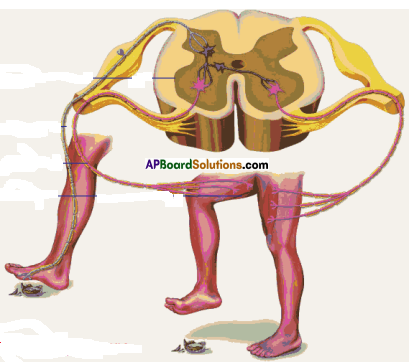 Answer:
Answer: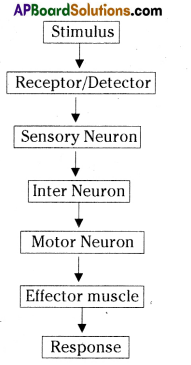
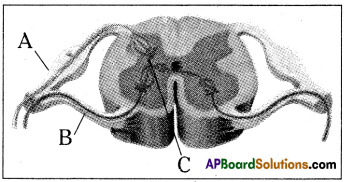 a) To which system does the diagram belong ?
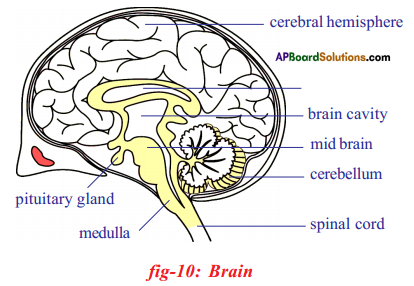
a) To which system does the diagram belong ?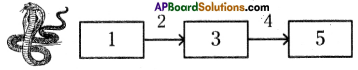 i) Brain receives the information, analyses and produces the reponse.
i) Brain receives the information, analyses and produces the reponse.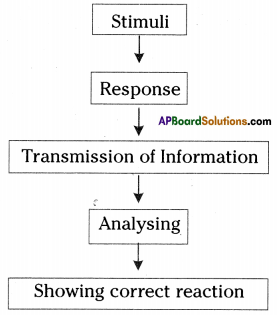
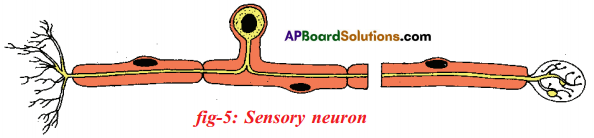
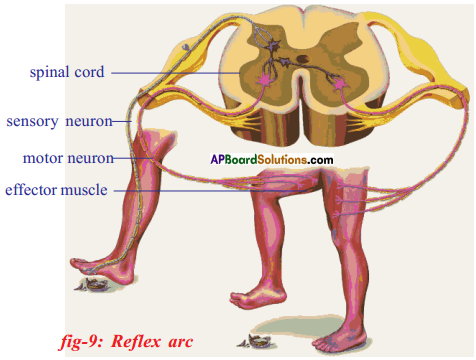 Functions of different parts of Reflex arc : Reflex arc consists of a receptor, a sensory nerve (afferent) an association neuron or inter neuron, motor nerve (effferent) and a effector organ.
Functions of different parts of Reflex arc : Reflex arc consists of a receptor, a sensory nerve (afferent) an association neuron or inter neuron, motor nerve (effferent) and a effector organ.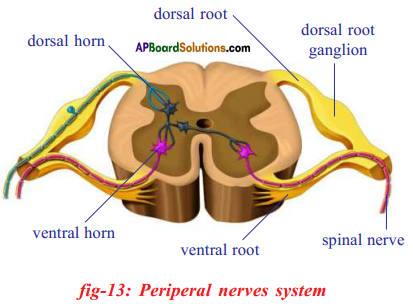
 i) To which organs of the body do the nerves go from the ganglions near the vertebral column ?
i) To which organs of the body do the nerves go from the ganglions near the vertebral column ?