AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 9 Our Environment.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions 9th Lesson Our Environment
10th Class Biology 9th Lesson Our Environment 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Suggest one alternative method in place of pesticides to protect crops?
Answer:
Alternative methods for using pesticides to save the crops from pests:
- Rotation of crops
- Studying the life histories of pests
- Biological Control
- Sterility
- Genetic Strains
![]()
Question 2.
By taking two plants of your surroundings as examples, explain how they protect themselves against the animals which eat them.
Answer:
- Neem Tree: Neem leaves contain an alkaloid Nimbin to protect themselves from the animals which eat them.
- Cactus: They have thorns to protect themselves.
- Datura: Datura leaves gives bad odour.
Question 3.
Identify one food chain from your surroundings. Name the producers and different levels of consumers in that food Chain.
Answer:
Grass → Insects → Frog → Snake.
Producers – Grass.
Primary Consumers – Insects.
Secondary Consumers – Frog
Tertiary consumers – Snake.
Aquatic Plants → Insects → Fish → Crane.
Producers – Aquatic Plant.
Primary Consumers – Insects
Secondary Consumers – Fish
Tertiary consumers – Crane
Question 4.
Write the names of producers and consumers in the food chain, you have observed.
Answer:
Producers – Plants, Green Algae
Consumers – All Animals.
![]()
Question 5.
Write any two slogans to promote awareness among the people about Ecofriendly programs.
Answer:
a) Lets go green to get global clean.
b) If you disturb the nature, the nature will disturb you.
c) The best solution to arrest pollution is plantation.
d) Reduce the usage of plastic and reduce the pollution.
Question 6.
What happens if decomposers are removed from the food web?
Answer:
- If decomposers are removed from the food web then the biological cycles are not completed.
- If the decomposers are not present in an ecosystem the remains of the other organisms accumulate.
Question 7.
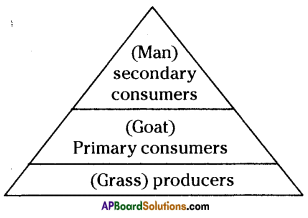
Observe the following given below. Draw the pyramid of numbers.
Grass → Goat → Man
Answer:
Question 8.
We can’t expect the world without sparrows. So how should be our concern towards their conservation?
Answer:
- Sparrows are useful to control harmful insects like locust which damage food grains.
- Chemical pesticides are the cause for destruction of sparrows and useful insects.
- By using biological methods we can conserve the sparrow population.
![]()
Question 9.
Human being is modifying agriculture lands and lakes into residential areas. What is its effect on Bio-diversity?
Answer:
- The shelter may not be provided for migratory birds.
- Food chain get disturbed.
- Decrease in the ground water level.
Question 10.
How do you protect the plants, which were planted in “Haritha Haaram” programme in your school?
Answer:
We protect the plants:
- Watering of plants at regular intervals.
- Fencing or gaurding of plants.
- Adoption of plants.
- Providing organic manure.
Question 11.
The figure given below represents a food pyramid. Study it and answer the following questions.

i) Which trophic level has maximum energy?
Answer:
T1 (or) Primary producers (green plants)
ii) Give one example for T4 trophic level.
Answer:
Lion, tiger, hawk, etc.
Question 12.
“We can’t imagine the world without insects and birds, conserve them.
Answer:
Methods to conserve insects and birds:
- Avoid indiscriminate usage of pesticides
- Protect the natural habitats of insects and birds.
- Development of bird sanctuaries
- Everyone should follow environmental ethics.
![]()
Question 13.
What is environment?
Answer:
The sum of physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism is called environment.
Question 14.
What is biosphere?
Answer:
The world of living things is called biosphere.
(OR)
The life supporting zone on the earth is called biosphere.
Question 15.
What are the physical or abiotic factors in a biosphere?
Answer:
Land, air, water, sunlight, humidity etc. are the physical or abiotic factors in a biosphere.
Question 16.
What does a food chain show?
Answer:
Food chain shows that how the energy is passed from one organism to another.
Question 17.
How the terrestrial ecosystems are determined?
Answer:
The terrestrial ecosystems are determined largely by the variations in climatic conditions between the poles and equator.
Question 18.
Where did the Kilimanjaro mountain located?
Answer:
The Kilimanjaro mountain is located in equatorial Africa (present in Tanzania, Africa).
Question 19.
What is the main source of energy for all the organisms in an ecosystem?
Answer:
Sunlight is the main source of energy for all the organisms in an ecosystem.
![]()
Question 20.
What is food web?
Answer:
The network of a large number of food chains existing in an ecosystem is called a food web.
Question 21.
What does a food web indicate?
Answer:
A food web indicates that the number of possible links for food in an ecosystem and reflects the fact that the whole community is a complex inter-connected unit.
Question 22.
What is ‘niche’?
Answer:
The position of organisms in a food web.
Question 23.
What does the word ‘niche’ denotes?
Answer:
‘Niche’ is the term used to describe not only the animals position in the food web and what it eats but also its mode of life.
Question 24.
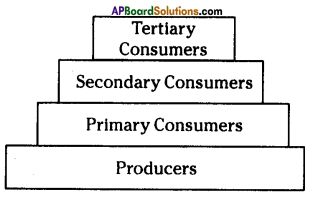
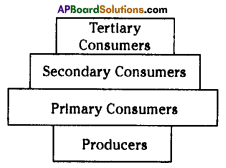
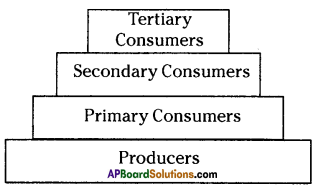
What is an ecological pyramid?
Answer:
The graphic representation of the feeding level structure of an ecosystem by taking the shape of a pyramid is called “Ecological pyramid”.
Question 25.
Who was the first one to introduce “Ecological pyramid”?
Answer:
Ecological pyramid was first introduced by a British Ecologist Charles Elton in 1927.
Question 26.
In ecological pyramids the producers are represented at?
Answer:
The producers are represented at the base of the ecological pyramids.
Question 27.
What is pyramid of number?
Answer:
A graphical representation designed to show the number of organisms at each tropic level in a given ecosystem is called “pyramid of number”.
![]()
Question 28.
What does the pyramid of number show?
Answer:
Pyramid of number shows the population of organisms at each tropic level in a food chain.
Question 29.
What does each bar represent in a pyramid of number?
Answer:
In a pyramid of number, each bar represents the number of individuals at each tropic level in a food chain.
Question 30.
When does the pyramid of number not look like a pyramid at all?
Answer:
If the producer is a large plant such as tree or if one of the organisms at any tropic level is very small, then the pyramid of number does not look like a pyramid.
Question 31.
What is biomass?
Answer:
Any type of plant or animal material that can be converted into energy is called biomass.
Question 32.
What is biofuels?
Answer:
The materials which are used for energy production are known as biofuels.
Question 33.
What is Pyramid of biomass?
Answer:
A graphical representation designed to show the quantity of living matter at each tropic level in a given ecosystem is called “Pyramid of biomass”.
Question 34.
Why Pyramid of biomass inverted in case of aquatic ecosystem?
Answer:
- In an aquatic ecosystem, the biomass of phytoplankton is quite negligible as compared to that of the crustaceans and small herbivorous fish that feed on these producers.
- The biomass of large carnivorous fish living on small fishes is still greater. This makes the pyramid of biomass inverted.
![]()
Question 35.
How much percentage of the biomass is transferred from one tropic level to the next in a food chain?
Answer:
The percentage of the biomass transferred from one tropic level to the next level in food chain is nearly 10 – 20%.
Question 36.
When does the species at the top of the pyramid get more energy?
Answer:
The species at the top of the pyramid get, more energy when the steps in a food chain are fewer.
Question 37.
What are bio-geochemical cycles?
Answer:
Flow of materials between organisms and their environment is called cycling of materials or bio-geochemical cycles.
Question 38.
What is ecological efficiency?
Answer:
The ratio between energy flows at different tropic levels among the food chain expressed as percentage is called ecological efficiency.
Question 39.
What is ten per cent law?
Answer:
During the transfer of energy from one tropic level to the next, only about ten per cent of the energy from organic matter is stored as flesh. This is called “Ten per cent law”.
Question 40.
Where do Kolleru one of the largest fresh water lakes in India exists?
Answer:
Kolleru is one of the largest fresh water lakes in India exists between West Godavari and Krishna districts of Andhra Pradesh.
Question 41.
What is the catchment area of the lake Kolleru?
Answer:
A catchment area of the Kolleru lake extends up to 6121 Km2.
Question 42.
Through which The lake Kolleru discharges its excess water into Bay of Bengal?
Answer:
The lake Kolleru discharges its excess water into Bay of Bengal through the twisty channel called Upputeru which is about 65 km long.
![]()
Question 43.
When did Government of Andhra Pradesh had declared the lake as Bird Sanctuary?
Answer:
In November 1999, Government of Andhra Pradesh had declared the lake as Bird Sanctuary.
Question 44.
What is the number of species of birds being hosted by the Kolleru?
Answer:
The Kolleru lake is hosting 193 species of birds.
Question 45.
What are the major sources of pollution in Kolleru lake?
Answer:
The major sources of pollution are agricultural runoff containing residues of several agrochemicals, fertilizers, fish tank discharges, industrial effluents containing chemical residues and different types of organic substances, municipal and domestic sewage.
Question 46.
What is the objective of “Operation Kolleru” by the ministry of environment and forest, Government of India?
Answer:
The objective of operation Kolleru by the ministry of environment and forest, Government of India is to bring back the ecological balance of Kolleru lake which is a gift of nature.
Question 47.
What is Bioaccumulation?
Answer:
The process of entering of pollutants in a food chain is known as Bioaccumulation.
Question 48.
What is Biomagnification?
Answer:
The tendency of pollutants to concentrate as they move from one tropic level to the next is known as Biomagnification.
Question 49.
What are pesticides?
Answer:
The chemical materials used to control pests that attack crop plants or live as parasites on the body of farm animals are called pesticides.
![]()
Question 50.
What is a perfect pesticide?
Answer:
The perfect pesticide is one which destroys a particular pest and is completely harmless to every other form of life.
Question 51.
Why did the egg breaking among the peregrines increase?
Answer:
Egg breaking among the peregrines increased due to their disturbed behaviour caused by the nerve poisons that entered into their tissues through food chain.
Question 52.
Why did the aquatic biota is being contaminated?
Answer:
The aquatic biota is being contaminated with heavy metals due to industrialization and anthropogenic activities.
Question 53.
Why fish are considered to be the bioindicators of metal contamination?
Answer:
Fish are considered to be the bioindicators of metal contamination in environmental monitoring because fish species are strongly respond to stress conditions.
Question 54.
Where did Edulabad water reservoir located?
Answer:
Edulabad water reservoir is located in urban areas of Ranga Reddy district of Telangana.
Question 55.
Which fish species is grown in Edulabad water reservoir?
Answer:
Cyprinus carpio (common scale carp) is the fish species grown in Edulabad water reservoir.
![]()
Question 56.
What are the effects of bioaccumulation of metals in human beings that eat cyprinus carpio?
Answer:
The bioaccumulation of various metals in cyprinus carpio cause disorders. Such as hypertensions, sporadic fever, renal damage, nausea, etc.
Question 57.
In which country sparrows were hunted extensively in 1958?
Answer:
In China sparrows were hunted extensively in 1958.
Question 58.
In your opinion what are the effective methods to control pests?
Answer:
Rotation of crops, biological control, developing genetically modified plants are the effective methods to control pests in my opinon.
Question 59.
Why the temperatures are very high during the day and cold during the nights in deserts?
Answer:
In deserts, the rainfall and humidity are very low, so the sun’s rays easily penetrate the atmosphere making ground temperatures very high during the day. But the nights are often cold as the earth loses heat rapidly.
Question 60.
How can we draw a food chain?
Answer:
We can draw a food chain by connecting the pictures or names of organisms by putting arrows between them. These arrows should always point from food to the feeder.
![]()
Question 61.
How many types of ecological pyramids are there in practice? Name them.
Answer:
There are three types of ecological pyramids. They are:
- Pyramid of number
- Pyramid of biomass and
- Pyramid of energy.
Question 62.
Which process helps to convert the solar energy into suitable form of energy for animals to consume?
Answer:
Photosynthesis helps to convert the solar energy into suitable form of energy (food) for animals to consume.
10th Class Biology 9th Lesson Our Environment 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
What will happen if we remove Frog from the above food chain? Explain.
Answer:
- Frog is secondary consumer in this food chain.
- If we remove frog from the food chain, the number of grasshopper will increase on other hand the number of snakes which depend on frogs will decrease.
- Hence, ecological balance may be damaged.
![]()
Question 2.
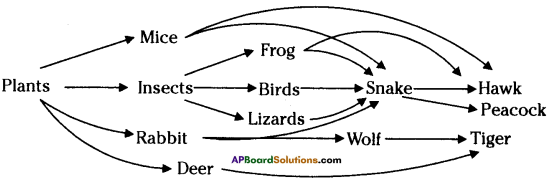
Observe the diagram and answer the following.
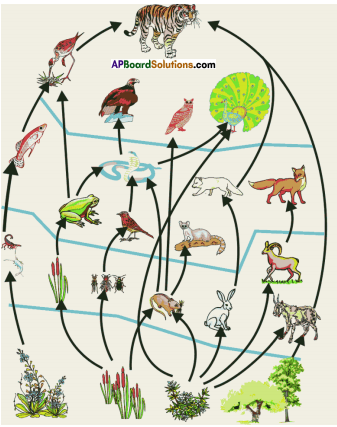 i) Write any two food chains from the diagram.
i) Write any two food chains from the diagram.
ii) What are the secondary consumers in the food chain that are written by you?
Answer:
i) a) Plants → Goat → Tiger
b) Plants → Rabbit → Wolf / Fox
ii) Tiger, Wolf / Fox
Question 3.
Study the given paragraph and answer the questions.
Solar energy from sun enters into the producers of an ecosystem. No organisms except green plants and photosynthetic bacteria can absorb solar energy and convert it into chemical energy.
A) What are the producers mentioned in the given paragraph?
B) What form is energy converted into photosynthesis? In Photosynthesis, which form is energy converted into?
Answer:
A) Green plants and photosynthetic bacteria.
B) In photosynthesis, the light (or) solar energy is converted into chemical energy.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the flow chart given below.
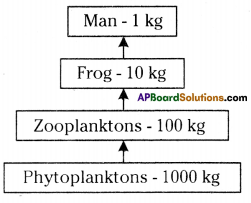 Answer:
Answer:
It is the pyramid of biomass.
- In this pyramid 10% of the food will reach to the next trophical level and so on at each level.
- It would take 1000 kg of phytoplankton to provide 100 kg of zooplankton and to form 1 kg of human tissue, 10 kg of frog is needed.
- The fewer the steps in the food chain, the more energy will be for the species at the top.
Question 5.
Observe the pyramid of number which is given below and answer the questions.
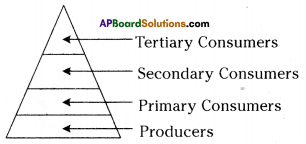 i) As per the number of organisms in the tropic level, which group of organisms
i) As per the number of organisms in the tropic level, which group of organisms
are more in number and which are less in number?
ii) What happens if Secondary consumers disappear?
Answer:
i) If producers are more in number, then tertiary consumers are less in number,
ii) If secondary consumers disappear the primary consumers increase in number and the tertiary consumers found no food to live. It leads to death.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain in brief about the alternate methods to be followed to prevent the harmful effects of over usage of pesticides.
(OR)
Mention any four effective methods of controlling pests, which are less harmful on environment based on biological principles.
Answer:
Some of alternative pest control methods are
- Rotation of Crop: Growing different crops on a particular piece of land in successive years.
- Studying the life histories of the pests: When this is done it is sometimes possible to sow the crops at a time when least damage will be caused.
- Biological Control: Introducing Natural predator or parasite of the pest.
- Sterility: Rendering the males of a pest species sterile.
- Genetic Strains: The development of genetic strains (genetically modified plants) which are resistant to certain pest.
- Environmental ethics: People need to know besides laws regarding environment there are some basic ethics what is right and what is wrong in view of environment.
Question 7.
Write any 4 slogans on the necessity of forests and on their conservation.
Answer:
- Save the trees, save the earth. We are the guardians of nature’s birth.
- Don’t destroy the greenary and don’t spoil the scenery.
- Don’t make trees rare, we should keep them with care.
- To live for future in rest, saving forest is the best.
Question 8.
How does the given below concepts differs?
(a) Bioaccumulation b) Biomagnification
Answer:
a) Bioaccumulation: The process of entry of pollutants into a food chain is known as bioaccumulation.
b) Biomagnification: It is the tendency of pollutants to concentrate as they move from one tropic level to the next is known as biomagnification.
![]()
Question 9.
The biomass of a producer in an ecosystem is calculated as 3500 kgs. Calculate the biomass of primary, secondary, tertiary consumers.
Answer:
In a food chain roughly 90% of the food is lost at each step. So if the biomass of a producer in an ecosystem is calculated as 3500 kgs. the biomass of primary consumer as will be 350 kgs. and of secondary consumer is 35 kgs and biomass of tertiary consumer is 3.5 kgs.
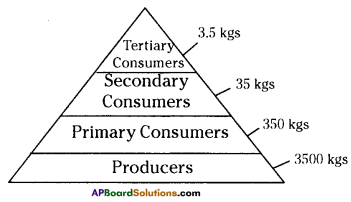
Question 10.
Write a short note on food chain and food web.
Answer:
- Food chain is a pathway along which food is transferred from one tropic level to another tropic level beginning with producers.
- It shows who eats what in a particular habitat.
- The arrows between each item in the chain always point from the food to the feeder.
- For example
Grass → Rabbit → Snake → Hawk - The elaborate interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem is said to be food web.
- Many of the food chains in an ecosystem are crosslinked to form food web.
- For example,
- Food chain and food web help us to understand the food relations among living things.
![]()
Question 11.
Write a short notes on ecological pyramids.
Answer:
- The graphical representation of the feeding level structure of an ecosystem by taking the shape of a pyramid is called “Ecological pyramid”.
- It was first introduced by a British Ecologist Charles Elton in 1927.
- In the ecological pyramid, the producers (First tropic level) are represented at the base, and the successive tropic levels (primary, secondary and tertiary consumers) are represented one above the other with top carnivores at the tip.
- There are three types of pyramids.
i) Pyramid of number ii) Pyramid of biomass and iii) Pyramid of energy. - Pyramid of number shows the population of organisms at each tropic level in a food chain.
- Pyramid of biomass represents the available food as a source of energy at each tropic level in the food chain.
- Pyramid of energy represents the available energy at each tropic level in food chain.
Question 12.
Write a short notes on pyramid of number.
Answer:
- Pyramid of number is a graphical representation designed to show the number of organisms at each tropic level in a given ecosystem.
- The shape of this pyramid varies from eco-system to ecosystem.
- In aquatic and grassland ecosystems, numerous small autotrophs support lesser herbivores which support further small number of carnivores and hence the pyramid structure is upright.
- In forest ecosystem, less number of producers support greater number of herbivores who in turn support a fewer number of carnivores. Hence the pyramid structure is partly upright.
- In parasitic food chain, one primary producer supports numerous parasites which support still more hyperparasites. Hence the pyramid structure is inverted.

![]()
Question 13.
Write a short notes on pyramid of biomass.
Answer:
- Pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation designed to show the quantity of living matter (biomass) at each tropic level in a given ecosystem.
- In terrestrial ecosystems, the biomass progressively decreases from producers to top carnivores. Hence the pyramid structure is upright.
- In an aquatic ecosystem, the biomass of phytoplankton (producers) is quite negligible as compared to that of crustaceans and small herbivorous fish that feed on these producers. The biomass of large carnivorous fish living on small fishes is still greater. This makes the pyramid of biomass inverted.

Question 14.
How do pesticides cause Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification?
(OR)
What are the effects of pesticides on environment?
Answer:
- Pesticides are the toxic chemicals used to destroy pest and insects which damage our crops and stored foods.
- These pesticides vary in their length of life as toxic materials.
- Some of the pesticides are degradable that can be broken down into harmless substances in a comparatively short time and others are non-degradable.
- Non-degradable pesticides accumulate in the bodies of animal and pass right through food web.
- Thus the pesticides cause bioaccumulation.
- These accumulated pesticides concentrate as they move from one tropic level to the next, thus leads to biomagnification.
![]()
Question 15.
List out some human activities which altered the communities of plants and animals in their natural ecosystem.
Answer:
- Industrialization
- Damming rivers
- Draining marshes
- Re-claiming land from the sea
- Cutting down forests
- Using chemical fertilisers and pesticides
- Building towns, cities, canals and motor ways.
Question 16.
What kind of changes may come in 2m ecosystem due to development of a large town?
Answer:
The following changes are expected due to development of a large town.
- Some plants and animal species will die out.
- Some will adapt to the new conditions sufficiently to survive in reduced numbers.
- Some will benefit by the new conditions and will increase in numbers.
Question 17.
Write a comparative note on pyramid of number and pyramid of biomass.
(OR)
Write the differences between pyramid of number and pyramid of biomass.
Answer:
| Pyramid of number | Pyramid of biomass |
| 1. Pyramid of number is a graphical representation designed to show the number of organisms at each tropic level in a given ecosystem. | 1. Pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation designed to show the quantity of living matter at each tropic level in a given ecosystem. |
| 2. It shows the population of organisms at each tropic level in a food chain. | 2. It represents the available food as a source of energy at each tropic level in the food chain. |
| 3. This pyramid sometimes does not look like a pyramid at all. It may be upright like in grassland ecosystem, partly upright like in forest ecosystem or inverted like in parasitic ecosystem. | 3. This pyramid may be upright like in terrestrial ecosystem or inverted like in aquatic ecosystem. |
![]()
Question 18.
Write a comparative note on pyramid of biomass and pyramid of energy.
(OR)
What are the differences between pyramid of biomass and pyramid of energy?
Answer:
| Pyramid of biomass | Pyramid of energy |
| 1. Pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation designed to show the quantity of living matter at each tropic level in a given ecosystem. | 1. Pyramid of energy is a graphical representation designed to show the quantity of energy present at each tropic level in a given ecosystem. |
| 2. It represents the available food as a source of energy at each tropic level in the food chain. | 2. It represents the available energy at each tropic level in the food chain. |
| 3. This pyramid may be upright like in terrestrial ecosystem or inverted like in aquatic ecosystem. | 3. This pyramid is always upright as only 10% of energy from one level is transfering to the next level. |
Question 19.
Write a comparative note on pyramid of number and pyramid of energy?
(OR)
What are the differences between pyramid of number and pyramid of energy?
Answer:
| Pyramid of number | Pyramid of energy |
| 1. Pyramid of number is a graphical representation designed to show the number of organisms at each tropic level in a given ecosystem. | 1. Pyramid of energy is a graphical representation designed to show the quantity of energy present at each tropic level in a given ecosystem. |
| 2. It shows the population of organisms at each tropic level in a food chain. | 2. It shows the available energy at each tropic level in a food chain. |
| 3. This pyramid sometimes does not look like a pyramid at all. It may be upright like in a grassland ecosystem partly upright like in forest ecosystem or inverted like in parasitic ecosystem. | 3. This pyramid is always upright, as only 10% of energy is transfering from one tropic level to other. |
Question 20.
What is ecological efficiency? Write a short notes on Ten per cent law?
Answer:
Ecological efficiency: The ratio between energy flows at different tropic levels along the food chain expressed as percentage is called “ecological efficiency”.
Ten per cent law:
- The amount of energy transferred decreases with successive tropic levels.
- Slobodkin (1959) suggested that the transfer of energy from one tropic level to the next is of the order of 10% and this is called “Gross ecological efficiency”.
![]()
Question 21.
Geetha said “a given species may occupy more than one tropic level in the same ecosystem at the same time”. Do you support her or not? Explain your answer with example.
Answer:
I support her for the following reason.
- A snake eating a mouse in a field or lawn occupies the third tropic level.
Plant → Mouse → Snake - When the snake eats a frog in the same field, it occupies the fourth tropic level in a food chain. It is because the frog feed on some of the insects that depend on the plants.
Plant → Insect → Frog → Snake - Thus, a given species may occupy more than one tropic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.
- This is to satisfy its food needs, as it cannot do so by occupying one tropic level.
Question 22.
If we introduce a man into a forest ecosystem, at which level of food chain we will place him? Explain your answer.
Answer:
- If we introduce a man into a forest ecosystem, he can fit for any level of consumers of food chain.
- He may feed on plant parts such as fruits. Then we can place him at primary consumer level.
Plant → Man - He may feed on some of the herbivorous organisms such as rabbit, then we can place him at secondary consumers level.
Plant → Rabbit → Man - He may also feed on some of the carnivorous organisms such as insectivorous birds then we can place him at tertiary consumers level.
Plant → Insect → Bird → Man - This is possible to place him at any level of consumers, as he is an omnivore, who feed on both plant originated and animal originated foods.
![]()
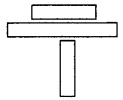
Question 23.
Draw the ecological pyramids for the given food chain.
Banyan Tree → Herbivorous birds → Carnivorous birds.
Answer:
1) Pyramid of number
2) Pyramid of biomass
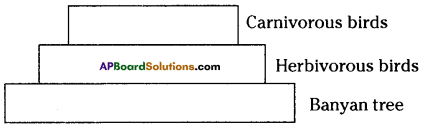
3) Pyramid of energy
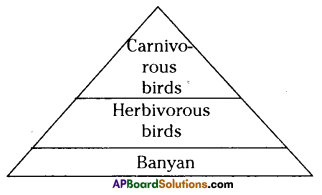
Question 24.
Write briefly about Minamata disease.
Answer:
- Minamata disease was first discovered in Minamata city in Kumamoto prefecture, Japan, in 1956.
- It was caused by the release of methyl mercury in the industrial waste water from the Chisso corporation’s chemical factory, which continued from 1932 to 1968.
- This highly toxic chemical bioaccumulated in shellfish and fish in Minimata Bay and the Shiranui Sea, which, when eaten by the local populace, resulted in mercury poisoning.
- While cat, dog, pig and humans death continued for 36 years.
![]()
Question 25.
What are trophic levels? Give an example of a food chain and state the different trophic levels in it.
Answer:
- Trophic levels is the feeding position in a food chain.
- It is the functional level occupied by an organism in a food chain.
- Examples of trophic levels include ‘herbivores’ and ‘decomposers’
- An example of food chain depicting various trophic levels is as follows:

Question 26.
What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem? (OR)
How decomposers help in cleaning the environment?
Answer:
- If the decomposers are not present in an ecosystem the remains of the other organisms accumulate.
- Eventually the world would run out of carbon dioxide or nitrate or phosphate or other inorganisms material essential for life.
- The decomposers breakdown the organic waste products and dead remains of organisms into the inorganic substances needed by the producers.
- Most decomposition is carried out by saprophytic fungi, by bacteria and by invertebrates.
![]()
10th Class Biology 9th Lesson Our Environment 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Prepare some slogans about ‘Vanam – Manam’ programme to display in your school rally?
Answer:
- Save paper – Save trees
- Plant a tree – Plant a life
- Saving trees is our duty
- Think green – Go green
- If we protect plants – they protects us
- Conserve plants – Conserve life
- Plant a tree – get the air free
- Plant a tree – Reduce the pollution.
- Tree on – Global warming gone.
- If cut a tree – It kills a life.
![]()
Question 2.
Read the information about Kolleru lake in the given table and answer the following questions.
| Classes | Area in 1967 (Km2) | Area In 2004 (Km2) |
| Lake-water spread area | 70.70 | 62.65 |
| Lake with sparse weed | 0 | 47.45 |
| Lake with dense weed | 0 | 15.20 |
| Lake-liable to flood in rainy season | 100.97 | 0 |
| Aquaculture ponds | 0 | 99.74 |
| Rice fields | 8.40 | 16.62 |
| Encroachment | 0.31 | 1.37 |
| Total | 180.38 | 180.38 |
a) In which year, lake water spread area is more?
b) Why do you think weeds are more in the lake?
c) Guess the reasons for decrease in the lake area.
d) What measures are to be taken to control pollution in the lake?
Answer:
a) In the year 1967
b) Addition of excessive nutrients from aquaculture ponds and rice fields.
c) Aquaculture ponds, Ricefields and Encroachment are the reasons for decrease in lake area.
d) Anthropogenic activities are to be controlled in the lake catchment area. (Or)
Fish ponds are to be removed in the lake catchment area. (Or)
Agricultural practices in the lake area should be minimised as per the norms of government.
Question 3.
Observe the following pyramid of biomass and answer the following questions.
a) This pyramid shows a decrease in the biomass as we move up, why the biomass is decreasing?
Answer:
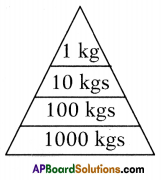 The pyramid of biomass for the given food chain, at each step 90% of the food is lost. That means 1000 kg of phytoplankton to produce 100 kg of Zooplankton to form 10 kg of fish to produce 1kg of human tissues. The fewer the steps in the food chain the more energy will be for the species at the top.
The pyramid of biomass for the given food chain, at each step 90% of the food is lost. That means 1000 kg of phytoplankton to produce 100 kg of Zooplankton to form 10 kg of fish to produce 1kg of human tissues. The fewer the steps in the food chain the more energy will be for the species at the top.
b) Give some examples of producers and primary consumers.
Answer:
Examples for producers: Plants, Grass, Diatoms.
Examples for primary consumers: Grasshopper, Rabbit, Deer,
c) Where do producers get the energy from?
Answer:
From the sun.
d) How much biomass is lost at each step?
Answer:
90%
![]()
Question 4.
Observe the following diagram and answer the following questions.
 i) Name the primary producers in the given food web.
i) Name the primary producers in the given food web.
ii) Prepare any one food – chain from the diagram.
iii) What are the tertiary consumers?
iv) Write names of any two herbivores.
Answer:
i) Plants, Grass, Trees Phytoplanktons etc.
ii) Grass → Rabbit → Fox → Tiger
iii) Tiger, Vulture, Crane, Owl, Peacock etc.
(OR)
The animals which are at 4th trophic level in a food chain are called as Tertiary Consumers.
iv) Rabbit, Deer, Goat, Cow
Question 5.
What is number pyramid? What does it indicate?
Answer:
- The number of organisms in a food chain can be represented graphically in a pyramid of number.
- Each bar represents the number of individuals at each tropic level in a food chain.
- At each link in a food chain, from the first order consumers to the large carnivores, there is normally an increase in size but decrease in number.
- For example in a wood, the aphids are very small and occur in astronomical numbers.
- The lady birds which feed on them are distinctly larger and not so numerous.
- The insectivorous birds which feed on the lady birds are larger still and are only present in a small number and there may only be a single pair of hawks of much larger size than the insectivorous birds on which they prey.
![]()
Question 6.
Draw the diagram of number pyramid keeping foxes as third consumers. What are the consequences if their number increases?
Answer:
- If the number of foxes increases, then the competition for food will be very severe and less amount of food will be available for them.
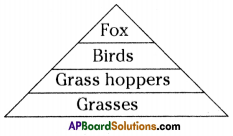
- As a result some of the foxes may not get enough food and die due to starvation.
- This reduces the population of foxes and very few foxes will be left in the forest.
- This increases the chances of survival of secondary consumers birds, hence their number increases.
- This increases the availability of food for foxes. Very soon a balance will be established between the number of secondary consumers and foxes.
Question 7.
What reasons are responsible for decrease in number of top carnivores and biomass starting production in a food chain?
(OR)
Why the number of organisms get decreased as we move from producers to consumer levels?
Answer:
- In a food chain as we move from producers to different levels of consumers the energy available will decrease gradually.
- Only ten percent of the energy present in one tropic level transfer to another tropic level.
- Biomass also decreases gradually as only 10 – 20% of the biomass is transferred from one tropic level to the next in a food chain.
- As there is less energy of less biomass available at top levels, number of organisms also less generally.
- So the number of organisms get decreased as we move from producers to different level of consumer.
![]()
Question 8.
Show food chain of different organisms, number of pyramid of your school.
Answer:
Food chain of different organisms in our school:
Plant → aphids → spiders thirds.
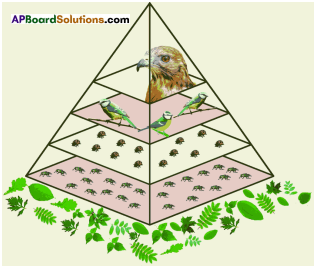
- The pyramid of organisms in a food chain can be represented graphically in a pyramid of number.
- Each bar represents the number of individuals at each tropic level in a food chain.
- At each link in a food chain, from the first order consumers to the large carnivores, there is normally an increase in size, but decrease in number.
Question 9.
What determines the terrestrial ecosystems on the earth?
Answer:
- The terrestrial ecosystems on the earth are being determined largely by the variations in climatic conditions between the poles and equator.
- The main climatic influences which determine these ecosystems are rainfall, temperature and availability of light from the sun.
- For instance, forests are usually associated with high rainfall, but the type Is influenced by temperature and light.
- The same applies to deserts which occur in regions where rainfall is extremely low.
- Thus, the climatic conditions along the horizontal climatic regions determined the terrestrial ecosystems on the earth.
- If we move from equatorial region to the polar region, we can come across tropical rain forests, savannah, deciduous forest, coniferous forests and then tundras respectively.
- Similarly altitude of the place is also a determining factor.
- If we climb a mountain such as Kilimanjaro in equatorial Africa, we can go through a comparable system of ecosystems, starting with tropical rain forest at the base and ending with perpetual snow and ice at the summit.
![]()
Question 10.
“All the energy in the ecosystem is ultimately derived from sunlight.” Justify.
Answer:
- All the organisms in an ecosystem derive energy from food.
- The food by its nature is the chemical energy and by in its stored form, it is the potential energy.
- In an ecosystem, all the consumers at any level depend upon producers for their food either directly or indirectly.
- The producers in any ecosystem are nothing but photosynthetic organisms such as plants, phytoplanktons and photosynthetic bacteria.
- Energy enters the producers in the ecosystem from the sun in the form of solar energy during photosynthesis.
- From the producers, the chemical energy passes to the consumers from one tropic level to the next through food.
- For example, in a grassland ecosystem, grass traps the solar energy and stores in its body.
- When this grass is eaten and assimilated by insects this stored energy enters into the body of insects.
- From the insects it will pass to frog, from them to snake and so on to eagle.
- Thus, all the energy in the ecosystem is ultimately derived from sunlight.
Question 11.
What is biological magnification? Will the levels of this magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem?
Answer:
- The tendency of pollutants to concentrate as they move from one trophic level to the next trophic level is known as Biomagnification.
- Plants absorb pesticides, heavy metals from the soil.
- The primary consumers when eat these plants the remaining of pesticides and heavy metals enter their bodies.
- As these chemicals are not degradable, they accumulate in the bodies of organisms of all trophic levels in the food chain.
- Most of the plants products which we eat are grown in fields in which pesticides and fertilisers have been used.
- These are absorbed by the plants and cannot be removed by washing or other means.
- Human beings are at the top level of the food chain these chemicals get accumulated in our bodies and cause various disorders.
- Levels of biological magnification would increase as the trophic level increases.
![]()
Question 12.
Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels ? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem?
Answer:
- If we remove producers from ecosystem, herbivores will not survive and the entire ecosystem collapse.
- Removing herbivores result in increase number of producers and carnivores would not get food.
- Removing carnivores result in increase of herbivores to unsustainable levels.
- If we remove decomposers from ecosystem waste material and animal dead remains would pile up and nutrients would not be available to the producers.
- Some or the other damage would be caused to the ecosystem if the organisms of any trophic level is removed.
- However impact of removing producers or decomposers would be serve as the whole ecosystem would collapse.
- Without plants sun’s energy cannot be converted to chemical energy which is the basis of life on earth.
- Without decomposers the nutrients cannot be recycled and made available to producers.
Question 13.
Every organism has got the right to live on this planet. Write slogans to motivate the people on preservation of biodiversity.
Answer:
- Live and let live.
- Conserve nature – conserve life.
- Clean the environment, live happily.
- Think eco-friendly and live eco-friendly.
- If we protect the environment, it protect us.
- Reduce pollution – conserve the biodiversity.
![]()
Question 14.
Write some friendly ecosystem activities you will conduct in your school.
Answer:
- Forming eco-clubs: These clubs consists of student representatives from each class. They will take up the eco-friendly activities and encourage the people of that village to follow environment friendly activities.
- Setting up garden at school: This ensures the school and its premises green through planting of flowering plants, vegetables and fruit trees. It is a symbol of biodiversity because various plants and animals inhabit the garden.
- Electricity conservation programme: To save energy the school implements certain hours to be switched off habit. This switching off programme for one hour from 3.30 p.m. to 4.30 p.m. help conserve electricity in every classroom.
- Pollution prevention programme: A ‘no burning of trash policy should be implemented in the school. Waste materials are recycled and properly disposed to ensure a clean, waste-free environment.
- Making compost by organic wastes: By digging a pit at one corner of the school and throwing the organic waste particularly of mid day meal waste into pit and covering with soil layers prepares compost which can be used as manure for plants. This creates a clean environment in the school.
- Using cloth bags instead of polythene bags by pupil.
- Collection of solid waste materials and proper management of its helps in reducing soil pollution.
- Children should be encouraged to follow ‘3R’ system i.e. Reduce, Re use and Recycle different substances.
Question 15.
What is Ecological pyramid? Describe different types of Ecological pyramids.
Answer:
- The graphical representation of the feeding level structure of an ecosystem by taking the shape of a pyramid is called ecological pyramid.

- There are three types of ecological pyramids. They are
1) Pyramid of number, 2) Pyramid of biomass and 3) Pyramid of energy. - Pyramid of number is a graphical representation designed to show the number of organisms at each tropic level in a given ecosystem.
- The shape of this pyramid varies from ecosystem to ecosystem.
- In forest ecosystem the pyramid structure is partly upright and in parasitic food chain is inverted.
- Pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation designed to show the quantity of living matter (bio mass) at each trophic level in a given ecosystem.
- In terrestrial ecosystems, the biomass progressively decreases from producers to top carnivores hence the pyramid structure is upright whereas in aquatic ecosystem it is inverted.
- Pyramid of energy is a graphical representation designed to show the quantity of energy present at each tropic level in a given ecosystem. The pyramid of energy is always upright.
![]()
Question 16.
Collect information regarding pesticides commonly used in your area and prepare a chart showing pesticide and common name and on which crop and pest it is commonly used.
Answer:
| S.No. | Pesticide | Crop | |
| 1. | Imidaclopriol | Cotton, Chillies | Aphid, White fly, Jassids, Thrips |
| Paddy | BPH, WBPH, GWT | ||
| 2. | Triazophos | Cotton | Bollworm |
| Paddy | Leaf folder, Green leaf hopper, Hispa | ||
| 3. | Chlorpyriphos | Paddy | Leaf roller, Hispa gall midge, Stem borer, Whorl maggot |
| Cotton | Aphid, Bollworm, White fly | ||
| 4. | Monocrotophos | Paddy | Brown plant hopper, Green leaf hopper, Leaf roller, Yellow stem borer |
| Maize Bengal gram Green gram Black gram | Shoot fly Pod borer | ||
| Sugarcane | Early shoot borer, Mealy bug | ||
| Cotton Oil seeds Vegetables | Insects | ||
| 5. | Acephate | Cotton | Jassid, Bollworms |
| Sunflower | Aphids | ||
| 6. | Dichlorvos | Paddy | Leaf roller |
| Sugarcane | Pyrilla | ||
| Oil seeds, Vegetables | Insect pests | ||
| 7. | Acetamiprid | Cotton | Aphids, Jassids, White flies |
![]()
 symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.
symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.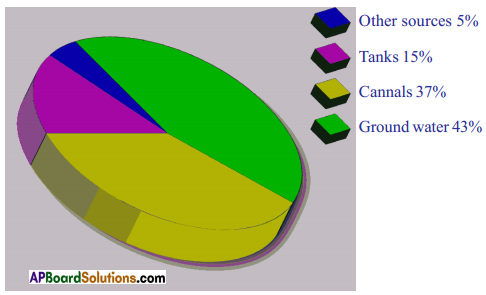 A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?
A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?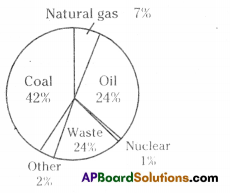 i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.
i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.
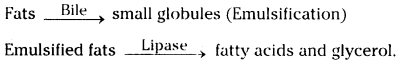

 Answer:
Answer:
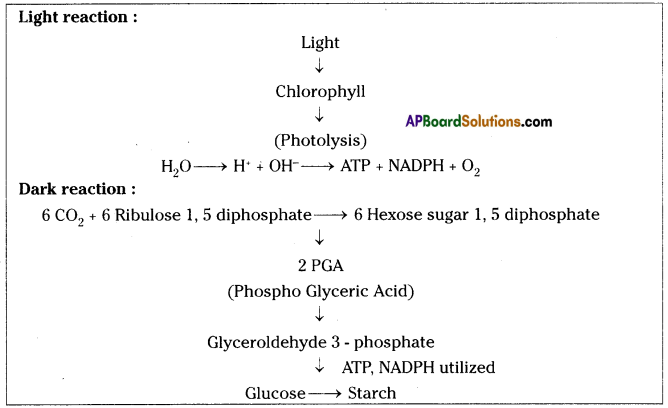
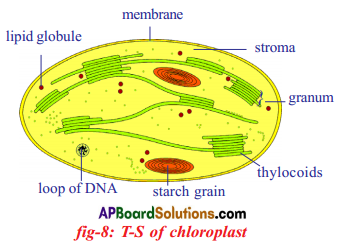
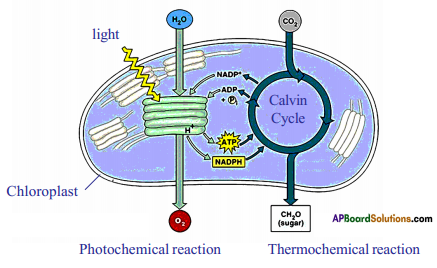
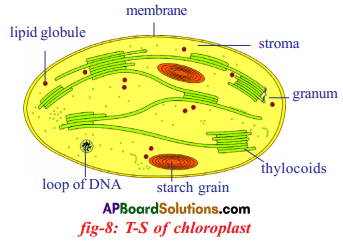 Role of Chloroplast in photosynthesis:
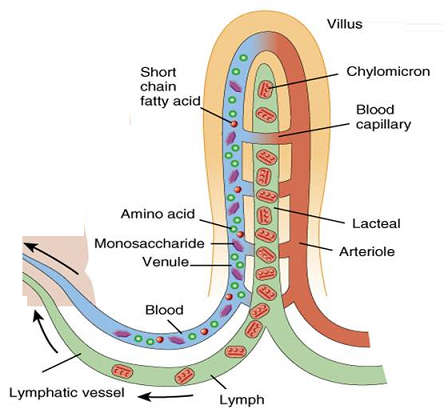
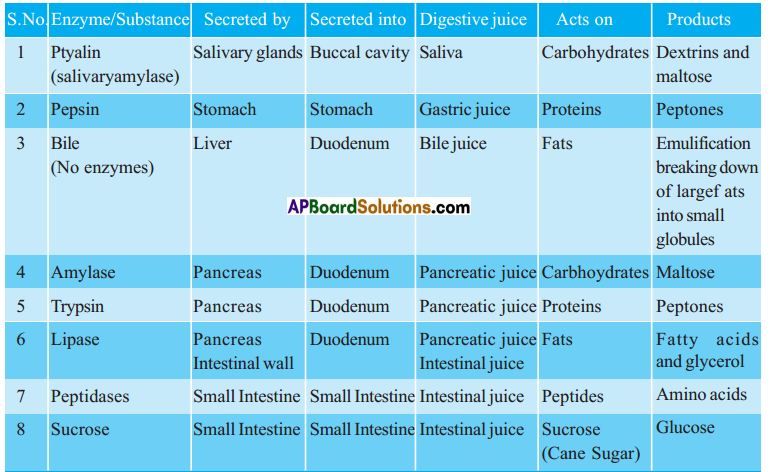
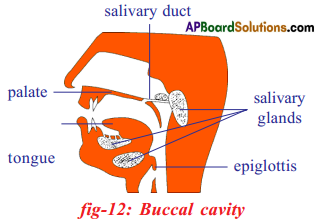
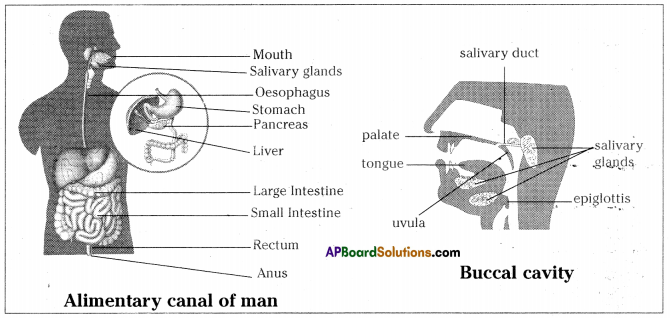
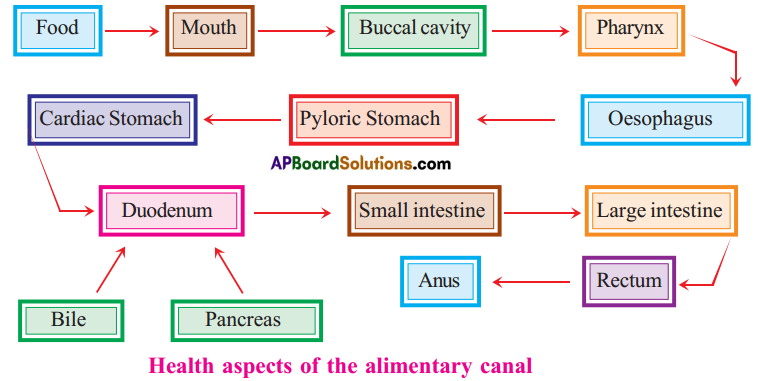
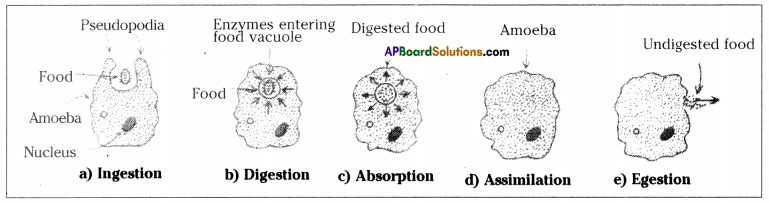
Role of Chloroplast in photosynthesis: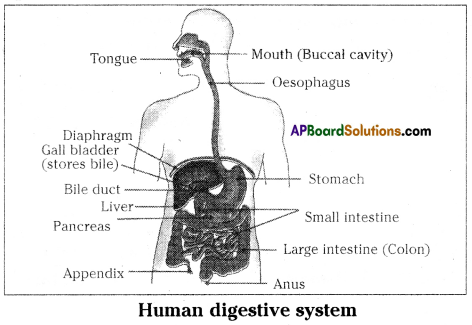 Parts where peristalsis takes place: Oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.
Parts where peristalsis takes place: Oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine.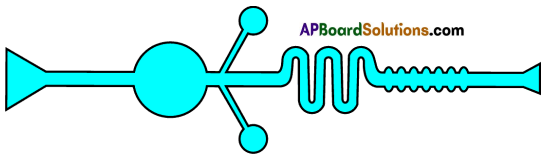 Answer:
Answer: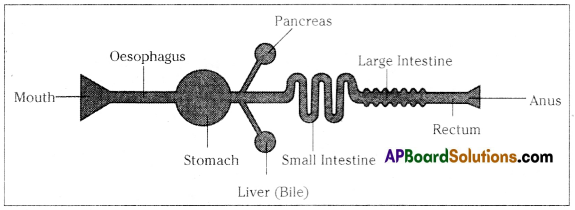
 Answer:
Answer: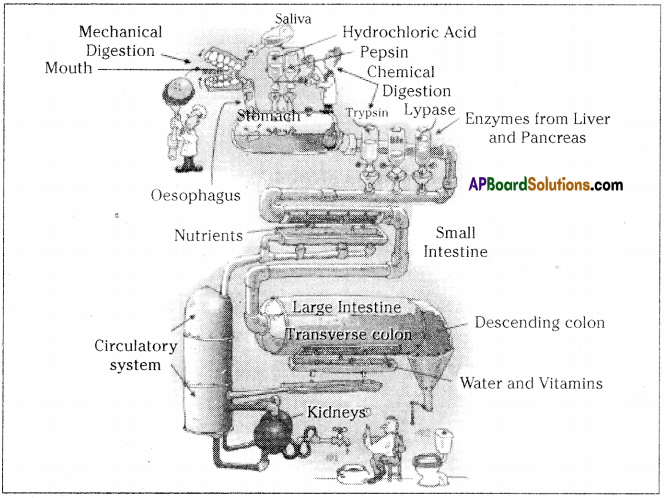
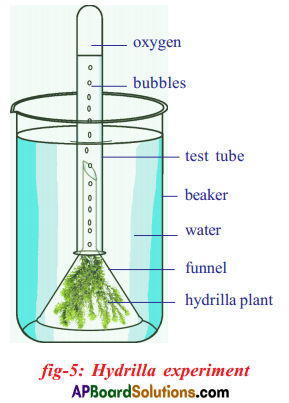
 Apparatus:
Apparatus:
 Priestly should have tilted the bell jar to one side and introduced the mint plant without disturbing the experimental set up.
Priestly should have tilted the bell jar to one side and introduced the mint plant without disturbing the experimental set up.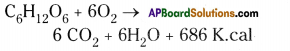
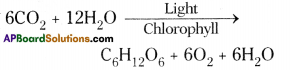




 Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer:
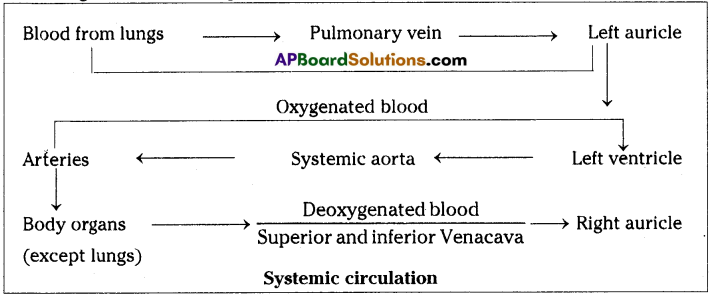

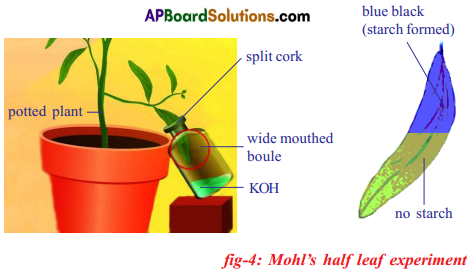
 Required material: A healthy potted plant, a polythene cover, water.
Required material: A healthy potted plant, a polythene cover, water.
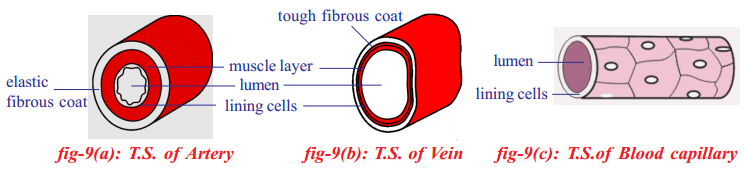
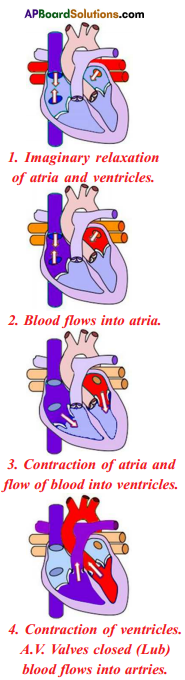
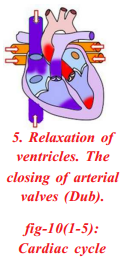

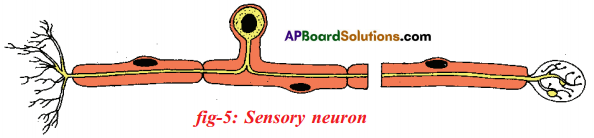 Answer:
Answer: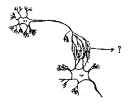 Answer:
Answer: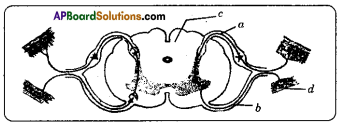 Answer:
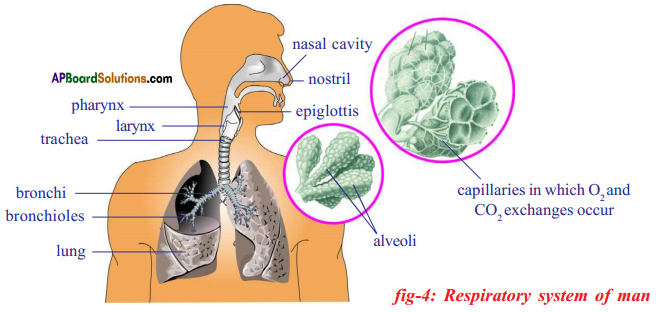
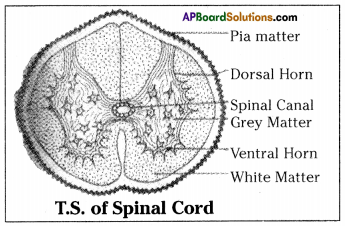
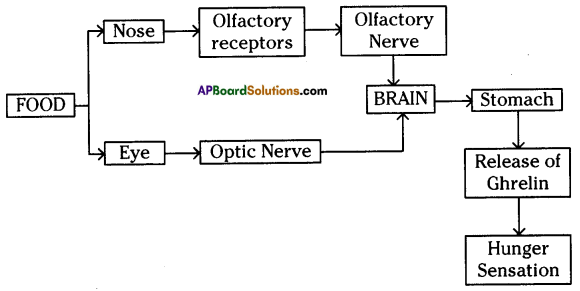
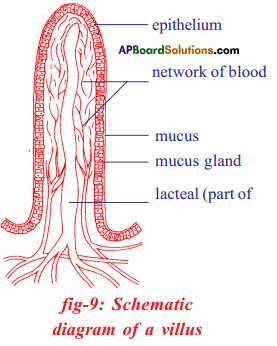
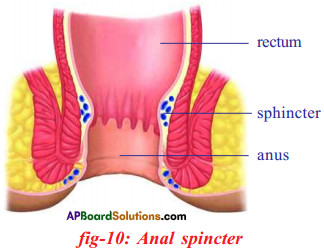
Answer: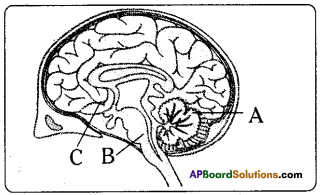 i) This diagram belongs to which system of the body?
i) This diagram belongs to which system of the body?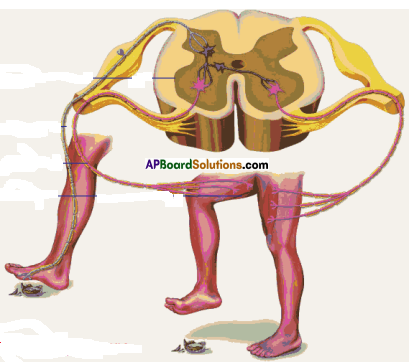 Answer:
Answer: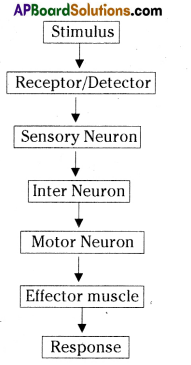
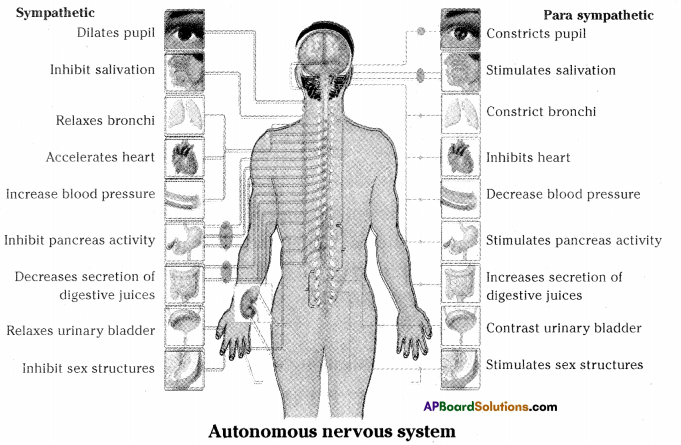
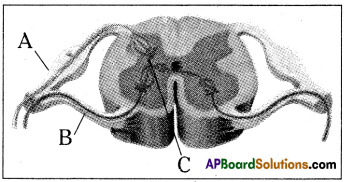 a) To which system does the diagram belong ?
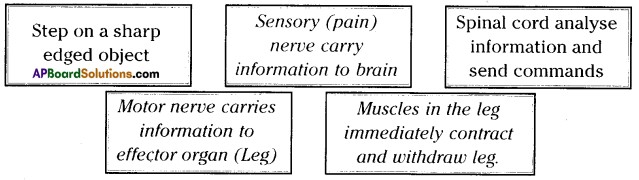
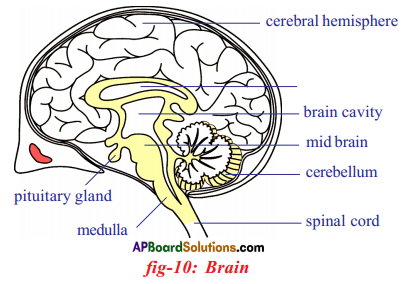
a) To which system does the diagram belong ? i) Brain receives the information, analyses and produces the reponse.
i) Brain receives the information, analyses and produces the reponse.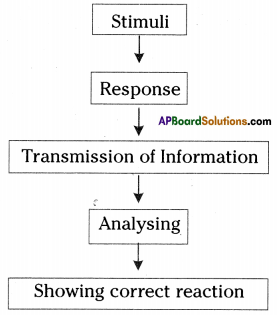
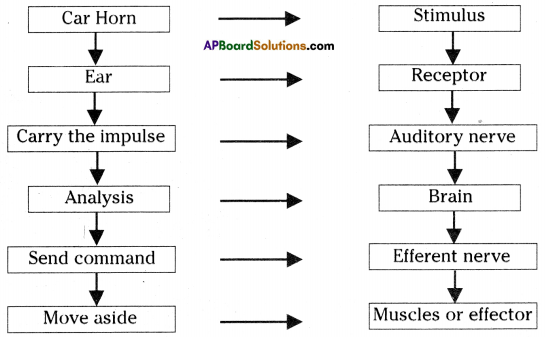
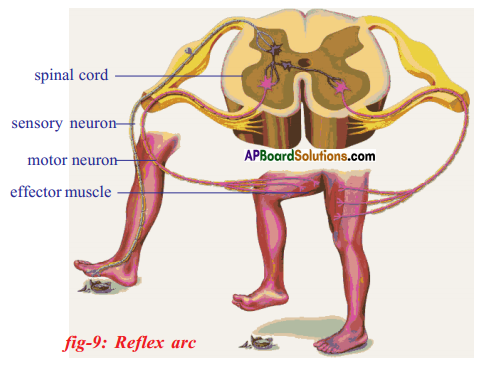
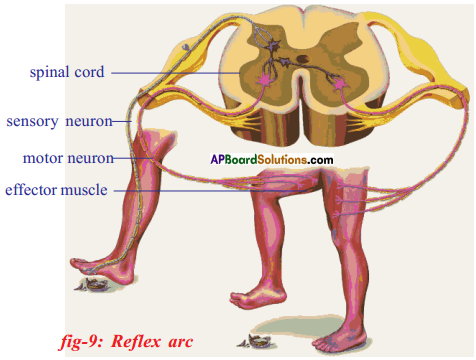 Functions of different parts of Reflex arc : Reflex arc consists of a receptor, a sensory nerve (afferent) an association neuron or inter neuron, motor nerve (effferent) and a effector organ.
Functions of different parts of Reflex arc : Reflex arc consists of a receptor, a sensory nerve (afferent) an association neuron or inter neuron, motor nerve (effferent) and a effector organ.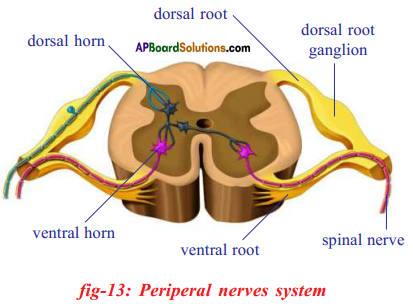
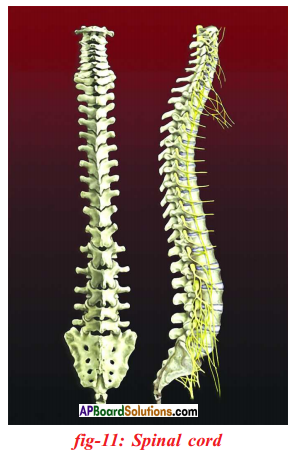
 i) To which organs of the body do the nerves go from the ganglions near the vertebral column ?
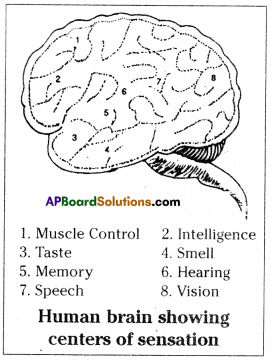
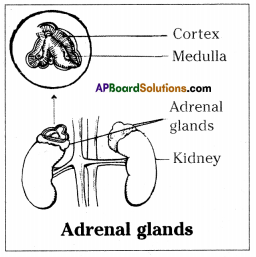
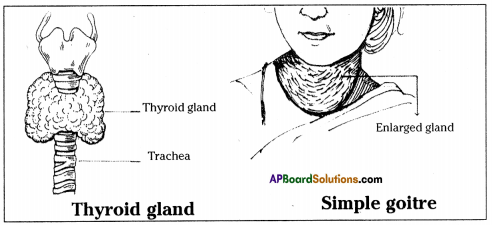
i) To which organs of the body do the nerves go from the ganglions near the vertebral column ?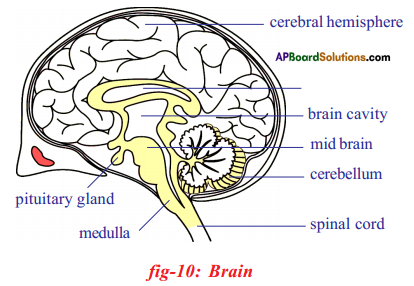

 Answer:
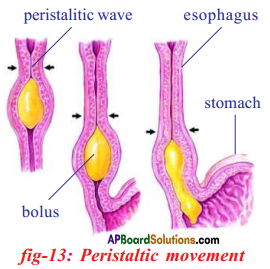
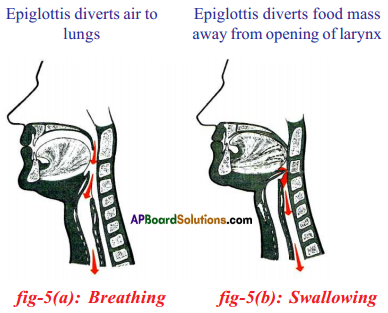
Answer: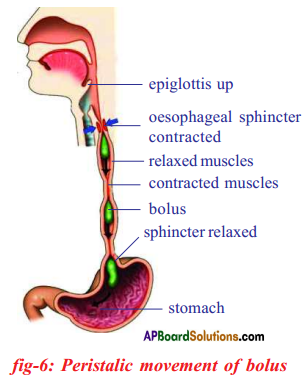 b) Circular muscles and longitudinal muscles of oesophagus help in the movement of food ‘bolus’.
b) Circular muscles and longitudinal muscles of oesophagus help in the movement of food ‘bolus’.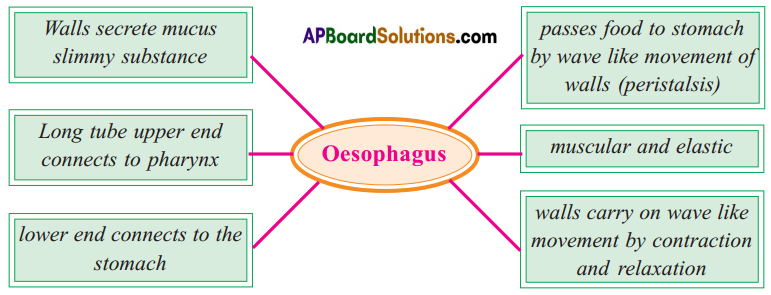
 Procedure:
Procedure: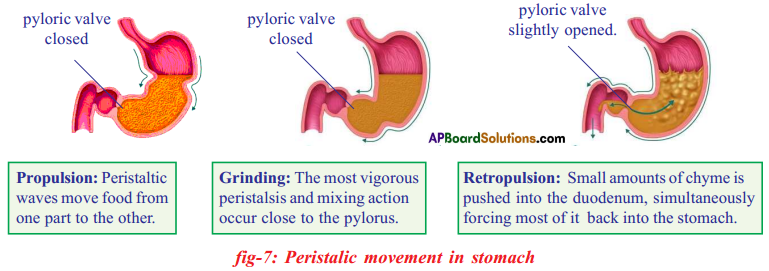
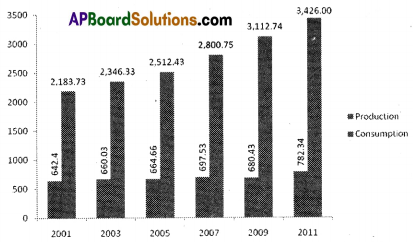 i) No, the production of oil doesn’t meet the consumption in India.
i) No, the production of oil doesn’t meet the consumption in India.

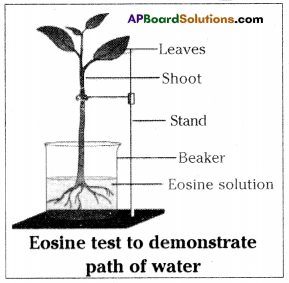
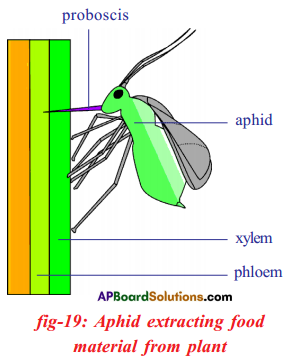
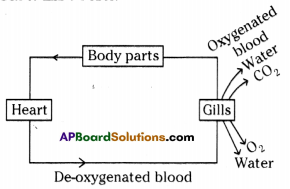
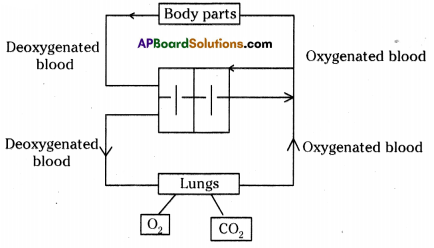
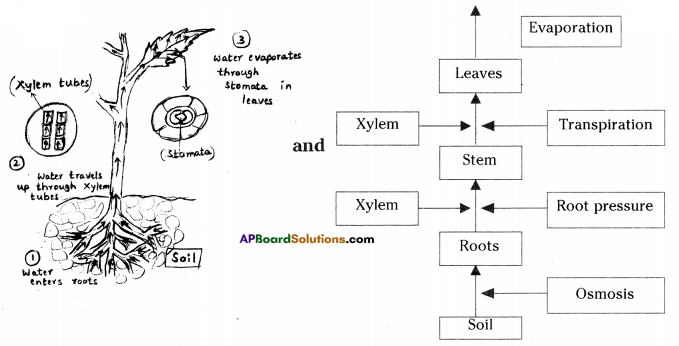
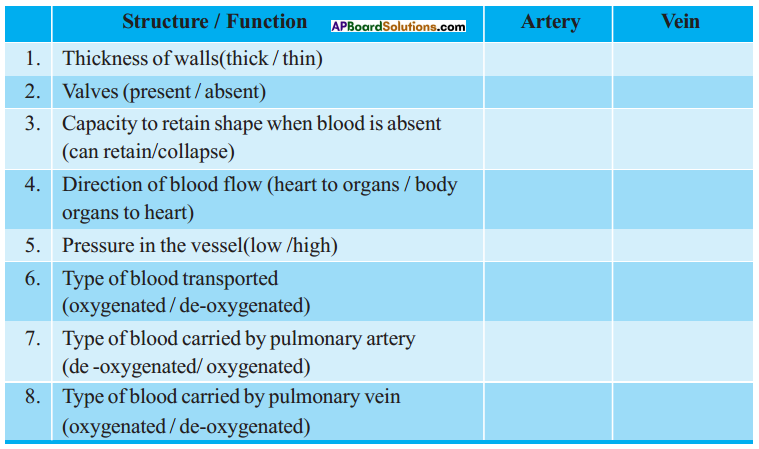 Answer:
Answer: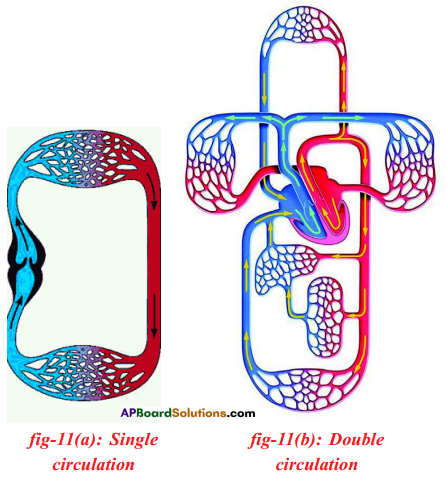
 2) You feel something pushing your fingers rhythmically up and down.
2) You feel something pushing your fingers rhythmically up and down.

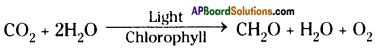
 a) What will you prove by this experiment?
a) What will you prove by this experiment? a) What will you prove by this experiment?
a) What will you prove by this experiment?
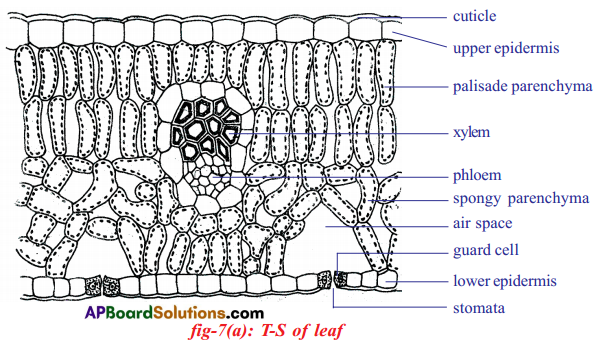 Palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma consist of chloroplast.
Palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma consist of chloroplast. i) What is the aim of this experiment?
i) What is the aim of this experiment?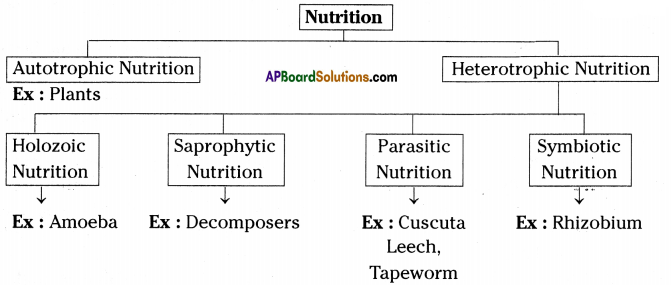 Parasitic Nutrition in Cuscuta :
Parasitic Nutrition in Cuscuta :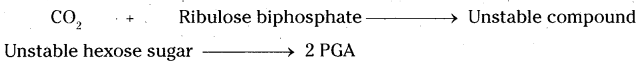
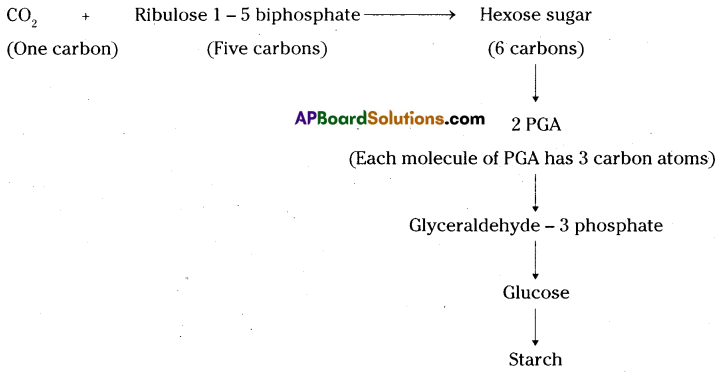
 a) What apparatus do you use during the conduction of the experiment?
a) What apparatus do you use during the conduction of the experiment?



 Required materials: A chart, twine thread, fevicol, sticker.
Required materials: A chart, twine thread, fevicol, sticker.


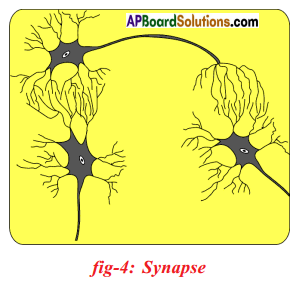
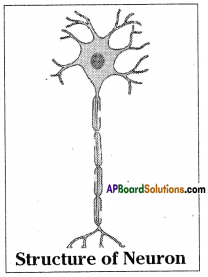
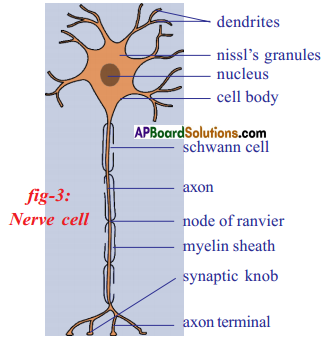 Structural unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell or neuron. Neuron is highly specialised cell. Neurons carry impulses or messages. New nerve cells are not produced to replace the damaged or destroyed nerve cell. A neuron has three parts. They are
Structural unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell or neuron. Neuron is highly specialised cell. Neurons carry impulses or messages. New nerve cells are not produced to replace the damaged or destroyed nerve cell. A neuron has three parts. They are


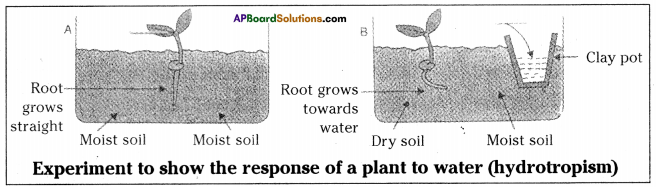
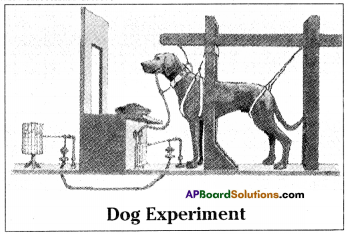
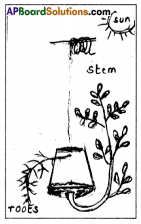
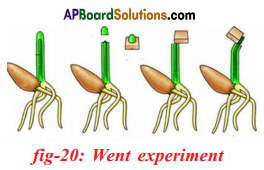
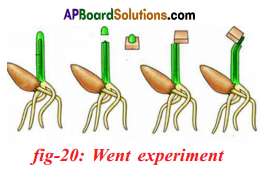 Went interpreted these experiments as showing that the coleoptile tip exerted it’s effect by means of chemical stimulus rather than a physical stimulus such as an electrical impulse.
Went interpreted these experiments as showing that the coleoptile tip exerted it’s effect by means of chemical stimulus rather than a physical stimulus such as an electrical impulse.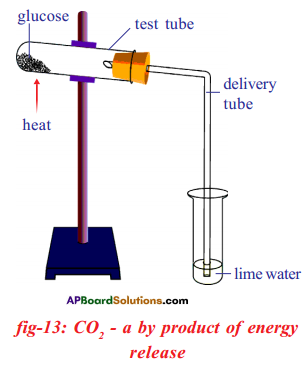

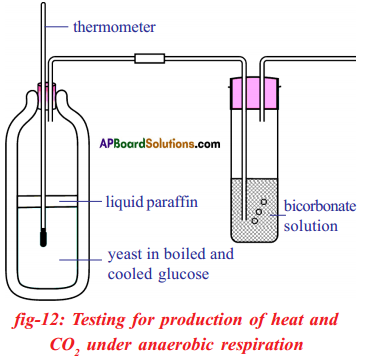
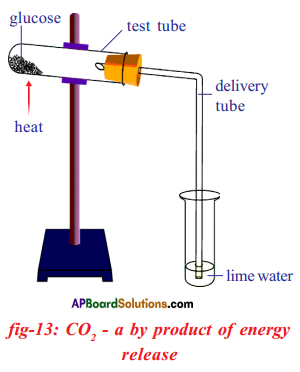
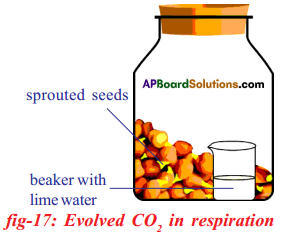
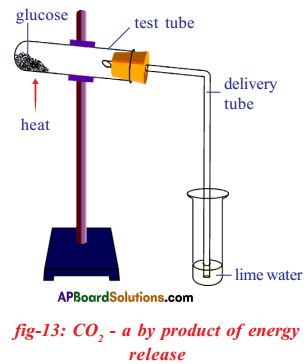
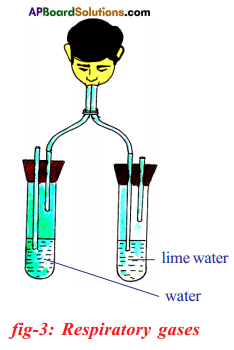 (a) Which gas turns lime water milky in this experiment?
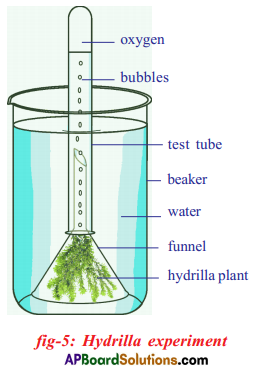
(a) Which gas turns lime water milky in this experiment?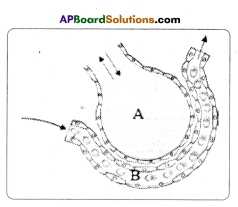 A) To which biosystem is this picture related?
A) To which biosystem is this picture related?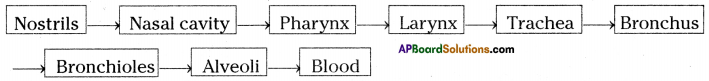
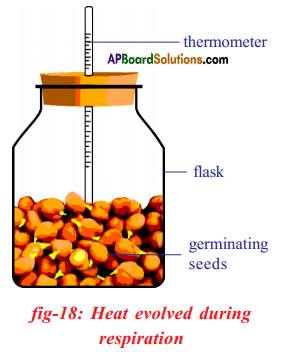 a) What is the aim of this experiment?
a) What is the aim of this experiment?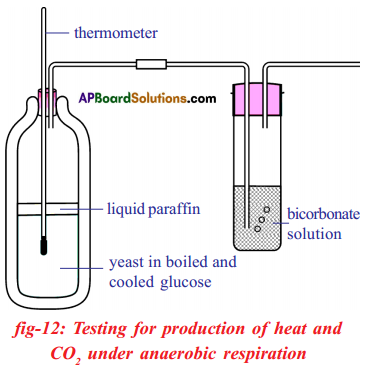 a) What do you prove by conducting this experiment?
a) What do you prove by conducting this experiment?
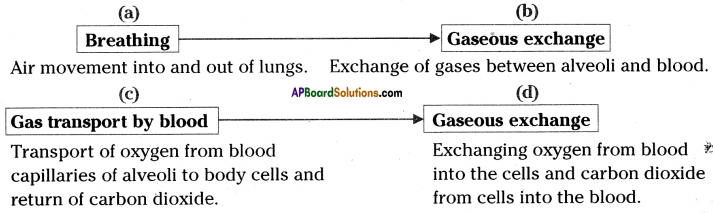
 i) Which process do we know with the help of this experiment?
i) Which process do we know with the help of this experiment?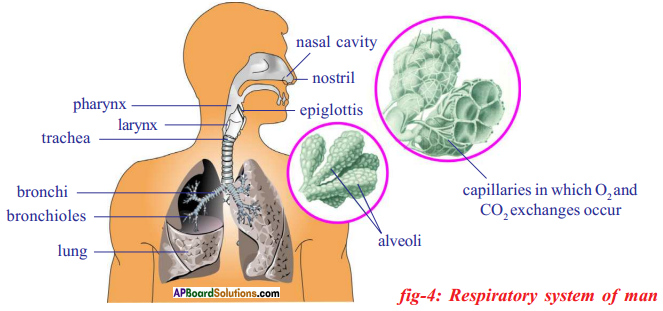

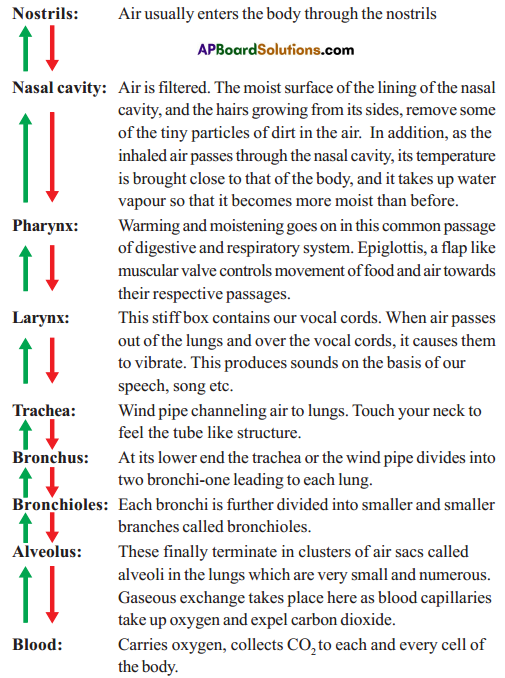
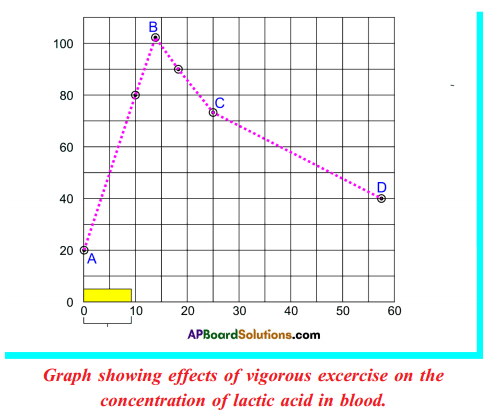
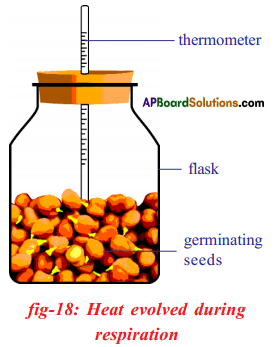
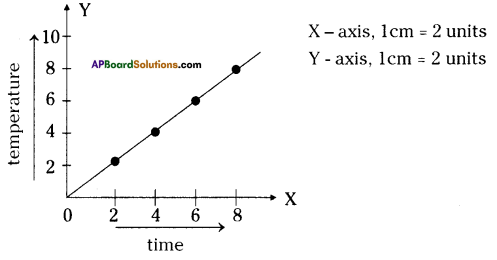
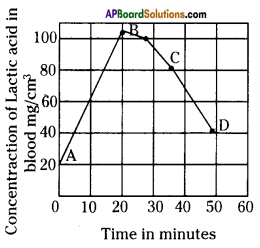 Graph showing effects of vigorous excercise on the concentration of lactic acid in blood.
Graph showing effects of vigorous excercise on the concentration of lactic acid in blood.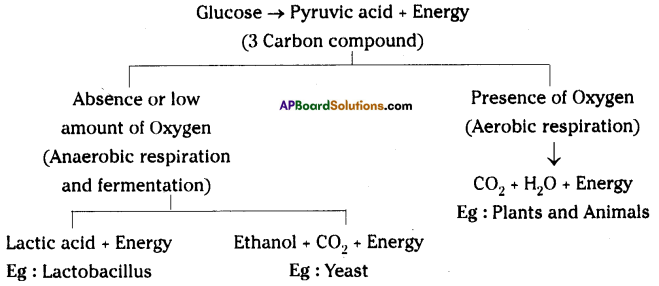
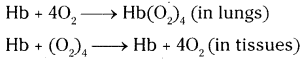

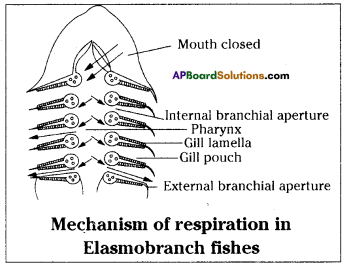
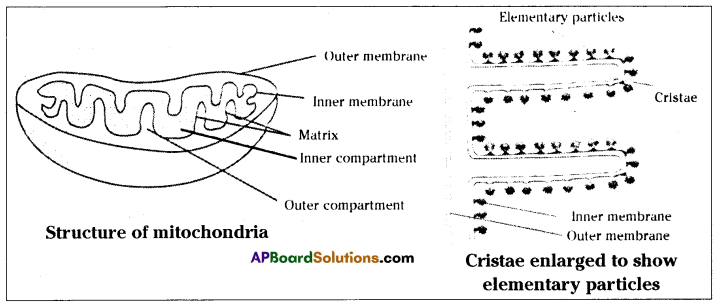
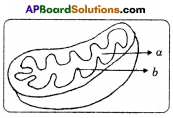
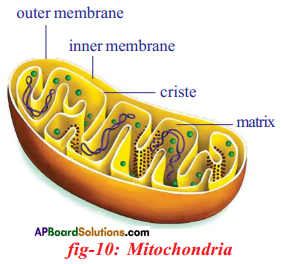 Oxidation of glucose molecule occurs in the mitochondria, ot cell. This is known as cellular respiration. The energy produced during cellular respiration stored in the form of ATP molecule. Energy producing cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria hence we call it cell of power or power house of the ceil.
Oxidation of glucose molecule occurs in the mitochondria, ot cell. This is known as cellular respiration. The energy produced during cellular respiration stored in the form of ATP molecule. Energy producing cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria hence we call it cell of power or power house of the ceil.