AP State Syllabus AP Board 7th Class English Textbook Solutions Chapter 1B The Town Child & The Country Child Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class English Solutions Chapter 1B The Town Child & The Country Child
7th Class English Chapter 1B The Town Child & The Country Child Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Where does the town child want to live?
Answer:
The town child wants to live in a country.
Question 2.
Why is there smoke in the towns?
Answer:
There is smoke in the towns because there are buses and motors and trams, plying often.
![]()
Question 3.
There is one thing that the town child loves. What is it?
Answer:
The town child loves the sky which is far above.
Question 4.
“There is no one to play with at all”. This sentence means
a) there are no people in villages.
b) there are no players in villages.
c) the villages have lesser population than the towns.
Answer:
b) There are no players in villages.
Question 5.
What is the wish of the country child?
Answer:
The country child’s wish is that he lived in a town.
Question 6.
Which child is able to watch meadows and lambs?
Answer:
The country child is able to watch meadows and iambs.
Question 7.
Why are the lanes in the country so quiet?
Answer:
The lanes in the country are so quiet because they are not crowded with traffic and feet.
Question 8.
Why are nights colourful in towns?
Answer:
Nights are colourful in towns because of the bright and twinkling streets. There are electric lights at night in towns.
Question 9.
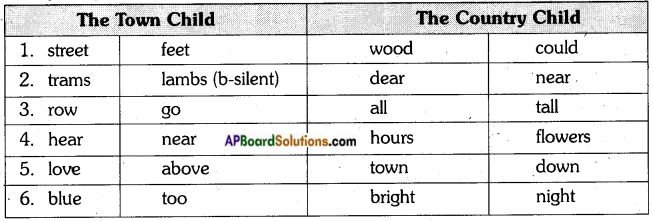
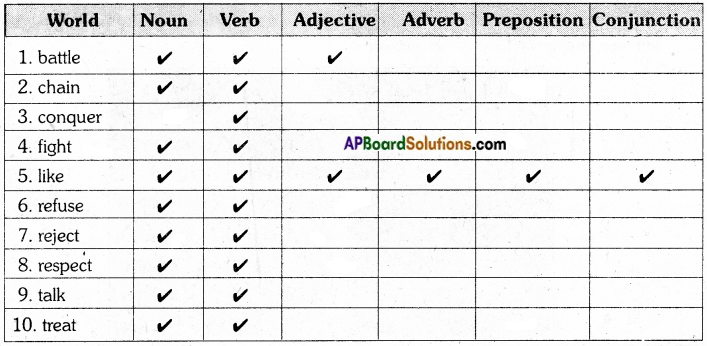
Pick out the rhyming words from both the poems.
The first one is done for you.
| go | row |
| hear | |
| bright | |
| blue | |
| hours | |
| near |
Answer:
The rhyming words from the poems are:
![]()
Question 10.
If you were given an option to live in a town or a country, where would you prefer to live? Give reasons for your option.
Answer:
I would prefer to live in a country. I like the greenery there. It is a pollution free place. People are innocent and courteous. It is always quiet and calm. Hence I like to live in a village.
Project
Conduct a Survey
Study the following questionnaire and discuss the points in small groups.
Contact people in your School/your locality and put these questions to them. Collect information by ticking in the relevant column.
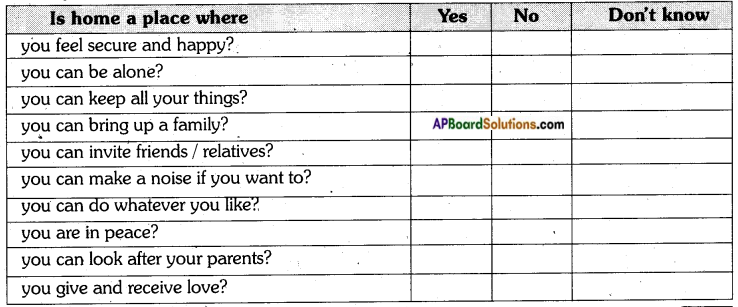
Analyse the results in the group and write a brief report on the result of your survey.
Use phrases such as the following:
Most people think that ……………………………….
A few people think that ……………………………….
Hardly anyone thinks that ……………………………….
No one thinks that ……………………………….
THE REPORT
Most people think that home is a place where they feel secure and happy. Some people- not many-think that you can be alone at home if you choose to be. A large number of people feel that they can keep all their things at home. Almost everyone agreed that home is the place where we can bring up a family. A considerable number of persons opine that one can invite friends and relatives to home. Only a very few persons agree to the idea that one can make a noise or do whatever one likes at home. A great part of the participants are of the view that one can be at peace at home. Many people contribute to the point that home is the place where we look after parents and exchange love.
![]()
The Town Child & The Country Child Summary in English
The Town Child
The town child lives in a street full of buses, cars, producing a lot of noise and discharging smoke. The boy wishes to have meadows and lambs around. He hates those rows of houses filled with noises. He loves to have woods near. The only thing he loves in the town is the blue sky. He says the sky alone has room for him and lots of clouds.
The Country Child
The country child lives close to a wood. The streets are quiet. The lanes are not crowded. The boy wants players all around. The trees are too tall and the boy feels lonely. He has the company of just birds and flowers. He wishes to have a home in a town. He loves to watch trams all around. He longs to see colourful lights glitter at nights. He prays to have town life.
The Town Child & The Country Child Glossary
feet (n): (here) people who walk in streets
tram (s): an electric vehicle that transports people in cities
meadow (n): a field with grass and often wild flowers
castle (n): a large strong building
lane (n): a narrow road in the countryside or, in a town
twinkling (adj): shining strongly and then weakly
woods (pl.n): an area of trees, smaller than a forest
![]()
quiet (adj): silent! peaceful
lonely (adj): unhappy because you have no friends or people to talk to
wood (noun): the hard material that the trunk and branches of a tree are made of.


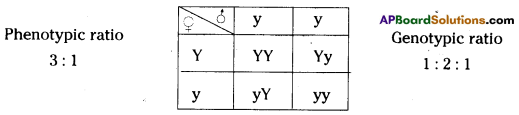
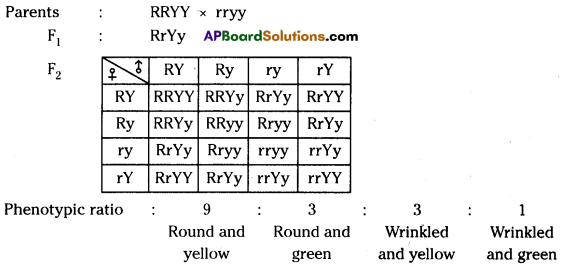

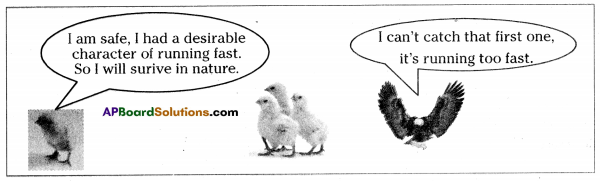

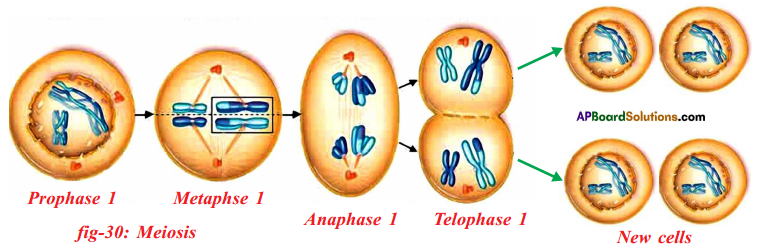
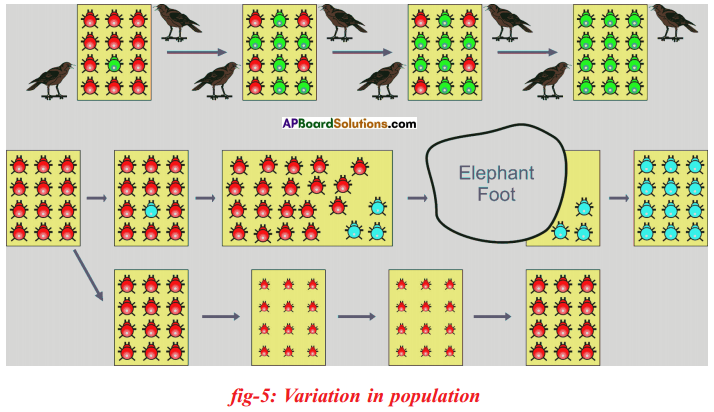 Let us consider a group of twelve beetles. They live in bushes on green leaves. Their population will grow by sexual reproduction. So they were able to generate variations in population. Let us assume crows eat these red beetles. If the crows eat more Red beetles, their population is slowly reduced. Let us discuss the above three different situations in detail.
Let us consider a group of twelve beetles. They live in bushes on green leaves. Their population will grow by sexual reproduction. So they were able to generate variations in population. Let us assume crows eat these red beetles. If the crows eat more Red beetles, their population is slowly reduced. Let us discuss the above three different situations in detail.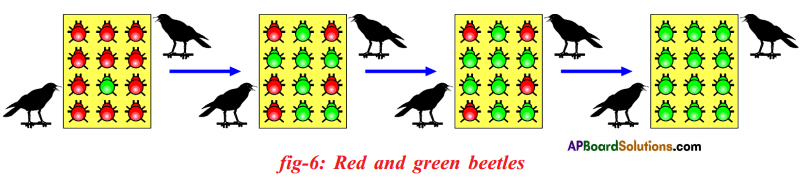 Moreover, this green coloured beetle passes its colour to Its offspring (Progeny). So that all its progeny are green. Crows cannot see the green coloured beetles on green leaves of the bushes and therefore crows cannot eat them. But crows can see the red beetles and eat them. As a result there are more and more green beetles than red ones which decrease in their number.
Moreover, this green coloured beetle passes its colour to Its offspring (Progeny). So that all its progeny are green. Crows cannot see the green coloured beetles on green leaves of the bushes and therefore crows cannot eat them. But crows can see the red beetles and eat them. As a result there are more and more green beetles than red ones which decrease in their number.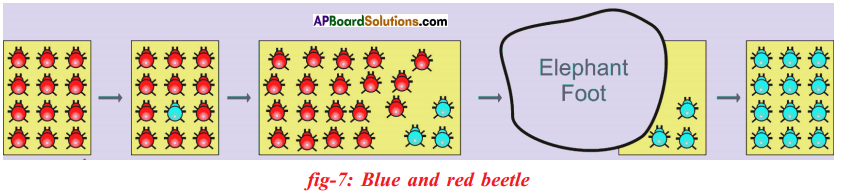 Crows can see blue coloured beetles on the green leaves of the bushes and the red ones as well. And therefore crows can eat both red and blue coloured beetles. In this case there is no survival advantage for blue coloured beetles as we have seen in case of green coloured beetles.
Crows can see blue coloured beetles on the green leaves of the bushes and the red ones as well. And therefore crows can eat both red and blue coloured beetles. In this case there is no survival advantage for blue coloured beetles as we have seen in case of green coloured beetles.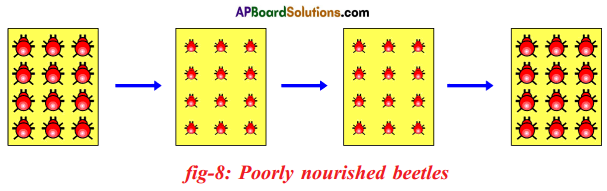 So beetles are poorly nourished. So the weight of beetles decrease but no changes take place in their genetic material (DNA). After a few years the plant disease are eliminated. Bushes are healthy with plenty of leaves.
So beetles are poorly nourished. So the weight of beetles decrease but no changes take place in their genetic material (DNA). After a few years the plant disease are eliminated. Bushes are healthy with plenty of leaves.




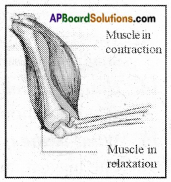
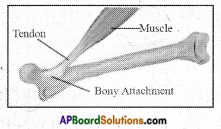
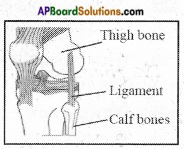








 Answer:
Answer: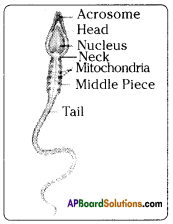
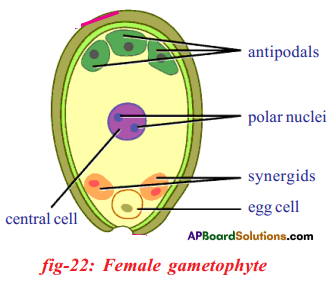
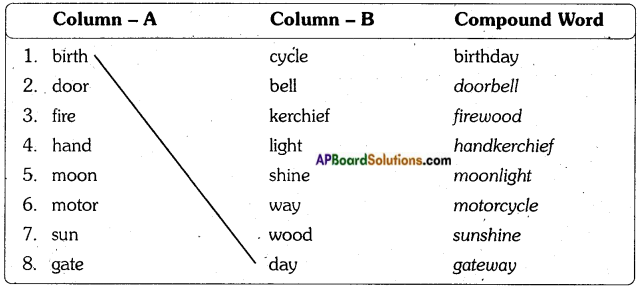
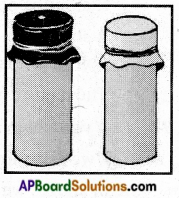
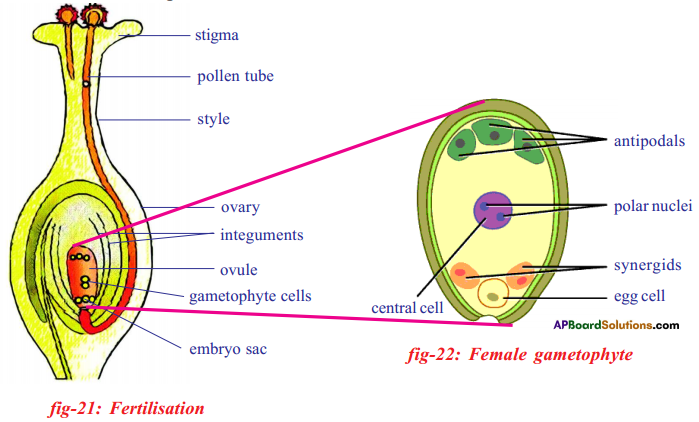
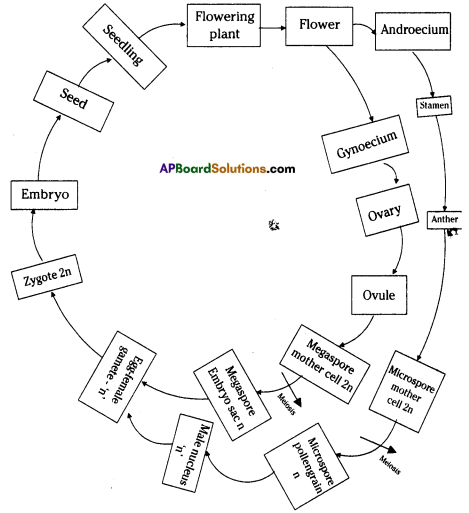
 i) Name male and female reproductive parts of the above figure.
i) Name male and female reproductive parts of the above figure.
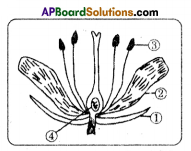
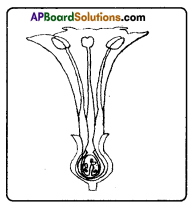 i) What are the four main parts of a flower?
i) What are the four main parts of a flower?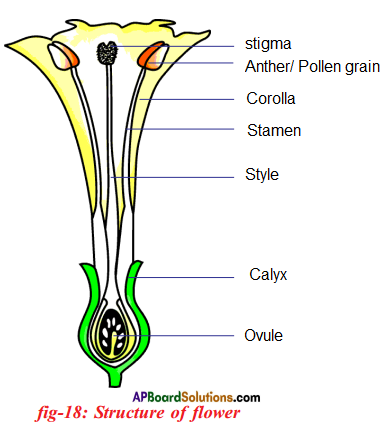 ii) A. Androecium or Stamen
ii) A. Androecium or Stamen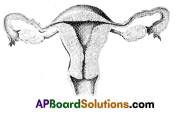
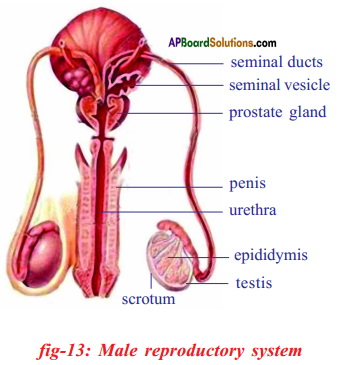 ii) The function of testosterone hormone is maintaining of secondary sexual chracters in males.
ii) The function of testosterone hormone is maintaining of secondary sexual chracters in males.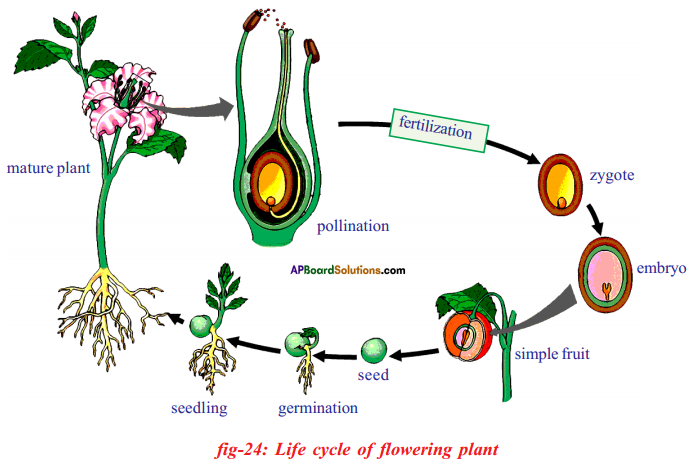
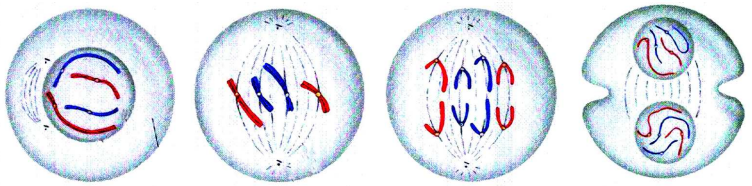 Answer:
Answer: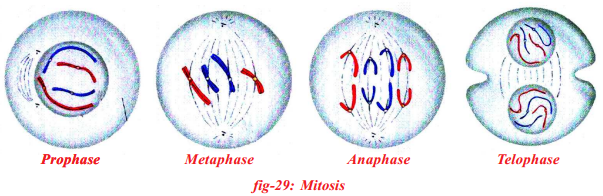
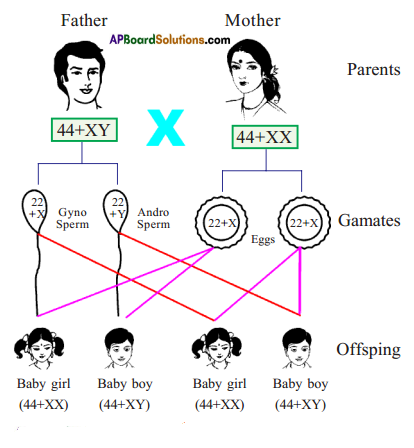
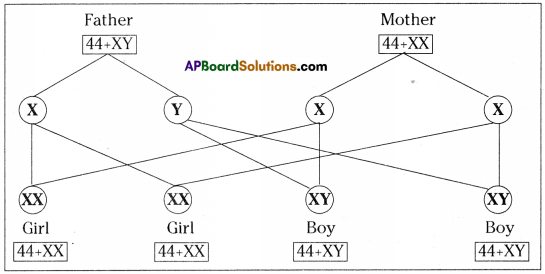
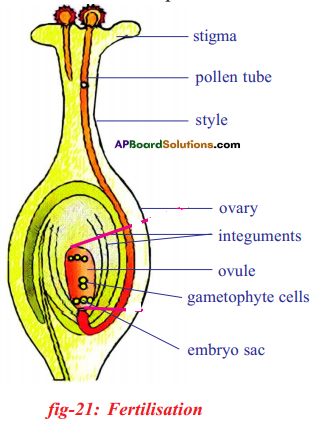
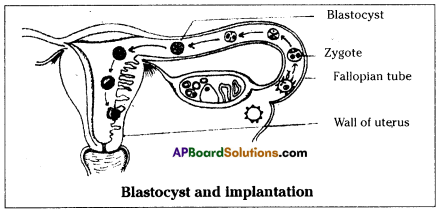
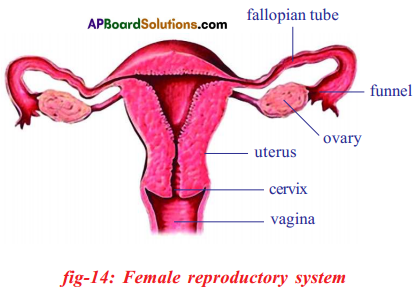 b) If fallopian tubes are closed the sperm can not reach the ova, fertilization will not happen and zygote will not form.
b) If fallopian tubes are closed the sperm can not reach the ova, fertilization will not happen and zygote will not form.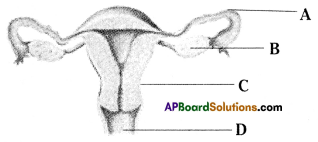
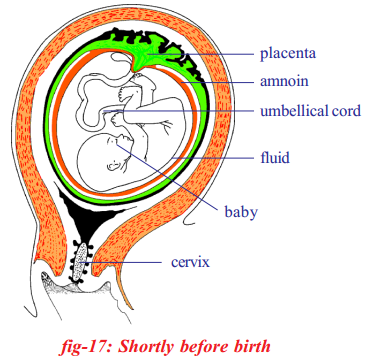




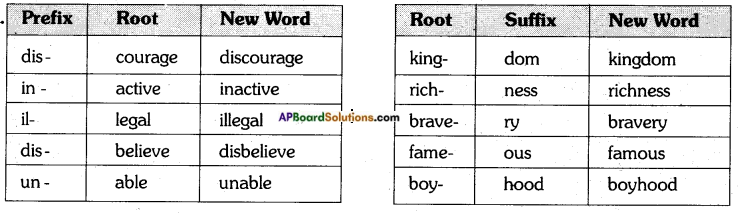
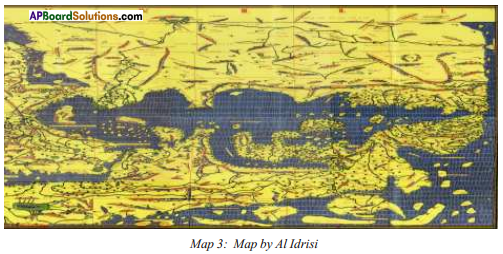 Note: To read this map we should turn it upside down.
Note: To read this map we should turn it upside down. Answer:
Answer: